A&P1.. Practical exam 2
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Supination
rotation of forearm and palm of hand anteriorly or upwards
pronation
rotation of forearm and palm of hand posteriorly or downwards
elevation
movement of body part upward
depression
movement of of body downward
dorsiflexion
movement of ankle joint superior or closer to the body
plantar flexion
movement of ankle joint closer to the ground
inerversion
medial movement of sole of foot at ankle joint
eversion
lateral movement of sole of foot at ankle joint
protraction
anterior movement in the transverse plane
retraction
movement in the transverse plane
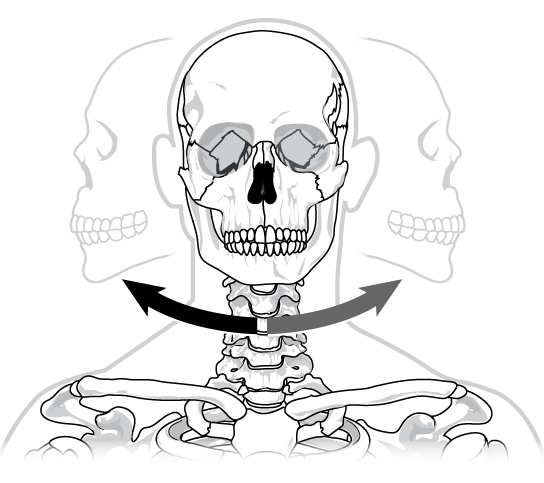
medial rotation
movement towards midline of the body
lateral rotation
movement away from midline
abduction
movement away from body
adduction
movement towards body
flexion
bending joint closer to and angle
extention
straighten joint or making less of an angle
hyperextention
going past 180 angle
circumduction
full 360 rotation of a joint
pivot joint
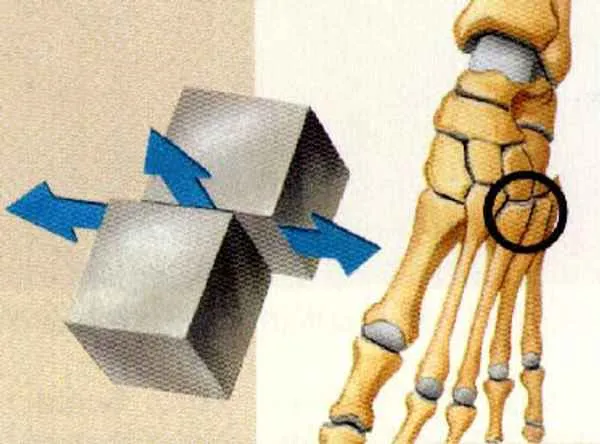
gliding joint
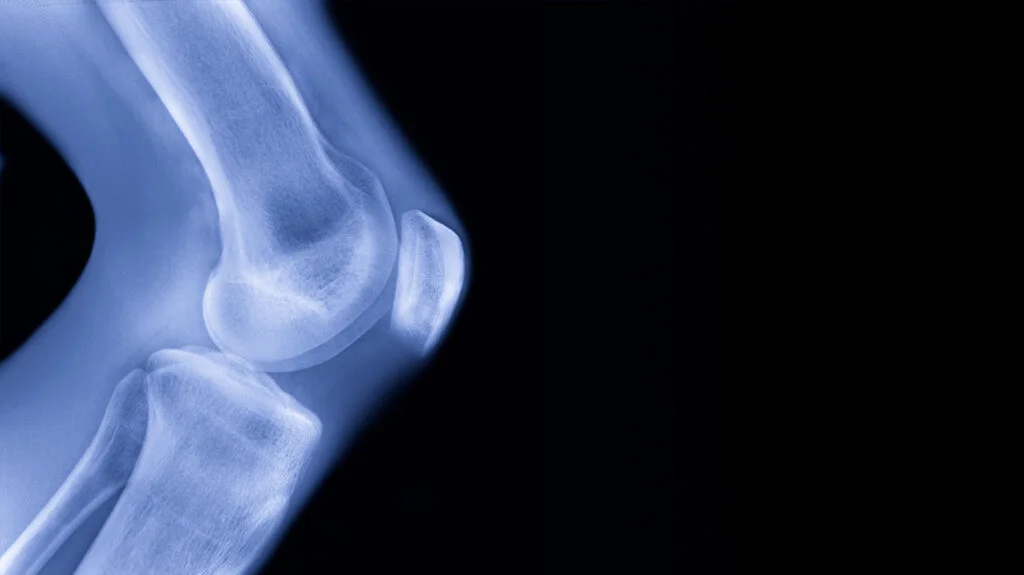
hinge joint
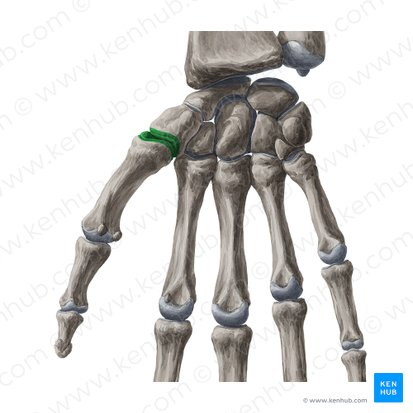
saddle joint
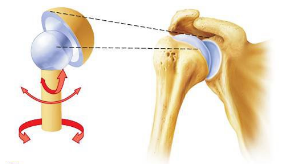
condyle joint
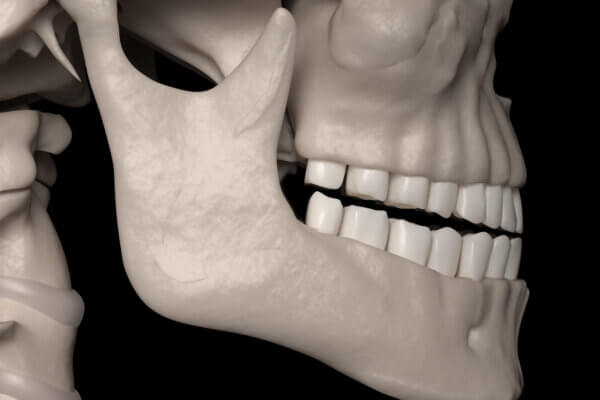
ball-in-socket joint
tendon
muscle to bone
ligament
bone to bone
fascia
a thin casing of connective tissue that surrounds and holds every organ, blood vessel, bone, nerve fiber and muscle in place
epimysium
surrounds the entire muscle
perimysium
the sheath of connective tissue surrounding a bundle of muscle fibers.
