Support & Movement
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
All Cells Cellular Support System
cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
provides internal support; microtubule, actin microfilament, intermediate filament; allows cell movement; allows movement and positioning of internal materials and organelles; cytokinesis and movement of chromosomes; flagella and cilia
Microtubule
long, hallow, cylindrical protein filament; thickest; forms cytoskeleton; moves material within the cell
Actin Microfilament
gives cell shape, muscle contraction, thinnest, not hallow; near cell membrane/wall
Intermediate filament
not hollow; rope-like; resists tension/stretching; from one side of cell to the other side
Bacteria Cellular Support
cell membrane surrounded by peptidoglycan cell wall; provides external support; can be surrounded by an outer membrane
Archaea Cellular Support System
many use protein surface layer for support; some build cell wall of pseudo-peptidoglycan
Ancestral eurkaryotes support systems
no cell wall
Fungi Cellular Support System
secondarily evolve a cell wall; contains chitin that resists tension
Plant Cellular Support System
secondarily evolve a cell wall; contain cellulose that resists tension
Algae Cellular Support System
secondarily evolve cell walls; highly variable
Diatoms
planktonic unicellular brown algae, grow external support structures made of silicone; silicone shells of dead diatoms make up a large amount of marine sediment
Animal Cells Wall
do not have; cells can move
Hydrostat
any biological structure that uses internal fluid pressure for support, shape, or movement; support without regid structure
Adding fluid to tension resisting membrane surrounding fixed volume of space
pressurized volume of fluid pushed out; tension resisting membrane pushes in; → stiffens structure
Eukaryote cell membrane ____ elastic
is not
Plant Hydrostat
each cell bc cell walls resist tension (act as tension resisting membrane)
Animal Hydrostat
use tissues
Tension resisting elements of plant cell wall
cellulose, hemicellulose, water
Cellulose
orange rods; strong support fibers; high tensile stiffness = resists being pulled
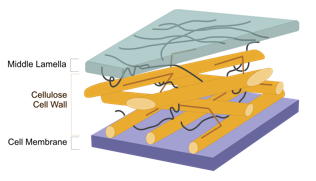
Hemicellulose
brown lines; cross-linking fibers; high elasticity = allows for energy storage with deformation
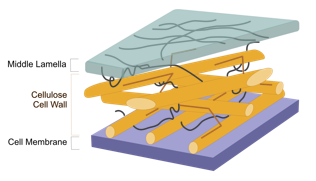
Water
surrounds fibers in apoplast; adhesion resists tensile pulling too
Central Vacuole
controls volume and pressure of fluid; usually large
Osmotic gradient
causes water to enter cell → increase pressure inside cell → pushes against cell wall → stiffens cell
True/False. Stiffness can be directional.
True
Orientation of cellulose fibers in cell wall
controls how cell deforms
Cellulose Fibers arranges in circular orientation
elongates (out)
Cellulose Fibers arranged in longitudinal orientation
left/right
Wilting
not enoguh water to inflate cells
Stomatal Guard Cells
open and close to control gas exchange and prevent water loss; depend on hydrostat pressure and fiber orientation
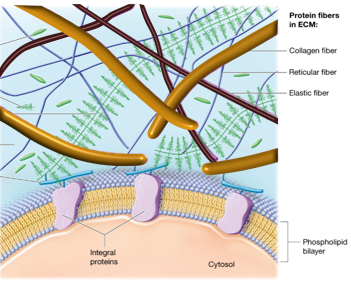
Tensino Resisting Elements of Animal Extra Cellular Matrix
collagen and elastin
Collagen
orange rods; most common protein in ECM; high tensile stiffness = resists being pulled
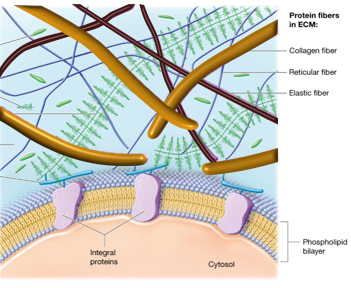
Elastin
brown lines; cross-linking fibers; high elasticity = allows for energy storage with deformation
Pressurized volume in animal hydrostats
gut, connective tissue with lots of water, body cavity
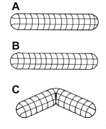
doesn’t allow expansion in any direction so causes a kink, failure is likely
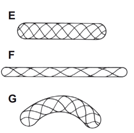
spiral wound allows movement so less likely to fail
Muscle contractions can
increase pressure on volume (stiffen hydrostat) or apply force to hydrostat (deform or move hydrostat)
Sea Anemones Hydrostatic Support
to withstand forces of flow; contraction of muscles in column increase pressure on column tissue → stiffen body
Earth Worm Hydrostatic Locomotive
contractions elongates segments, pushing them forward; contraction of longitudinal muscles shortens segments, pulling trailing segments forward; alternating waves of muscle ocntraction
Muscular Hydrostat
muscle wrapped around muscle; highly flexible and deformable; strong; no need for rigid support
Tension Resisting Membrane in Muscular Hydrostat
circular muscle; muscle action and connective tissues
Pressurized Volume of fluid in Muscular Hydrostat
longitudinal muscle; muscle cells mostly in water
Contract circular muscle
hydrostat gets long and skinny; lengthens longitudinal muscles
Contract Longitudinal muscle
hydrostat gets short and wide; lengthens circular muscles
Contract circular and longitudinal muscle
muscles contract and bulge (increase pressure), push out against elastic membrane of circular muscles that are also contracting → stiffens hydrostat
examples of muscular hydrostats
octopus & squid tentacles; elephant trunks; most vertebrate tongues
Hydrostatic skeletons work great when
the organism is small and/or supported by water or some other external forces
Larger organisms on land with hydrostatic skeletons
body weight; increases regional tension concentrates force in smaller area; increase stress on body walls
Organisms need stiff structures to
resist external loads
Hydrostats stiffen via
tension-resisting membrane; pressurized volume of fluid
Organisms need rigid structures to
support larger body weight; protect soft tissue
Composite materials
composed of different types of materials to resist different types of forces
Tension
resist pulling loads
compression
resist squishing loads
Rigid Structures
resist deformation; typically subject to bending loads & must resist tension and compression
Arrangement of materials in composite
controls how material resists different types of loads
Plant Rigid Support
Xylem
Plant Rigid Support Structure
parallel cylindrical columns; resist compression within tube as water is pulled upmaterials arranged far from neutral axis → resistant to bend; yearly growth adds tubes in parallel → increases strength
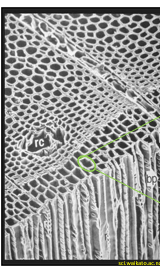
Plant Rigid Structure Material
composite cell walls; hemicellulose and cellulose hold things together; primary cell wall → cellulose; secondary cell wall → cellulose & lignin
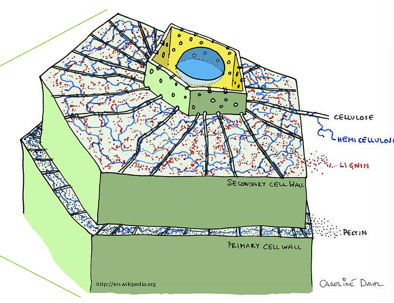
Plant Composite Material
cell wall; cellulose and lignin
Woody Plants Secondary Cell Wall
cellulose (resists tension) & lignin (resists compression)
What plants are the secondary cell wall in?
