9. Predator Prey Behaviours
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Antipredator Behaviour - Individuals
NS favors evolution of efficient foraging behaviours -increase fitness by having more energy available for reproduction
NS also favours evolution of behaviours that allow animals to successfuly avoid being captured
Animals perform number of behaviours that lower their risk of predation
Antipredator behaviour - any behaviour that decreases the probability that organisms will be depredated
Behaviours can be categorized as making detection, capture, and attack less likley

Avoid Detection: Avoid detection
Birds - set up feeder
1 meter away or 4 meters away- Close to cover or away
Behind cover was fake hawk
Took down cover and expose hawk to birds and wanted to see
further from hawk - longer time to resume feeding and dropped feeding - risky to be out in open
close to hawk - safer - used cover took more time
Avoid Detection: Crypsis
Blending with background via evolutionary modification of coloration, marking, morphology and behaviour
2 methods to achieve crypsis
change appearance to match background
Physiological colour change
distort pattern/color with motion
Cuttlefish - on screen that looks like checkerboard - change to checkerboard
Chose background that matches your appearance
Via color,
Via orientation/positioning to match patterning
Moths - large moth has verticle lines, small maoths have horizontal lines - place on trees (naturally vertical) but also horizsontal. Put them on trees - when larger moth put on verticle - took long time for predator to detect them, but put verticle on horizontal predator found them fast and vice versa
Avoid Detection: Time spent moving
Movement of prey (foragin, travel), influences the risk of being killed by a predator
Activity level of prey will be lower when predators are present
Avoid Detection: Feed in areas of low risk
some build their own safe food locations
American pika - feed amongst boulders and rocks and even make runs of rocks to forage out into meadow
Avoid Capture - Increase vigilance
Predators rely on surprise to capture prey, once detected their success is diminished
Vigilance - when animals scan their surrounding for potential predators
Vigilance decreases probability of predation but also decreases short term energy gain (animals eat with face down)
Long term benefit of trade offs is access to additional food patches
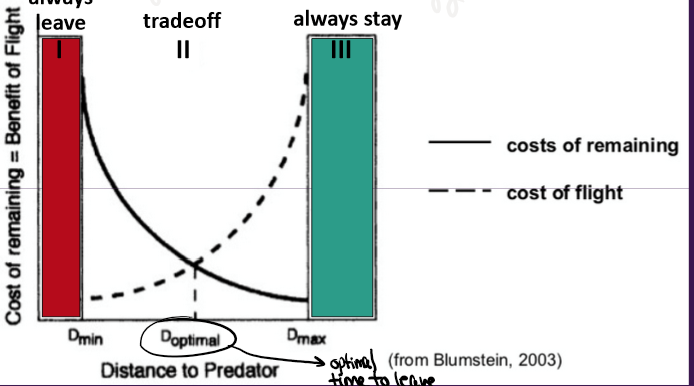
Avoid Capture - Initiate flee
Flight Initiation distance is the distance at which an animal moves away from an approaching threat - but if foraging and you notice do you flee? Depends on distance
further - stay bc can eat more and save energy
Factors that affect FID
Energetic state
more conspecifics - shorter (wait)
predator speed - longer (ASAP)
distance to cover
prey hungry or not
Dont mistake this for habituation
Protean flee behaviours - animals enhance escape by moving in an erratic unpredictable way making it hard for predator to follow target (butterfly, mice)
Avoid Capture - Aposematism
dangerous/unpleasent attributes
Visual signals, acoustic signals (rattle), chemical signals (smell)
Behaviour enhances aposematism
Aposematic individuals are usually:
Diurnal - active during the day
Likely to be detected by visual predatory, flaunt their displays and little eed for speed
Aggregative
associate with other aposematic individuals - necessary for reinforced learning for predator - mullerian mimicry - look like venemous species thus predators learn to avoid (monarch butterfly)
Avoid Capture - Mimicry
Batesean mimicry - members of a harmless species that have evolved morphology / behaviour that mimics dangerous
ant mimicking spiders (legs mimic antennae)
Cost - fitness of mimics is negativley frequency dependent - spiders too common then wont work
Avoid Capture - Pronouncment of vigilance
predators reply on remaining undetected, once detected predator will often not attack
Pronouncement of vigilance displays show predator that it has been detected
jumping up and down i have energy, or deer white tail
Deflecting attack - display false structures
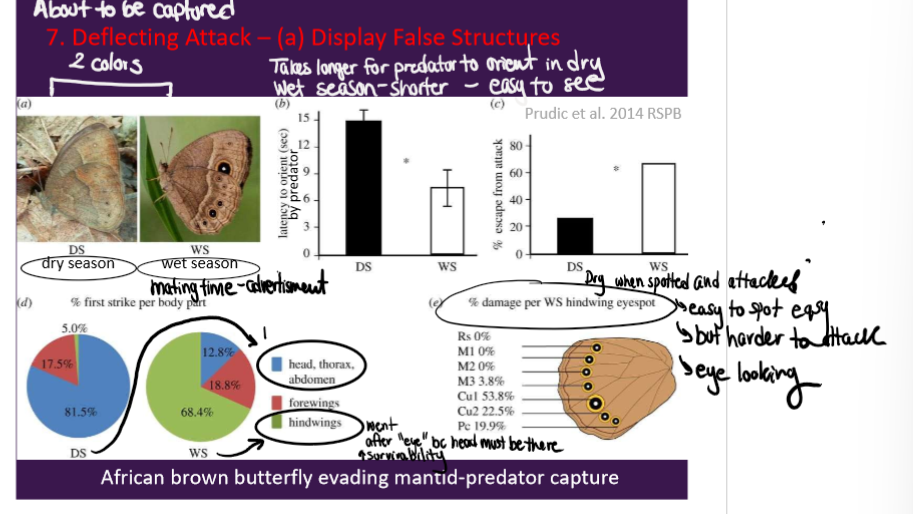
Deflecting attack - (3)
Distraction - pretend to be injured
Autonomy - drop tail
Feigning injury or death - play dead snake and stink
Deflecting attack - Startle or imitation displays
Intimidate predator at moment of attack
May serve to deter attack or distract predator long enough to allow escape
False eye spots on caterpillar to look like snake
Deflecting attack - fight back
spines, teeth
Alarm call - visual, auditory, chemical (shrek), mechanical - to broadcast presence of predator and trigger escape or call in other predators to increase confusion or get support
