Carnegie 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Mechanism of action of peptide/protein hormones and catecholamines
cell surface receptors
second messengers
regulation of enzyme activity
no latent period
Mechanism of action of steroid Hormones & Thyroid Hormones (Lipophilic)
enter cells by diffusion
intracellular receptors
regulation of gene
transcription
latent period
Receptors (cell surface or intracellular)
confer specificity
can have different affinities
can be saturated
can be up-regulated or down-regulated to influence cell responsiveness (by the hormone itself or by another hormone)
notion of permissiveness (sometimes accomplished by receptor up-regulation, but not always)
Example of permissiveness
Thyroid hormone is permissive of epinephrine-stimulated release of fatty acids by adipose tissue
What is hormone permissivness?
those that must be present for another hormone to exert its full effects, acting as a prerequisite or enhancer for a second hormone's action
MECHANISM OF ACTION OF HYDROPHILIC HORMONES
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) second messenger system
IP3 -Ca2+ & DAG second messenger pathways
Cyclic AMP 2 nd Messenger System
Binding of extra-cellular messenger to receptor activates a G protein, the or subunit of which shuttles to and activates adenylyl cyclase.
Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP.
CAMP activates protein kinase A.
Protein kinase A phosphorylates inactive target protein, activating it.
Active target protein brings about desired response.
Cellular response
What is protein kinase?
An enzyme that phosphorylates and thereby induces a change in the shape and function of a particular intracellular protein
Possible things PKA can do
Membrane effects
Metabolic effects
Gene expression
Calcium fluxes
Structural effects
Phosphodiesterase importance
Necessary to deactivate cell so that it can be ready to be activated again
Enzyme that catalyzes conversion of cAMP to AMP
IP3 -Ca2+ & DAG 2nd messenger pathways
Binding of extra-cellular messenger to receptor activates a G protein, the a subunit of which shuttles to and activates phospholipase C.
Phospholipase C converts PIP2 to IP3 and DAG.
IP3 mobilizes intracellular Cat
Ca2+ from ER activates calmodulin.
Cat-calmodulin complex activates Ca?+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM kinase).
CaM kinase phosphorylates inactive target protein, activating it.
Activate target protein brings about desired response
Cellular response
Binding of extra-cellular messenger to receptor activates a G protein, the a subunit of which shuttles to and activates phospholipase C.
Phospholipase C converts PIP2 to IP3 and DAG.
DAG activates protein kinase C.
Protein kinase C phosphorylates inactive target protein, activating it.
Active target protein brings about desired response.
Cellular response
Second messenger pathways
different cells have different proteins/enzymes that can be modified by phosphorylation once a protein kinase is activated, allowing hormones to have varying effects depending on the specific cell being activated
the cAMP and Ca2+ pathways can ______ each other
support
calcium-activated calmodulin can influence adenylate cyclase activity
protein kinase A phosphorylates calcium channels to open or close them
What do we mean when we say that hormones are POTENT?
Don’t need a whole lot of each hormone for an appropriate response
One hormone is amplified to create lots of products
Lipid-soluble hormones act within the nucleus- amplification
Amplification at step of synthesis of mRNA leading to increased physiology response
Thyroid hormone deiodination
T4 enters cell (1º hormone released by thyroid gland)
deiodination to T3 (T3 more easily reaches and binds in nucleur membrane)
conveyed toward nucleus by binding protein – T3 easily traverses nuclear membrane
nuclear receptor and activation of specific gene transcription
What is the ultimate goal of negative feedback?
Keep level of something within optimal range for the body
What is a physiological example of negative feedback?
Anterior pituitary → thyroid stimulating hormone → thyroid glands → thyroid hormone→ ANterior pituatary
1 hormone regulating a process negative feedback
acts to decrease its secretion once process or blood concentration of substance back in range
Process regulated in opposite directions by 2 different hormones
opposite effects on one factor (ex: blood glucose levels)
What is the ultimate goal of positive feedback?
reinforce successful actions and behaviors and to motivate continued growth and improved performance
Best example of positive feedback?
Labour & delivery and hormonal control of breastfeeding
Brain stimulates pituitary gland to secrete oxytocin
Oxytocin carried in bloodstream to uterus
Oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions and pushes baby towards cervix
Head of baby pushes against cervix
Nerve impulses from cervix transmitted to brain
The endocrine function of the posterior pituitary gland
composed of axonal terminals of neurons that originate in the supraoptic & paraventricular nuclei (SON & PVN)
really a site of hormone storage
Both posterior pituitary hormones are _________ that are similar in structure
nonapeptides
oxytocin
vaspressin
Oxytocin
uterine contractions & milk let-down (primarily PVN)
Vasopressin
also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – water conservation at the level of the kidney (primarily SON)
What are neurophysins I and II?
components of oxytocin (I) & ADH (II) precursor molecules
neurons of paraventricular and supraoptic neurons produce precursor molecules that consist of the hormone plus its neurophysin
packaged into vesicles for transport to posterior pituitary
endopeptidases cleave precursor – hormone stays with neurophysin carrier until hormone release by axonal terminals is stimulated (depolarization + Ca++ influx)
neurophysins serve combined roles of structural component of hormone precursor molecules and carrier proteins during axonal transit
What is the neural stimulus of labour?
