History of the Atom
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what did James Chadwick discover?
he discovered the existence of neutrons
what was James Chadwick’s model of an atom look like?
it had a nucleus containing protons and neutrons
the nucleus was surrounded by electrons —> which occupied shells
(similar to modern day model of atom)
explain how Chadwick’s experiments on the atom led to a better understanding of isotopes?
he discovered neutrons
which meant that it explained why atoms of the same element had the same atomic number (same no.protons) —> but had different mass numbers (different no.neutrons)
therefore created a better understanding of isotopes
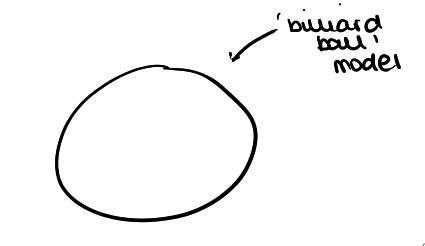
what did John Dalton believe?
he believed that atoms were solid spheres
and that different spheres made up different elements
what was John Dalton’s model? and describe it?
the ‘Billiard Ball’ model
solid ball (sphere)
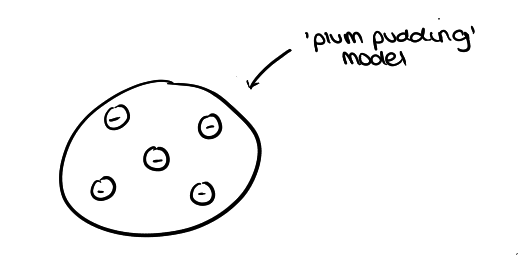
what did JJ Thompson discover?
he concluded that atoms weren’t solid spheres (disproving John Dalton’s model)
he discovered the existence of electrons
what was JJ Thompson’s model? and describe it?
the ‘plum pudding’ model
positively charged ball with negative charges placed in it
what did Ernest Rutherford discover?
he discovered that most of the atom is empty space and positive charges in the atom must be concentrated in the centre
what experiment did Ernest Rutherford carry out to discover what he discovered?
he fired positively charged alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold —> it was called the Gold Foil experiment
what was observed by the Gold Foil experiment?
most alpha particles passed straight through the foil
some alpha particles were deflected
this meant that the ‘plum pudding’ model couldn’t have been right
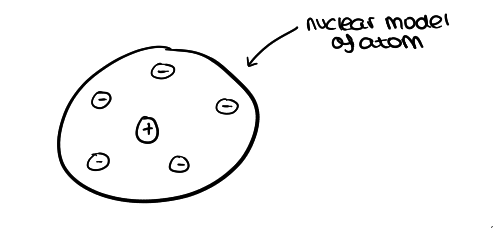
what was Ernest Rutherford’s model? and describe it?
the ‘nuclear’ model
tiny positively charged nucleus in the centre (where most of the mass is concentrated)
and ‘cloud’ of negative electrons surrounding the nucleus
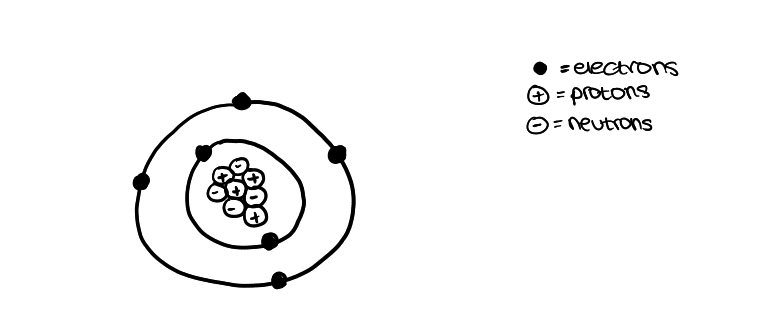
what did Niels Bohr discover?
he discovered that a ‘cloud’ of electrons around the nucleus would be attracted to the nucleus causing the atom to collapse
and so he suggested that all the electrons were contained in shells
(he took Rutherford’s model and improved it bascially)
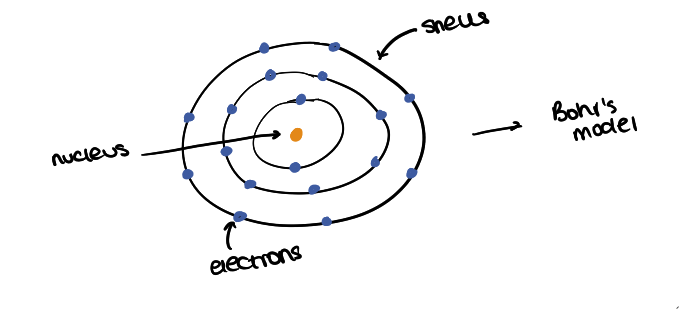
what was Niels Bohr’s model? and describe it?
Bohr’s nuclear model
electrons orbit nucleus in shells
electrons are at specific distances from the nucleus
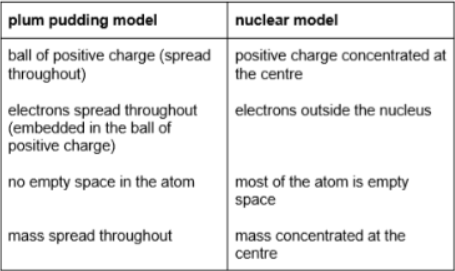
what are the similarities between the ‘plum pudding’ model and the ‘nuclear’ model?
both have positive charges
both have negative charges
both have no neutrons (not yet discovered)
what are the differences between the ‘plum pudding’ model and the ‘nuclear’ model?