Casts, Crystals, and other elements
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Hyaline cast
Increased with exercise, dehydration, heat, and emotional stress.
May be seen in acute glomerularnephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease, and congestive heart failure.
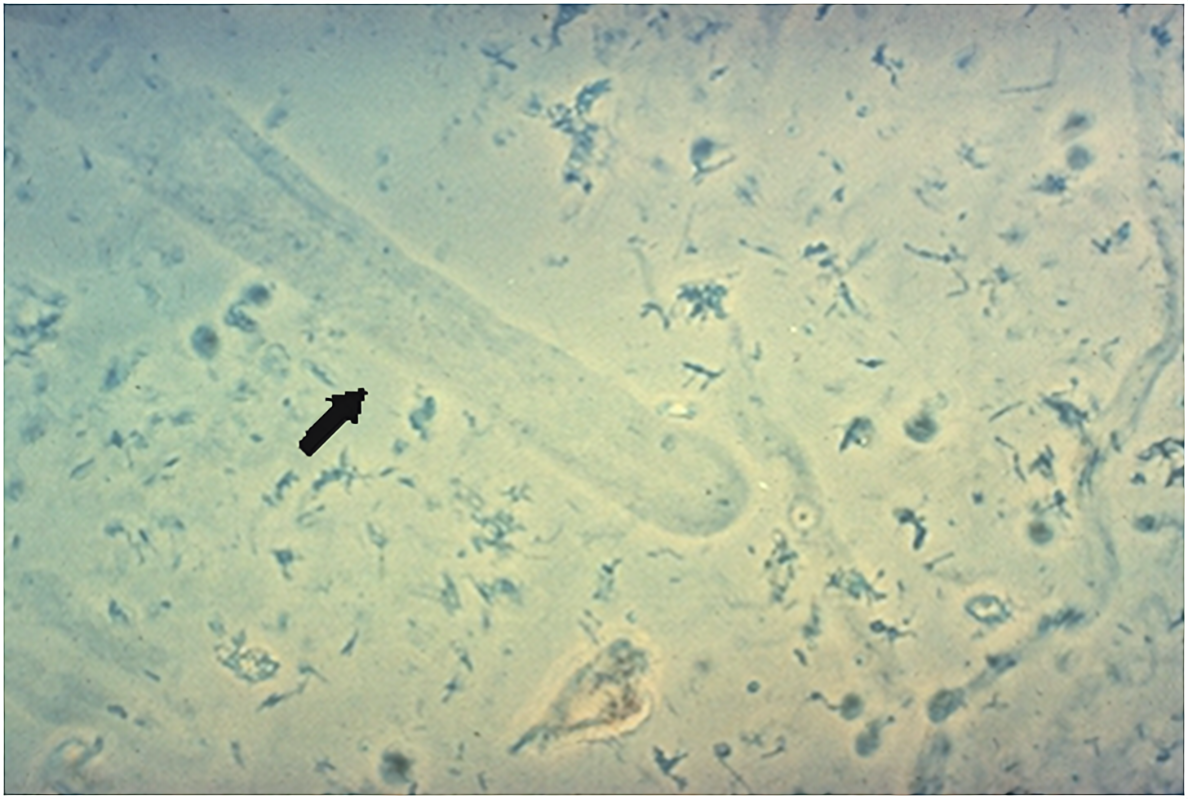
RBC cast
RBCs are embedded in the matrix and must be clearly identifiable. Presence indicates acute glomerulonephritis, glomerular disease or glomerular damage.
Also seen in strenuous sports.
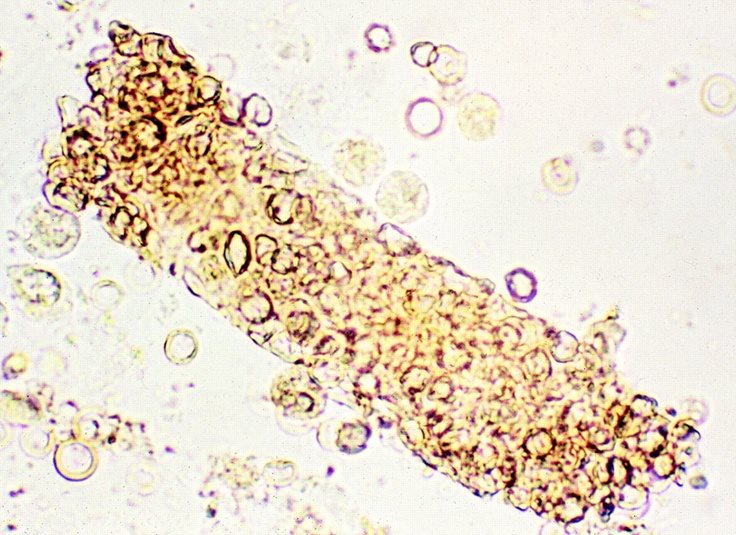
Hemoglobin cast
This cast is associated glomerular disease glomerular damage, and acute glomerulonephritis.
