Cancer drugs
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Name the 5 categories of DNA-reactive drugs
Nitrogen mustards: Mustine, Chlorambucil, Bendamustin
Phosphoramide mustards: Cyclophosphamide
N-Alkyl-N-Nitrosoureas: Carmustine; Lomustine
Alkylating agents: Procarbazine, Dacarbazine, Temozolomide
Platinum compounds: Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Oxaliplatin
Name the 3 antimetabolites?
Thymidylate synthase inhibitors: 5FU, Capecitabine
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibitor: Methotrexate
DNA replication inhibitor: Gemcitabine, Fludarabine, Cytarabine
Name the 5 Natural Product Antitumor Antibiotics
DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors: Doxorubicin (DNA intercalators) and Etoposide (Non intercalator)
DNA topoisomerase I inhibitors: Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan
Transcription inhibitor: Actinomycin D
DNA degradation: Bleomycin
Mitotic inhibitors: Vinca alkaloids, Paclitaxel and Docetaxel
Name the antibody therapy?
HER2
EGFR
VEGF
CD20
PD-1
CTLA-4
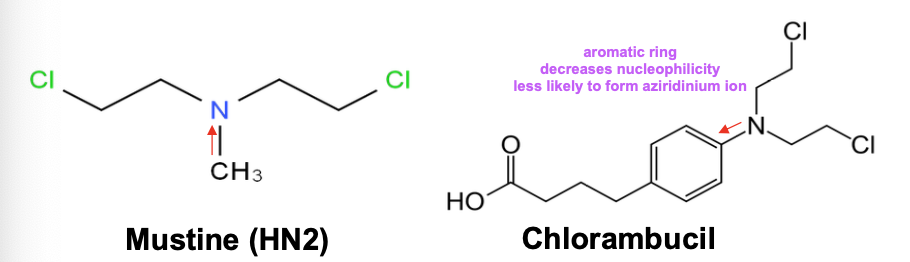
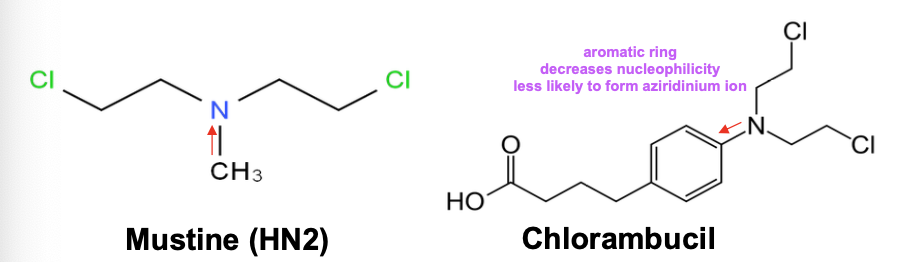
What is the difference between chlorambucil and mustine?
