genetics CH. 6 genetic analysis and mapping in bacteria and bacteriophage
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
genome simplicy
fewer genes and fewer bases than other organism
haploid genomes
mutations can b observed directly bc there is one copy of each gene
hot take
enormous number of progeny allows for detection of rare events
hot take
mutants r easily created, identified, isolated, and multiplied for study
binary fission
bacteria propagate by BLANK
binary fission
chromosome replicates and a copy is distributed to each of the progeny cells
colony
cluster of millions of identify cells
hot take
bacteria made me grown on a solid or liquid growth medium
carbon source (glucose)
nitrogen source
water
additionally elements
what does a medium contain (roughly)
each colony on a growth medium should come from 1 bacerial cell
minimal medium
contains glucose, a nitrogen source, some inorganic material and water
prototrophs
bacterial species that can grow in minimal medium are called BLANK
prototrophs
BLANK do not possess any mutations that would block their ability to produce a compound required for growth
- fully functional and can thrive with minimal resources available
auxotrophs
bacteria that mutant for one or more genes that lack the ability to produce a compound or preform a function required for growth
-cant grow on a minimal medium
complete medium
medium that contains glucose, a nitrogen source, and ALL other compounds required for growth and reproduction (amino acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides)
supplemented medium
it is a minimal medium that has the specific compound that the autotroph cannot produce on its own.
replica plating
technique that involves transferring some cells from each of the bacterial colonies on an original growth plate to one or more other growth plates.
complete ---- minimal
single chromosome
bacterial genomes r usually composed of a BLANK chromosome
bacterial chromosome
the BLANK is usually a covalently closed circular molecule of double stranded DNA
single
everything bacteria needs to live is found on a BLANK chromosome
Plasmids
small double stranded circular DNA molecules containing nonessential genes
hot take
plasmids dont have essential genes, they carry extra materials the cells may need or ultlize
hot take
plasmids r considerable SMALLER than bacterial chromosomes
F (fertility) plasmid
plasmid types
contains genes that promote their own transfer from donors to recipients
R (resistance) genes
plasmid types
carries antibiotic resistance genes that can be transferred to recipient cells
independently
many plasmids replicate BLANK of the bacterial chromosome so that the number of plasmids per cell can increase rapidly
high copy number chromosomes
plasmids that replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome
low copy number chromosomes
plasmids that r present in one or two copy number per bacterial cell and cannot replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome
conjugation
transformation
transduction
bacterial transfer occurs by 3 procesess
one way transfer
bacteria can transfer genetic material form one bacterium to another, it is BLANK way transfer
plasmid , a portion of bacterial DNA or both
the DNA transfered in bacterial gene transfer may be a BLANK, a BLANK or BLANK
conjugation
is the transfer of replicated DNA from a donor to a recipient
transformation
is the uptake of DNA from the environment
Transduction
is the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another by a viral vector
conjugation
BLANK is when one bacterium passes DNA directly to another through a physical connection.
transformation
BLANK is when a bacterium takes DNA from its surroundings and incorporates it into its genome.
Transduction
BLANK when a virus carries bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another.
