BIOL 124 Exam 4 Central Nervous System (CNS) Flashcards
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
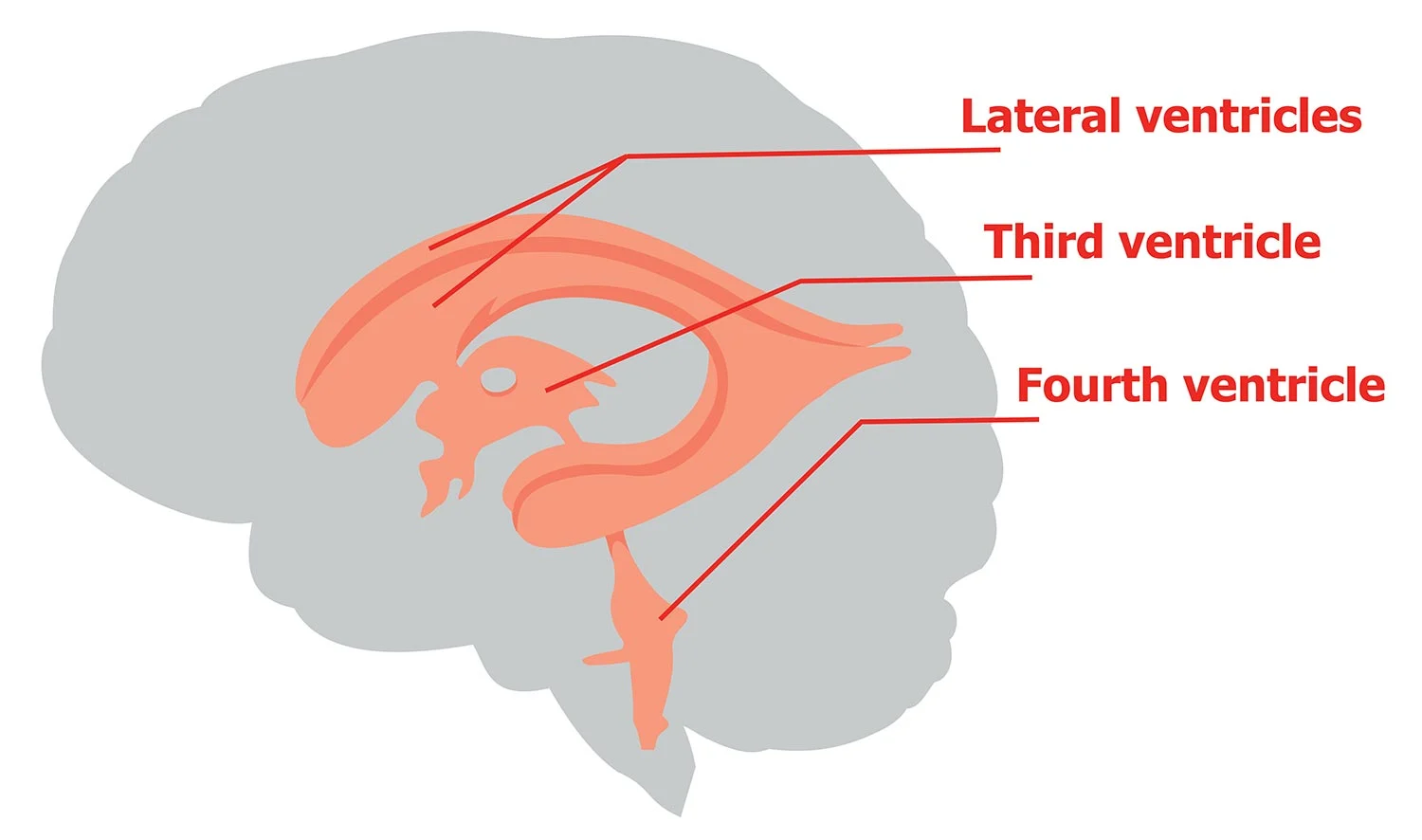
What are the ventricle spaces in the brain?
Lateral (one on each side)
Third (inside diencephalon)
Fourth (between brainstem and cerebellum)
List the components of the layers that protect the brain. This includes the blood brain barrier and maters.
