Eukayotic Homework Exam #3
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
The subdivision of the eukaryotic cell into organelles:
Physically separates the events of gene expression
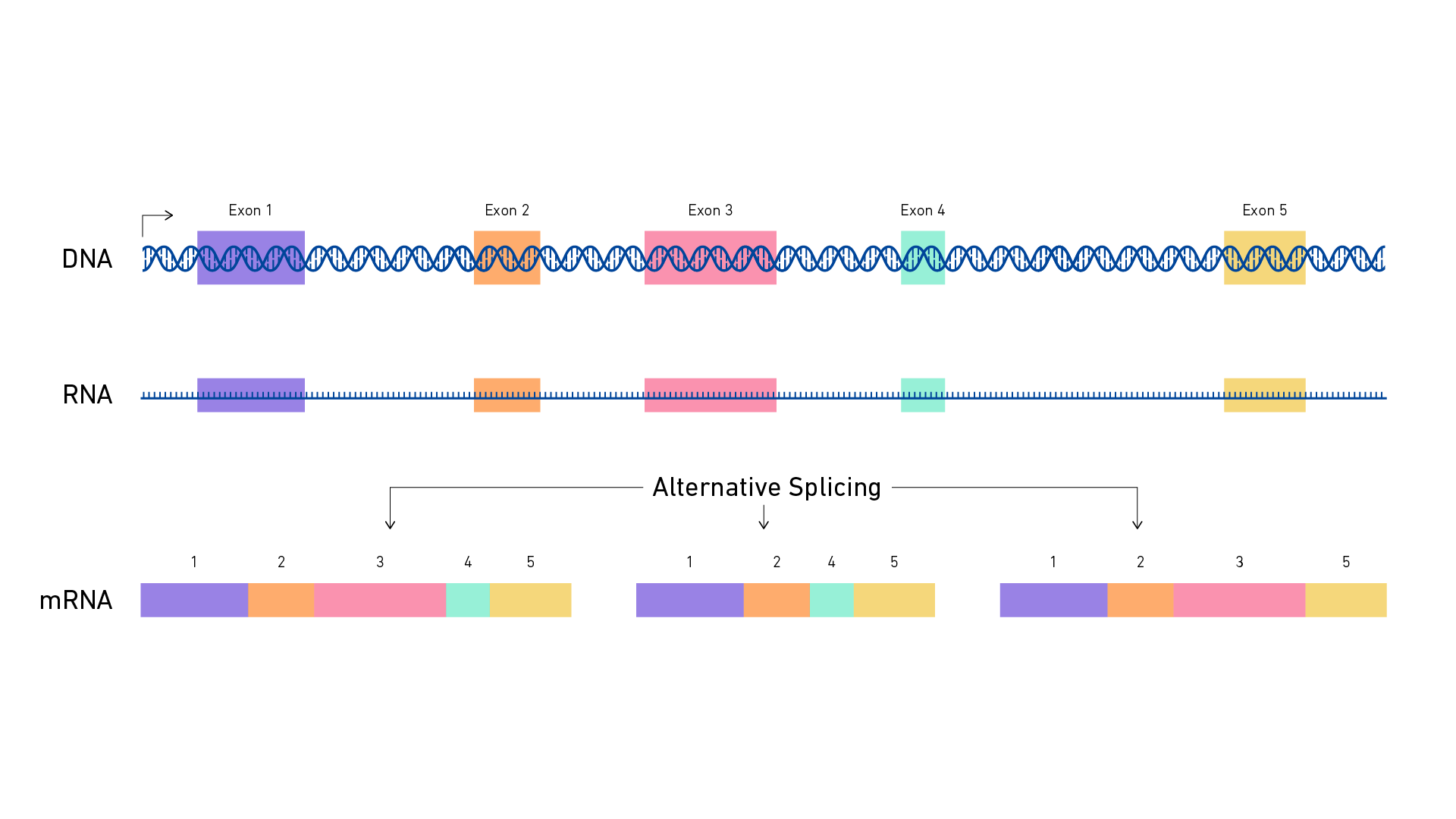
The process of alternate splicing make what possible?
