GYN study guide
1/450
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
451 Terms
The fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and upper 2/3s of the vagina develop from ______
2 paired mullerian ducts
What kind of abnormalities commonly accompany Müllerian duct defects due to the close proximity of development?
renal
When one or both Müllerian ducts don’t develop fully, producing abnormalities such as uterine agenesis or hypoplasia (b/l) or unicornuate uterus (u/l), this is known as ______
organogenesis
The process during which the lower segments of paired Müllerian ducts fuse to form the uterus, cervix, and upper vagina, this is known as _____
lateral fusion
Fusion of the ascending sinovaginal bulb with the descending mullerian system, resulting in a patent vagina, is referred to as ____
vertical fusion
incomplete vertical fusion results in _____
imperforate hymen
failure of lateral fusion results in _____
bicornuate or didelphys uterus
What phase of Müllerian development consists of a central septum after the lower Müllerian ducts fuse?
septal resorption
failure of septal resorption results in ____
septate uterus
What are the 3 phases of development of complete formation and differentiation of the mullerian defects?
organogenesis, fusion, septal resorption
What class mullerian defect is this?
hypoplasia / agenesis → no reproductive potential aside from IVF of harvested ova and implantation in a host
class I
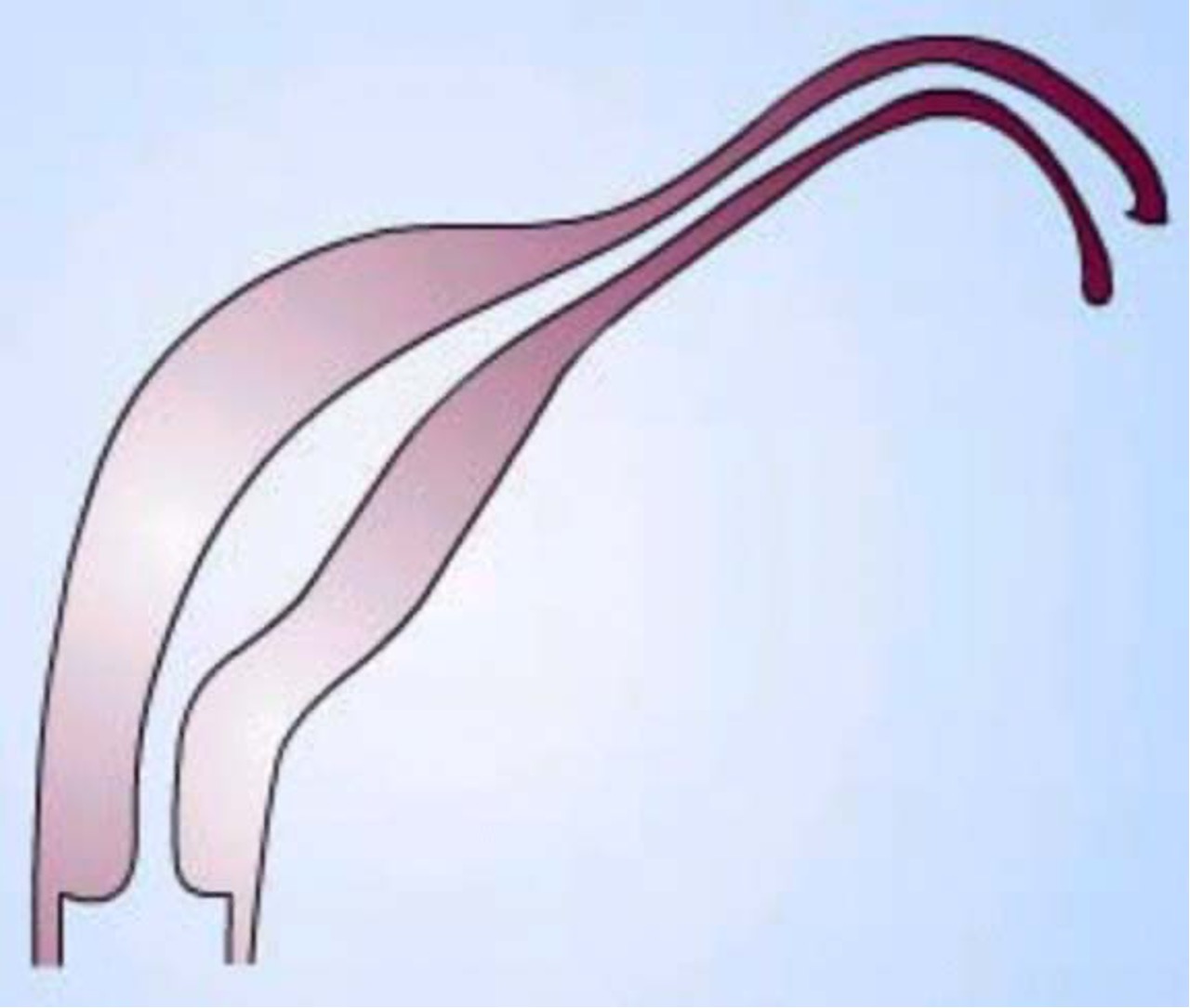
What class mullerian defect is this?
