Week 4 - Reflexes and Autonomic Nervous System Review
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Forty question and answer flashcards covering key concepts from reflexes and the autonomic nervous system, as detailed in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is a reflex?
A rapid, predictable response to a stimulus.
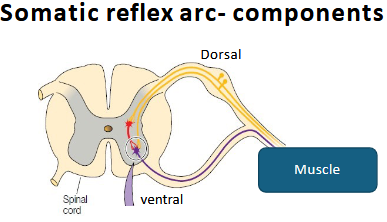
What are the two main types of reflexes?
Somatic (skeletal muscle) and visceral/autonomic (smooth/cardiac/glands).
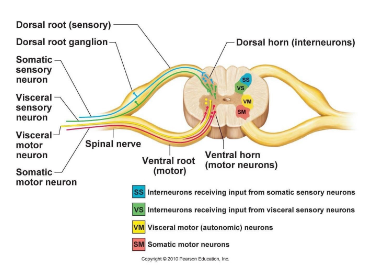
Where are interneurons located in the spinal cord?
In the dorsal horn.
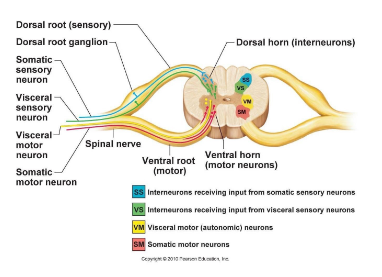
Where are somatic motor neurons located?
Ventral horn.
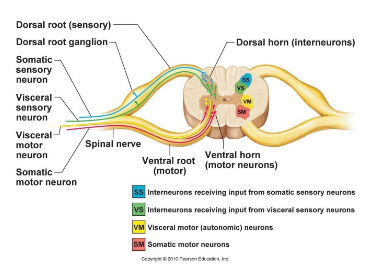
Which horn contains sympathetic motor neurons?
Lateral horn.
What are the 5 components of a somatic reflex arc?
Receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector.
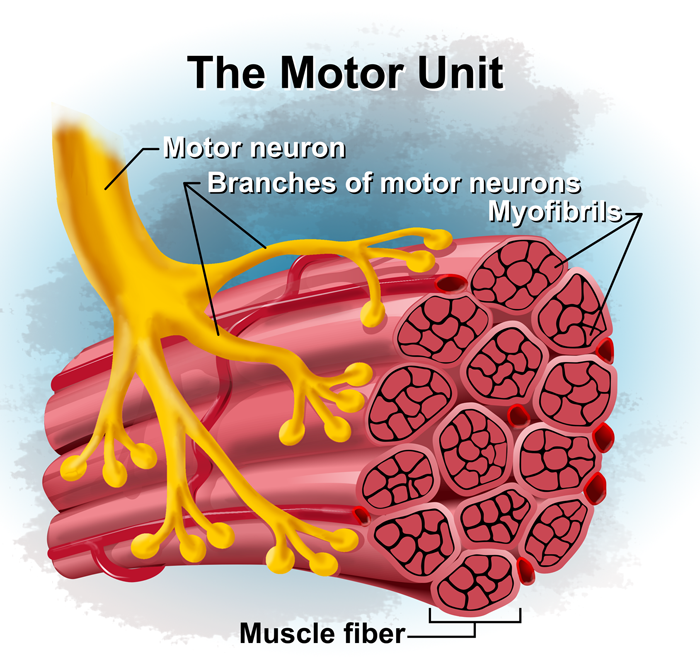
What is a motor unit?
A motor neuron and all muscle fibers it innervates.
What is the neuromuscular junction?
Synapse between motor neuron axon and muscle fiber.
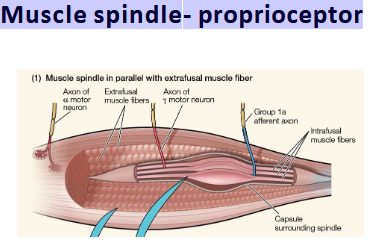
What is a muscle spindle?
A proprioceptor detecting muscle length/stretch.