Oral - Aryl substituted nitrogen mustard with aromatic ring
Less likely to form aziridinium ion - N decreases nucleophilicity of nitrogen
Acts more slowly and less toxic than mustine
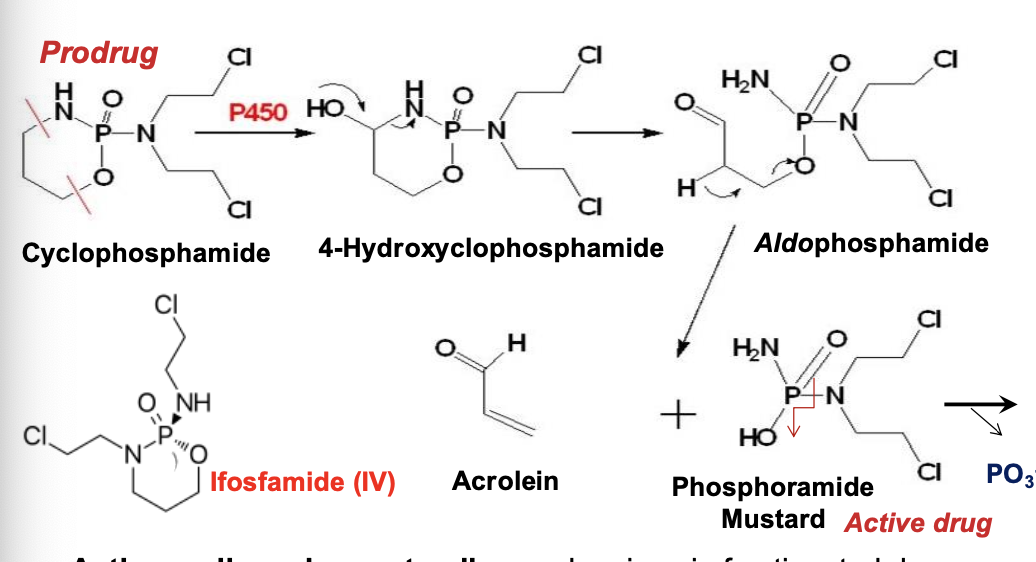
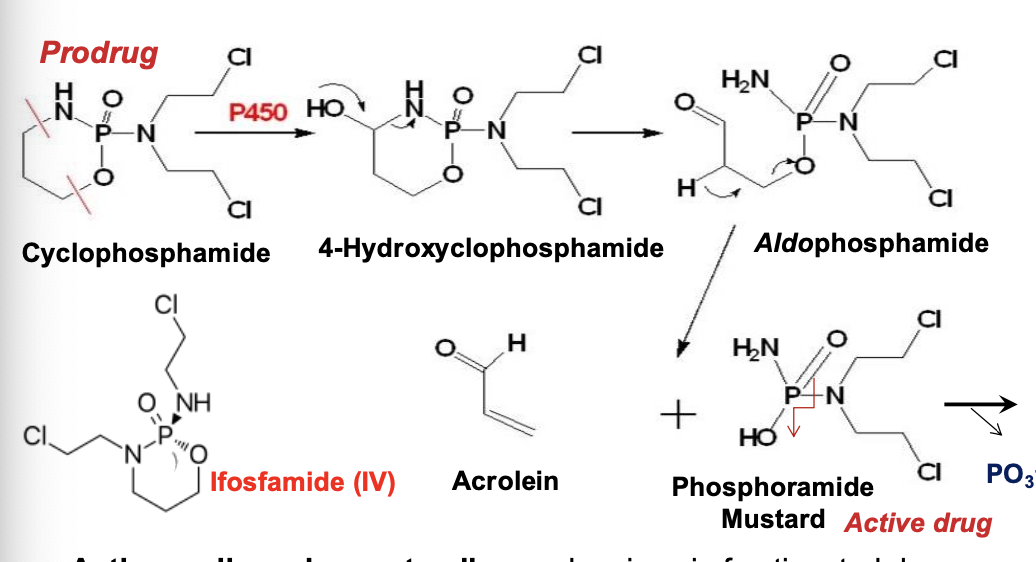
What class of drug is cyclophosphamide?