Appears reddish brown due to hematin formation. Accompanied by hematuria. Associated

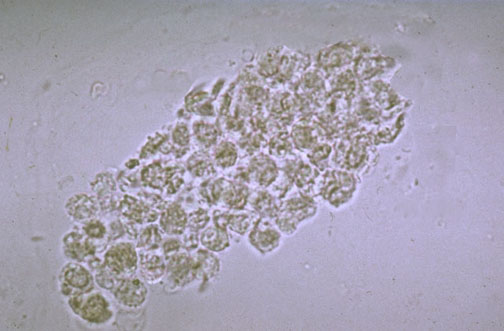
WBC cast
Cast with leukocytes embedded in the matrix.
Associated with inflammation, infection, and renal tubular disease.
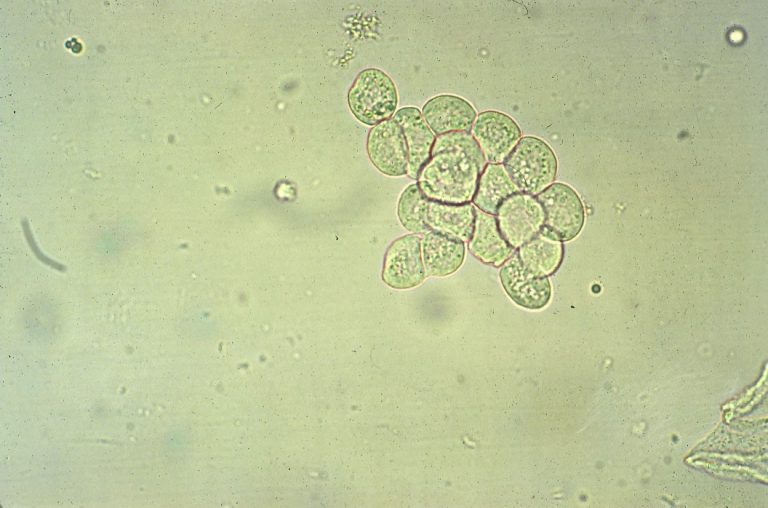
Renal tubular epithelial cast
Form as a result of stasis and necrosis of the tubules.
Presence can be seen in severe chronic kidney disease, exposure to nephrotic agents or viruses, rejection to kidney transplants.
Granular Casts
Thought to be from breakdown of cellular cast components.
Progressive cellular deterioration leads to appearance of coarse granules which transition into fine granules.
Presence is associated with renal disease.
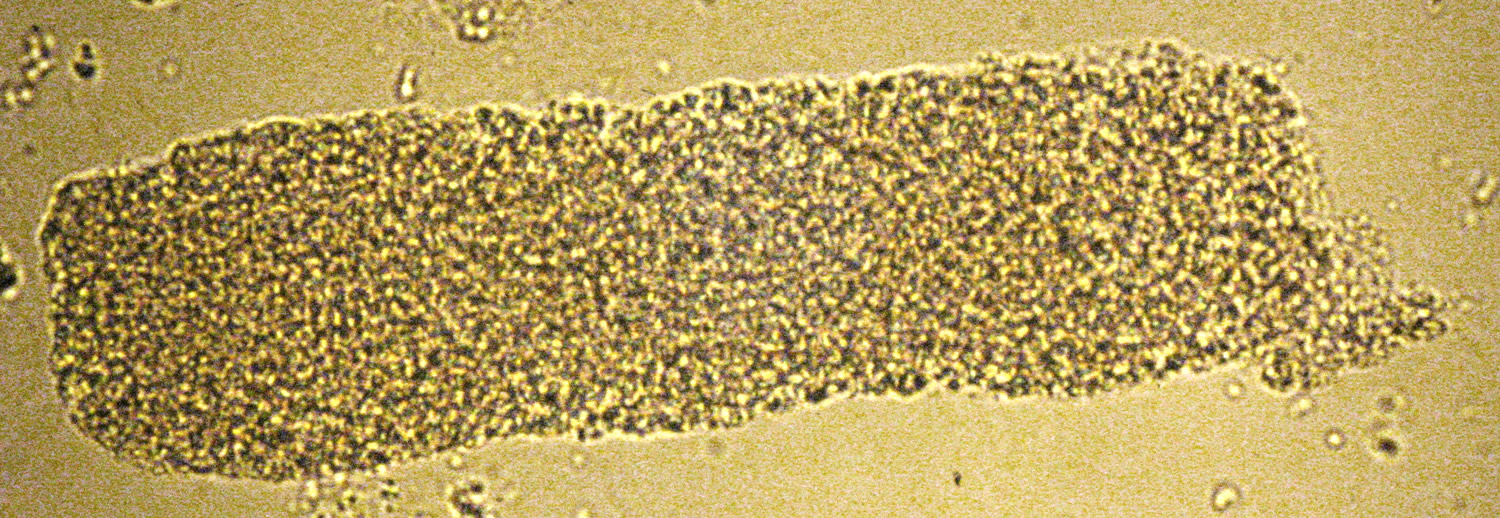
Waxy cast
Appear as smooth homogenous cylinders with blunt broken ends and cracked and serrated edges that are highly refractile.
