The brain
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
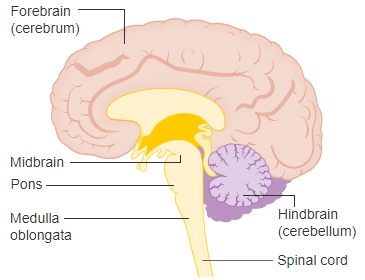
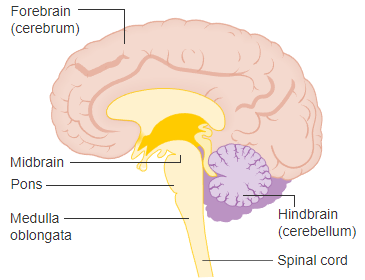
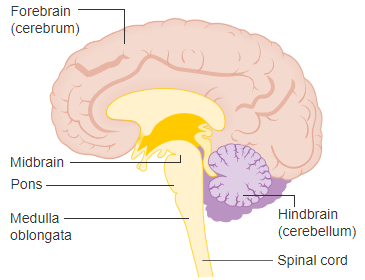
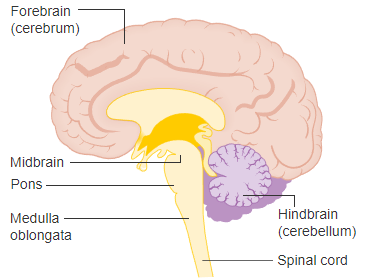
Brain steam
connects the prosencephalon and cerebellum to the spinal cord
Cerebellum
is the the second largest part of the brain and it develops from the metencephalon
Diencephalon
arises from the prosencephalon and eventually forms the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
cerebrum
is the location of conscious thought processes and the orgin of all complex intellectual functions
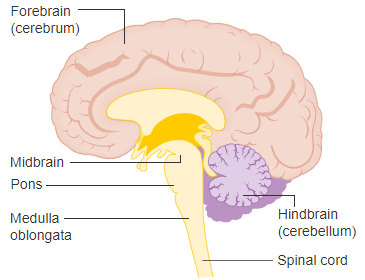
Medulla Oblongata
is formed from the myelencephalon. It is the most inferior part of the brain steam and is continuous with the spinal cord inferiorly
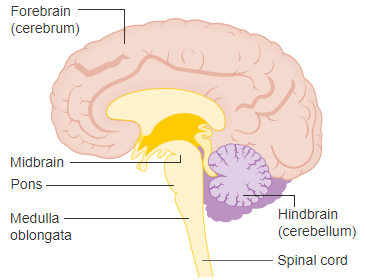
Pons
is a bulging region on the anterior part if the brainstem that forms from part of the metencephalon
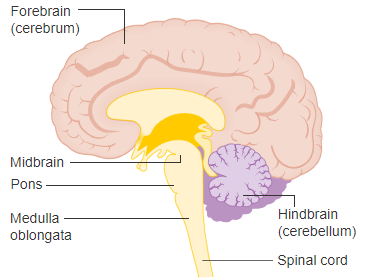
Mesencephalon or Midbrain
is the superior portion of the brainstem.
Arbor Vitae
The white matter of the cerebellum
Vermis
a narrow band of cortex separates the left and right cerebellar hemispheres
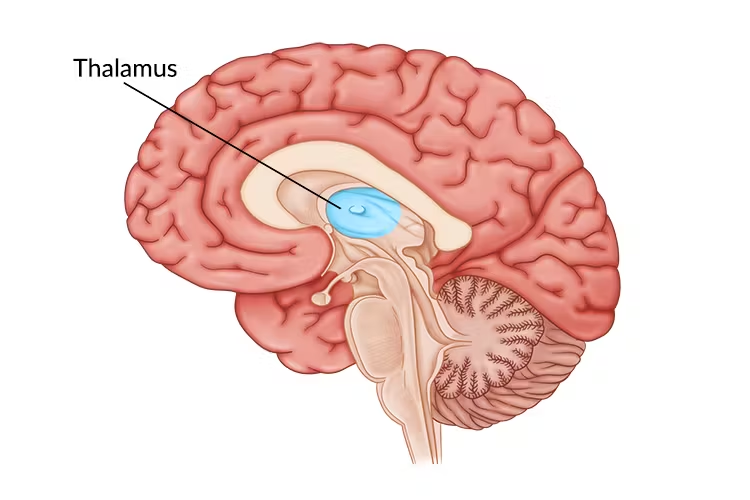
Thalamus
refers to the paired oval masses of grey matter that lie in each side of the third ventricle
Epithalamus
partially forms the posterior roof of the diencephalon and covers the third ventricle
Hypothalamus
-Master control of the autonomic nervous system
-Master control of the endocrine system
-Regulation of body temperature
-Control of emotional behavior
-Control of food intake
-Control water intake
-Regulation of sleep-wake
What connects the right and left hemispheres
corpus callosum
Frontal Lobe
-primary motor cortex
-Premotor cortex
-Motor speech area
-Frontal eye field
Parietal Lobe
-Primary somatosensory cortex.