Baby’d head pushing against cervix
What is the endocrine response of labour?
Release of oxytocin
ADH has two effects that both act to increase blood pressure
vasoconstriction of blood vessels
water conservation by kidney
release of ADH results in ____ urine flow rate & production of a ______ urine
low
concentrated
What is the effect of alcohol on ADH secretion?
Suppress the release of ADH (cause feeling of dehydration)
What is diabetes insipidus?
Autoimmune disease where you can’t regulate ADH production
ADH needs to be taken to regulate this (easy to control with medication not like diabetes mellitus
Why is it called diabetes?
comes from ancient Greek, meaning "siphon" or "to pass through," referring to the excessive urination (passing of fluid) it causes, while the full name, Diabetes Mellitus, adds the Latin "mellitus" meaning "honey-sweet," because the urine of people with the condition was sweet due to excess sugar.
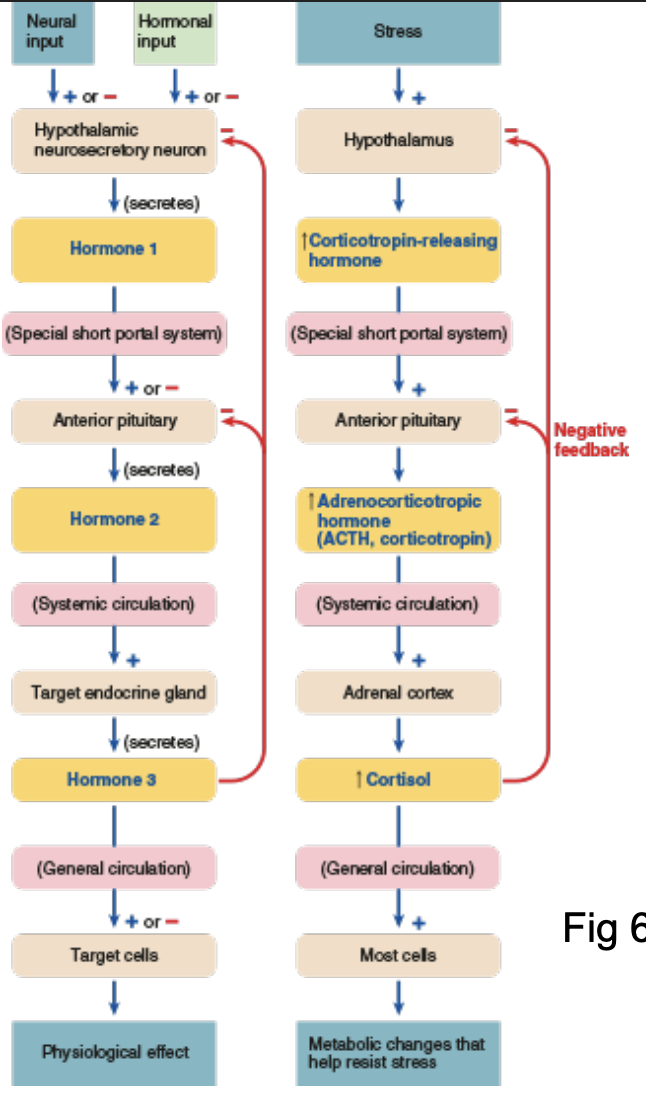
Describe the hypothalamic regulation of anterior pituitary hormone secretion
Stimulus → Hypothalamus (↑ Hormone 1 secretion) → 1 Plasma hormone 1 (in hypothalamo-pituitary portal vessels) → Anterior pituitary (↑ Hormone 2 secretion) → ↑ Plasma hormone 2 → Third endocrine gland († Hormone 3 secretion) → ↑ Plasma hormone 3 → Target cells of hormone 3 (Respond to hormone 3)
Hierarchic Chain of Command
The six classical anterior pituitary hormones
LH and FSH
TSH
ACTH
GH
Prolactin
LH and FSH
gonadotropins involved in reproduction (egg & sperm development and stimulation of production of reproductive steroid hormones)
GnRH (+) → FSH and LH → Germ cell development and gonads secrete hormones (F: Estradiol and progesterone, M: testosterone)
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
CRH (+) → ACTH → adrenal cortex- linear 39 a.a. hormone that increases cortisol production
GH (growth hormone)
also called somatotropin (~200 a.a.)
GHRH (+) and SS (-) → GH → liver and other cells → secrete IGF-1
many organs and tissues- protein synthesis, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism
Prolactin
DA (-) → Prolactin → mammary gland development & milk production