endomysium
a wispy layer of areolar connective tissue that ensheaths each individual muscle fiber, or muscle cell
fascicle
a bundle of structures, such as nerve or muscle fibers
axon of motor neuron
transmits signal to other neurons, muscles, and glands or from sensory end organs
muscle fiber
consist of a single muscle cell
sarcolemma
cell membrane surrounding a skeletal muscle fibre
sarcoplasmic reticulum
is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other cells
myofibril
a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell
actin
globular multi-functional proteins
myosin
prototype of a molecular motor
thick filaments
made up of myosin, a protein consisting of a tail and two globular heads
thin filaments
protein actin
transverse tubule
extensions of the cell membrane that penetrate into the center of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells
agonist
muscle responsible for the action movement
antagonist
muscle responsible for action in the opposite direction of an agonist or for resistance to an agonist
synergist
muscle that assists an agonist, often by supplementing the contraction force
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscles cell
astrocyte
star-shaped neuroglial between neuron and blood vessels
axon
nerve fiber arising from a slight elevation of the cell body that conducts an impulse away from the cell body
Nissl bodies
corresponds to rough endoplasmic reticulum in other cells
collateral
branching of an axon
dendrite
neuron process with many branches that conducts an impulse towards the cell body
myelin sheath
substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein that insulates axon and increases impulse speed
nerilemma
sheath of Schwann cell contain cytoplasm and nucleus that encloses myelin
neurofirbrils
network if fine threads extending into nerve fiber
effector
structure capable of responding into motor impulse
ependymal cell
cells that cover the inside spaces of the brain ventricles and help regulate cerebrospinal fluid
ganglion
specialized mass of neuron cell bodies outside the brain or spinal cord
interneuron
transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within central nervous system
microglia
phagocytic neuroglia
motor efferent neuron
transmits impulse out of the brain or spinal cord to effectors
oligodendrocyte
myelin-forming neuroglia in the brain and spinal cord
sensory afferent neuron
transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
cerebral cortex
thin layer of gray matter on surface of cerebrum; memory, thinking, learning, reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, consciousness, and sensory functions
corpus callosum
connects cerebral hemispheres
falx cereblli
layer of dura mater that separates cerebellar hemispheres
gyrus
ridge on surface of cerbrum
hypothalamus
part of diencephalon that forms lower walls and floor of third ventricle; body temperature, hunger and thirst, mood, sex drive, blood pressure and sleep.
diencephalon
inner ventricle of brain
insula
part of the brainstem between diencephalon and pons; o basic survival needs, such as taste, visceral sensation, and autonomic control
medulla oblongata
part of the brainstem continuous with the spinal cord; heartbeat
optic chiasma
structure formed by the crossing-over of the optic nerves; visual information from the eye to the corte
pineal gland
cone-shaped gland attached to upper posterior portion of the diencephalon; circadian rhythm by secreting the hormone melatonin
pons
rounded bulge on underside of brainstem; handles unconscious processes and jobs, such as your sleep-wake cycle and breathing
abducens
stimulates lateral rectus muscle of eye
accessory
controls neck and shoulder movement
facial
stimulates superiors oblique muscle of eye
glossopharyngeal
swallowing
hypoglossal
controls tongue movement
oculomotor
pupil constriction and eyelid opening
olfactory
smell
optic
vision
trigeminal
sensory impulse from teeth and face
trochlear
taste, salvation, and secretion of tears
vagus
regulates heart rate
vestibulocochlear
equilibrium and hearing
arachnoid mater
thin, web-like middle membrane
denticulate ligament
band of pia mater that anchors dura mater to cord
dura sinus
channel through which venous blood flows
dura mater
outermost layer of meninges
epidural space
separates dura mater from bone of verebra
pia mater
follows irregular contours of spinal cord surface
subarachnoid space
contains cerebrospinal fluid
auditory tube
connects middle ear in temporal bone
bony (osseous) labyrinth
boney canal of inner ear in temporal bone
ceruminous gland
wax-secreting structure
external acoustic meatus
S-shaped tube leading to tympanic membrane
malleus
auditory ossicle attached to tympanic membrane
membranous labyrinth
tube containing endolymph within boney (osseous) labyrinth
Scala tympani
extends from apex of cochlea to round window and contains perilymph
Scala vestibuil
leads from oval window to apex of cochlea and contains perilymph