unicornuate uterus → result of complete/almost complete arrest of development of 1 Müllerian duct
incomplete arrest (MC) → rudimentary horn w/ or w/o functioning endometrium
if horn obstructed, may need surgery, enlarging pelvic mass
if contralateral healthy horn is almost fully developed, a full term pregnancy is believed to be possible
class II
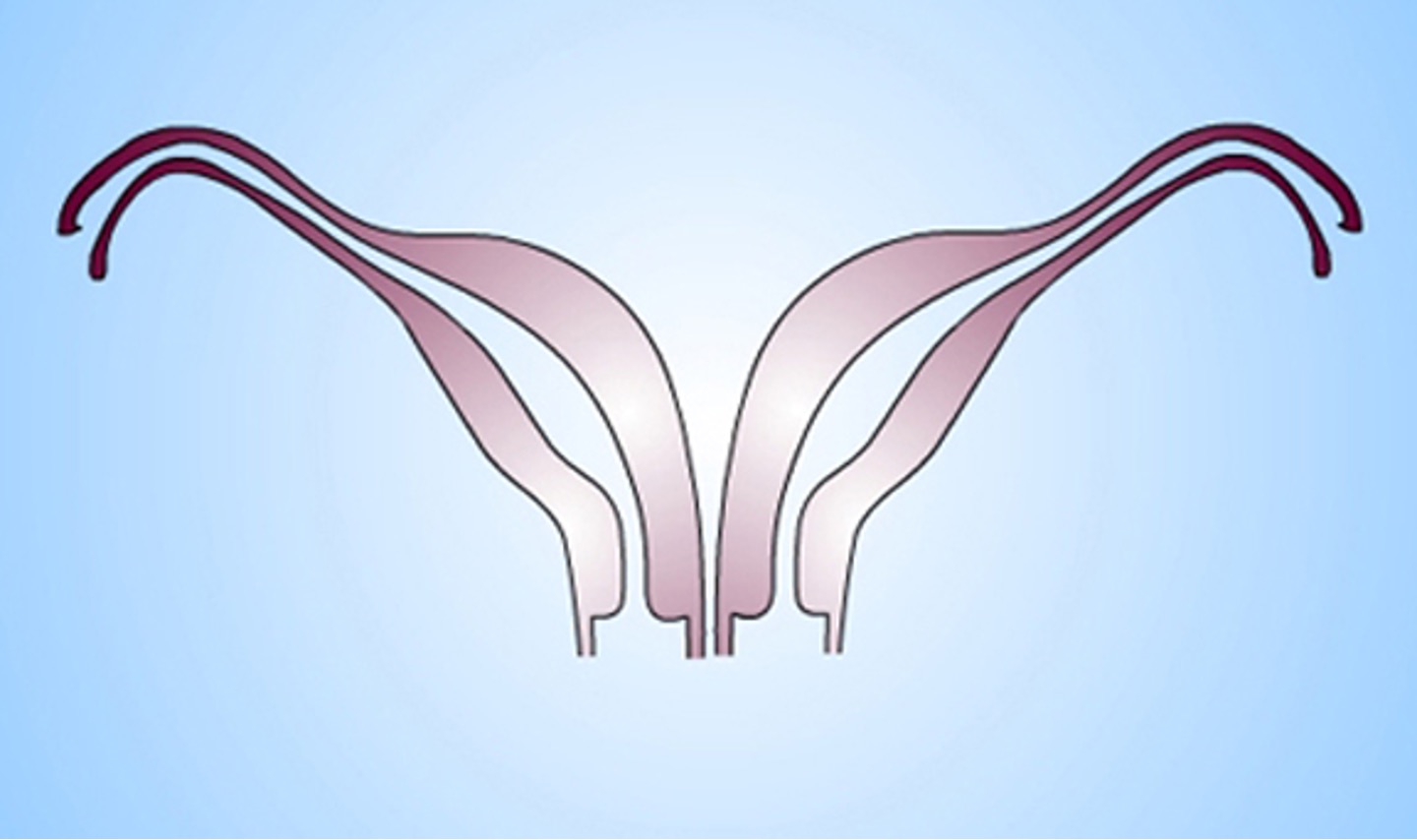
What class mullerian defect is this?
