Organic Chemistry pKa Values & Cation/Anion Donor/Acceptor Activity
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Memorize for ranking cations/anions on acidity/basicity.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
High pKa Value = Strong/Weak ACID
Weak ACID
High pKa Value = Strong/Weak BASE
Weak BASE
Cation
Positive Formal Charge
Electron Acceptor
H+ (proton) Donor
Electrophile
Usually an Acid —> Remove H to make CB
Weak CB (low pKa value) = Strong Acid
Anion
Negative Formal Charge
Electron Donor
H+ (proton) Acceptor
Nucleophile
Usually a Base —> Add H to make CA
Weak CA (high pKa) = Strong Base
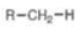
Alkane
pKa = 50

Alkene
pKa = 44
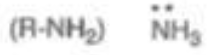
Ammonia/Amino Radical
pKa = 35

Alkyne
pKa = 25
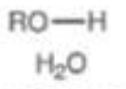
Alcohols/Water
pKa = 16
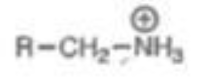
Ammonia Attached to C
pKa = 11
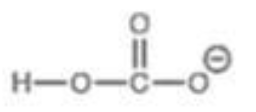
Ester Attached to Alcohol
pKa = 10

Thiol
pKa = 10
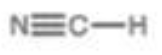
Nitrile
pKa = 9
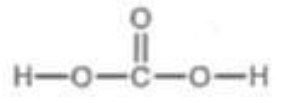
Carboxylic Acid Attached to Alcohol
pKa = 6
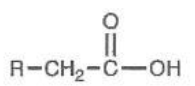
Carboxylic Acid Attached to C
pKa = 5

Hydrofluoric Acid
pKa = 3

Nitric Acid
pKa = -1
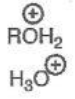
Hydronium/Oxonium Ion
pKa = -2
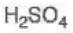
Sulfuric Acid
pKa = -5

Hydrochloric Acid
pKa = -7

Hydrobromic Acid
pKa = -9
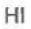
Hydroiodic Acid
pKa = -10