Associated with severe chronic renal failure, malignant hypertensions, diabetic nephropathy, acute renal disease, and renal transplant rejection.
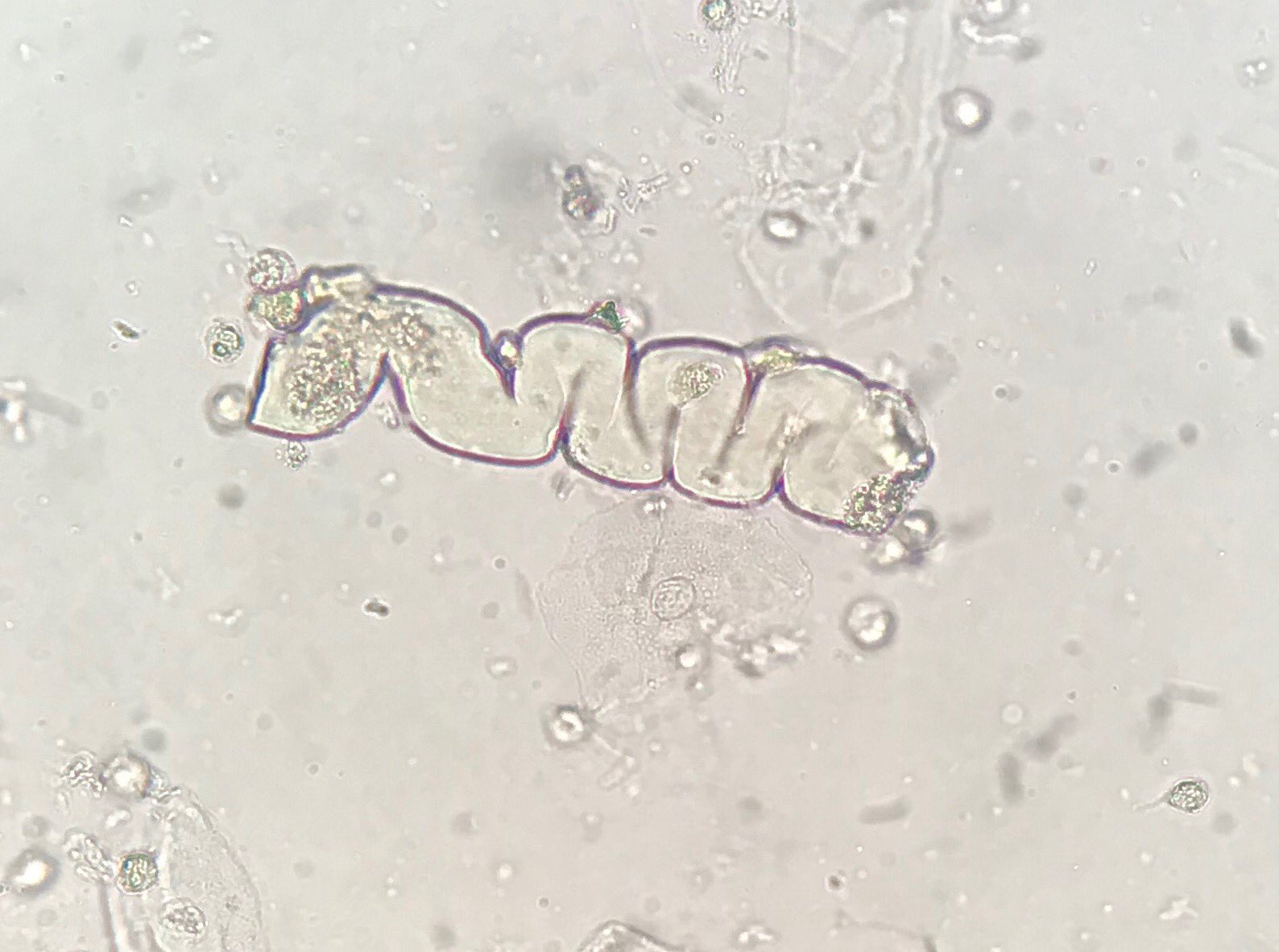
Fatty cast
Cast with incorporated fat droplets. If cholesterol is present it makes a Maltese cross under light.