A single gene to code for more than one polypeptide
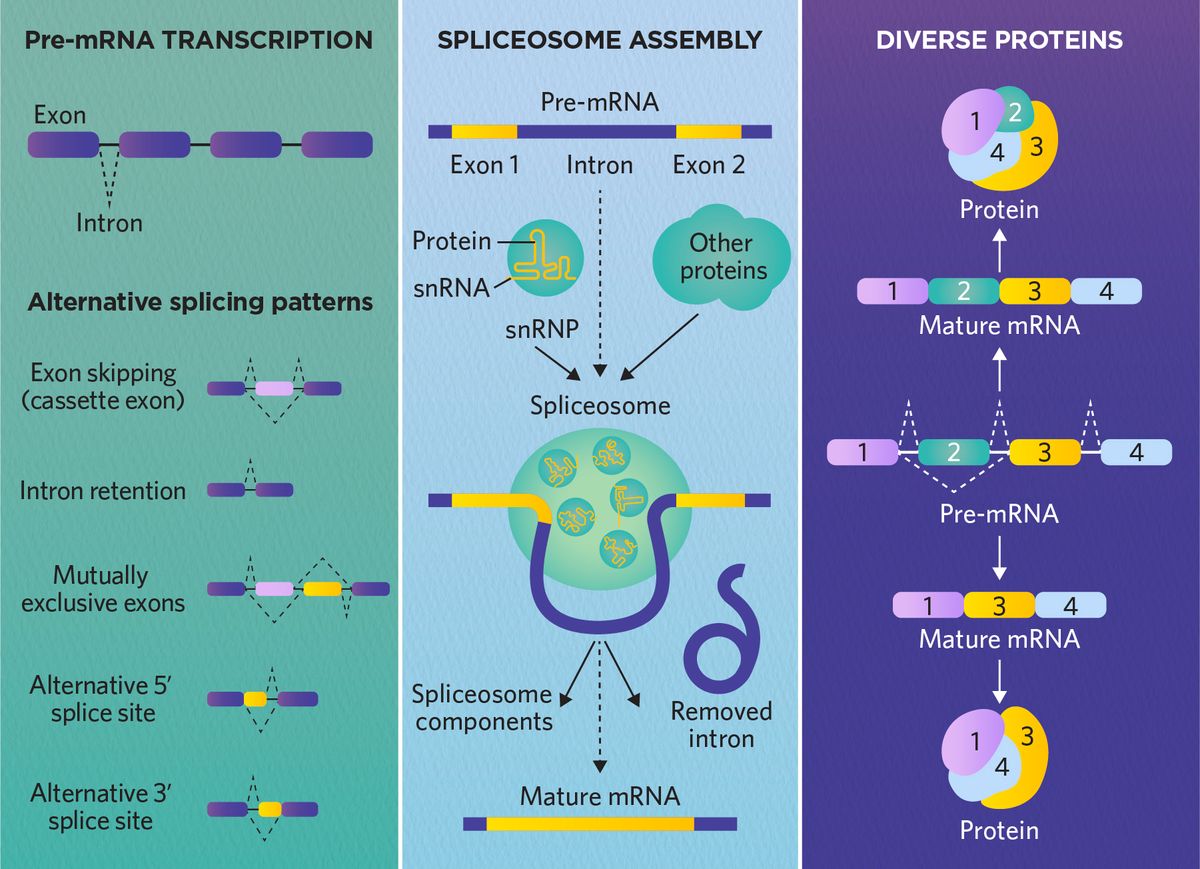
What is alternative splicing?
A process where a single gene can produce multiple different mRNA transcripts, leading to the creation of various proteins with distinct structures and functions
How is heat shock induced in drosophila?
Heat causes the HSTF to become phosphylorated, which in turn allows it to bind to the HSE
What is HSTF?
Heat Shock Transcription Factor (HSTF) is a crucial protein that plays a vital role in regulating the expression of heat shock genes in response to stress conditions
HSTF is a transcription factor that binds to specific DNA sequences called:
Heat Shock Elements (HSE) located on the promoters of heat shock genes
In Drosophila (small fruit fly), HSTF is essential for :
The active transcription of the hsp70 gene, requiring it in addition to RNA polymerase 2
In essence, HSTF acts as a molecular switch, enabling:
Enabling cells to respond to environmental stress by turning on genes that produce proteins to help them survive
What is signal transduction?