-Somatosensory association area
-Part of Wernicke area
Occipital Lobe
-Primary visual cortex
-Visual association area
Temporal Lobe
-Primary auditory cortex
-Primary olfactory cortex
-Auditory association area
-Part of Wernicke areas
Insula Lobe
Primary gustatory cortex
Gyrus
a ridge or fold between two clefts on the cerebral surface in the brain.
Sulcus
furrow, groove. especially : a shallow furrow on the surface of the brain separating adjacent convolutions.
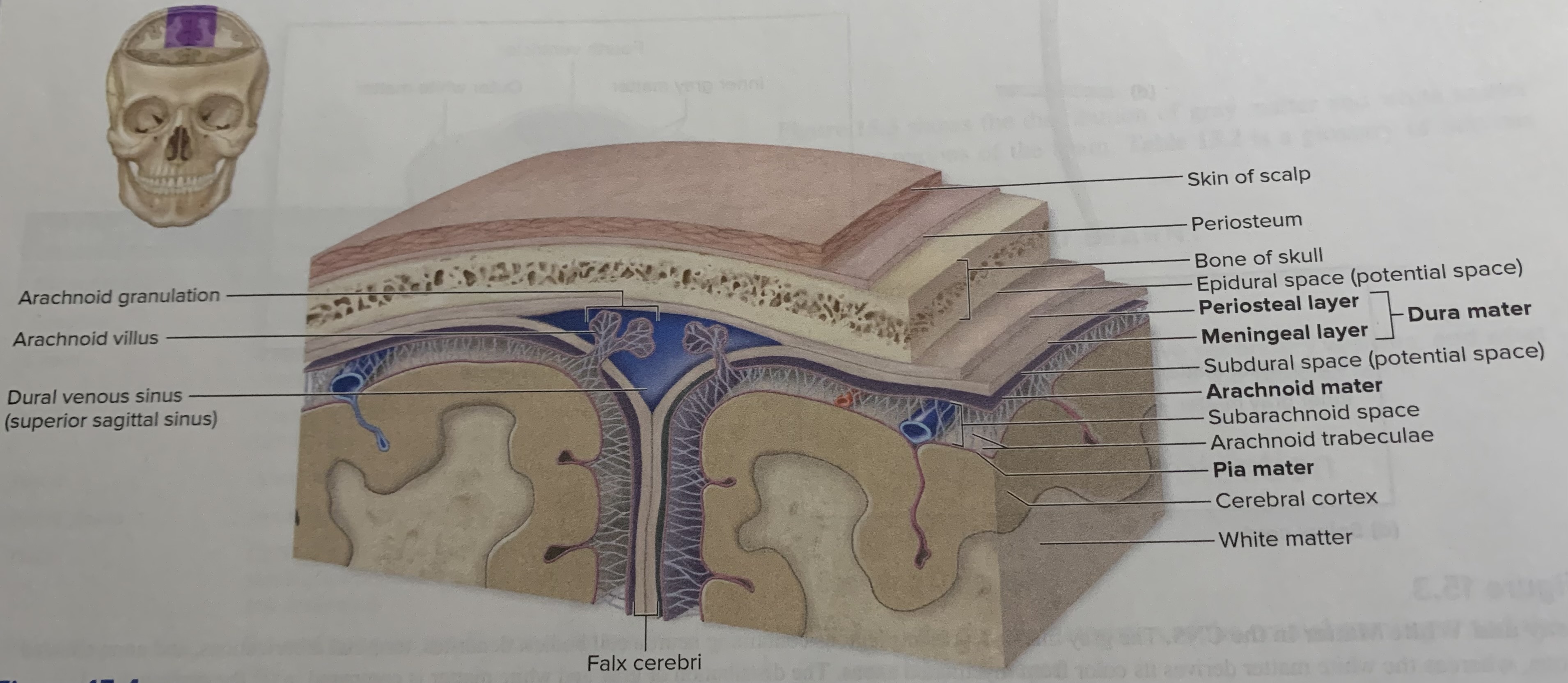
Dura mater
is an external tough dense irregular connective tissue layer is composed of two fibrous layers
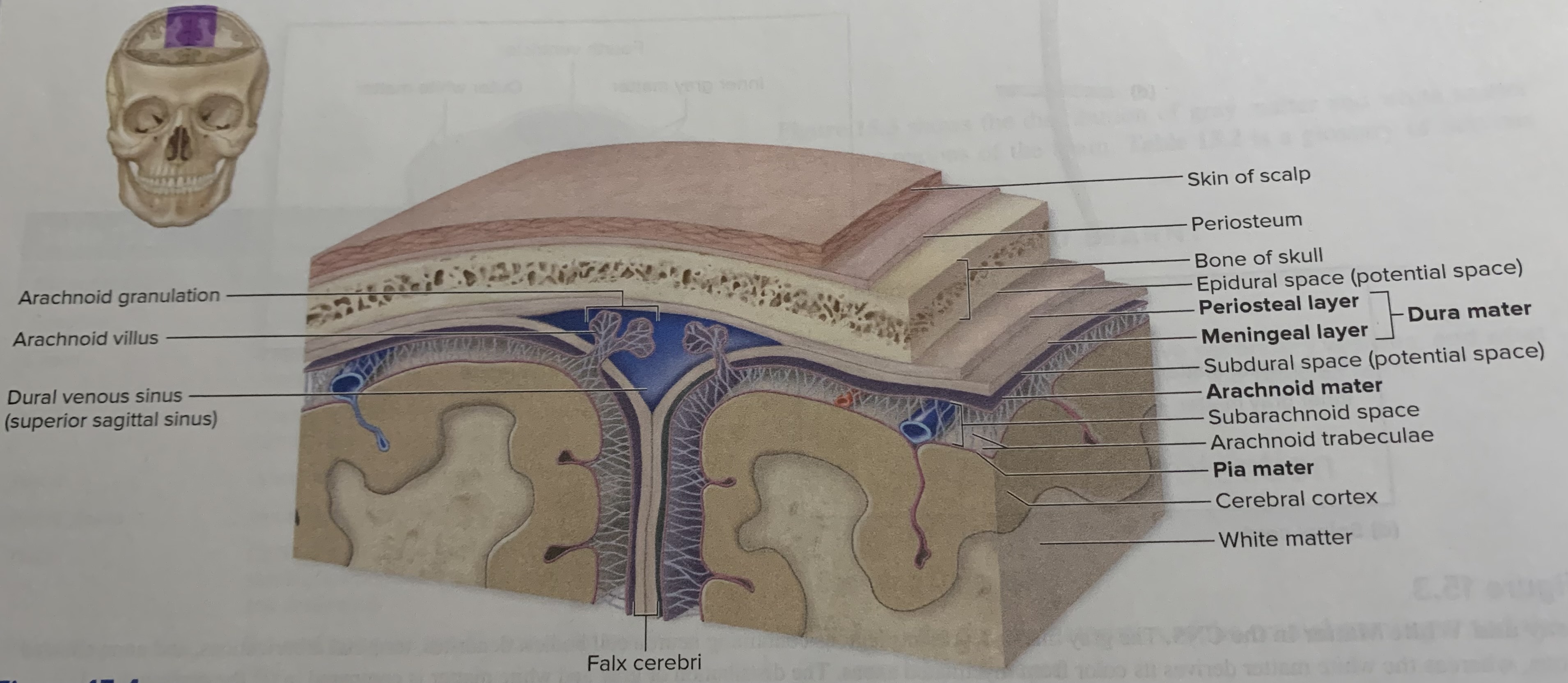
Arachnoid mater
lies external to the pia mater
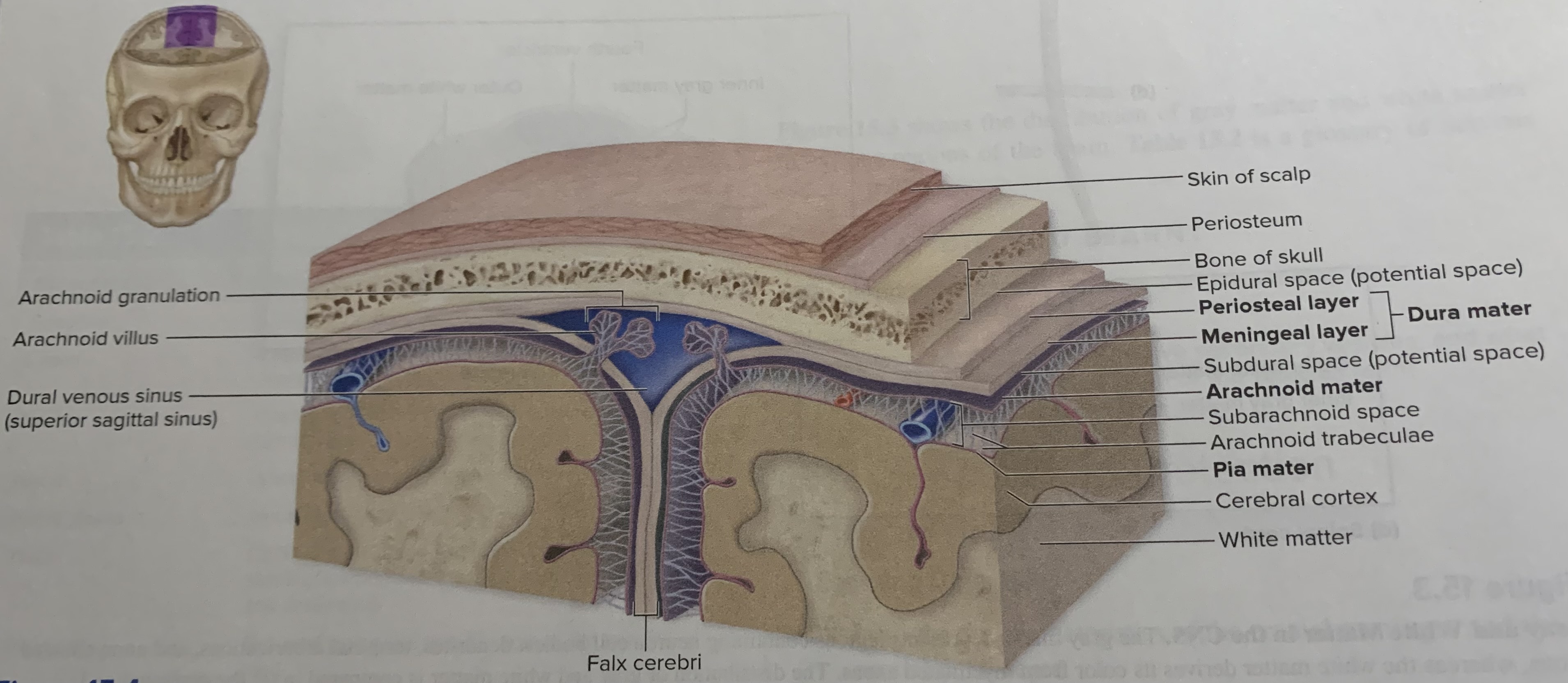
Pia mater
is the innermost of the cranial meninges it is thin and composed of delicate areolar connective tissue that is highly vascularized and tightly adheres to the brain
Between the arachnoid mater and overlying dura mater is a potential space _____ becomes an actual space if blood or fluid accumulates
Subdural space
Immediately deep to the arachnoid mater is_____.