didelphys uterus → results from complete nonfusion of both ducts
individual horns are fully developed and almost normal in size
2 cervices inevitably present
longitudinal or transverse vaginal septum possible
consider metroplasty (removing septum & fusing both)
can carry pregnancy to full term since each horn is almost a fully developed uterus
class III
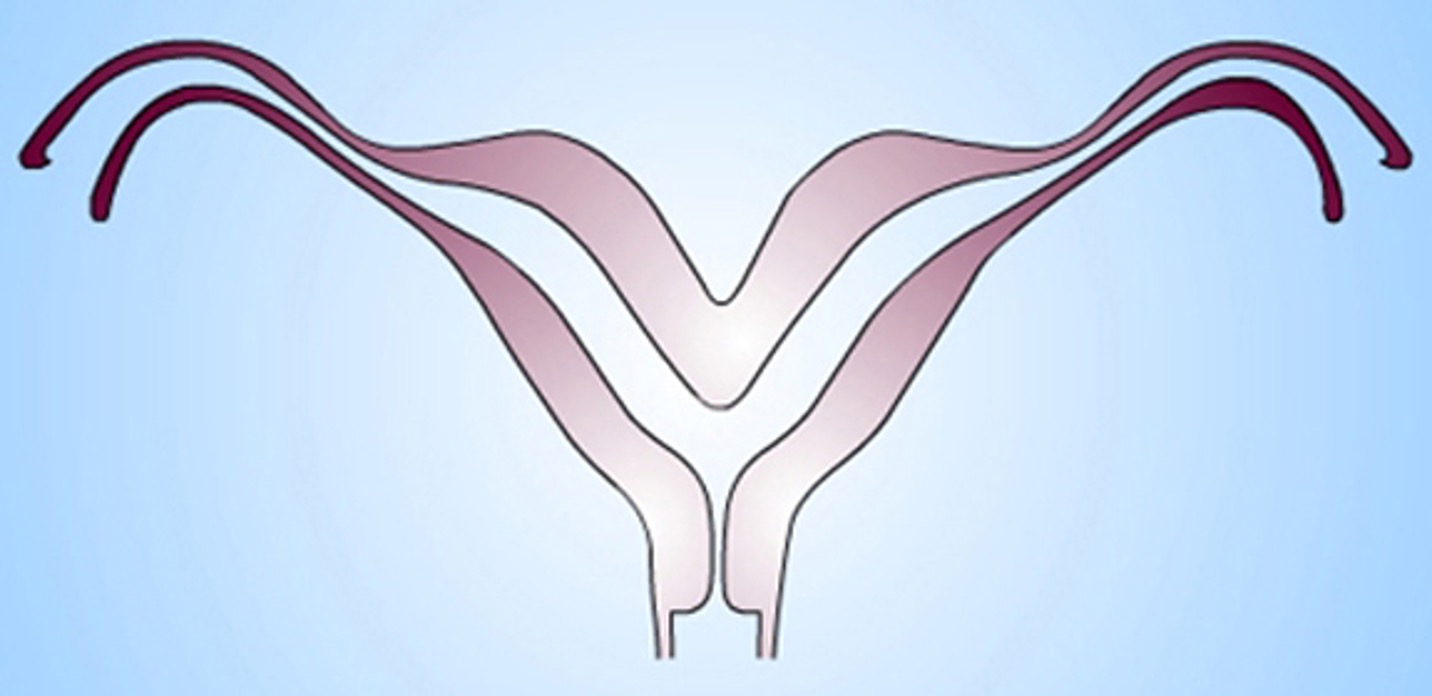
What class mullerian defect?