Predation risks affects prey decision making
trade offs
Behavioural - sacrificing one behaviour for another
Risk effects arise when prey alter behaviout in response to predators and these responses carry costs
Vigilance - foraging tradeoff
scaning environment for predators, many cat feed and be vigilant at same time - thus adjust tradeoff according to local threat (more cautius in tall grass)
Predation senstitive foraging
areas of low risk can sometimes come at the cost os reduced forace intake (elk moving to areas with more protection but then less food) e
State dependent foraging
animals consider variability in food abundance in deciding where to forage - these habitats all carry some form of predation risk
Risk senstitivity depends on state of satiation and need of forager
Willingness to endure risk reduces probability of starvation
Predator strategies for hunting prey
like prey, predators also evolved strategies
Predator prey interactions- predator hunting mode
hunting mode - set of behavioural strategies that a predator employs while searching for prey
sit and wait or ambush - motionless until catching distance
sit and pursue - motionless until chasing distance
active hunting - predator continuously moves through environment to find follow and chase down prey
Active vs Passive strategies
Passive
save energy but relies on prey coming to you
risky to wait for prey but dont spend energy looking
small home
active mobile prey
Active
Expends mor eenrgy but encounter rate is higher
can be eaten by sit and wait
range widley
feed on sedentary and mobile prey
Predator prey interactions - Non-consumptive effects
consumptive interactions - predators kill and consume prey
non- consumptive interactions - the threat od predation generates behvioural, morph, of phys anti predator responses in prey (ecology of fear)
physiological stress response
Stress alters prey physiology (dcreased survival), behaviour (movement), morphology (escape)
behavioural modification
sound of predator in song sparrows fed their young few times per hours
can also alter trophic cascades - wolves scare elk to towns, humans scare wolves and cottonwood started to grow and beavers increased
Predator prey interactions - Behavioural Game Theory
Ideal free distribution predicts resource matching to that intake rates are equalized
- The oucome od this assumption is high degree of overlap in patch use by predator and prey
But predators can move in search of patchy prey and prey can move to resources or hide to avoid predators
Most predator -prey interactions insist of 2 player game in which a responsive prey is trying to avoid being killed by equally responsivr predator (track each others behaviour)
Game example: fear management under time contraints
Seabirds eat worms when tide is out (time sensitive) and predator watches this - a predator must choose when to attack after foragers settle into patch - individual prey must choose how to allocate their limited time bt anti-predator viilance and feeding - solution involves unpredictability in BOTH predator attack time and gradual decrease in responsiveness for prey
Game example - fear managment
attacking after predictable time (10 min laways) not good or being vigilant all the time not good thus, predator should do non predictable early attacks but not all the time and decreasing prey vigilance overtime wil detect early attacks and reduce wasteful vigilance should predator is absent - keeping each other on their toes
Predator prey interactions - Long time frame
2 criteria tells us this
escalation -coevolving species in an arms race continually develop adaptations and counter adaptations against each other
local co-adaptation - co-adaptations become increasingly powerful (weapons) yet species are not any better off/adapted
Results in geographic mosaic pattern where both species have roughly matched abilities across their shared range - where species dont overlap there is no escalation
Example of arms race - antlion sit and wait for ant arrival - ants tha tlive in viscinity of antloins posess ability to rescue nestmates from antlion home and learn from their own experiences
Escilation in this example — antlion firther associates vibrations when rescuer has arrived - ands capable of forming generalizable memeory of home/pit when they or nest mate are trapped to avoid future encounters
Local coadaptation in this example - many ant species have the potential to perform rescue behaviour but those tha tlive in same ecological niche as antlions are capable of performing highly integrated precise rescue behaviour patterns

Summary