conjugation pilius
genetic information is transfered during conjugation between a BLANK
"fertility factor (F-factor)
the ability to act as a donor was hereditary and determined by a BLANK factor
- has genes that promote and build structures for transfer
recipent cell
donor cells transfer genetic info to a BLANK cell
exoconjugant cell
recipient cell with its genetic information modified by receiving DNA from the donor cell
get the F+ plasmid
in the conjugation of F+ and F- cells both the donor and the recipient get the BLANK plasmid
high frequency recombination strains
Hfr
rarely
formation of the Hfr stain occurs BLANK
high frequency recombination genes
genes that transferred bacterial genes at a high rate
Hfr chromosome
the F factor in Hfr strains integrates into the bacterial chromsome to form the BLANK
selective media
BLANK contains compounds that permit growth of exconjugant cells of specific genotypes and prevent donor and recipent growth
antibiotic sensitivity
BLANK can b used as a tool to control the growth of bacteria
homologous recombination
during Hfr and F- mating the transfer of one or more donor alleles into the recipient chromosome occurs by BLANK
F-
it is NOT converted to a donor cell
in Hfr and F- mating the recipent cell is still BLANK
Interuptted mating
BLANK is the cessation of conjugation by breaking the conjugation pilus
order
time
The BLANK of gene transfer and BLANK of first appearance of each in exconjugants r related to the distance of the gene from the origin of transfer (OriT)
4
transformation is a BLANK step process
transformant and non-transformant (unchanged)
after transformation, one daughter cell is a BLANK and the other is a BLANK
Co-transformation
simultaneous transformation if two or more genes
bacteriophage
transduction using an intermediate host to transfer genetic material called a BLANK
tranductant
integration of donor DNA into the recipient cell's chromosome by homologous recombination forms a BLANK
