bio 1 exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:09 PM on 9/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
232 Terms
1
New cards
polymer
built by linking monomers
2
New cards
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
4 Organic Molecules
3
New cards
Functional groups
small, reactive groups of atoms, which give larger molecules specific chemical properties
4
New cards
hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, phosphate,
functional groups that enter most frequently into biological reactions
5
New cards
functional groups
linked by covalent bonds to other atoms in biological molecules
6
New cards
functional groups
represented by the collective symbol R
7
New cards
hydroxyl
Polar. Hydrogen bonds with water to help dissolve molecules. Enables linkage to other molecules by condensation.
8
New cards
carbonyl
molecules with this func. grp. are major building blocks of carbohydrates and participate in the reactions supplying energy for cellular activities
9
New cards
aldehydes
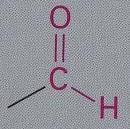
carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton
10
New cards
ketone
carbonyl group within carbon skeleton
11
New cards
carboxyl
functional grp that gives organic molecules acidic properties
12
New cards
amino
functl grp that acts as an organic base by accepting a proton
13
New cards
phosphate
molecules that contain this functl grp reacts as a weak acids
14
New cards
sulfhydryl
easily converted into a covalent linkage
15
New cards
isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures
16
New cards
structural isomers
same chemical formula but arrangement of atoms are different
17
New cards
glucose (aldehyde) and fructose (ketone)
example of structural isomers
18
New cards
glucose
carbonyl at the end
19
New cards
fructose
carbonyl at the middle
20
New cards
stereoisomers
differ in how groups attached, left and right
21
New cards
enantiomers
mirror image molecules, chiral carbon
22
New cards
glucose and galactose
examples of stereoisomers
23
New cards
galactose
24
New cards
monomer
small, similar, chemical subunits
25
New cards
dehydration synthesis
formation of large molecules by the removal of water, monomers are joined to form polymers
26
New cards
hydrolysis
breakdown of large molecules by the addition of water, polymers are broken down to monomers
27
New cards
Carbohydrates
1:2:1 ratio of C,H,O
28
New cards
(CH2O)n
29
New cards
Monosaccharide
contain 3 to 7 carbon atoms
30
New cards
Disaccharide
two monosaccharides polymerize to form
31
New cards
polysaccharides
carbohydrate polymers with more than 10 linked monosaccharide monomers
32
New cards
cellulose
polysaccharide
33
New cards
polysaccharides
structural carbohydrates and energy storage molecules are this type of carbohydrates
34
New cards
Monosaccharides
simplest carbohydrate
35
New cards
Monosaccharides
6 carbon sugars play important roles
36
New cards
C6H12O6
chemical formula for glucose
37
New cards
linear
all monosaccharides occur in this form
38
New cards
glucose, fructose, galactose
example of monosaccharides, hexoses
39
New cards
five or more
monosaccharides with \________ carbons can fold back on themselves to assume a ring form, ex glucose
40
New cards
alpha glucose
enantiomer of glucose
41
New cards
-OH group pointing below the plane of the ring
42
New cards
beta glucose
enantiomer of glucose
43
New cards
-OH group pointing above the plane of the ring
44
New cards
Disaccharide
assembled from two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis
45
New cards
maltose
ex of disaccharide
46
New cards
maltose
formed by a glycosidic bond linking two alpha glucose
47
New cards
alpha (1-4) linkage
48
New cards
sucrose
glucose + fructose
49
New cards
alpha (1-2) linkage
50
New cards
lactose
glucose + galactose
51
New cards
beta (1-4) linkage
52
New cards
Polysaccharides
long chains of monosaccharides
53
New cards
Polysaccharides
may be linear, unbranched, or one or more branches
54
New cards
glycogen
polysaccharide that animals use to store energy in (energy storage)
55
New cards
cellulose
polysaccharide plants use for structural support
56
New cards
chitin
polysaccharide arthropods and fungi use for structural support
57
New cards
modified glucose containing nitrogen-containing groups
58
New cards
amylose
polysaccharide joined by alpha (1-4) linkage, linear
59
New cards
glycogen
polysaccharide joined by alpha (1-4) linkage, linear
60
New cards
and alpha (1-6) linkage, branch
61
New cards
cellulose
glucose units joined by beta (1-4) linkages
62
New cards
cellulose microfibril
cellulose are packed into,
63
New cards
provides rigidity to cell wall
64
New cards
chitin
a reinforcing fiber in the external skeleton of arthropods and the cell walls of some fungi
65
New cards
lipids
water-insoluble, primarily nonpolar biological molecules composed mostly of hydrocarbons
66
New cards
Neutral lipids, phospholipids, steroids
three types of lipids
67
New cards
neutral lipids
energy source
68
New cards
energy storing molecules, no charged groups (nonpolar)
69
New cards
oils, fats
types of neutral lipids
70
New cards
oils
lipids that are liquid at room temperature
71
New cards
fats
lipids that are semisolid at room temperature
72
New cards
fatty acid
contains a single hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end
73
New cards
triglycerides
formed by dehydration synthesis between three-carbon glycerol and 3 fatty acid side chains
74
New cards
ester linkage
Covalent bond between glycerol and fatty acid
75
New cards
triglycerides
serves as energy reserves in animals
76
New cards
store more than twice the calories per gram as carbohydrates
77
New cards
Triglycerides
layer of fatty tissue just under the skin that acts as insulation in mammals and birds
78
New cards
triglycerides
help make bird feathers waterproof
79
New cards
14 to 22
most common fatty acids have \_______ carbons
80
New cards
increases
as chain length \_____, fatty acids become less water soluble and more oily
81
New cards
saturated fatty acid
binds the maximum number of hydrogen atoms, only single bonds
82
New cards
saturated fatty acid
found in solid animal fats such as butter
83
New cards
less healthy
84
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
bend at double bond, healthier
85
New cards
ex: vegetable oils
86
New cards
monounsaturated and polyunsaturated
types of unsaturated fats
87
New cards
monounsaturated
fatty acids with one double bond
88
New cards
polyunsaturated
fatty acids with more than one double bond and are more fluid at biological temps
89
New cards
stearic acid
saturated fats
90
New cards
oleic acid
unsaturated fatty acid, one double bond \= one kink
91
New cards
saturated
fatty acids that are stackable, stable, and solid
92
New cards
unsaturated
fats that are not stackable, compact and are liquid at room temp
93
New cards
trans fat
unsaturated fats, high LDL, formed by hydrogeneration
94
New cards
phospholipids
composed of head group, 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group
95
New cards
fatty acids
nonpolar tails of phospholipids
96
New cards
phosphate group
polar heads of phospholipids
97
New cards
phospholipid
if 3rd C in glycerol is attached to phosphate group
98
New cards
triglyceride
if 3rd C in glycerol is attached to fatty acid
99
New cards
phospholipids
form all biological membranes
100
New cards
phospholipids
structural plan of a \______