STA 13 Midterm 2
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is uniform distibution?
Simplest distribution. Continuous distribution that has constant probability. It gives equal probability to all interval
X ~ Uniform(a,b)
a = min
b = max
Curve = prob. density function
All probabilities are positive
Function for Uniform Distribution
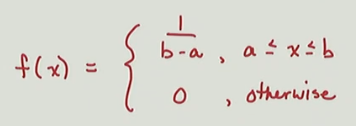
What distribution does NOT care about equality sign?
Uniform Distribution
How do you turn variance into the standard deviation?
Square root the variance
If selecting samples of size n ≤ 30 from a population with a known mean and standard deviation, what requirement, if any, must be satisfied in order to assume that the distribution of the sum is a normal distribution?
The population must have a normal distribution.
What is the central limit theory?
What does x̄ represent
What does X̄ represent
A random variable that represents the mean of all possible sample means
What does Σx mean
What does P(x) mean
The probability that X takes on the value of x. P(x=0) or P(x=1)
What is a random variable
They are typically denoted with capital letters (X,Y, Z). A random variable is a function that assigns a numerical value to each outcome in the sample space
Which ways can a probability distribution be listed
Tables, functions, or graphs
What are the two characteristics of a discrete probability distribution
Each probability is between 0 and 1, inclusive. 0 ≤ p(x) ≤ 1
The sum of the probabilities is 1
Is a table
What is the expected value
The “long-term” average or mean. If you conduct the experiment over and over, you would expect this average
What is a binomial distribution
Probability distribution that models the probability obtaining to TWO outcomes (“success” or “failure”), a certain number of times (x), out of a fixed number of trials (n), of a discrete random event.
How do you calculate the expected value in Binomial Distribution
Expected = (n)(p)