ANAPHY: U14 Urinary System
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
205 Terms
Urinary System
Essential for maintaining homeostasis by regulating body fluids, electrolyte balance, and waste elimination
Kidneys, Ureters, Urinary Bladder, Urethra
4 Primary Components of the Urinary System
Kidneys
One of the 4 Primary Components of the Urinary System
Filter blood and produce urine
Ureters
One of the 4 Primary Components of the Urinary System
Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder
Urinary Bladder
One of the 4 Primary Components of the Urinary System
Stores urine until excretion
Urethra
One of the 4 Primary Components of the Urinary System
Eliminates urine from the body
WBEEPD
Acronym for the 6 Functions of the Urinary System
Water & Electrolyte Balance
Blood Pressure Regulation
Waste Excretion
Erythropoiesis Support
pH Homeostasis
Detoxification
6 Functions of the Urinary System
Waste Excretion
One of the functions of the urinary system
In which the urinary system removes nitrogenous wastes (urea, uric acid, ammonia) and eliminates toxins and drugs through urine
Urea, Uric Acid, Ammonia
What nitrogenous wastes does the urinary system remove?
Toxins and Drugs
Aside from nitrogenous wastes, what other substances are eliminated through urine?
Water & Electrolyte Balance
One of the functions of the urinary system
Regulates sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), and chloride (CI-); Maintains osmolarity for proper cellular function.
Sodium (Na+), Potassium (K+), Calcium (Ca2+), Chloride (CI-)
What ion levels does the urinary system regulate?
Osmolarity
What does the urinary system have to maintain for proper cellular function?
Blood Pressure Regulation
One of the functions of the urinary system
Releases renin to activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); Adjusts blood volume by altering water reabsorption
Renin
What does the urinary system release to regulate blood pressure?
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
What process does the urinary system activate to regulate blood pressure?
Water Rebsorption
What does the urinary system alter to adjust blood volume?
pH Homeostasis
One of the functions of the urinary system
Balances hydrogen ion (H+) and bicarbonate (HCO3-) levels; Prevents acidosis or alkalosis.
Hydrogen Ion (H+) and Bicarbonate (HCO3-) Levels
What pH-related ion levels does the urinary system balance?
Acidosis & Alkalosis
What pH-related conditions does the urinary system prevent?
Erythropoiesis Support
One of the functions of the urinary system
Produces erythropoietin (EPO), stimulating RBC production
Erythropoietin
What does the urinary system produce that stimulates RBC production?
Detoxification
One of the functions of the urinary system
Eliminates metabolic byproducts and foreign substances
Kidneys
Bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally on either side of the spine; 10-12 cm long, 5 cm wide
10-12 cm
How long are the kidneys?
5 cm
How wide are the kidneys?
Ureters
Thin muscular tubes (25-30 cm long) that propel urine via peristalsis to the bladder
25-30 cm
How long are the ureters?
Peristalsis
How do the ureters propel urine to the bladder?
Urinary Bladder
Hollow, muscular organ capable of expanding; Stores ~400-600 mL of urine under normal conditions
400-600 mL
What volume of urine is the urinary bladder capable of storing?
Urethra
Single tube leading from the bladder to the external environment; 4 cm in females, 20 cm in males
4 cm
How long is the urethra in females?
20 cm
How long is the urethra in males?
Vascular Supply
Renal arteries deliver ~20-25% of cardiac output to the kidneys & Renal veins return filtered blood to systemic circulation.
Renal Arteries
What component of vascular supply deliver ~20-25% of cardiac output to the kidneys?
20-25%
What percentage of cardiac output do the renal arteries deliver to the kidneys?
Renal Veins
What component of vascular supply returns filtered blood to systemic circulation?
Renal Capsule, Adipose Capsule, Renal Fascia
3 Parts of the External Structure of the Kidney
Renal Capsule
Part of the external structure of the kidney
Fibrous outer layer for protection
Adipose Capsule
Part of the of external structure of the kidney
Cushioning layer of fat
Renal Fascia
Part of the of external structure of the kidney
Anchors kidneys to surrounding structures
Cortex, Medulla, Renal Pelvis, Major & Minor Calyces, Hilum
5 Main Parts of the Internal Structure of the Kidneys
Renal Cortex
One of the main parts of the internal structure of the kidney
Outer layer containing renal corpuscles
**Contain glomeruli, proximal and distal convoluted tubules, nephrons, and other blood vessels
Renal Cortex
What is the site of initial blood filtration in the kidneys?