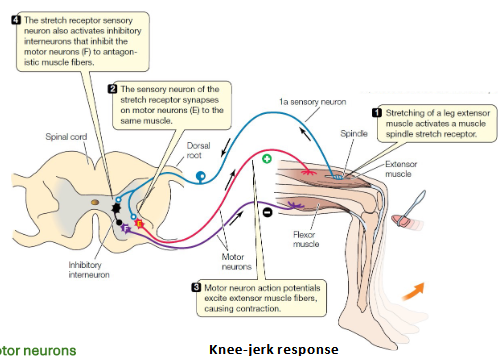
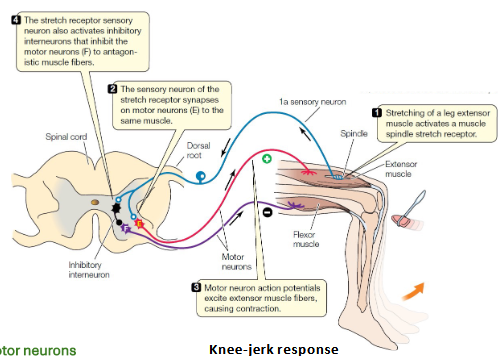
Which reflex prevents muscle overstretching?
Stretch reflex.
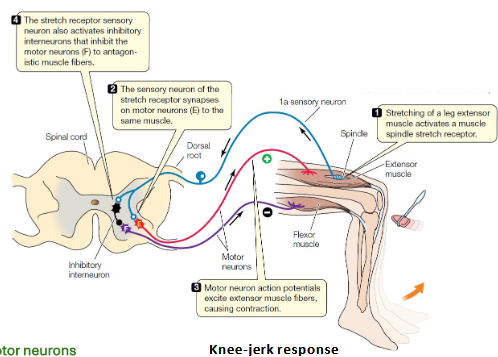
Example of a stretch reflex?
Patellar (knee-jerk) reflex.
How many cranial nerve pairs are there?
12.
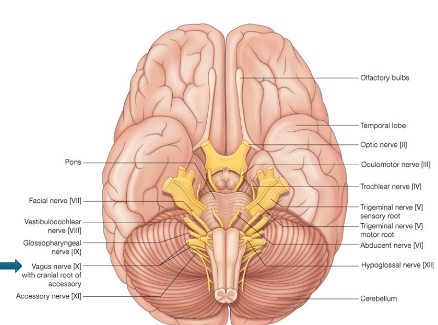
What do cranial nerves supply?
Sensory, motor, special sense innervation to head/neck.

What proportion of parasympathetic fibers are in cranial nerves?
About 75%.
What is a plexus?
A network where multiple nerves intersect.
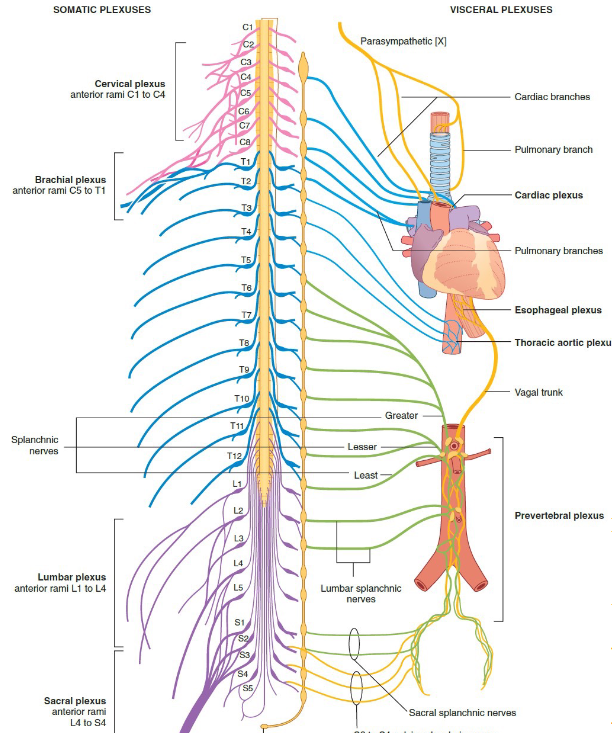
Examples of ANS (autonomic) targets?
Pupils, glands, viscera, adrenal glands.
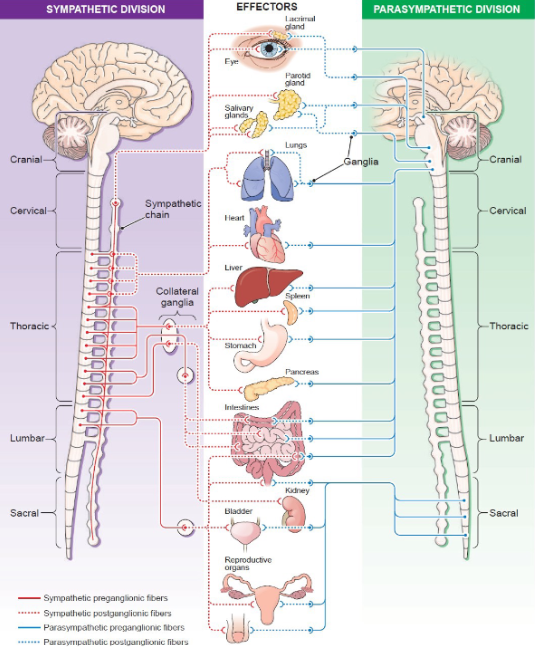
What does the ANS (Autonomic nervous system) regulate?