Seen with diabetes, and nephrotic syndrome.
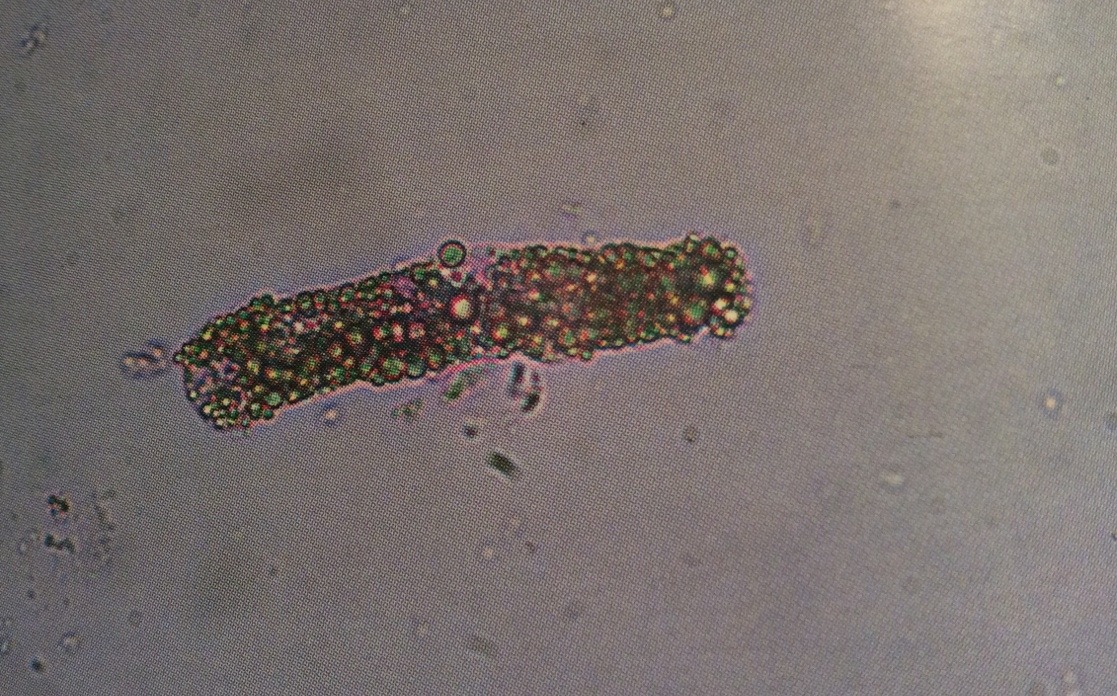
Uric acid crystal
Forms in acidic pH
Seen in patients with gout, chemotherapy, and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
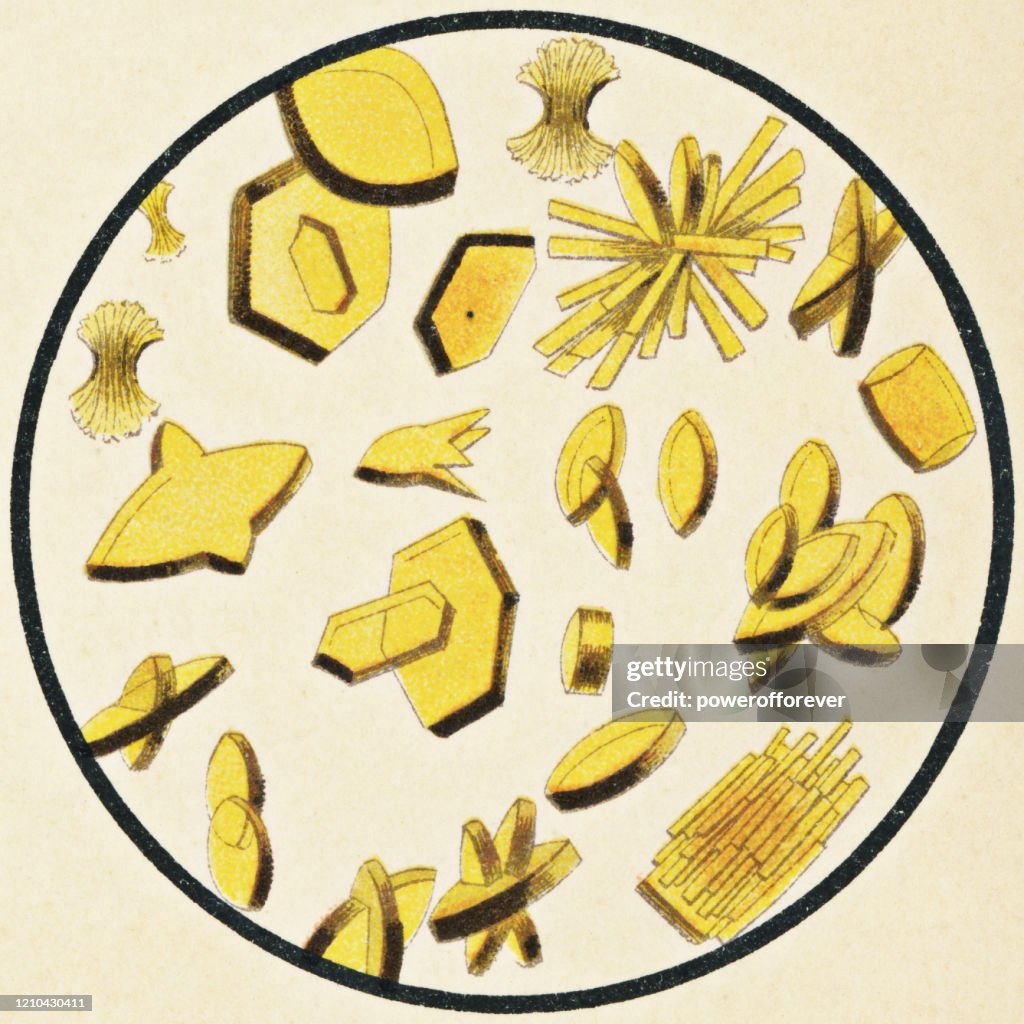
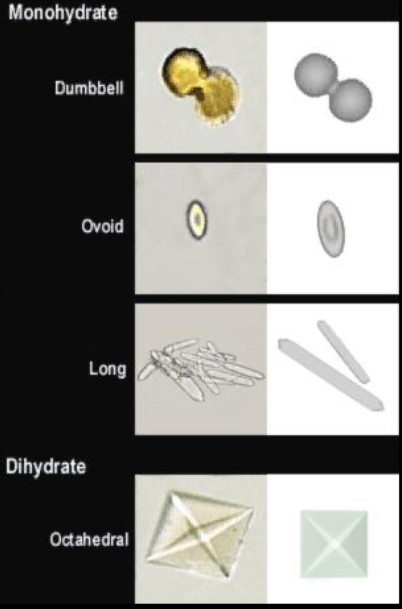
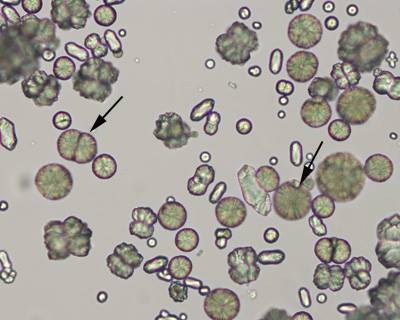
Calcium oxalate crystal
Forms in acidic, alkaline, and neutral urine
Dihydrate form: Predominate in urine from patients with diets rich in oxalic acid, most common cause of kidney stones
Monohydrate form: Predominate urine from patients who have ingested ethylene glycol.
Hippuric Acid
Form in acidic or neutral pH
Little to no clinical significance, seen in people who work with organic substances.