bicornuate uterus → results from partial confusion of ducts
demonstrates some degree of fusion b/t the 2 horns
horns not fully developed, typically smaller
some pts are candidates for metroplasty
class IV
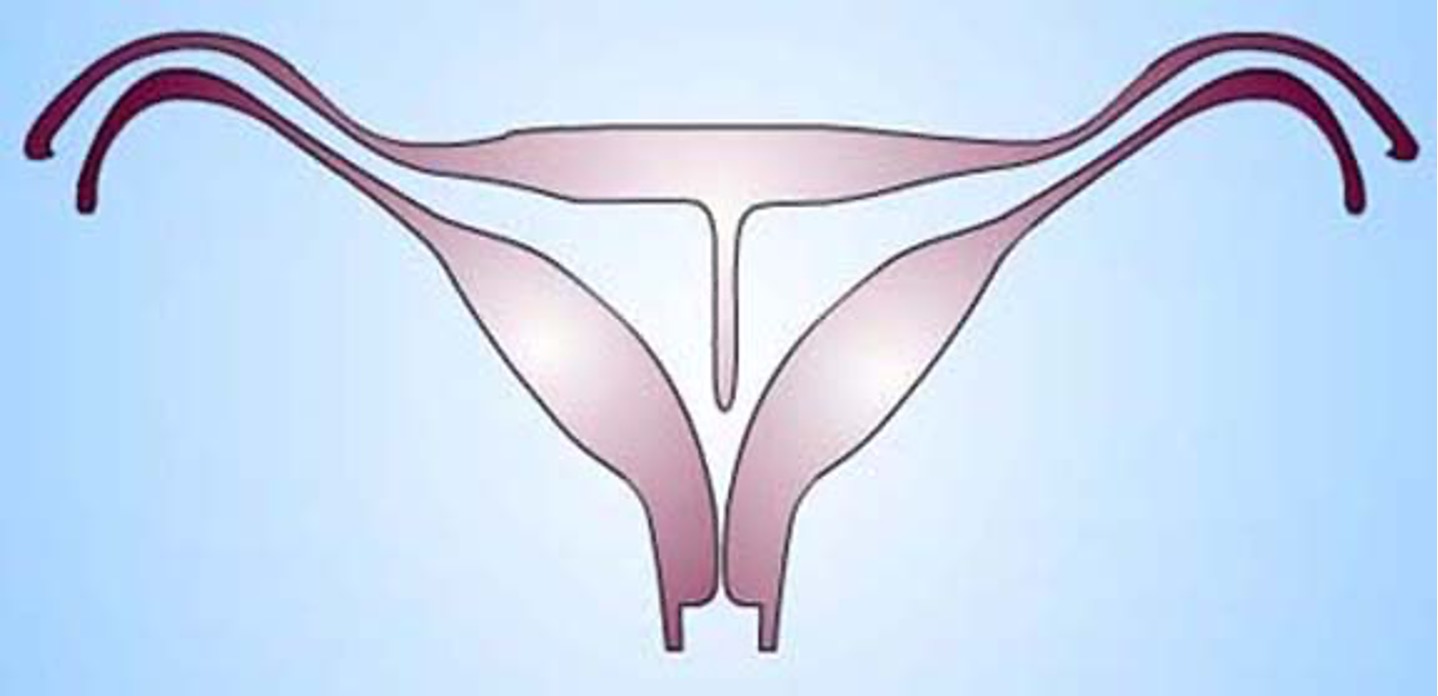
What class mullerian defect?