Phosphoramide mustard
An alkylating agent - PRODRUG
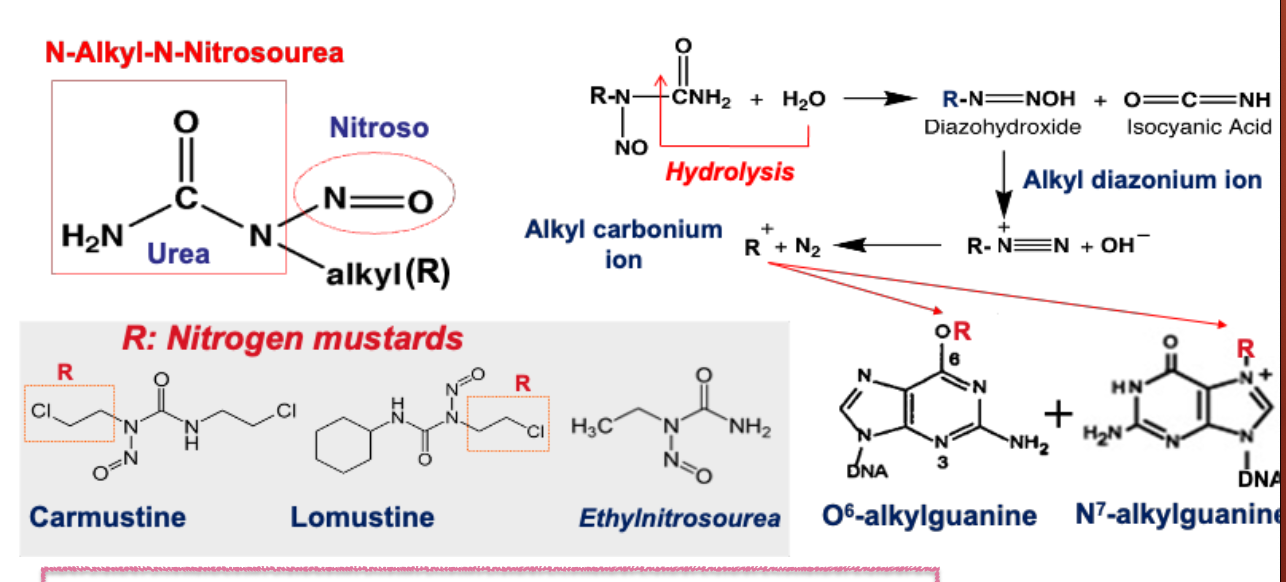
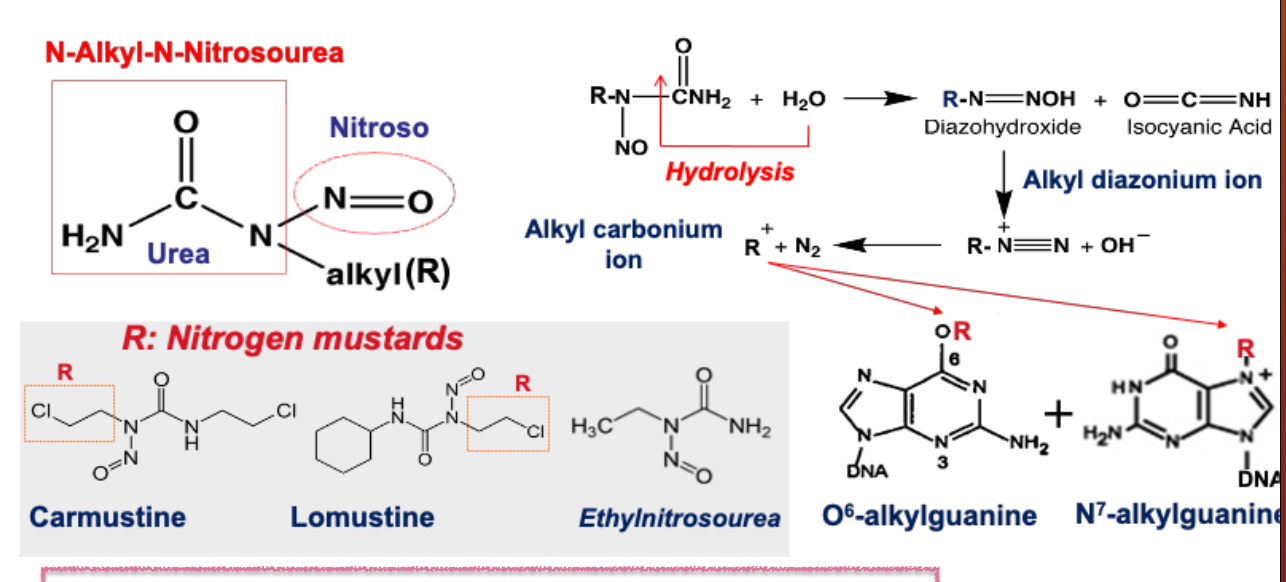
What class of drug is camustine?