Signal transduction transmitting an extracellular signal to the nucleus to affect transcription of a gene of a series of genes
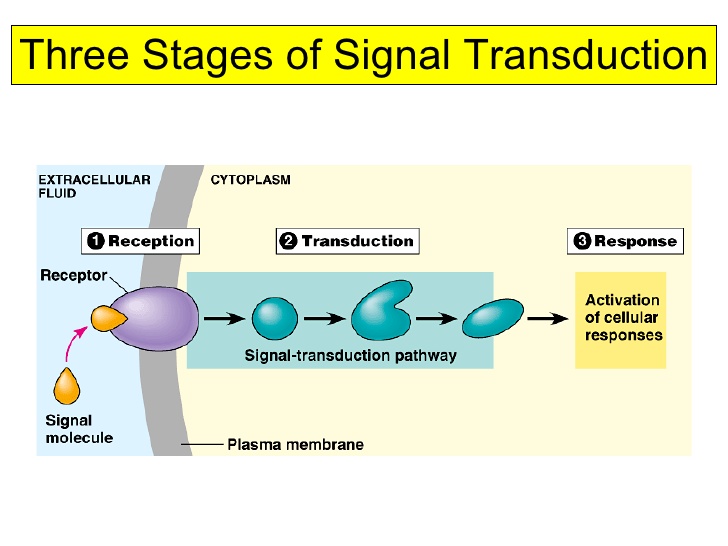
What is the function of basal transcription factors?
The function of basal transcription factors are to bind to the promotor region of a gene to facilitate the proper alignment of the RNA polymerase
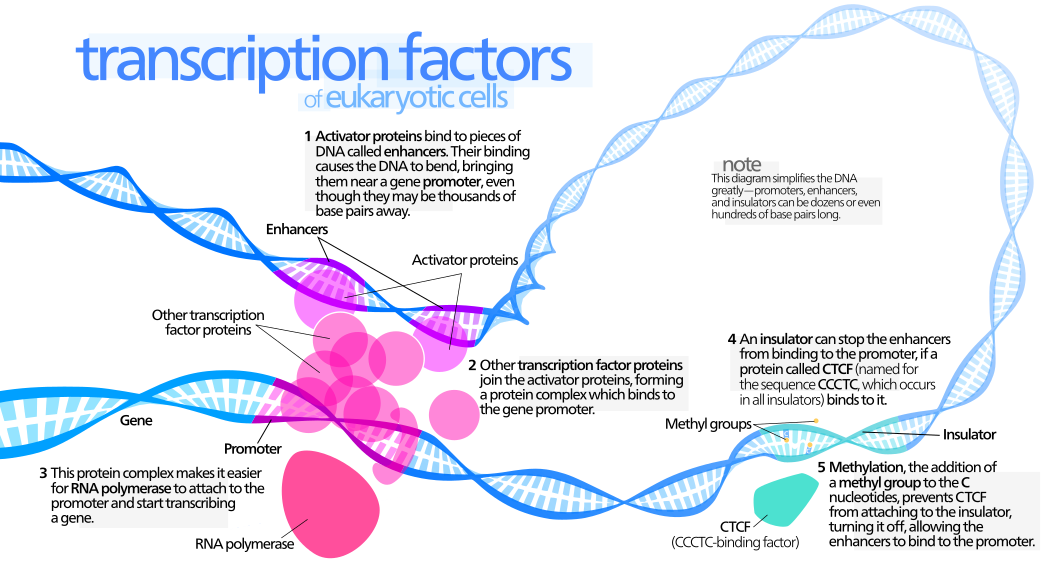
Enhancers differ from promoters in many aspects. What are some characteristics of an enhancer?
It can be far away from the coding region
It’s influence is independent of orientation
It’s effects are independent of position
What is an enhancer in eukaryotic cells?
A short DNA sequence that can significantly increase the rate of transcription of a particular gene. They can be upstream, downstream, or within the gene’s coding region
Enhancers are cis-acting, what does this mean?
