AP World: Unit 2 (Units 3-4/Chapters 12-15)
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Units 3-4/Chapters 12-15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Explorations Financed by Portugal
Prince Henry the Navigator
Vasco da Gama: explored eastern Africa, India
Explorations Financed by Spain
Christopher Columbus: explored Americas
Treaty of Tordesillas (1494)
agreement between Spain and Portugal to split colonized land between them
Explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1500)
South America
Ponce de Leon (1513)
Explored Florida
Vasco de Balboa (1513)
Explored Central America
Ferdinand Magellan (1519)
Explored South America to Philippines
Giovanni da Verrazzano (1524)
Explored the Atlantic coast North America
Sir Francis Drake (1578)
circumnavigated the globe
John Cabot (1497)
Explored North America
Henry Hudson (1609)
Explored the Hudson River
Products that aided new explorations
Sternpost Rudder
Lateen Sails
Astrolabe
Magnetic Compass
Three-Masted Caravels
Sternpost Rudder
invented in China - better control of ships
Lateen Sails
invented in Roman Empire - allowed directional control of ships
Astrolabe
navigation device that measured distance between sun and stars on horizon to determine latitude
Magnetic Compass
developed in China - determine direction
Three-Masted Caravels
large ships fit for longer journeys
Hernando Cortes
landed on coast of Mexico in 1519 - sought to exploit the Aztec Empire of their gold and spices
Became very hungry for wealth and quickly seized Montezuma and began a siege of Tenochtitlan
Disease in the Aztec Empire
Spanish brought smallpox which reduced their population from 20 million in 1520 to 2 million in 1580
Spanish were able to take control in 1525
Francisco Pizarro
took over Inca Empire in 1531 partially due to spreading disease to them
Pizarro was in control of the Inca Empire by 1535
Casta System
Spanish implemented a hierarchical colonial society as they took over the New World:
Peninsulares: Spanish officials governing the colonies
Creoles: Spanish born in colonies to Spanish parents - barred from high positions but were educated and wealthy
Mestizos: those with European/Native American ancestry
Mulattos: those with European/African ancestry
Native Americans
Viceroys
governors of each of 5 regions of New Spain - established the encomienda system
Start of the African Slave Trade
Europe exploited a system of slavery already existing in Africa - prisoners were supposed to serve their captors before being released
Europeans traded for their surplus of enslaved people, but didn’t understand that they were supposed to be released
Middle Passage
Ocean passage from Africa to Americas that was brutal with treacherous waters
Where did Europe take the African slaves?
Around 13 million Africans were taken - 60% to South America, 35% to Caribbean, 5% to North America, around 20% of people on each trip perished
Columbian Exchange
Transatlantic transfer of animals, plants, diseases, people, technology, ideas among Europe, Americas, and Africa
Never before had so much moved across the ocean
Key Products of the Columbian Exchange
sugar (plantations appeared all over Spanish colonies),
silver (mining also in Spanish colonies)
both used significant forced labour
Age or Exploration
trading, empire building, conquest - due to financing schemes
Joint-stock Company
pool resources of merchants to distribute costs and reducing dangers of individual investors
Led to huge profits and modern-day concept of stock markets
Mercantilism
theory that creating a favourable balance of import and export was best - of course, this led to Europe’s intense colonialism to match their import demand
Qing Dynasty
last imperial dynasty of China; preceded by the Ming Dynasty and succeeded by the People's Republic; founded in 1644 by the Manchus and ruled China for more than 260 years, until 1912; expanded China's borders to include Taiwan, Tibet, Chinese Central Asia, and Mongolia.
Manchus
Northeast Asian peoples who defeated the Ming Dynasty and founded the Qing Dynasty in 1644, which was the last of China's imperial dynasties.
Mughal Empire
Muslim state (1526-1857) exercising dominion over most of India in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries; often had difficulties managing such a large, diverse empire
Ottoman Empire
Islamic state of Turkic speaking peoples lasting from 1453-1922; conquered the Byzantine Empire in 1453; based at Istanbul (formerly Constantinople); encompassed lands in the Middle East, North Africa, the Caucasus, and eastern Europe.
Safavids
A Shi'ite Muslim dynasty that ruled in Persia (Iran and parts of Iraq) from the 16th-18th centuries that had a mixed culture of the Persians, Ottomans, and Arabs.
Songhai
an Islamic West African empire that conquered Mali and controlled trade from the into the 16th century; eventually defeated by the Moroccans who were broke after fighting with Portugal
Devshirme
'Selection' in Turkish. The system by which boys from Christian communities were taken by the Ottoman state to serve as Janissaries (elite military units)
Janissary
elite Ottoman guard (trained as foot soldiers or administrators) recruited from the Christian population through the devshirme system, that often converted to Islam; utilized gunpowder weapons
samurai
class of salaried warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble called a daimyo (who in turned pledged loyalty to a shogun) in return for land or rice payments
Divine Right
the idea that monarchs are God's representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God.
absolute monarchy
system of government in which the head of state is a hereditary position and the king or queen has almost complete power

