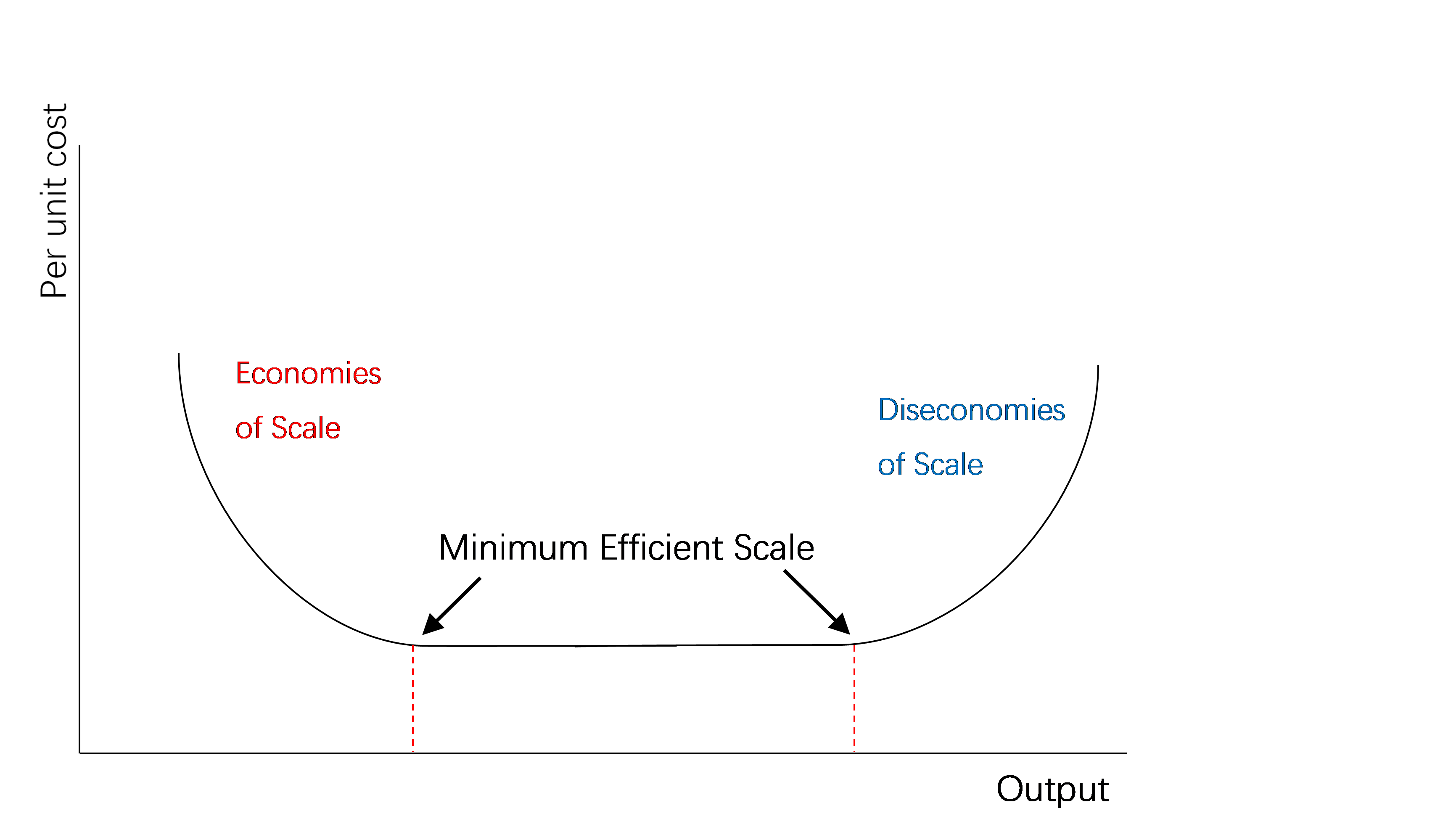
3.3.3 Economies and diseconomies of scale
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Do Economies of scale occur in the SR to the LR
EOS occur in the LR as LRAC fall as a result of increased scale of production
What are economies of scale
When per unit cost fall as a result of greater output.
What are external EOS
External EOS occur when LRAC fall for a firm as a result of of growth in their entire industry. They are out of the control of a firm
What are some examples of external EOS
Component suppliers move closer decrease shipping cost
R+D firms move closer allowing you to use there advancements to reduce costs
What are internal EOS
Internal EOS occur when LRAC fall for a firm as a result of the firms own growth
What are the 5 types of internal EOS and the acronym to remember them
Risk, Financial, Managerial, Technical, Marketing (commercial). Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies.
What are risk bearing economies of scale
Risk is a cost to firms but as they expand and grow this risk can be spread over a greater range of output
What are financial economies of scale
Larger firms can issue share on the stock market allowing them to gain favourable loans and borrow at lower interest rates thanks to there collateral
What are managerial economies of scale
As a firm gets bigger they can hire more specialist managers to monitor and boost worker productivity.
What are technical economies of scale
As a firm grows it has more capital to invest in more specialist machinery and tech allowing for greater productivity and lower cost per unit.
What are marketing (commercial) economies of scale
Larger firms can bulk buy this allows them to decrease there cost per unit as they grow.
How does EOS decrease AC
While TC are still increasing as a firms increases its output the number of units its producing increases more resulting in a lower cost per unit or a lower AC
What are diseconomies of scale
When a firm grows so much that a its cost per unit increases
What are the for reasons for diseconomies of scale
3 C’s and an M. Control, Communication, Coordination and Motivation.
What are control diseconomies of scale
As a firm grows it becomes harder for managers to control the work force so productivity falls
What are communication economies of scale
Messages take longer to get from the stop to bottom of vice versa this divide cause productivity to fall
What are coordination economies of scale
Larger firms have a harder time coordinating all their different departments causing a drop in productivity
What are motivation diseconomies of scale
Larger firms the less important the worker feel so lack motivation and this hurts productivity
What is the minimum efficient scale of production
The lowest level of output needed to be productively efficient ( if high can act as a barrier to entry)