bacteriophage
tiny viral particles that infect bacterial host cells
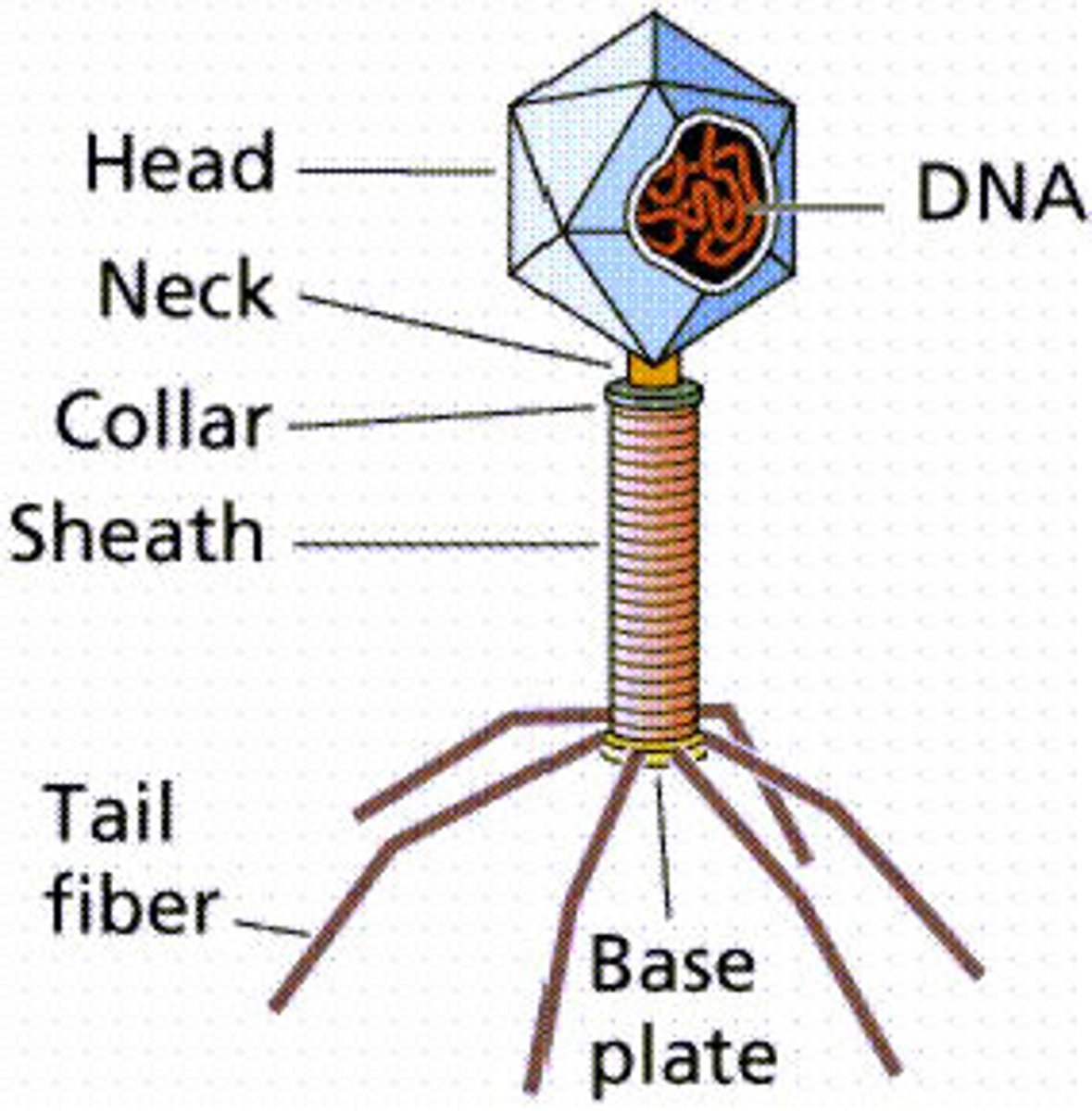
5000-200000
bacteriophage chromosome can be composed of BLANK to BLANK base pairs
head
the BLANK of the bacteriophage holds the genome (double stranded DNA)
lytic cycle
lysogenic cycle
what r the two cycles of transduction and bacteriophage cycle
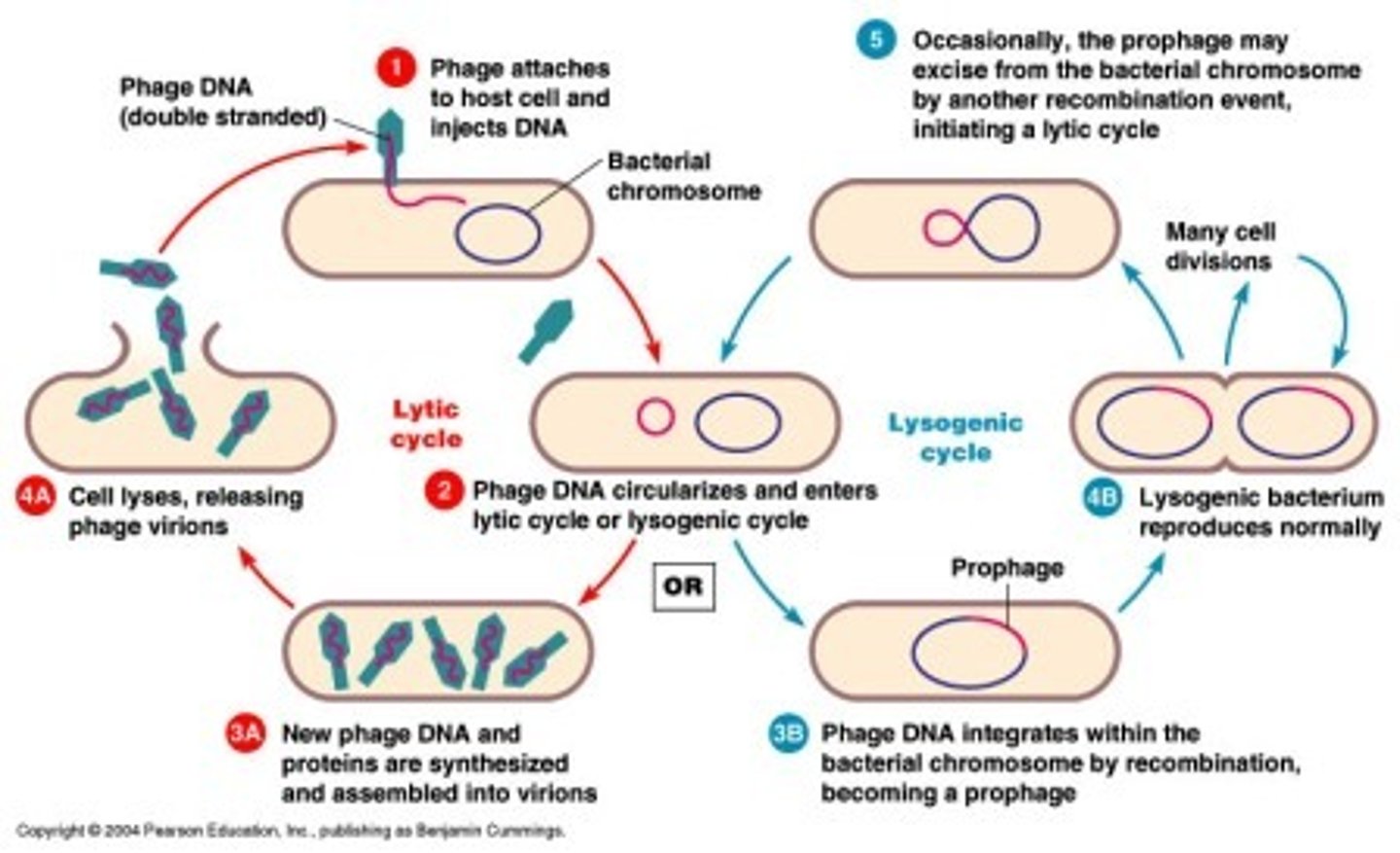
lysogenic cycle
alternate temporary life cycle involving integration of the phage chromosome into the bacterial chromosome
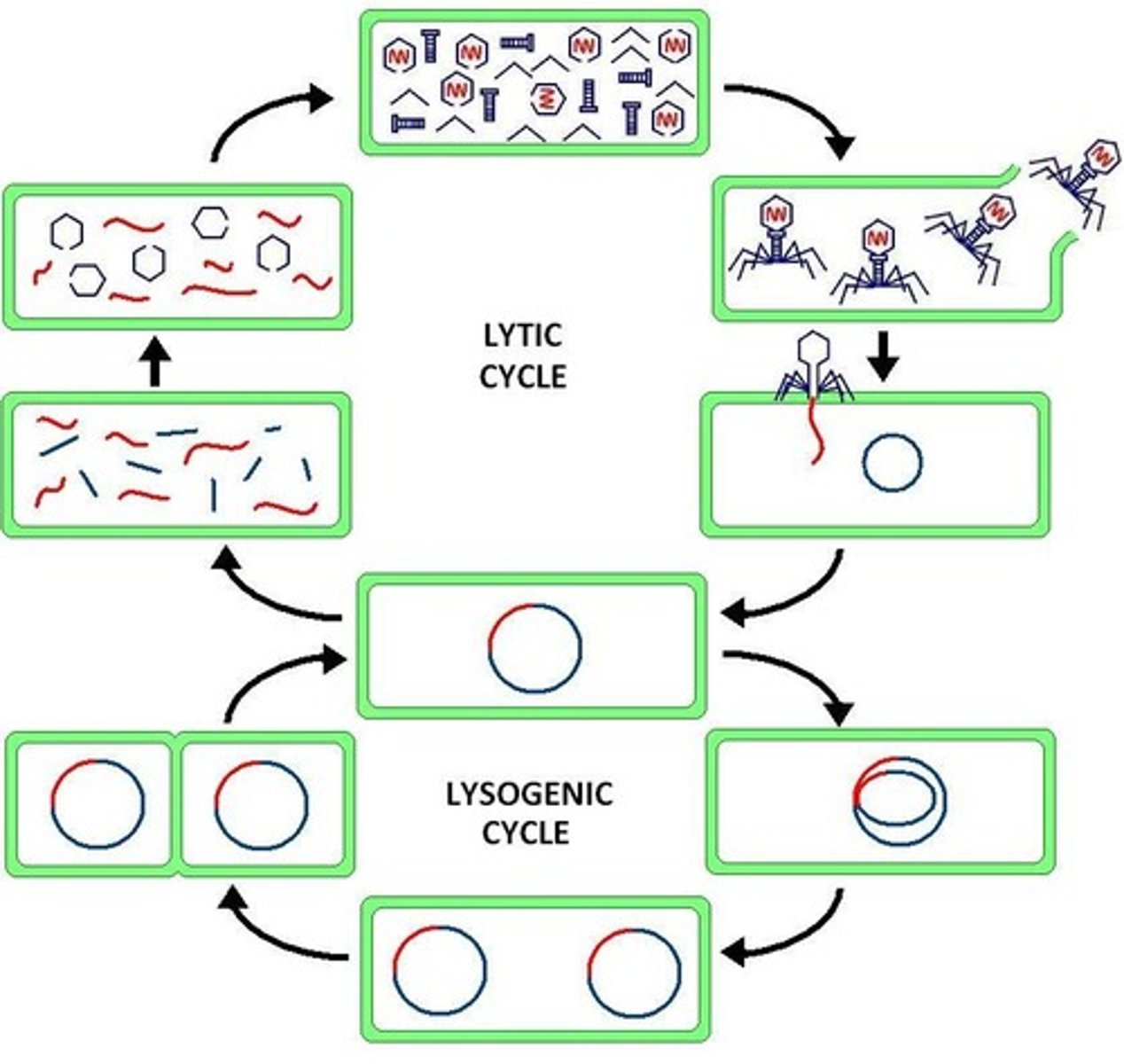
co-transduction
the closer two genes r on the donor chromosome, the more likely they will e transduced to a recipient togteher
Lateral Gene Transfer (LGT)
transfer of genetic material between individual bacteria or arhaea and other organisms
lateral gene transfer
BLANK has allowed for rapid organism adaptation of changing environmental conditions by aquiring antibiotic resistance