woody plants
Early Land Plants used
hydrostatic support; limited to small size and close proximity to water
Early Trees possible thanks to
evolution of specialized vascular tissues for support & transport
Animal Rigid Support
skeletons
Animal Rigid Support structure
highly variable morphologies; external → shells or exoskeletons; internal → ossicles or bones
Animal Rigid Support Materials
highly variable composites; tension resisting fibers and compression resisting minerals
External Shells as Skeletons Examples
mollusca (reduced/lost in some); brachiopoda
External Shells as Skeleton Materials
very rigid → brittle; secreted by ectodermal cells; mostly mineral (calcium carbonate); some proteins; arrange materials to control failure/crack formation
Exoskeleton Structure
body is fully enclosed; limits movement → material thinner at joints; limits growth → ecdysis
Exoskeleton Material
stiffness varies with components; secreted by ectodermal cells; tensile: chitin fibers cross-linked by proteins; compression (minerals)
Ecdysis
molting; grow new exoskelton under old; pre-weakened regions → controlled failure; new exoskeleton not stiff; organisms needs to increase size, make protein crosslinks, add minerals; in between expanding and hardening, they make their body hydrostats
True/False. Arthropoda can be hydrostats.
True- in period following molting but the new exoskeleton has not formed
Ossicles Structure
grow within body wall surround body cavity and covered by soft tissue; size and number may vary
Ossicles as Skeletons Examples
Echinodermata (sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers)
Ossicles are only found in
echinodermata (echinoderms)
Exoskeleton as Skeleton Example
arthropoda
Ossicles Material
connected by mutable connective tissue (MCT); formed by ectodermal cells
Ossicles
small, rigid, calcified elements that make up the internal skeleton of sea stars and sea urchins; mineral crystals
Mutable connective tissue
specialized collagen, stiffness under active control (controls stiffness → harden or relax) mainly in sea cucumbers & sea urchins
Bone Skeleton Structures
varies with function; long, cylindrical (materials arranged far from neutral axis → resistant to bending)
Bone as Skeleton Example
vertebrata; “cartilaginous fish” (chondrichthyes)
Bones as Skeleton Material
mineralized composite; formed by mesoderm and/or ectoderm; tensile (collagen fibers); compression (minerals- likely first evolved as chemical storage mechanism)
Metazoan Rigid Support
protection and movement; hydrostatic support and fossilized poorly
Protection in Metazoan Skeletons
prevent damage to soft tissues
Movement in Metazoan Skeletons
mucles can only shorten, need antagonist to lengthen; rigid structures act as levers to change muscle output
How do rigid structures act as levers?
transmit force from one point to another; translate output from force to movement; transform direction of force
Transmit
force from one point to another
Translate
output from force to movement
Transform
direction of force
Cambrian Explosion
result of increased fossilization of rigid support
Every lever has
one fulcrum, two forces, two lever arms
Fulcrum
pivot point; lever arms rotate around the fulcrum
2 Forces in a lever
forcein and forceout
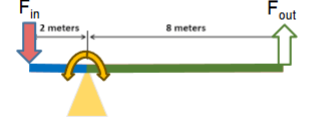
forcein
muscle force
forceout
force applied to external world
two lever arms
in-lever arm (blue); out-lever arm (green)
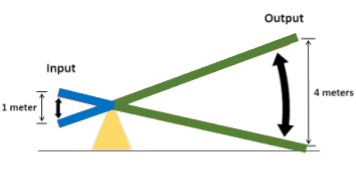
in-lever arm
from the center of the applied force to the fulcrum; blue
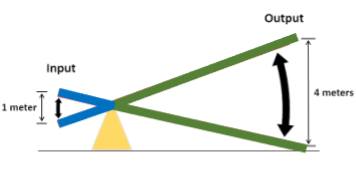
out-lever arm
from the center of the output force to fulcrum; green
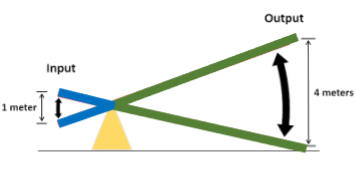
Energyin =
Energyout