Renal Medulla
One of the main parts of the internal structure of the kidney
Inner layer with renal pyramids and loops of Henle
**Beneath the renal cortex
Renal Pyramid
Part of the internal structure of the kidney
Cone-shaped structures in the renal medulla
Renal Papilla
Part of the internal structure of the kidney
At the apex of each renal pyramid; drains urine into the minor calyx
Minor Calyx
Part of the internal structure of the kidney
Where the renal papillae drain into
Renal Columns
Part of the internal structure of the kidney
Extensions of the cortex that separate the renal pyramids; provide passage for blood vessels
Major & Minor Calyces
One of the main parts of the internal structure of the kidney
Direct urine to the renal pelvis
Major Calyx
Part of the internal structure of the kidney
Formed by the convergences of minor calyces and empty into the renal pelvis
Hilum
One of the main parts of the internal structure of the kidney
Entry/exit for renal arteries, veins, lymphatics, and ureters
Renal Pelvis
One of the main parts of the internal structure of the kidney
Funnel-shaped cavity collecting urine
**Connects to the ureter
Nephron
Functional unit of the kidney
~1 million
How many nephrons are there per kidney?
Renal Corpuscle & Tubular System
2 General Components of the Nephron
Renal Corpuscle
One of the general components of the nephron
Composed of the Glomerulus & Bowman’s Capsule
**Initial filtering component located in the renal cortex
Glomerulus
Part of the renal corpuscle (one of the general components of the nephron)
Capillary tuft for filtration
Bowman’s Capsule
Part of the renal corpuscle (one of the general components of the nephron)
Encases glomerulus; collects filtrate
Podocytes
Specialized cells located in the inner layer of Bowman’s Capsule which further filtration of the blood
Tubular System
One of the general components of the nephron
Composed of the Proximal Convoluted Tubule, Loop of Henle, Distal Convoluted Tubule, Collecting Duct
Proximal Convoluted Tube (PCT)
Part of the tubular system (one of the general components of the nephron)
Reabsorbs most water, ions, and nutrients
**Located in cortex; first section after renal corpuscle; reabsorbs 70-80% water, sodiium, chloride, glucose, amino acids into blood stream; secretes waste products, like hydrogen ions and certain drugs into tubule
Loop of Henle/Nephron Loop
Part of the tubular system (one of the general components of the nephron)
Creates medullary osmotic gradient
**Dives into medulla and returns into cortex; has a descending limb that is permeable to water but not solutes, water leaves which concentrates the filtrate AND an ascending limb, which is permeable to solute, especially sodium and chloride, but not water
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Part of the tubular system (one of the general components of the nephron)
Fine-tunes ion and pH balance
**Located in the cortex; regulates ion exchange, especially sodium, potassium, and calcium; regulates through hormonal control (ADH & aldosterone)
Collecting Duct
Part of the tubular system (one of the general components of the nephron)
Concentrates and transports urine to renal pelvis
**Reabsorbs water under ADH control to concentrate urine
Cortical & Juxtamedullary Nephrons
2 Types of Nephrons
Cortical Nephrons
One of the types of nephrons
Short loops; majority of nephrons
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
One of the types of nephrons
Long loops; critical for urine concentration
Renal Pyramid
What specific internal part of the kidney are nephrons located in?