N-alkyl-N-nitrosoureas - Nitrogen Mustards
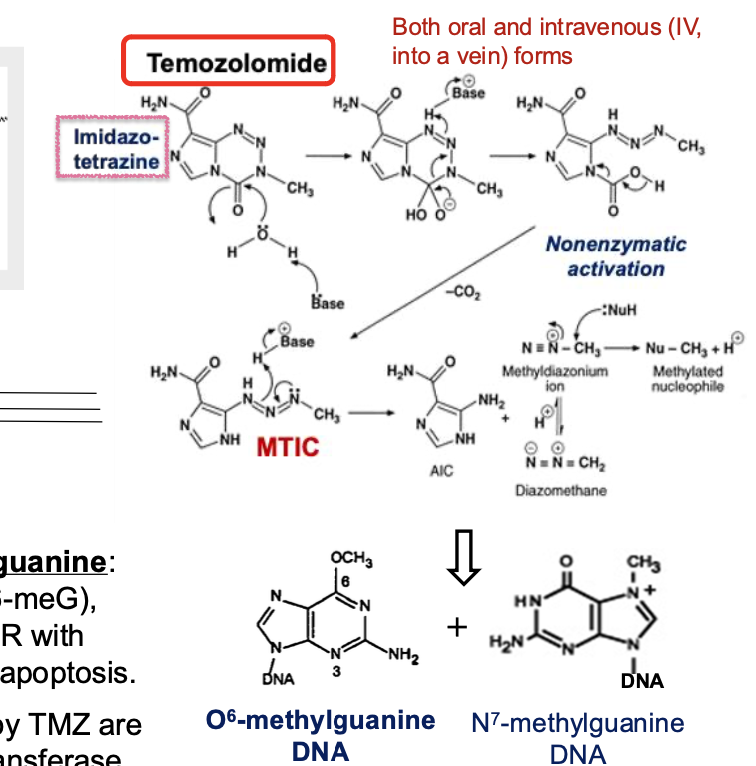
What class of chemotherapy are procarbazine, dacarbazine, and temozolomide?
DNA reacting drugs - alkylating agents
form methyldiazonium ion
Imidazocarboxamides
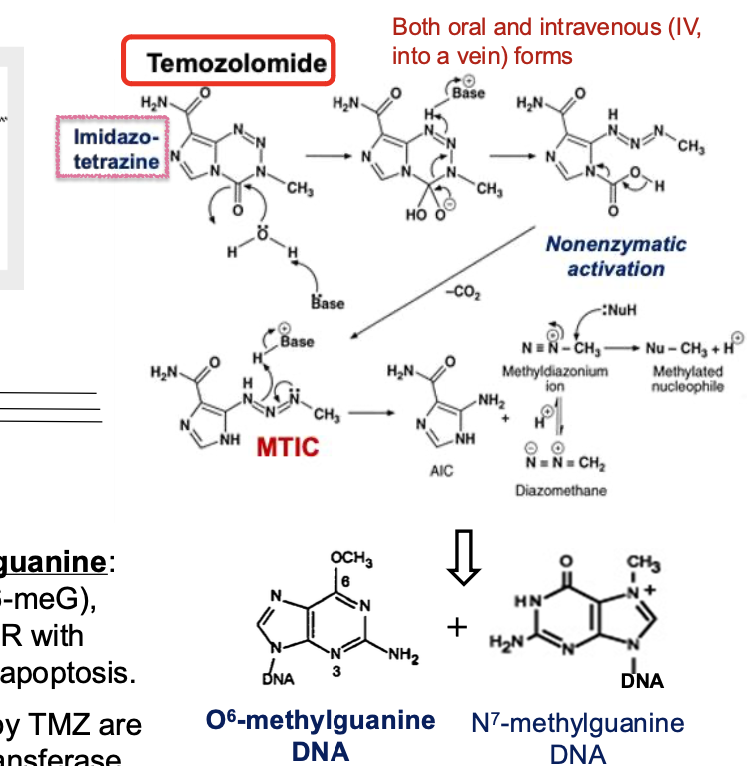
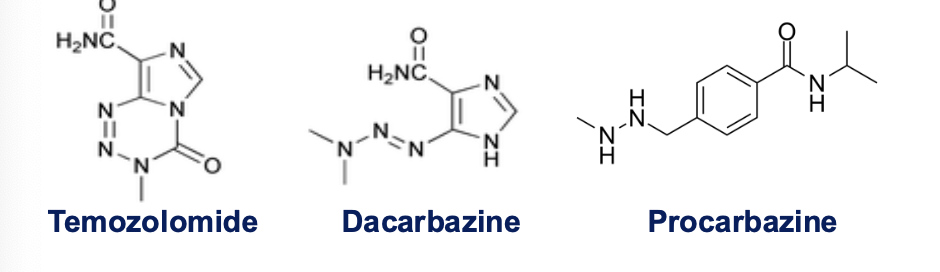
What are key differences between dacarbazine and temozolomide?
Dacarbazine = imidazole carboxamide
Temozolomide = imidazo-tetrazine
TMZ does NOT require metabolic activation via cytochrome P450 enzymes