Skull, CSF (cerebrospinal fluid), Meninges (dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater), Blood brain barrier (capillary endothelium and astrocytes)
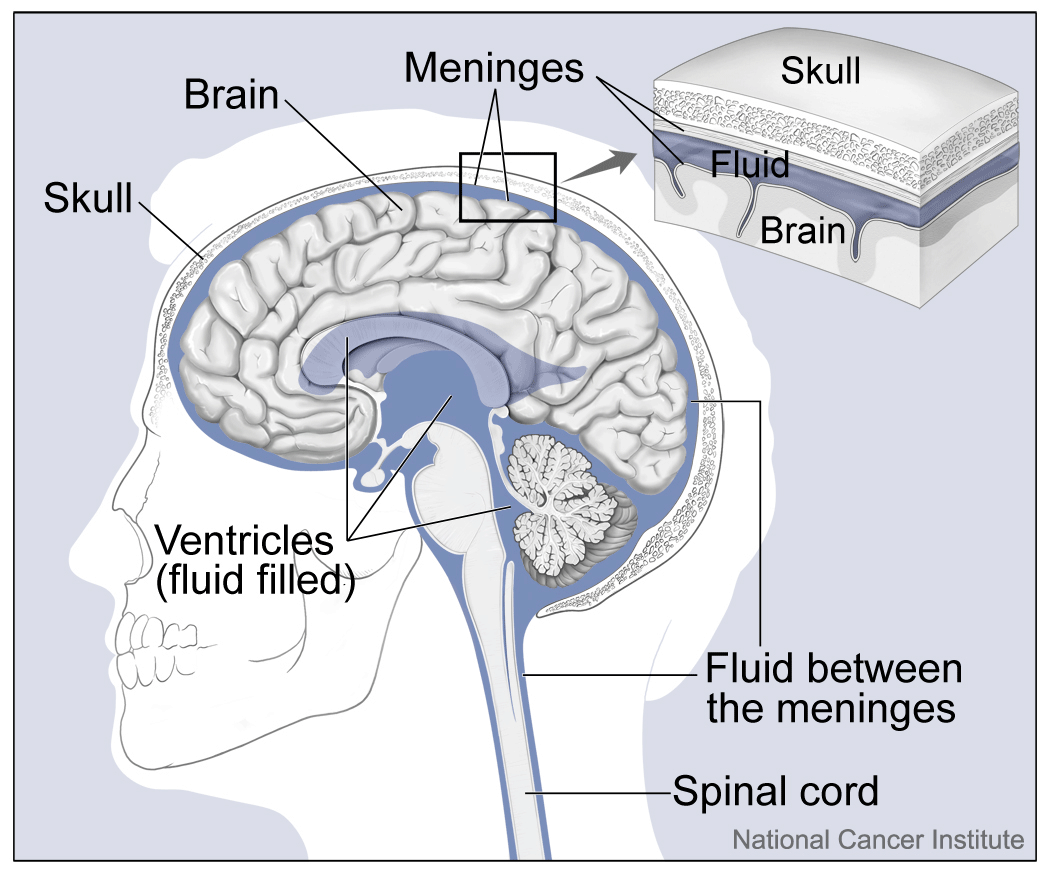
Where is the cerebrospinal fluid produced (be specific) and what is one of its functions?
Ependymal cells in the choroid plexus. (CSF flows from ventricles into subarachnoid space) Shock absorbers, optical chemical environment, circulation of nutrients, waste removal.
Association fibers
connect brain structures of the same hemisphere
Commissural fibers
connect gray areas of 2 hemispheres
Projection fibers
enter the hemispheres from lower brain regions
What are the 3 functional areas involved in interpreting pain (i.e. stubbing your toe)? List them in the order that they interpret pain.
Sensory
Associations
Motor
How does contralateral processing occur?
When hemispheres receive sensory information from opposite side of the body
What does the left hemisphere control?
Language, math, logic (and the right side of the body contralaterally)
What does the right hemisphere control?
Visual-spatial skills, emotion, and artistic (left side of body contralaterally)
Premotor cortex function
learned motor skills (repetition and pattern)
Broca’s area
motor speech
Primary motor cortex
skeletal muscle movement
Primary somatosensory cortex
receives and interprets sensory impulses
Cerebellum
posture and balance
Hypothalamus
regulates body temperature, hunger, water imbalances through hormones and endocrine system
Thalamus
relay center, sends afferent impulses to cerebral cortex. relay for all sensory information
Pineal gland
secretes hormone for sleep (melatonin)
Reticular formation
filters incoming sensory information, keeps cerebral cortex alert, controls/maintains consciousness
Brainstem
basic life functions → example: breathing
Limbic system
involves in emotion (amygdala) and memory (hippocampus)
Low glucose levels lead to (list symptoms):
dizziness, altered mental status, loss of conciousness
List the three layers of the spinal meninges:
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
Where does the cerebrospinal fluid circulate in the spine?
Subarachnoid space and central canal
In the spinal nerve, which root does the afferent neuron travel?
Dorsal root
Which cervical spinal nerve exists below the vertebrae?
C8
Which cervical spinal nerve exists above the vertebrae?
C1-C7
Why would each peripheral nerve have fibers from more than one spinal nerve?
Backup. Having more than one spinal nerve segment doesn’t completely disable connection to CNS.
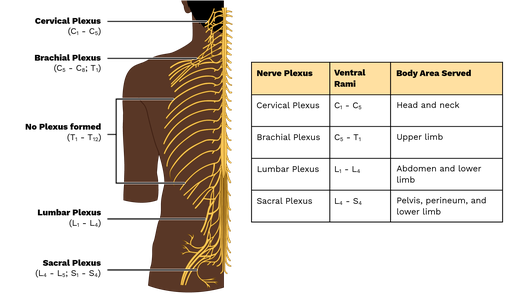
Name the four plexuses, and what they innervate
Cervical (C1-C5) - Head, neck, ear, posterior head, shoulder, diaphragm
Brachial (C5-T1) - Skin and muscle of pectoral girdle and upper limbs
Lumbar (L1-L4) - Skin and muscle of abdominopelvic region, anterior, and medial thigh
Sacral (L4-S4) - Skin and muscle of buttock, perineum, posterior thigh, lower leg, and foot
What is the importance of dermatomes?
Can determine which areas are damaged based on sensations of the skin through cutaneous pain. Dermatomes - area of the skin innervated by a single spinal nerve.