They act on the same DNA molecule as the gene they regulate
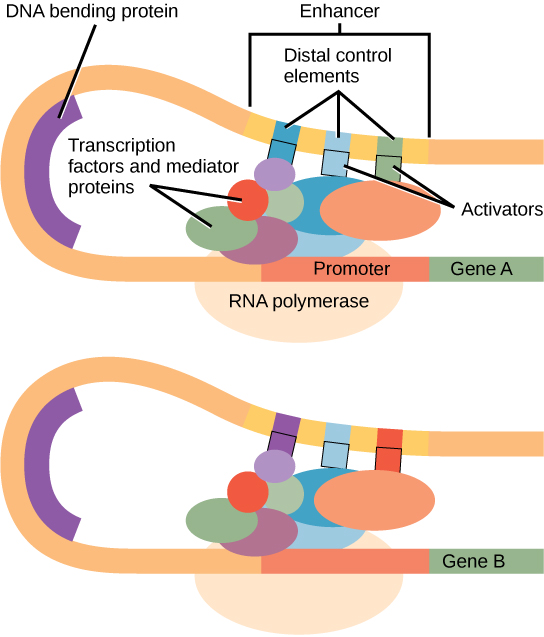
Enhancers act as a binding sites for specific proteins called?
Enhancers bind to transcription factors
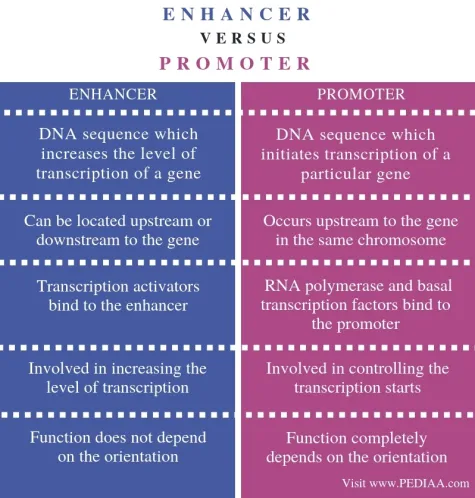
How do enhancers and promoters differ?
Enhancers are short nucleotide sequences that enhance the transcription rate in the genome but are not required for initiation. Promoters are located at the 5’ end of a gene and are large nucleotide sequences essential for initiating transcription
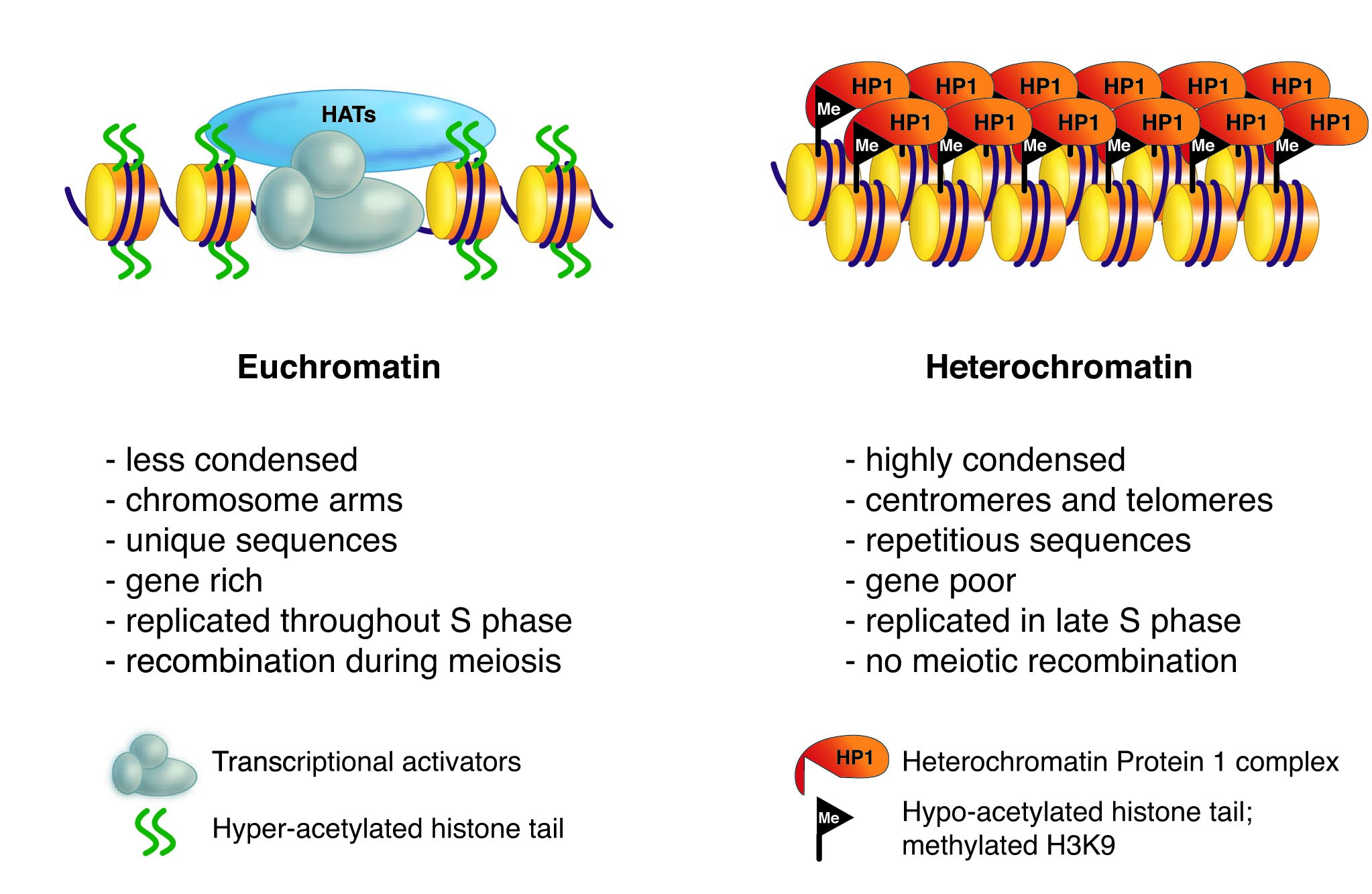
What happens when genes normally located in euchromatin are artificially transposed to heterochromatin?
Gene expression is decreased or inhibited all together. This is because heterochromatin tight packaging (unlike euchromatin, open