Filtration
Reabsorption
Secretion
3 Steps in the Process of Forming Urine
Filtration
One of the stages in the process of forming urine
Blood enters the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole
High hydrostatic pressure forces plasma and small molecules through the glomerular membrane into the Bowman’s capsule and larger molecules like proteins and blood cells remain in the bloodstream
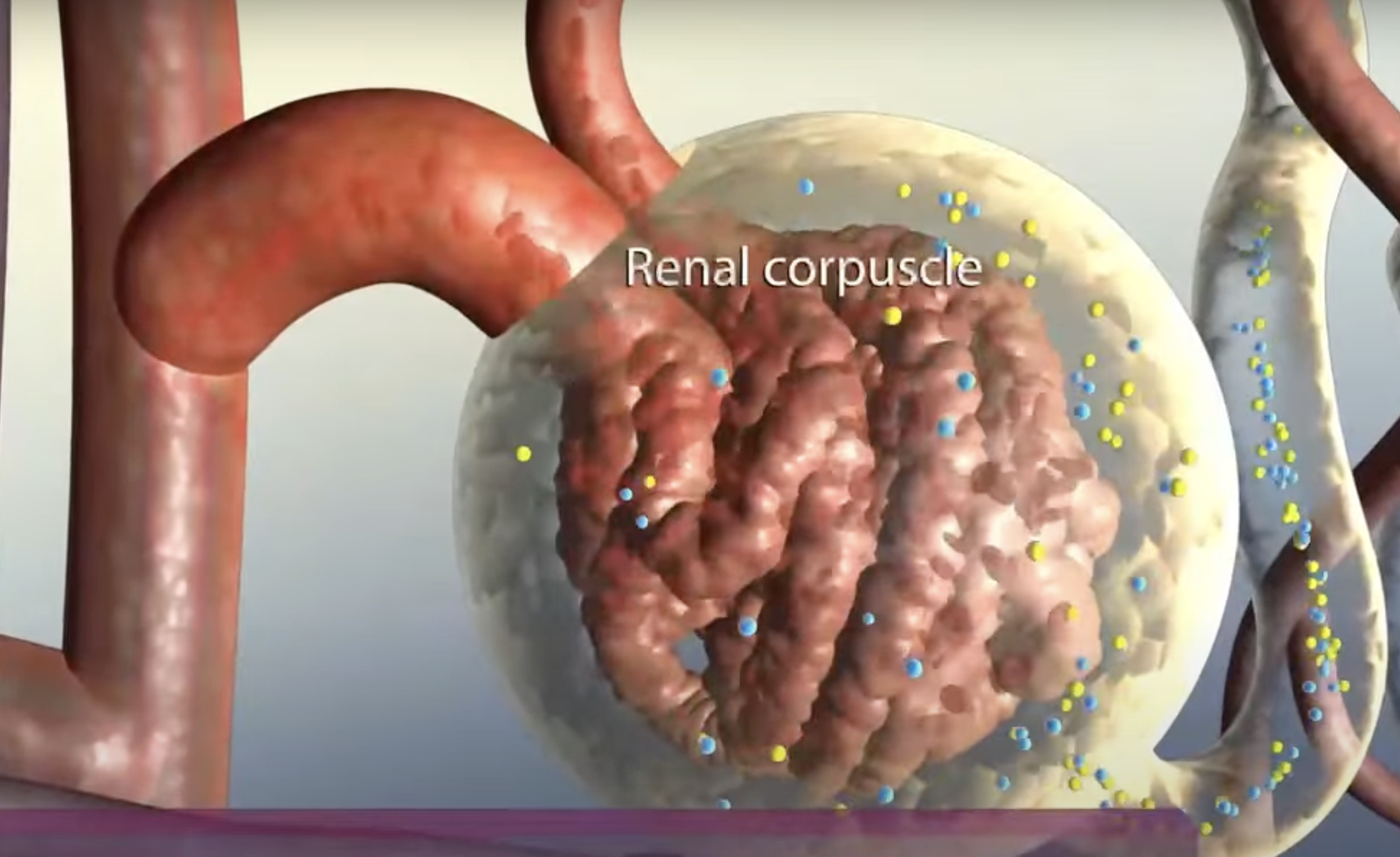
Glomerulus
Where does Filtration mainly occur?