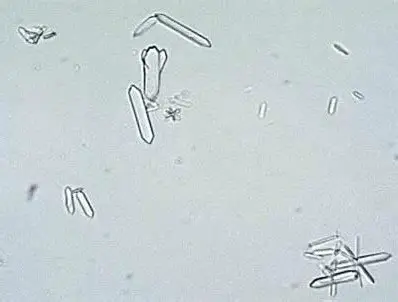
Calcium phosphate crystals
Form in neutral and alkaline pH
Seen in metabolic disorders and medications that alter pH
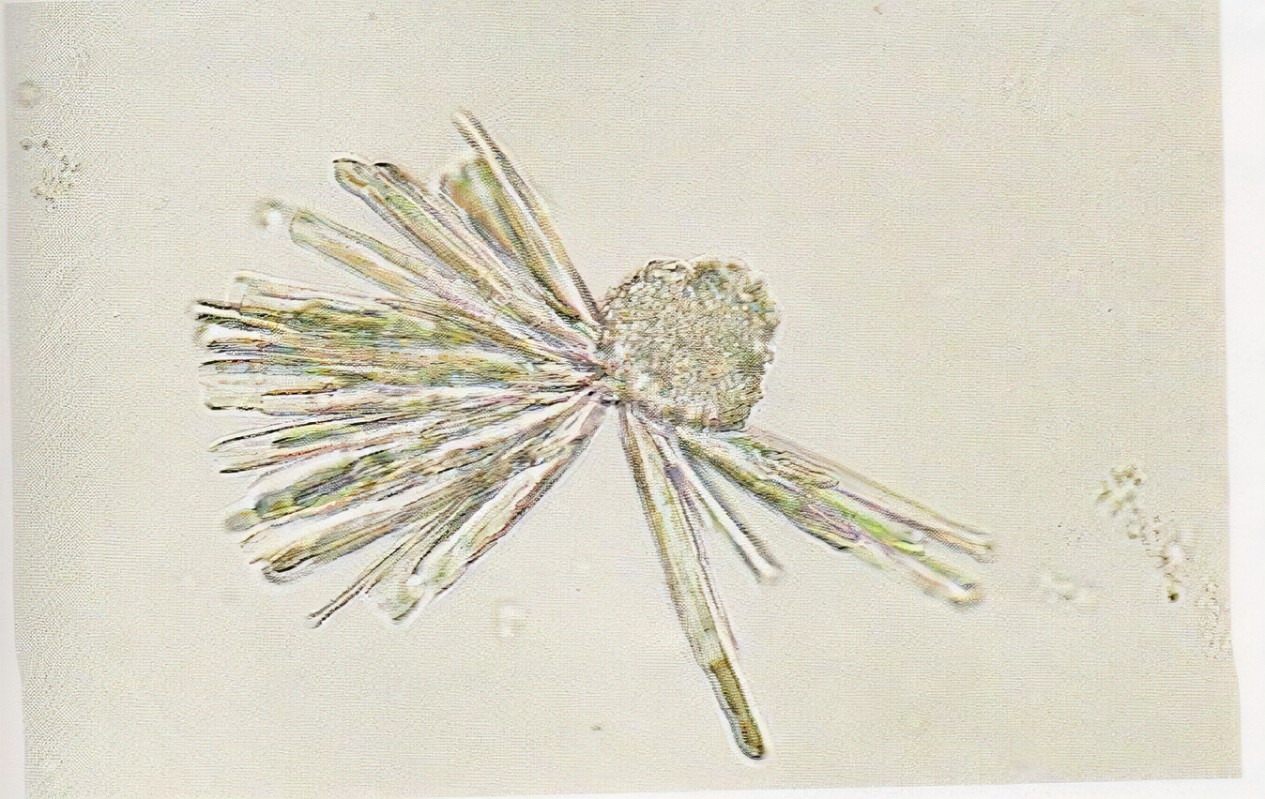

Triple phosphate crystals
Form in alkaline urine
Presence is insignificant
Seen in dog urine specimens with UTIs
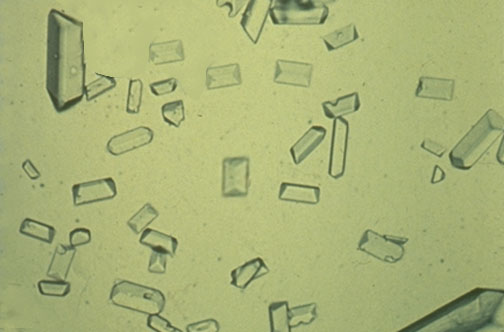
Calcium carbonate crystals
Form in alkaline pH
Not clinically significant
Ammonium biurate crystals
Form in alkaline pH
Presence may be significant if formed in-vivo (dehydration)
