Chemistry 3.5 - chemical kinetics
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is chemical kinetics?
The study of rate, or speed, of chemical reactions
What is the rate of a reaction?
The rate of change in concentration of a reactant (or product) per unit time
Rate = change in concentration of reactants or products/time for the change to take place
What are the units of rate?
moldm-3s-1
What are some methods of continuous monitoring to determine the rate of a reaction?
monitoring gas collection using a syringe or inverted measuring cylinder
monitoring changes in pressure caused by changes in the amount of gas present
monitoring mass loss by using a balance
monitoring intensity of light passing through a solution using a colorimeter
monitoring concentration of reactants or products though sampling and quenching
What is colorimetry?
A method of determining the concentration of a substance by shining light through the solution in a special glass tube called a cuvet
Describe the process of colorimetry
light is shined through the solution in a cuvet
amount of light absorbed is measured
a calibration graph is used to find the concentration
the instrument by which the measurements are made is called a colorimeter
a coloured filter is used so that the wavelength used are colours that the solution absorbed strongly e.g. using a yellow filter in measuring the concentration of a blue coloured solution like copper (I) sulphate
What is sampling and quenching?
Most complicated to monitor rates of reaction so only used when other methods are not possible
Describe the process of sampling and quenching
Small samples of the reaction mixture are removed (sampling)
they are added to ice cold water which decreases the concentration and lowers the temperature to stop the reaction (quenching)
samples are taken ar various times throughout the reaction and the concentration of either a reactant or product in each sample is determined e.g. by titration
What graphs are usually used when measuring rates?
Concentration-time graphs
often show the concentration of reactants falling with time
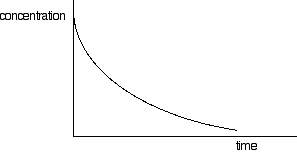
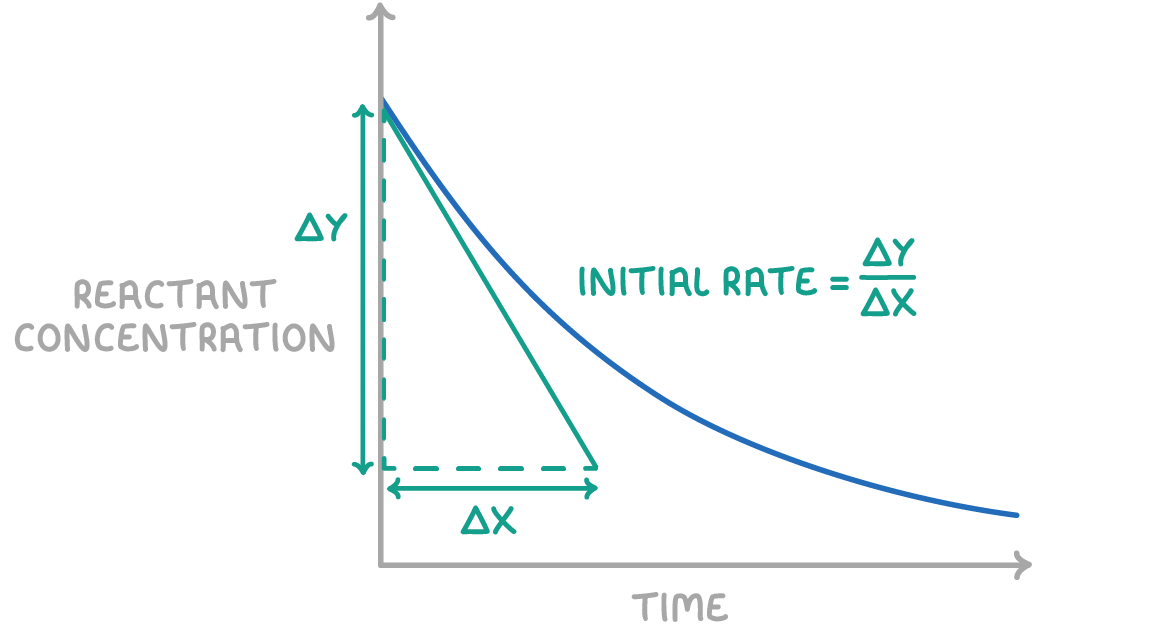
How do you measure the reaction rate from concentration-time curve graphs?
measure gradient of the curve by drawing a tangent
gradient = change in y/change in x
When does a reaction occur?
When reactant particles collide with energy greater than the activation energy
What does the rate of a reaction depend on?
The frequency of successful collisions
What is the order of a reaction?
Shows how the reaction rate is affected by changes in concentration of the reactant
What are the possible orders of a reaction?
0 order - doubling concentration has no effect on rate
1st order - doubling concentration doubles rate
2nd order - doubling concentration quadruples rate
What does the rate equation show?
The relationship between the rate of a reaction and the concentration of reactants
shows the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant
can only be determined from experiments unlike Kc (can be determined from the stoichiometric equation)
How do you write out each order with respect to the reactant?
0 order with respect to A = [A]
1st order with respect to B = [B]1
2nd order with respect to C = [C]2
Rate equation
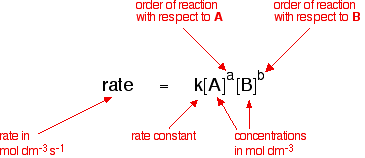
What is the overall order of a reaction?
The sum of the individual orders
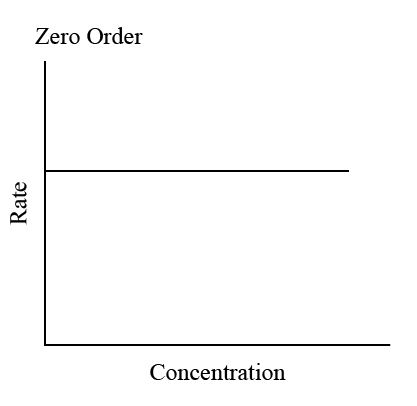
Describe the rate - concentration graph for 0th order
Reactant has no effect on the rate
Rate continues at a steady pace
Rate = K
Describe the rate - concentration graph for 1st order
As concentration doubles the rate also doubles (as concentration triples the rate triples etc)
The rate and concentration are indirectly proportional to each other
Rate = k[A]
![<ul><li><p>As concentration doubles the rate also doubles (as concentration triples the rate triples etc)</p></li><li><p>The rate and concentration are indirectly proportional to each other</p></li><li><p>Rate = k[A]</p></li></ul><p></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f90ab541-05a2-4988-a940-1c56554657f4.png)
Describe the rate - concentration graph for 2nd order
As concentration doubles the rate quadruples (as concentration triples the rate increases by 9 etc)
The rate increases by the square of the concentration
Rate = k[A]2
![<ul><li><p>As concentration doubles the rate quadruples (as concentration triples the rate increases by 9 etc)</p></li><li><p>The rate increases by the square of the concentration </p></li><li><p>Rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup></p></li></ul><p></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6363fba3-fe7b-4e8e-a86d-6d4b76605206.png)