Subarachnoid space
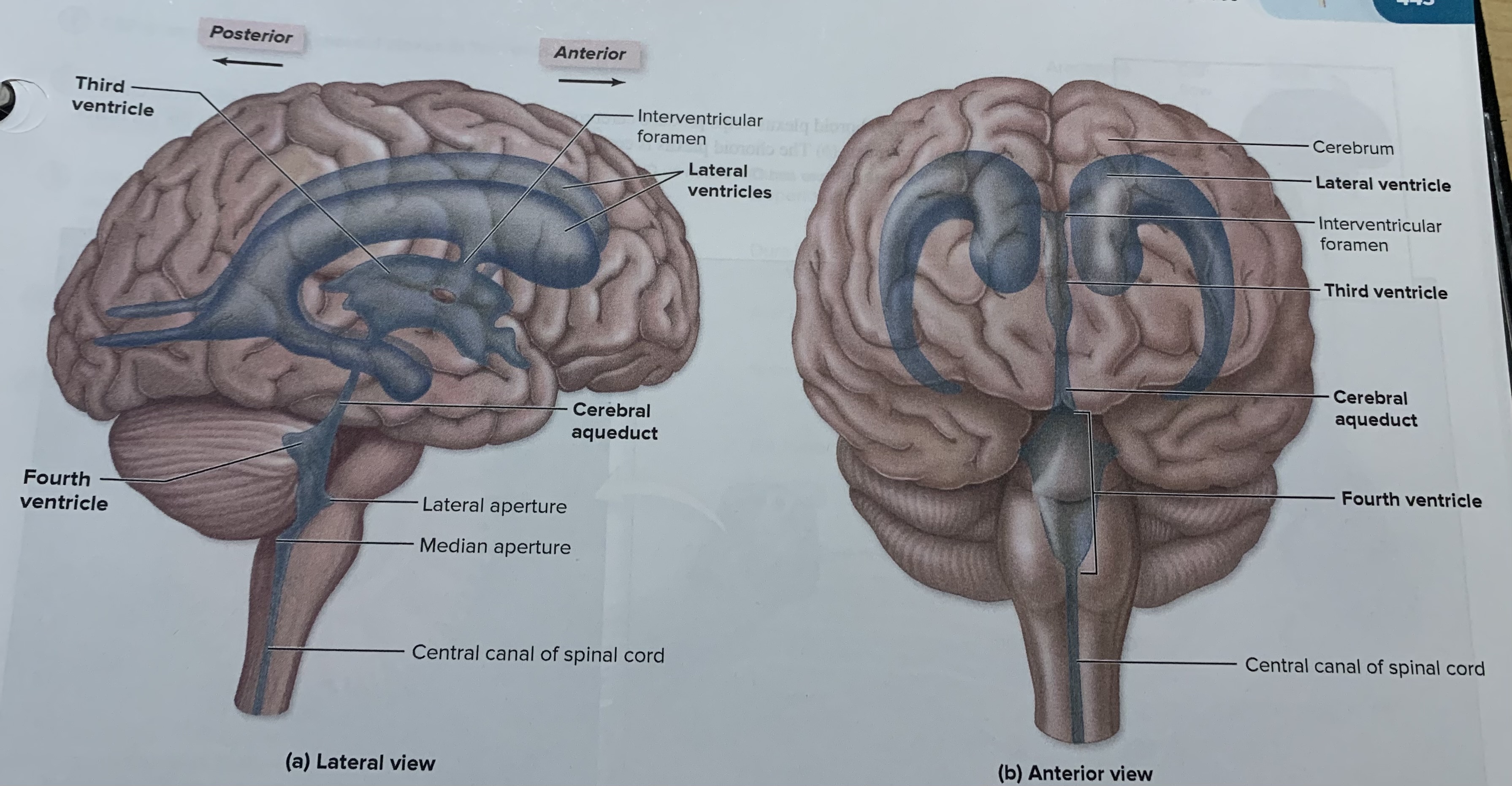
Lateral ventricles
2 of them are in the cerebrum and separated by a thin medial partition called the septum pellucidum
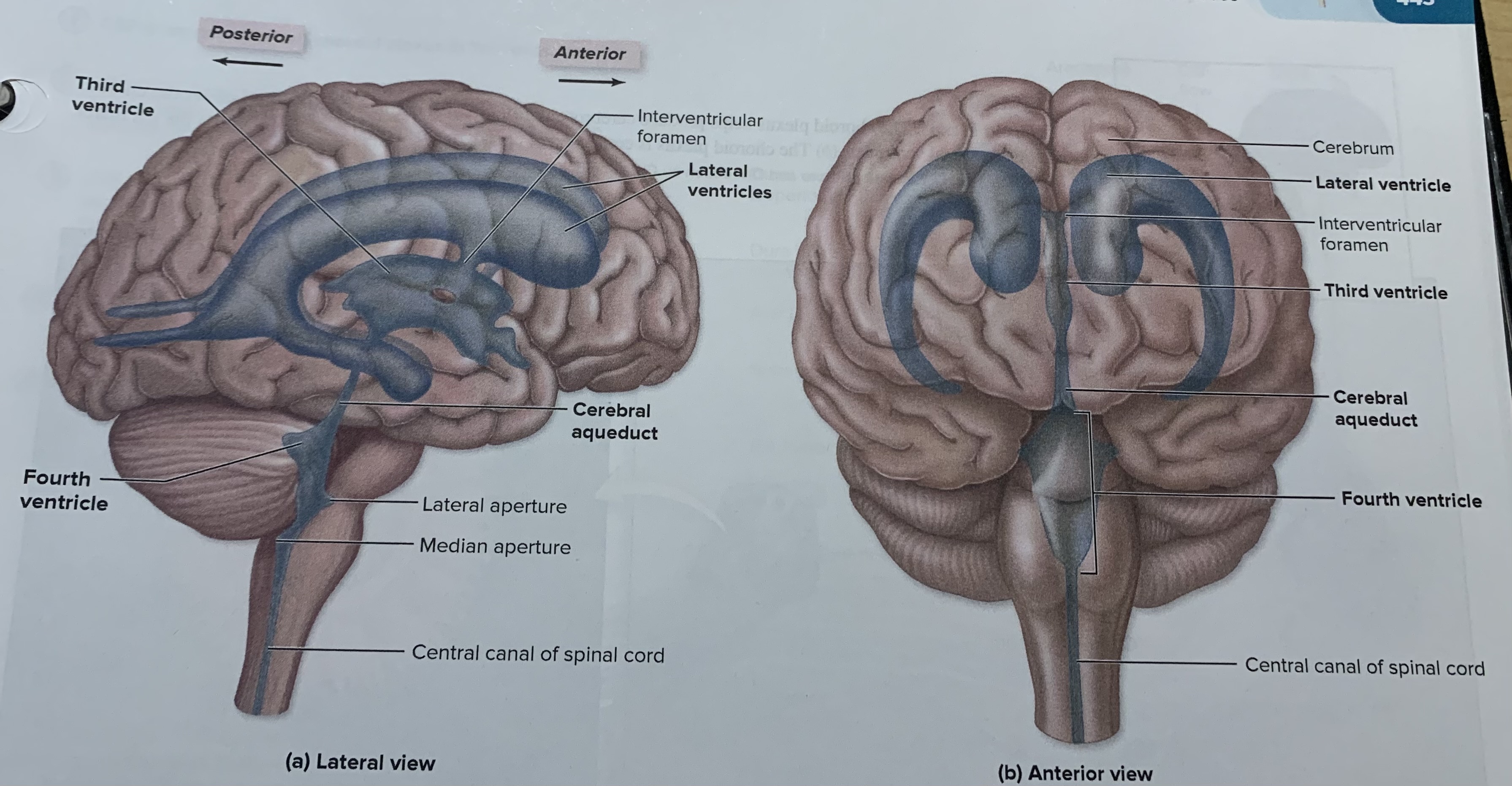
third ventricles
It is found in the diencephalon is a smaller venricle each lateral ventricle communicates with this ventricle through an opening called the interventricular foramen
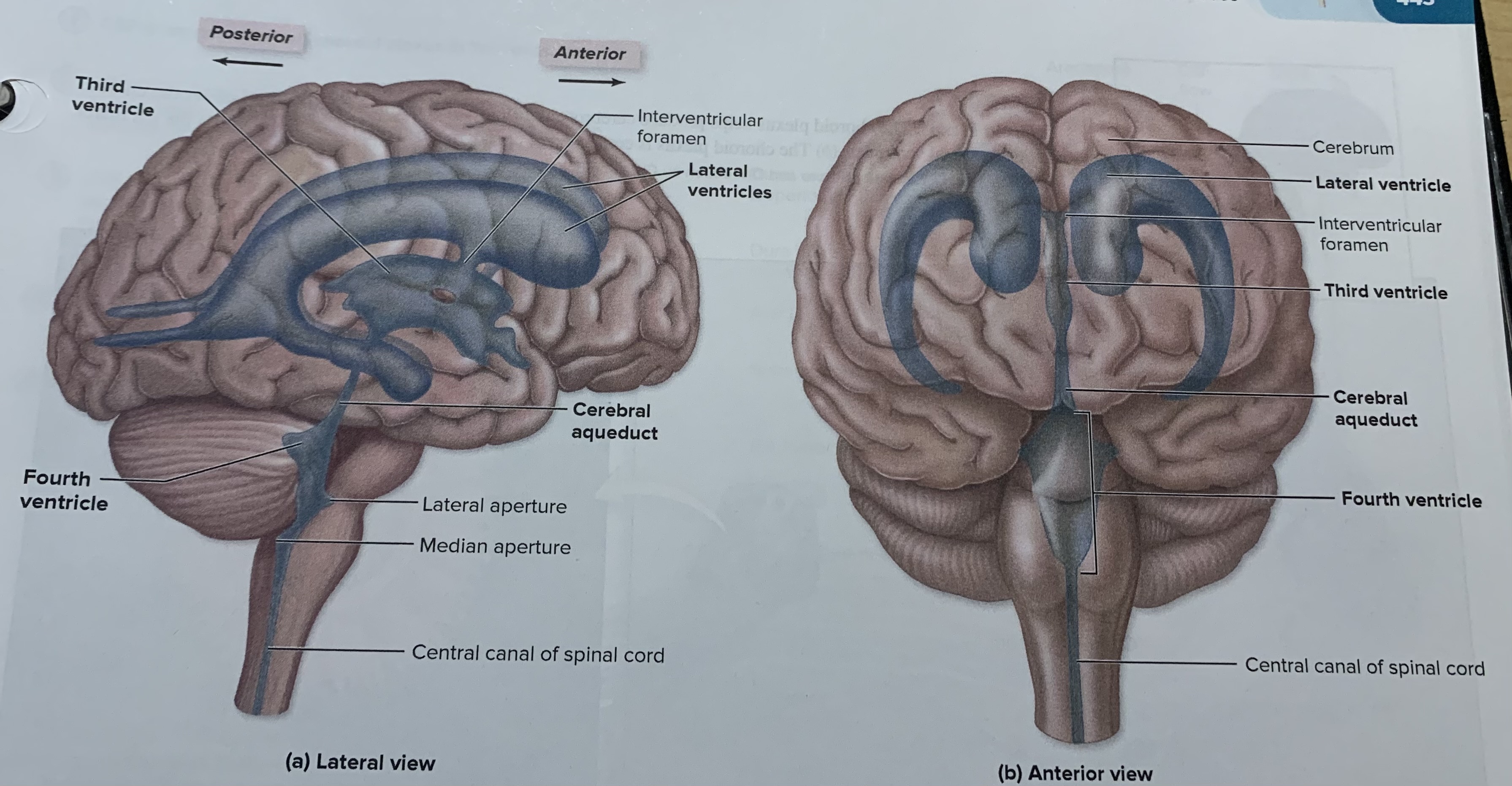
Fourth ventricles
The third ventricle connect with me and is located between the pons medulla and the cerebellum and at its inferior end before it merges withpro the slender central canal in the spinal cord.
Choroid plexus
produces CSF
Internal carotid arteries
a major blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain, eyes, and other parts of the head
Vertebral arteries
supply blood to the brain and spine
Blood brain barrier
which strictly regulates what substances can be enter the interstitial fluid of the brain
Dural Venous Sinuses
a network of channels located within the dura mater, the outermost layer of the brain's protective coverings
Internal jugular vein
a large vein located in the neck that plays a crucial role in draining blood from the brain, face, and neck back to the hear
What is part of the diencephalon
Pineal gland
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Epithalamus
The innermost layer of the meninges, delicate and closed applied to the surface off the brain is the
pia mater
An object penetrating through the temporal bone would impact first which of these regions of the brain
temporal lobe
If you were to separate the brainstem from the rest of the brain then you would cut between the mesencephalon (midbrain) and the
diencephalon
The space within the diencephalon is the
third ventricle
The most inferior ventricle of the brain is the
fourth ventricle
The vertebral arteries enter the cranial cavity through the
foramen magnum
Pineal gland
is an endocrine gland and secretes the hormone melatonin
Habenular nuclei
helps relay signals from the limbic system to the midbrain and are involved in visceral and emotional responses to odors