Ch. 20 Endocrine and Hematologic Emergencies
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
hypersecretion
more hormones are produced
hyposecretion
not enough hormones are produced
what 2 things does the brain need to survive?
glucose and oxygen
what 2 hormones does the pancreas produce and store?
glucagon and insulin
the pancreas stores and secretes these in response to the level of glucose in the blood
____ is necessary for glucose to enter cells
insulin
diabetes mellitus
a disorder of glucose metabolism, such that the body has an impaired ability to get glucose into cells to be used for energy
without treatment, blood glucose levels become too high
severe complications: blindness, cardiovascular disease, kidney failure
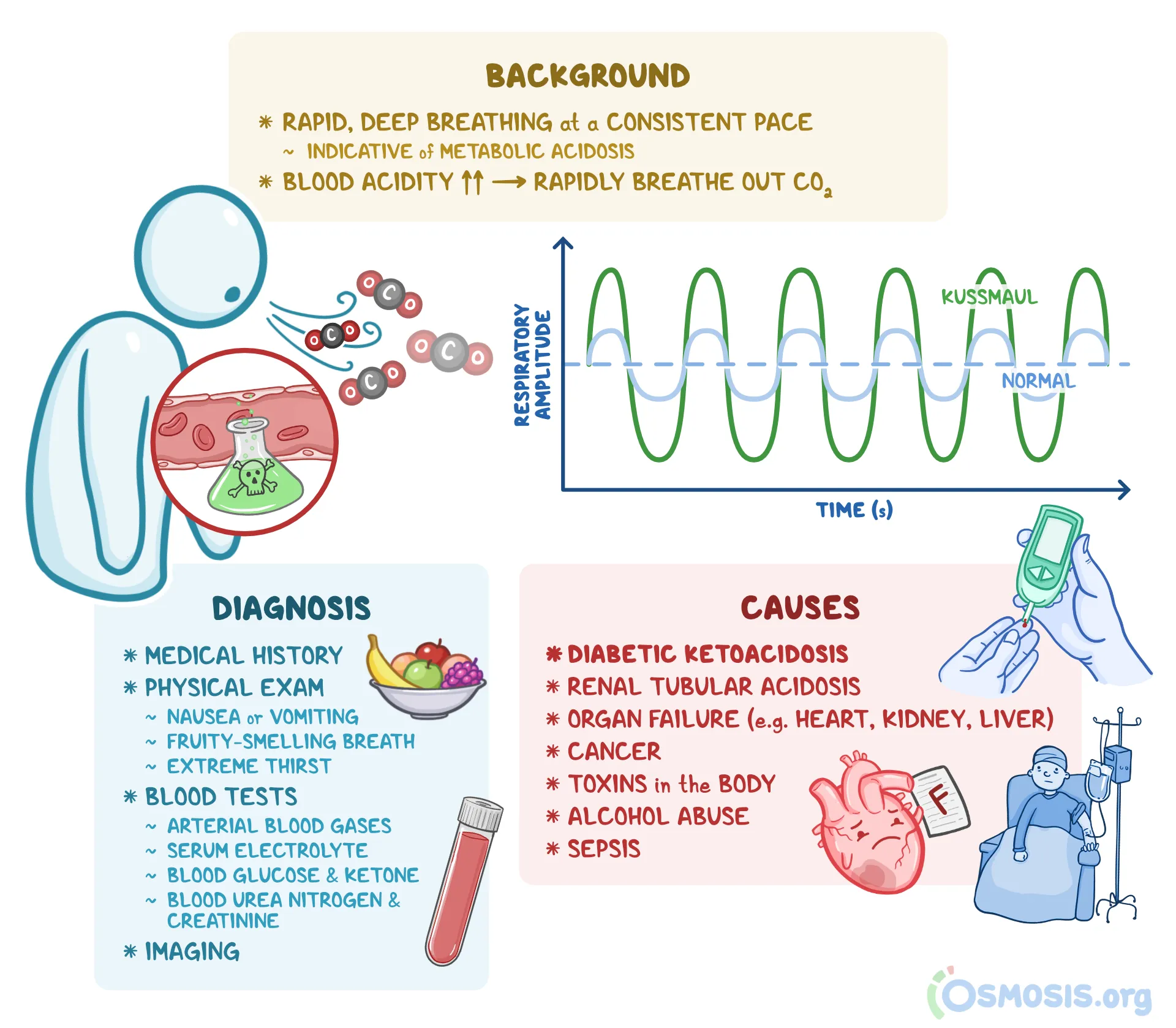
3 types of diabetes
diabetes mellitus type 1
diabetes mellitus type 2
pregnancy-induced, gestational diabetes
hyperglycemia
s state in which the blood glucose level is above normal
hypoglycemia
a state in which the blood glucose level is below normal
hypoglycemia can develop:
if a person takes their medications but fails to eat enough food
if a person takes too much medications, resulting in low blood glucose levels despite normal dietary intake
signs/symptoms of hyperglycemia
onset is gradual
skin is warm and dry
infection is common
intense thirst
increasing hunger
vomiting and abdominal pain is common
kussmaul respirations with
sweet, fruity breath odor
BP is normal to low
rapid, weak, and thready pulse
restless, abnormal or slurred speech, unsteady gait
signs/symptoms of hypoglycemia
rapid onset
skin is pale, cool, and moist
thirst and hunger are absent
normal breathing - may become shallow or ineffective
BP is normal to low
pulse is rapid and weak
irritability, confusion, seizure, coma; unsteady gait
diabetes mellitus type 1
definition: an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system produces antibodies against the pancreatic beta cells
missing insulin
onset: usually occurs from early childhood through the 4th decade of life
a pt with new-onset type 1 diabetes will have symptoms related to eating and drinking
implanted insulin pump
common in pts with type 1 diabetes
what it does: continuously measures glucose levels and provides insulin and correction doses of insulin based on carbohydrate intake at mealtimes
normal blood glucose level
80-120 mg/dL
polyuria
frequent urination
polydipsia
increase in fluid consumption
polyphagia
severe hunger and increased food intake
what happens when a pt’s blood glucose level is above normal?
the kidney’s filtration system becomes overwhelmed and glucose spills into the urine
causes more water to be pulled out of the bloodstream
increased urine production and urination cause dehydration and increased thirst
when glucose is unavailable to cells, what does the body do?
the body turns to burning fat - it produces acid waste (ketones)
as ketone levels go increase in the blood, they spill into the urine
kidneys become saturated with glucose and ketones cannot maintain acid-base balance in the body
pt breathes faster + deeper (Kussmaul respirations) as the body atttempts to reduce the acid level by releasing more carbon dioxide through the lungs
if metabolism and ketone production continue, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) can develop