septate uterus → results from failure of resorption of septum b/t 2 uterine horns
septum can be partial or complete
uterine fundus is typically convex but may be flat or slightly concave
highest incidence of reproductive complications
treated by using transvaginal hysteroscopic resection of septum
class V
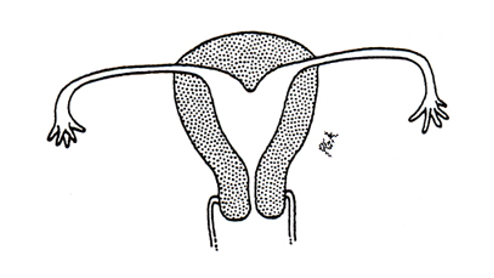
What class mullerian defect?
arcuate uterus → variant of normal, no adverse impact on fertility and pregnancy outcomes
has slight midline septum w/ minimal and often broad fundal cavity indentation
variously classified as septate, bicornuate, or normal variant
class VI
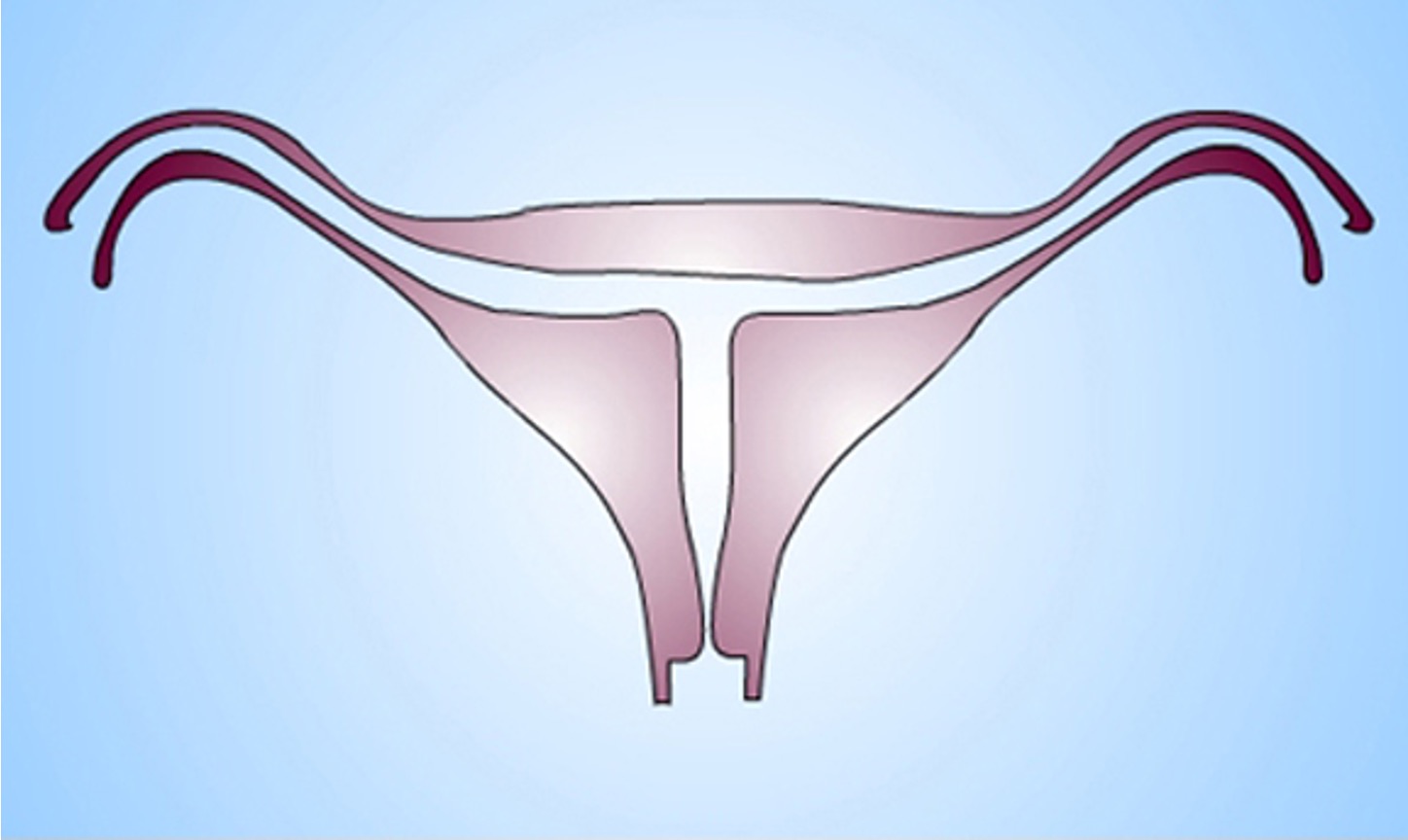
What class mullerian defect?