Smooth/cardiac muscle, glands, BP, temp, water balance.
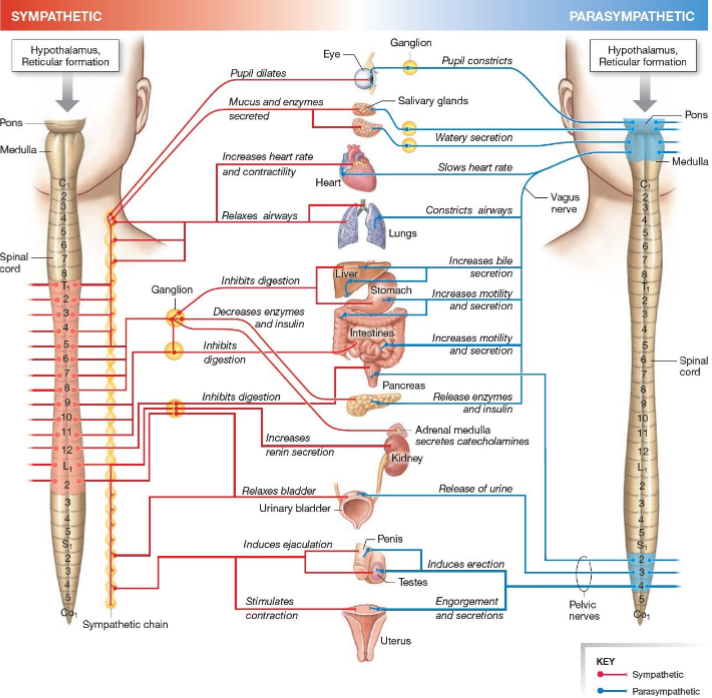
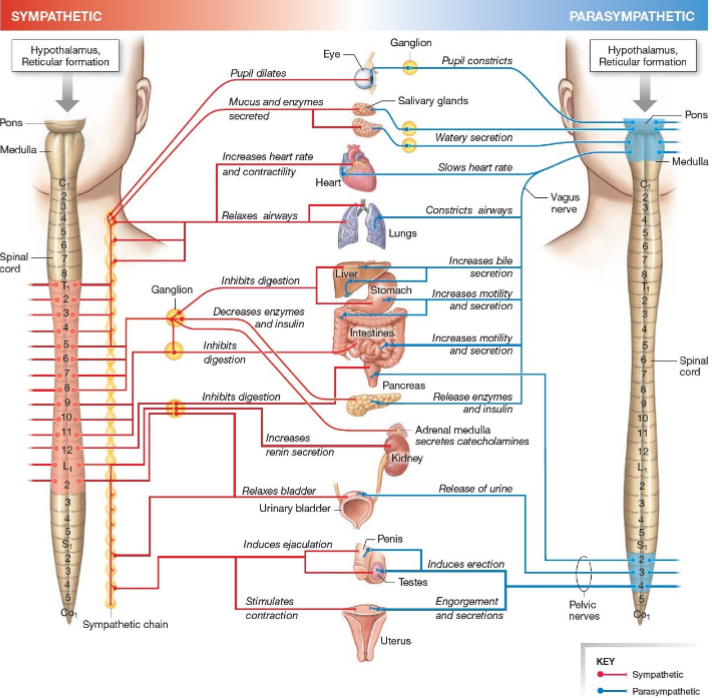
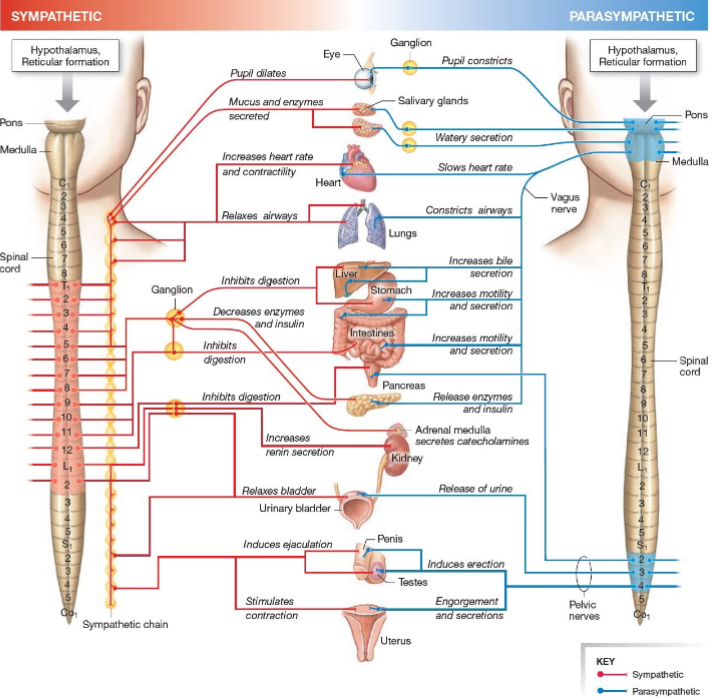
Sympathetic system function?