Reabsorption
One of the stages in the process of forming urine
Filtrate moves into the renal tubules; essential substances are taken into the peritubular capillaries and Loop of Henle will establish a concentrated gradient in the medulla
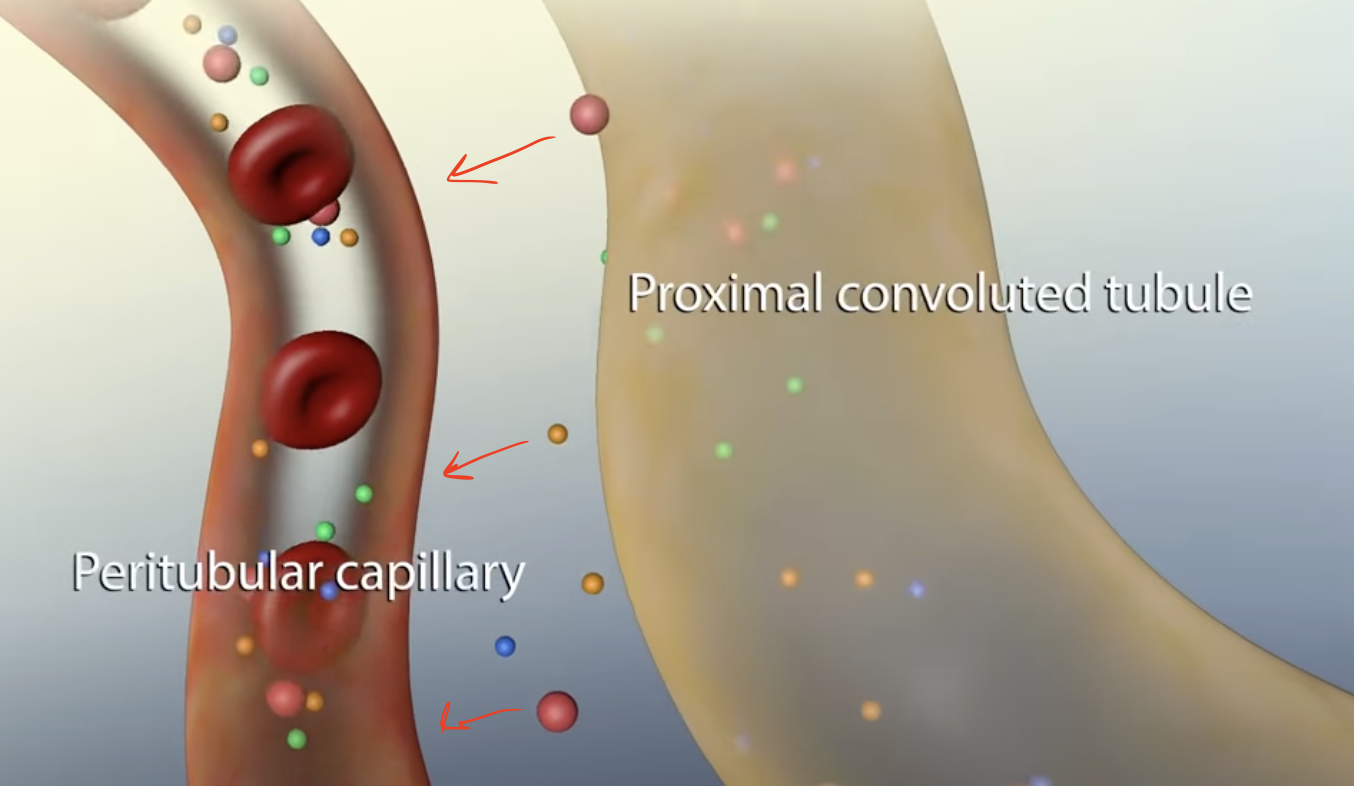
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) & Loop of Henle
Where does Reabsorption mainly occur?
Secretion
One of the stages in the process of forming urine
Additional waste products, such as hydrogen ions, potassium, and ammonia are actively transported from the blood into the tubules, eliminating toxins and regulating blood pH
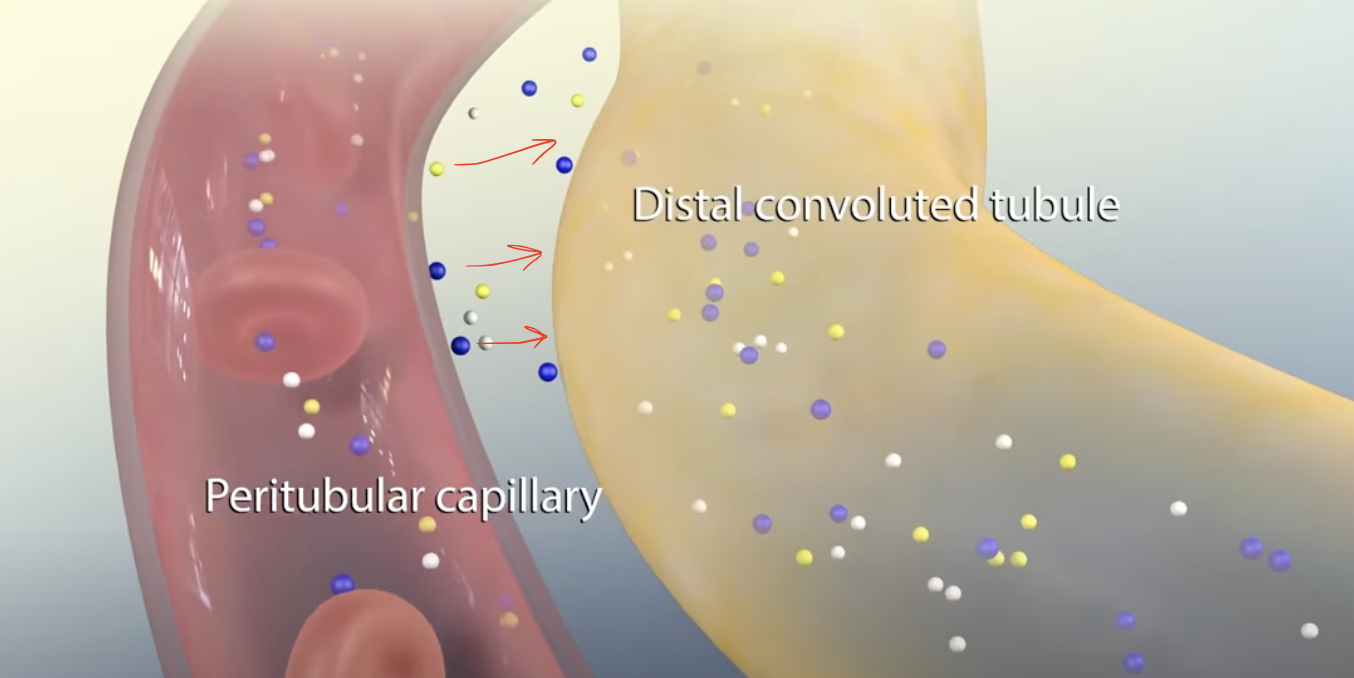
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) & Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Where does Secretion mainly occur?
Afferent Arteriole
What is the structure that brings the fluid from glomerulus to the renal tubules?
True
True or False: Loop of Henle is a convoluted tubule.
Aldosterone & ADH
Key Hormones that Regulates Nephrons
Aldosterone
One of the key hormones that regulates nephrons
Increases sodium/solute/ion reabsorption
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
One of the key hormones that regulates nephrons
Enhances water reabsorption in collecting duct
PCT; collecting ducts
Ions are especially reabsorbed in the ___ and water in the ___
Parathyroid Hormone
Hormone that causes calcium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Calcium reabsorption occurs in the ___
Glomerular Filtration
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Secretion
Excretion
4 Stages of Urine Formation