and accessible) hinders the access of transcription machinery to the DNA, preventing genes from being transcribed and expressed
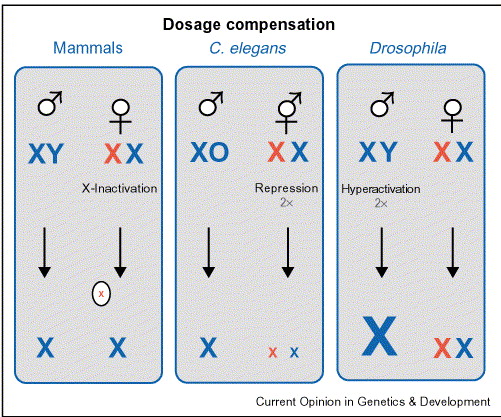
What is dosage compensation?
In humans, one X chromosome is inactivated in females
Males have one X and females have two X chromosomes, there must be a way to equalize gene expression from the X chromosome
In C. Elegans, one X chromosome is hypoactivated in hermaphrodiets
In drosophila, the male’s X chromosome is hyperactivated
What is the definition of dosage compensation
A mechanism by means of which the activity of X-linked or Z-linked genes in made equal in the two sexes of organism
What is RISC?
RISC is a ribonucleoprotein particle that prevents mRNA expression of the gene that produces the mRNAs
What does RISC stand for?