Fight-or-flight, stress response.
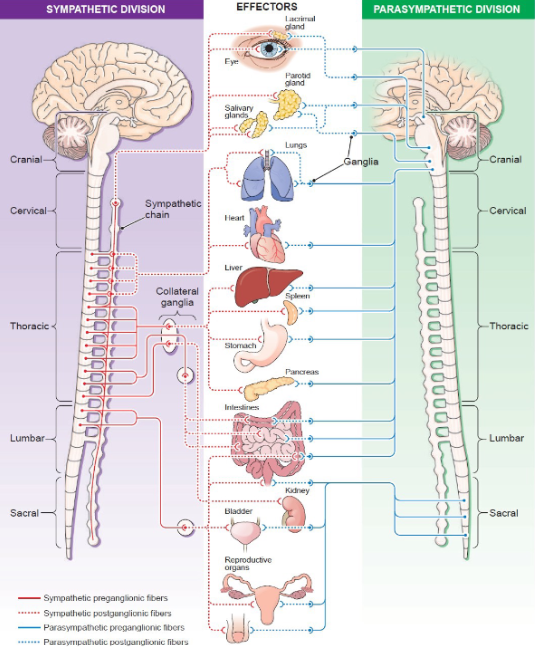
Parasympathetic system function?
Rest-and-digest, homeostasis.
Parasympathetic acronym SLUDD?
Salivation, Lacrimation, Urination, Digestion, Defecation.
Effect of parasympathetic on heart?
Decreases heart rate.
Effect of parasympathetic on pupils?
Constriction.
Effect of parasympathetic on digestion?
Increases motility.
Effect of sympathetic on HR?
Increases rate and force.
Effect of sympathetic on blood vessels?
Constricts vessels to skin/viscera, increases blood to muscles.
Effect of sympathetic on pupils?
Dilates.
Neurotransmitter of sympathetic preganglionic neurons?
Acetylcholine (ACh).
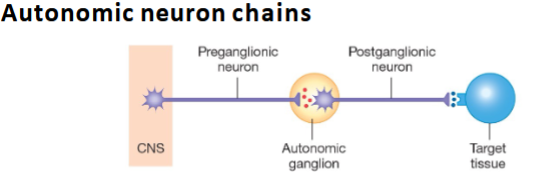
Neurotransmitter of sympathetic postganglionic neurons?
Norepinephrine (NE).
Sympathetic postganglionic neurons to sweat glands release?
Acetylcholine (ACh).
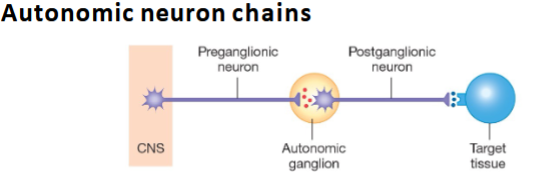
Neurotransmitter of parasympathetic neurons (pre & post)?
Acetylcholine (ACh).
Sympathetic preganglionic fibers length?
Short.
Sympathetic postganglionic fibers length?
Long.
Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers length?
Long.
Parasympathetic postganglionic fibers length?
Short.
What is the role of ANS in homeostasis?
Regulates involuntary body functions.
Example of ANS control on glands?
Saliva secretion.
Example of ANS control on circulation?
BP regulation.
What type of reflex is the baroreceptor reflex?
Visceral autonomic reflex.
What triggers the baroreceptor reflex?
Changes in blood pressure.
What is the integrating center in ANS reflex arcs?
CNS (spinal cord/brainstem).