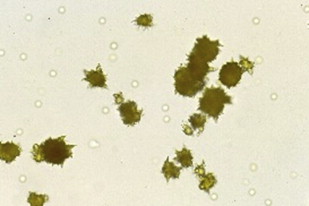
Amorphus urates
Form in acidic pH
Seen in refrigerated samples, soluble at alkaline pH or if heated over 60 Celsius
Amorphus phosphates
Form in alkaline pH
Seen in refrigerated samples as white sediment
Soluble in acetic acid and does not dissolve if heated over 60 Celsius
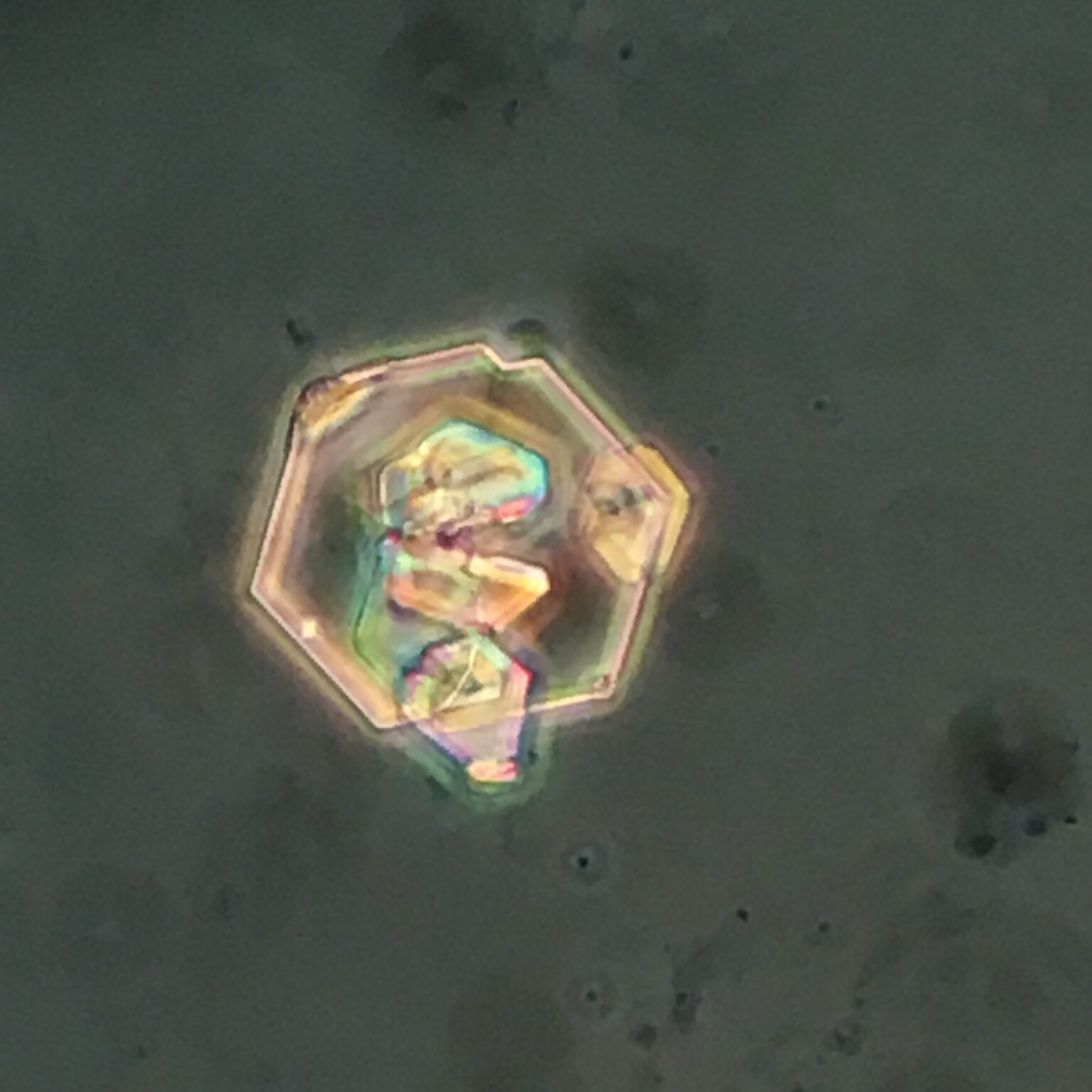
Cystine crystals
Form in acidic pH
Associated with inborn errors of metabolism such as hereditary cystinosis or cystinuria. Most common cause on kidney stones in children.