diethylstilbestrol (DES) related anomaly → synthetic form of estrogen prescribe to pregnant women to prevent pregnancy complications from 1945-1971
seen in female offspring in 15% women exposed to DES during pregnancy
variety of abnormal findings- uterine hypoplasia and t shaped uterine cavity; inc risk vaginal clear cell carcinoma
class VII
What are the 3 primary components of the menstrual cycle?
HPG axis (hypothalamus, pituitary gland, gonadal)
______ secretes LH and FSH to stimulate ovarian function.
anterior pituitary
Which cycle?
follicular phase
ovulation
luteal phase; pregnancy
ovarian
Which cycle?
proliferative phase
secretory phase
menses
uterine
What is the control center that responds to hormones and neurotransmitters and secretes GnRH every 90 minutes, pulsatile to the anterior pituitary via portal circulation?
hypothalamus
What phase of the ovarian cycle?
initiated by lack of estrogen at end of menses
FSH from ant pit stimulates follicle to grow & produce estrogen
Graafian follicle chosen by day 7
as estrogen inc, it inhibits release of FSH
LH from ant pit in small amounts prior to ovulation, surges mid cycle in response to peak amounts of estrogen from mature follicle, stimulates ovary to produce progesterone after ovulation
10-14 days
follicular / phase I
Which phase of the ovarian cycle?
estrogen peaks at 200-300 pg/ml
GnRH inhibited by high estrogen & amt of FSH being secreted drops off
ant pit releases LH surge ahead of ovulation
one egg released 36-42 hours from onset of surge
corpus luteum formed at site of follicle that hs matured and released ovum
secretes progesterone to ready uterus for pregnancy
if not fertilized, becomes inactive after 10-14 days, involutes and becomes corpus albicans (fibrous scar tissue) and menstruation occurs
ovulatory / phase II
what phase of the ovarian cycle?
progesterone dominant (secreted by corpus luteum)
relatively constant in length (12-14 days)
progesterone increases and peaks (day 20 of the cycle - 6 days post ovulation)
estrogen levels off
corpus luteum involutes after 14 days, resulting in drop of progesterone levels
if implantation, progesterone levels stay up due to production of hCG, progesterone would then further inhibit FSH and new follicular recruitment
luteal / phase III
What phase of the uterine cycle?
roughly corresponds with follicular phase of ovarian cycle
influenced by estrogen
thickness of endometrium rapidly increases by the drawing out of the uterine glands
dont convolute or secrete in this phase
proliferative phase
What phase of the uterine cycle?
roughly corresponds with luteal phase of ovarian cycle
progesterone influence from corpus luteum
lining becomes highly vascularized, slightly edematous, glands become coiled and tortuous and begin to secrete clear fluid
secretory phase
What process occurs when the corpus luteum involutes, progesterone & estrogen dec,, PG inc & smooth muscle contraction, & endometrium loses its blood supply and sloughs its functional layer?
menstruation
What is the average length of perimenopause?
4 years; ends after 12 consecutive months w/o a menstrual cycle (menopause)
The following symptoms are associated with what condition?
change in periods - shorter or longer, lighter or heavier, more/less time in between
hot flashes, night sweats, trouble sleeping
vaginal dryness
mood swings, trouble focusing
less hair on head, more on face and breasts
Perimenopause
What marks the permanent end of fertility with reduced functionaling of the ovaries, confirmed with the absence of menses for 12 consecutive months?
menopause
T/F: ovulation can still sporadically occur during menopause.
true
What condition might happen during menopause due to the increased loss of estrogen?
osteoporosis
What is the most common symptom of endometriosis?
pelvic pain
When does PMS regularly onset?
luteal phase - 1-2 wks before menses
must completely resolve w/ menses & cannot present before menarche
If a woman has ≥5 sx, with one being an affective sx (mood swings, anger, etc), is it more accurate to diagnose her with PMDD or PMS?