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
may present as: generalized illness and:
abdominal pain, body aches, nausea, vomiting, altered mental status or unconsciousness
if not rapidly recognized and treated is can result in death
obtain a glucose level
Kussmaul respirations
do NOT attempt to have the pt slow their breathing because the rapid, deep breathing is helping to get rid of the acids
diabetes mellitus type 2
cause: resistance to the effects of insulin at the cellular level
fewer insulin receptors
obesity predisposes pts to type 2 diabetes
the body’s response: the pancreas produces more insulin to make up for the increased levels of blood glucose and dysfunction of cellular insulin receptors
diagnosed: usually from complaints related to high blood glucose levels: recurrent infection, change in vision, numbness in the feet
insulin resistance
definition: blood glucose levels continue to rise and do not respond when the pancreas secretes insulin
can sometimes be improved by exercise and dietary modification
oral medications used to treat type 2 diabetes
types:
some increase the secretion of insulin - pose a high risk of hypoglycemic reaction
some stimulate receptors for insulin
others decrease the effects of glucagon and decrease the release of glucose stored in the liver
names:
Glipizide (Glucotrol); Glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase, Micronase); Metformin (Glumetza, Glucophage); Pioglitazone (Actos); rosiglitazone (Avandia); Exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon); liraglutide (Victoza); Sitagliptan (januvia)
symptomatic hyperglycemia
occurs when blood glucose levels are very high
type 1 diabetes: leads to ketoacidosis with dehydration from excessive urination
type 2 diabetes: leads to nonketotic hyperosmolar state of dehydration due to the discharge of fluids from all of the body systems and eventually out through the kidneys, leading to fluid imbalance
if a pt has hyperglycemia for a prolonged time, secondary consequences of diabetes can occur
wounds that do not heal, numbness in the hands and feet, blindness, renal failure, gastric motility problems
hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS)
definition: life-threatening condition resulting from high blood glucose that typically occurs in older adults; causing altered mental status, dehydration, organ damage
signs/symptoms: hyperglycemia, altered mental status, drowsiness, lethargy, severe dehydration, thirst, dark urine, visual or sensory deficits, partial paralysis or muscle weakness, seizures
pts struggle to drink enough fluid to keep up with the high glucose levels in the blood
symptomatic hypoglycemia
definition: an acute emergency in which a pt’s blood glucose level drops and must be corrected swiftly
mental status declines and pt may become aggressive or display unusual behavior
common causes: a correct dose of insulin with a change in routine, more insulin that necessary, a correct does of insulin without the pt eating enough, a correct dose of insulin and the pt developed an acute illness
signs/symptoms: normal to shallow respirations, pale and moist skin, diaphoresis, dizziness, headache, rapid pulse, normal to low BP, altered mental status, anxious or combative behavior, seizure, fainting, coma, weakness on one side of the body, rapid changes in mental status
