Chapter 2 - Investing and Financing Decisions and the Accounting System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
primary objective of financial reporting to external users
to provide financial information about the reporting entity that is useful to existing and potential investors, lenders, and other creditors in making decisions about providing resources to the entity
relavant information
information that can influence a decision; it has predictive and/or feedback value
faithful representation
requires that the information be complete, neutral, and free from error
three assumptions for balance sheets
-separate entity assumption
-going concern assumption
-monetary unit assumption
separate entity assumption
states that business transactions are separate from the transactions of the owners
going concern assumotion
states that businesses are assumed to continue to operate into the foreseeable future (also the continuity assumption)
monetary unit assumption
states that accounting information should be measured and reported in the national monetary unit without any adjustment for changes in purchasing power
mixed attribute measurement model
applied to measuring different assets and liabilities of the balance sheet
cost (historical cost)
most balance sheets are recorded at their historical cost- cash equivalent value of an asset on the date of the transaction
assets
probable future economic benefits owned by the entity as a result of past transactions (most companies list assets in order of liquidity)
four financial statements
balance sheet, income statement, statement of stockholders equity, statement of cash flows
current assets
cash and other assets expected to be exchanged for cash or consumed within a year
noncurrent assets
long-term investments, plant assets, intangible assets
liabilities
probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of a particular entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions or events (usually listed on balance sheet in order of maturity, how soon an obligation is to be paid)
creditors
entities that a company owes money to
current liabilities
liabilities due within a short time, usually within a year
noncurrent liabilities
obligations that a company does not expect to pay within one year
stockholders' equity/shareholders' equity/ owners' equity
the financing provided by the owners and the operations of the business
contributed capital
financing provided by owners (owners invest in the business by providing cash and sometimes other assets, receiving in exchange shares of stock as evidence of ownership)
earned capital/retained earnings
financing provided by operations (portion of profits reinvested in business)
transaction
(1) An exchange between a business and one or more external parties to a business or (2) a measurable internal event such as the use of assets in operations.
what to record on balance sheet
only economic resources and obligations resulting from past transactions
external events
exchanges of assets, goods, or services by one party for assets, services, or promises to pay (liabilities) from one or more other parties
ex. purchasing of a machine from a supplier
internal events
certain events that are not exchanges between the business and other parties but nevertheless have a direct and measurable effect on the entity
Ex. using up insurance paid in advance and using buildings and equipment over several years
is signing a contract considered a transaction?
no
account
a standardized format that organizations use to accumulate the dollar effect of transactions on each financial statement item
chart of accounts
a list of accounts used by a business
transaction analysis
the process of identifying the specific effects of economic events on the accounting equation
two principles underlying the transaction analysis process
-every transaction affects at least two accounts; correctly identifying those accounts and the direction of the effect (whether an increase or a decrease) is critical
-the accounting equation must remain in balance after each transaction
dual effects concept
the idea that every transaction has at least two effects on the basic accounting equation
balancing equation
assets = total liabilities + stockholders' equity
investing
company typically buys or sells its noncurrent assets . as well as investments (current or noncurrent)
financing
activities in which the company borrows or repays loans (typically from banks) and sells or repurchases its common stock and pays dividends (activities with stockholders)
par value
a value assigned to a share of stock and printed on the stock certificate
common stock
Term used to describe the total amount paid in by stockholders for the shares they purchase.
additional paid in capital/contributed capital
the excess of amounts paid in over the par or stated value
accounting cycle
process used by entities to analyze and record transactions, adjust the records at the end of the period, prepare financial statements, and prepare the records for the next cycle
general journal
listing in chronological order for each transaction's effects
general ledger
a record or effects to and balances of each amount
T accounts
An accounting device used to analyze transactions. shows direction of . effects. increases in asset accounts are on the left. increases in liabilities and stockholders' equity accounts are on the right.
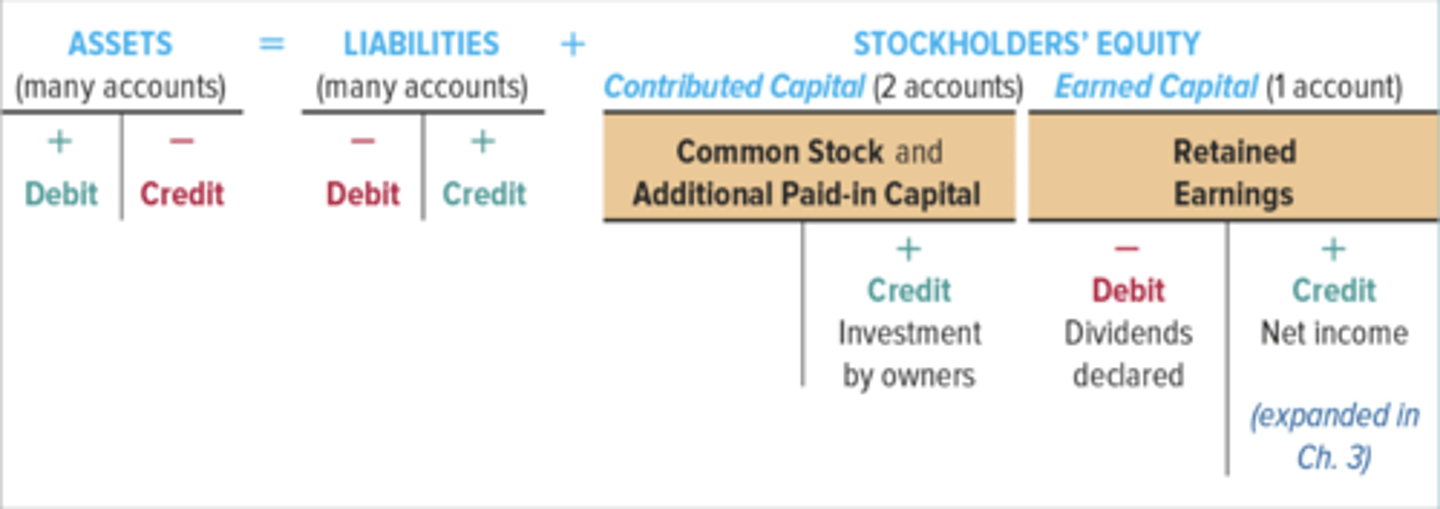
debt
left side of an account
credit
right side of an account