PMDD
Perimenopause or Menopause?
transition from normal ovulatory cycling to cessation of menses
avg age of onset - 46 y/o
can last 2-8 yrs & be asx or sx
Perimenopause
Perimenopause or menopause?
spontaneous amenorrhea x 1 yr due to natural ovarian failure
age related & genetic component
avg age - 50-52 y/o
mildly dependent on age of menarche
Menopause
Premature menopause happens before what age?
40 y/o
What factors are protective against early menopause?
Pregnancies & breastfeeding
What is the most common first symptom of menopause?
menstrual changes; usually in this order
heavier or lighter flow
longer or shorter cycles
irregularity
Are mood disturbances more associated with perimenopause or menopause?
Perimenopause
What symptoms are associated with menopause?
dude alot there’s like 3 slides on it but here’s what’s bolded
Inc CV risk → CAD MCC of death in women
greater central obesity (visceral fat → metabolic disturbances)
hour glass figure → shot glass
osteopenia, osteoporosis, inc fx risk
atrophic vagintiis
How is menopause diagnosed?
1 year w/o period, elevated FSH & LH, decreased estradiol,
diagnostics to monitor RF (DEXA, mammogram, lipid panel, cardiac workup)
What is the most sensitive marker and best initial test for menopause?
elevated FSH (> 30 IU/mL)
Which type of HRT can be used in those without a uterus?
Estrogen only (ET or ERT)
Which HRT should be used in those with an intact uterus?
Estrogen and progesterone combo therapy
Which dosage form of ERT is preferred in those with increased triglycerides?
Transdermal- gels / creams / patches (less liver metabolism)
What are benefits to ERT for menopause treatment?
most effective for sx & dec risk of CV, stroke, osteoporosis, & dementia
not a significantly inc risk of breast cancer compared to general population
What are risks of ERT for menopause treatment?
inc risk of endometrial cancer, VTE, liver dz, gallbladder complications
What are benefits to estrogen & progesterone combined therapy for menopause?
sx relief, dec risk of CV, stroke, osteoporosis, dementia
protective against endometrial cancer
What are risks to estrogen & progesterone combined therapy for menopause?
slight increased risk of breast cancer, VTE, liver dz, gallbladder complications
What are contraindications for use of HRT?
Hx estrogen sensitive breast CA, endometrial CA, VTE, thrombophilic d/o
Undx breast lesions
Unexplained uterine/vaginal bleeding
Confirmed CVD, CAD
Active liver disease
Migraine w/ aura
Smoker
*caution w/ HTN, DM, HLD, autoimmune (SLE), obesity, Fhx breast CA
How is normal menses defined?
regular cyclical shedding secondary to successful ovulation
normal cycle length 21-35; normal menses duration 2-7 days
What causes AUB in neonates?
Estrogen withdrawal after birth
What is frequent bleeding where the internal between periods are < 24 days?
Polymenorrhea
What is infrequent bleeding where the interval between periods are > 38 days (< 12 / yr)?
Oligomenorrhea
what is considered irregular bleeding from menarche to 25 y/o and 42 y/o to menopause?
> 9 days difference between cycle lengths
What is considered irregular bleeding in ages 26-41?
>7 days difference between cycle lengths
What is prolonged menstrual bleeding?
Menses lasting > 8 days
What is considered a heavy menstrual volume?
> 80 mL or volume that interferes with quality of life
What is considered a light menstrual volume?
< 5 mL
What is abnormal genital bleeding?
Generic term used when source of bleeding is not yet identified
What organs are involved in bleeds from the lower genital tract?
Cervix, vagina, vulva
What organs are involved in upper genital tract bleeding?
Uterus, ovary, fallopian tube
What is abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
Indicated uterine source but not yet classified as anatomic, hormonal, systemic dz or cancer
What is excessive non cyclic endometrial bleeding unrelated to anatomical lesions of the uterus or systemic dz (dx of exclusion; outdated term)?
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)
What is anovulation that may be related to a disease state vs other factors that effect the HPG-A; irregular menses from no ovulation?
Anovulatory bleeding
What is the MC type of AUB?