Glomerular Filtration
One of the 4 Stages of Urine Formation
In which ~180L of plasma is filtered daily; Hydrostatic pressure drives water and solutes into Bowman's capsule; Large molecules (e.g., proteins) and blood cells are excluded
~180 L
During glomerular filtration, what volume of plasma is filtered daily?
Hydrostatic Pressure
During glomerular filtration, what drives water and solutes into Bowman’s capsule?
Large Molecules (like proteins) & Blood Cells
During glomerular filtration, what are excluded from being filtered?
Tubular Reabsorption
One of the 4 Stages of Urine Formation
Reclaims -99% of filtered water, glucose, and ions; Occurs mainly in the PCT
~99%
During tubular reabsorption, how much filtered water, glucose, and ions are reclaimed?
Filtered Water, Glucose, Ions
During glomerular filtration, ~99% of what is reclaimed?
Tubular Secretion
One of the 4 Stages of Urine Formation
Occurs primarily in DCT and Collecting Ducts; Active transport of wastes (e.g., H+, K+, drugs) into tubular fluid; Final adjustments to urine composition
Excretion
One of the 4 Stages of Urine Formation
Urine is expelled from the body via the urethra
Fenestrated Endothelium
Basement Membrane
Podocytes
3 Layers the Filtration Membrane is Composed of
Fenestrated Endothelium
One of the 3 Layers the Filtration Membrane is Composed of
Allows passage of small solutes and water
Basement Membrane
One of the 3 Layers the Filtration Membrane is Composed of
Restricts larger molecules (like proteins).
Podocytes
One of the 3 Layers the Filtration Membrane is Composed of
Specialized epithelial cells with filtration slits