RNA-Induced silencing complex: A protein complex that plays a crucial role in gene regulation, specifically in the process of RNA interference (RNAi)
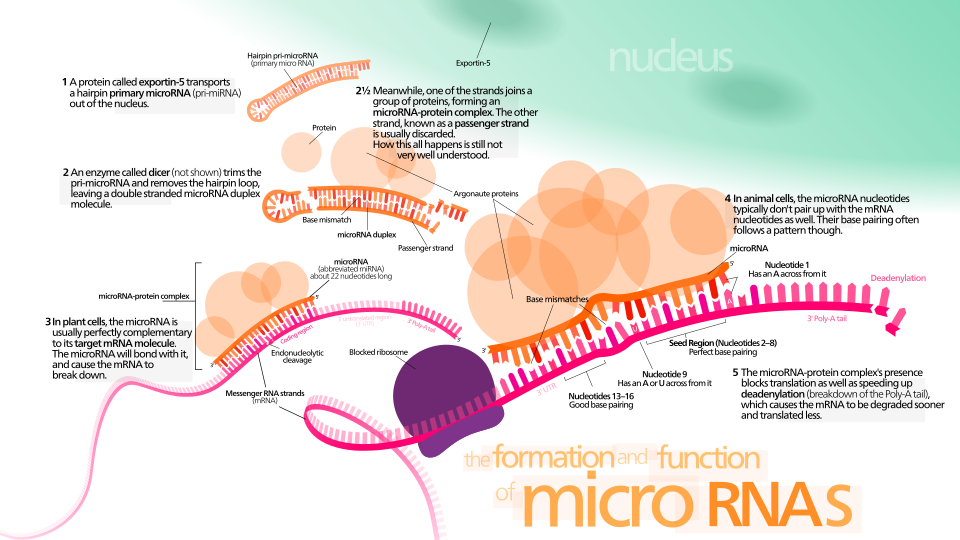
What is siRNA?
Small interfering RNA are short, double-stranded RNA molecules. Play an important role in RNA interference. SiRNAs are synthesized to match the sequence of target mRNA
What are some structural motifs to transcription factors that help them interact with DNA?
Zinc finger
leucine zipper
Helix-loop-helix
NOT helix-beta-helix
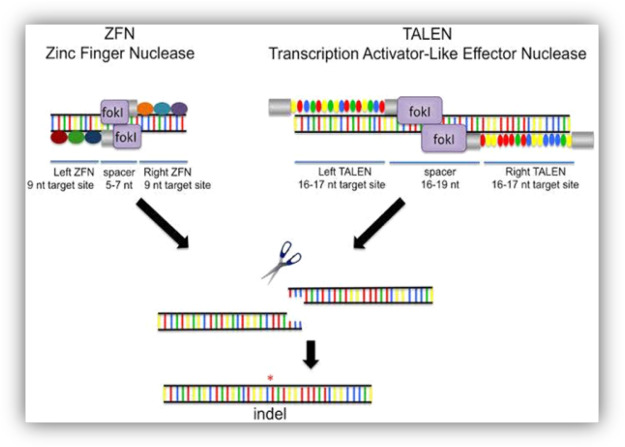
What are zinc finger nucleases (ZFN’s)(DNA Scissors)?
Small protein domains that bind zinc ions and are involved in various cellular process, particularly DNA binding
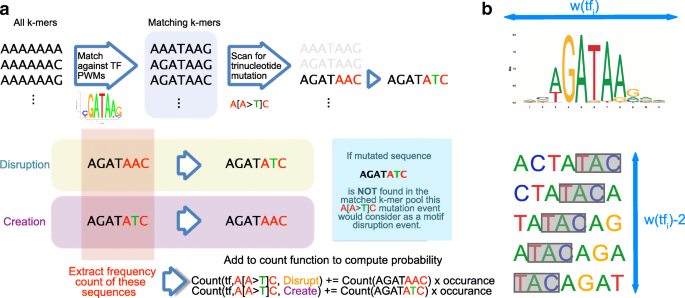
What are Transcription Factor Binding Motifs (TFBMs)?
Transcription factor motifs are specific DNA sequences recognized by transcription factors, proteins that control gene expression
What is a leucine zipper?
A leucine zipper is a structural motif in proteins, particularly DNA-binding proteins, characterized by a periodic repetition of leucine residues every seventh amino acid position within an alpha-helix. This motif allows proteins to dimerize, forming a coiled-coil structure
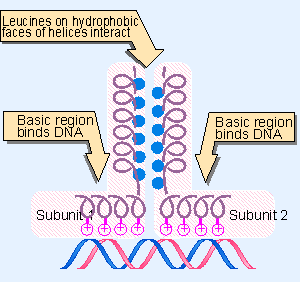
What is a helix-loop-helix (HLH)?
HLH motif is a protein structural domain found in many DNA-binding proteins, particularly transcription factors. It consists of two alpha-helices connected by a flexible loop region