Anovulatory
Who is anovulatory AUB MC in?
extremes of age
What is the pathophys of anovulatory AUB?
Disruption of HPG-A → ovulation failure → lack of CLC formation → failure of normal progesterone secretion → unopposed estrogen causes endometrium to outgrow blood supply → necrosis & abnormal bleeding
what does Anovulatory AUB increase the risk for?
Hyperplasia w/ atypia or or dysplasia which can lead to malignancy
What is heavy and/or prolonged bleeding at normal intervals (cyclic, ovulatory)?
Menorrhagia
What causes menorrhagia?
Hormonal imbalance (estrogen > progesterone [MC] or progesterone + PG > estrogen)
structural (PALM- polyps, adenomyosis, leiomyoma, malformations)
liver dz, pregnancy comp, VWD, IUDs, meds
what is bleeding that occurs bt menses aka intermenstrual bleeding?
Metrorrhagia
What is heavy bleeding and intermenstrual bleeding/spotting?
Menometrorrhagia
What is bleeding that occurs after contact with cervix or vaginal walls, commonly after sex (post coital)?
Contact bleeding
What should contact bleeding be considered until proven otherwise?
Cervical cancer
What is the term for light periods?
Hypomenorrhea / cryptomenorrhea
What is the absence of menses / uterine bleeding?
Amenorrhea
Primary or secondary amenorrhea?
failure of onset of menarche
by age 13 if no secondary sex characteristics
by age 15 if characteristics are present
Primary
Primary or secondary amenorrhea?
New absence of menses but has menstruated for atleast 6 mos prior to
> 3 mos if regular before onset
> 6 mos if oligomenorrhea or irregular before onset
Secondary
What are causes of primary amenorrhea if the breast and uterus are absent?
Mullerian agenesis, androgen insensitivity (genetically male but resistant androgen effects - presents like prepubertal female)
What are causes of primary amenorrhea if breasts are absent and uterus is present with high FSH/LH?
Ovarian problems - premature ovarian failure, gonadal dysgenesis (Turney’s syndrome MC)
What are causes of primary amenorrhea if breasts are absent and uterus is present with normal to low FSH or LH?
Hypothalamic pituitary failure, pubertal delay (athletes, illness, anorexia(
What are causes of primary amenorrhea with breasts and uterus present?
Outflow obstruction - transverse vaginal septum, imperforate hymen
What are causes of primary amenorrhea if breasts are present and uterus is absent?
Defect in testosterone synthesis, presents like adolescent female but has intra-abdominal tests
What is the MCC of secondary amenorrhea?
Pregnancy
What are causes of secondary amenorrhea?
Pregnancy, Hypothalamic dysfunction, pituitary dysfunction, ovarian disorders (MC PCOS), uterine disorder, uterine outflow tract problem
What is bleeding occurring after confirmed menopause (1 full year w/o bleeding)?
Postmenopausal AUB
What is postmenopausal AUB considered until proven otherwise?
Endometrial cancer
Does the following correlate with ovulatory AUB or anovulatory AUB?
regular cycles days 21-35
PMS- bloating, breast pain, irritability
Dysmenorrhea (1st/2nd day)
Basal body temp (BBT) inc when ovulating
cervical mucus changes to clear & stretchy
Ovulatory
What should always be done first when evaluating a patient presenting with AUB?
Pregnancy test
What should be included in the PE for an AUB patient?
Speculum & bimanual exam, general exam to look for systemic signs
What diagnostic testing should be considered for AUB?
Pregnancy test, Pap/cervical cultures, endometrial sampling (esp if risk for endometrial hyperplasia), U/S, MRI ± contrast, hysterosalpingogram, progesterone challenge
What labs should be considered for AUB?
CBC, CMP, TFTs, Testosterone, Insulin, Prolactin, 17hydrogyprogesterone, FSH/LH/Estradiol/Progesterone
What is a normal endometrial thickness in premenopausal females?
10-14mm
What endometrial thickness is considered thickened in premenopausal females?
≥ 15 mm
What endometrial thickness is normal in postmenopausal females?
≤ 4 mm
What endometrial thickness is considered thickened in postmenopausal females?
≥ 5 mm