hyperosmolarity
describes very concentrated blood as a result of relative dehydration
if pt has eaten but not taken insulin, ____ is more likely
hyperglycemia
if pt has taken insulin but not eaten, _____ is more likely
hypoglycemia
for a known pt with diabetes, ask:
do you take insulin or pills that lower your blood sugar?
do you wear an insulin pump?
have you taken your usual insulin dose (or pills) today?
have you eaten normally today?
have you had any illness, unusual amount of activity, or stress?
neonates should be above ___ mg/dL
70
giving oral glucose
3 types
rapidly dissolving gel, large chewable tablets, liquid
contraindications: the inability to swallow; unconsciousness
wear ppe and follow local protocols for administration
reassess the pt frequently
squeeze the glucose under the tongue or into the buccal space and then swallow
seizures
hypoglycemia can cause seizures
management:
ensure airway is clear
place pt on side if no cervical trauma
do not place anything is pt’s mouth
have suctioning ready
administer oxygen if necessary
transport promptly
acidosis
the buildup of excess acid in the blood or body tissues that can result from primary illness
altered mental status
may be caused by complication of diabetes
hypoglycemia; ketoacidosis
use AEIOU-TIPS
always check blood glucose in these pts
management:
ensure the airway is clear
be prepared to provide ventilations
be prepared to suction
provide prompt transport
AEIOU-TIPS
A = Alcohol
E = epilepsy, endocrine, electrolytes
I = Insulin
O = Opiates and other drugs
U = Uremia
T = Trauma
I = Infection
P = Poisoning, psychogenic causes
S = Shock, stroke, seizure, space-occupying lesion, subarachnoid hemorrhage
blood is made up of 4 components:
erythrocytes (red blood cells)
leukocytes (white blood cells)
platelets
plasma
red blood cells
contain hemoglobin
make up 42% - 47% of a person’s total blood volume
white blood cells
make up 0.1% - 0.2% of a person’s blood cell volume
respond to infection and collect dead cells for their correct disposal
platelets
help form clots to stop bleeding
make up 4% - 7% of a person’s blood cell volume
plasma
serves as the transportation medium for all blood components, proteins, and minerals
sickle cell disease (Hemoglobin S disease)
description: an inherited blood disorder that affects RBCs - leads to dysfunction in oxygen binding and unintentional clot formation
clots may result in a blockage known as vasooclusive crisis
can result in hypoxia, substantial pain, and organ damage
found predominantly in people of African, Caribbean, and South American ancestry
complications: anemia, gallstones, jaundice, splenic dysfunction, vascular occlusion with ischemia
sickled cells have a short life span - contribute to sludging (clumping) of the blood
hemophilia
rare
affects mostly males
pts with hemophilia A have a decreased ability to create a clot after an injury
pts can be prescribed medications
complications: long-term joint problems, bleeding in the brain, thrombosis due to treatment
thrombophilia
description: a disorder in the body’s ability to maintain the smooth flow of blood through the venous and arterial systems