Leucine crystals
Form in acid pH
Presence associated with inborn errors of metabolism
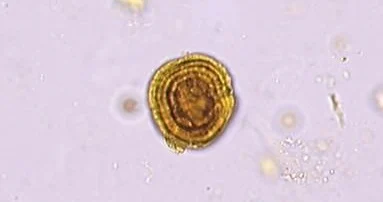
Tyrosine crystals
Form in acidic pH
Associated with inborn errors of metabolism such as tyrosinemia and certain liver disorders.
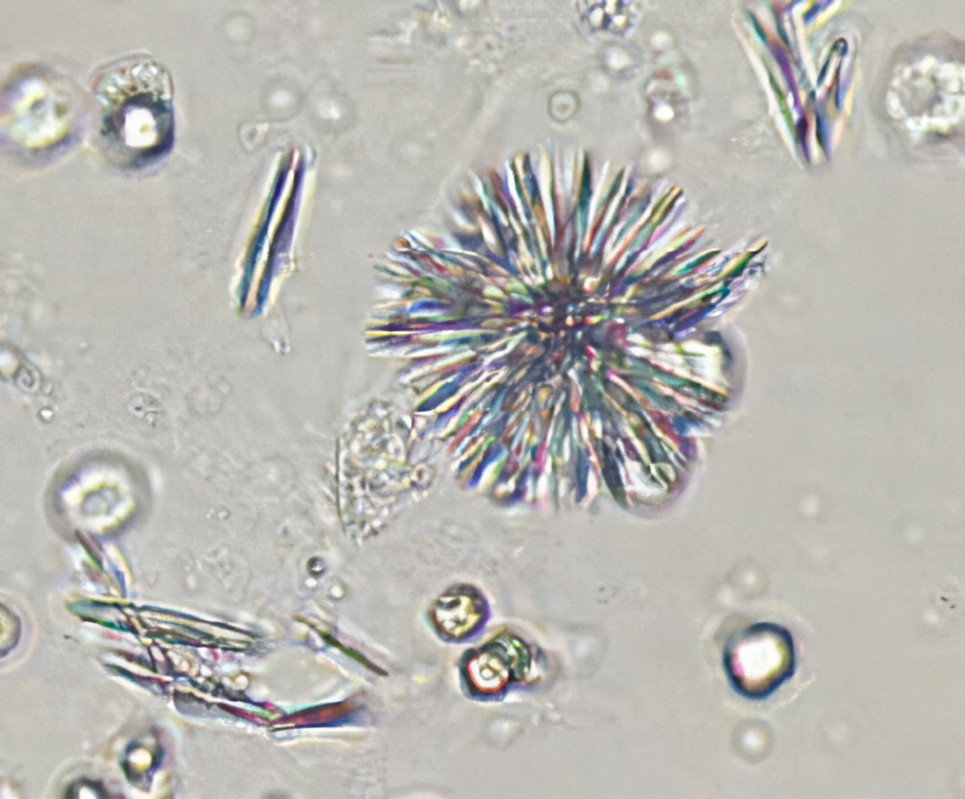
Ampicillin crystals
Form in acidic pH

Sulfonamide crystals
Form in acidic pH

Indinavir crystals
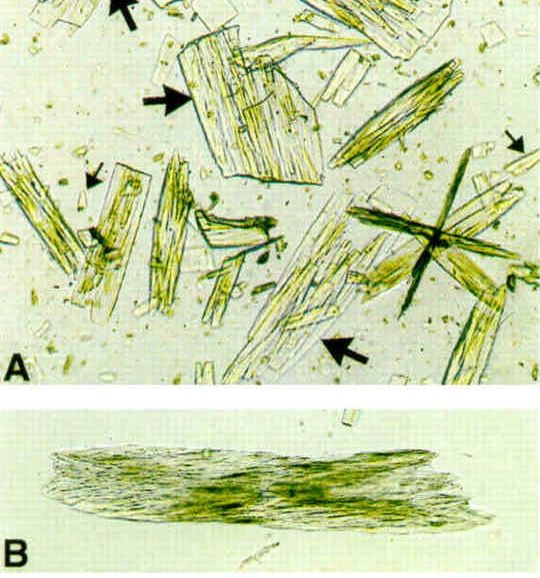
Radiopaque dye crystals
Associated with high SG results by refractometer
Bilirubin crystals
Form in acidic pH
Form from conjugated _________
Associated with hepatic disorders and liver disease