Versailles
Palace constructed by Louis XIV outside of Paris to glorify his rule and subdue the nobility; late 17th-early 18th century (became his primary residence around 1670)
zamindars
Mughal empire's taxation system where decentralized lords collected tribute/taxes for the emperor
Taj Mahal
beautiful mausoleum (tomb) at Agra (India) built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (completed in 1649) in memory of his favorite wife; illustrates syncretic blend between Indian and Arabic architectural styles
tax farming
tax-collection system utilized by the Ottoman Empire to generate money for territorial expansion; the government hired private individuals to collect taxes
Protestant Reformation
religious movement begun by German monk Martin Luther who began to question the practices of the Catholic Church beginning in 1519; split the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the 'protesters' forming several new Christian denominations: Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican Churches (among many others)
95 Theses
arguments written by Martin Luther against the Catholic church. They were posted on October 31, 1517; ultimately led to Martin Luther's excommunication and the Protestant Reformation
Martin Luther
a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices; began the Protestant Reformation
Counter/Catholic Reformation
the reaction of the Roman Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation; reaffirming the veneration of saints and the authority of the Pope (to which Protestants objected), ended sale of indulgences and simony, created Jesuits missionaries, but also the began the Inquisition
Jesuits
Also known as the Society of Jesus; a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism (a result of the Counter Reformation); sent to China, Japan, and the New World to gain Catholic converts

indulgence
a pardon given by the Roman Catholic Church in return for repentance for sins and payment; "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins"
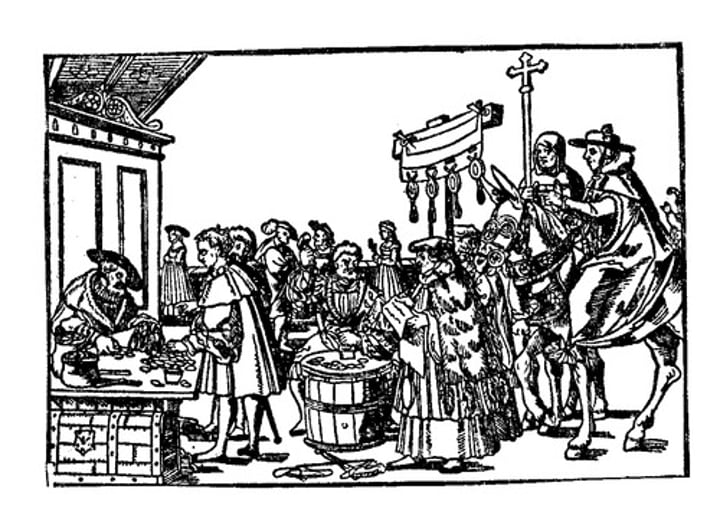

Simony
the buying and selling of church offices, seen as a corrupt practice, this practice was outlawed by the Catholic Church during the Counter Reformation
Inquisition
Roman Catholic tribunal for investigating and prosecuting charges of heresy, a reaction to the Protestant Reformation

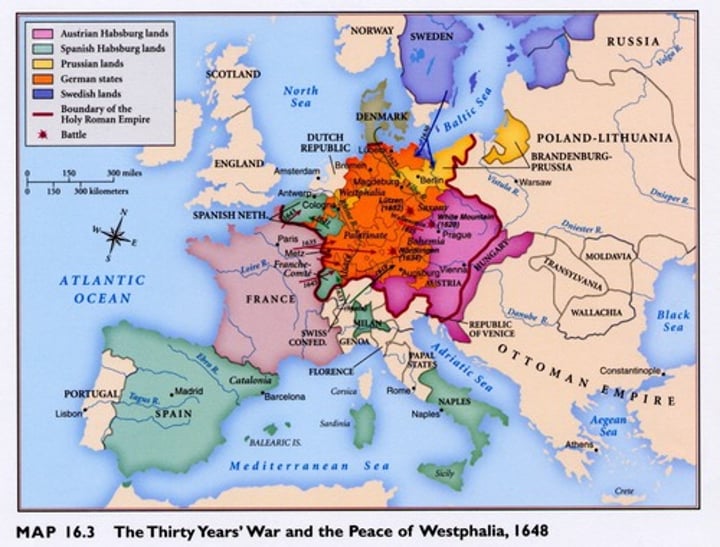
Thirty Years War
a war that resulted from the Protestant Reformation (1618-1648 CE); occurred in the Holy Roman Empire between German Protestants and their allies (Sweden, Denmark, France) and the emperor and his ally, Spain who supported Roman Catholicism; ended in 1648 after great destruction with Treaty of Westphalia
John Calvin
1509-1564. French theologian who developed the Christian theology known as Calvinism; attracted Protestant followers with his teachings; believed in predestination
Sikhism
the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and combining elements of Hinduism and Islam; a result of the presence of the Mughal Empire in India

Shogunate
Japanese system of government under a shogun (military warlord), who exercised actual power while the emperor was reduced to a figurehead
Daimyo
Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai; owed allegiance to the shogun
Jizya
tax paid by Christians and Jews (and sometimes other faiths) who lived in Muslim communities to allow them to continue to practice their own religion; often utilized by Islamic states to manage diverse populations within their empires
Millet System
A system used by the Ottomans whereby subjects were divided into religious communities, with each millet (nation) enjoying autonomous self-government under its religious leaders; a unique way to manage a diverse empire
Encomienda System
A labor system instituted by the Spanish crown during the colonization of the Americas, where Spanish settlers were granted the right to extract labor and tribute from Indigenous peoples in exchange for protection and religious instruction. This system was significant in shaping colonial society and economy in Spanish America, as it laid the groundwork for a class-based society heavily reliant on Indigenous labor.