What is the mechanism of action of platinum compounds?
Platinum compounds react with DNA in vivo, causing monoalkylation or crosslinking of DNA which ultimately triggers apoptosis (programmed cell death)
What is a primary MOA of 5-FU? Is this drug a reversible or irreversible inhibitor?
5-FU is activated by anabolism to 5-deoxyuridyl monophosphate (Fdump), which acts as an irreversible thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitor.
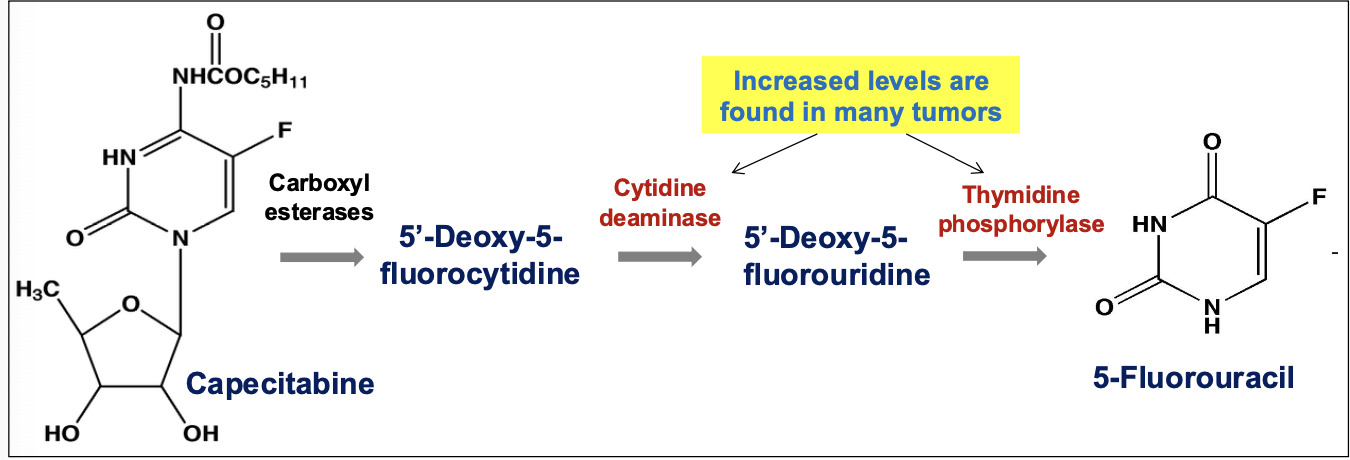
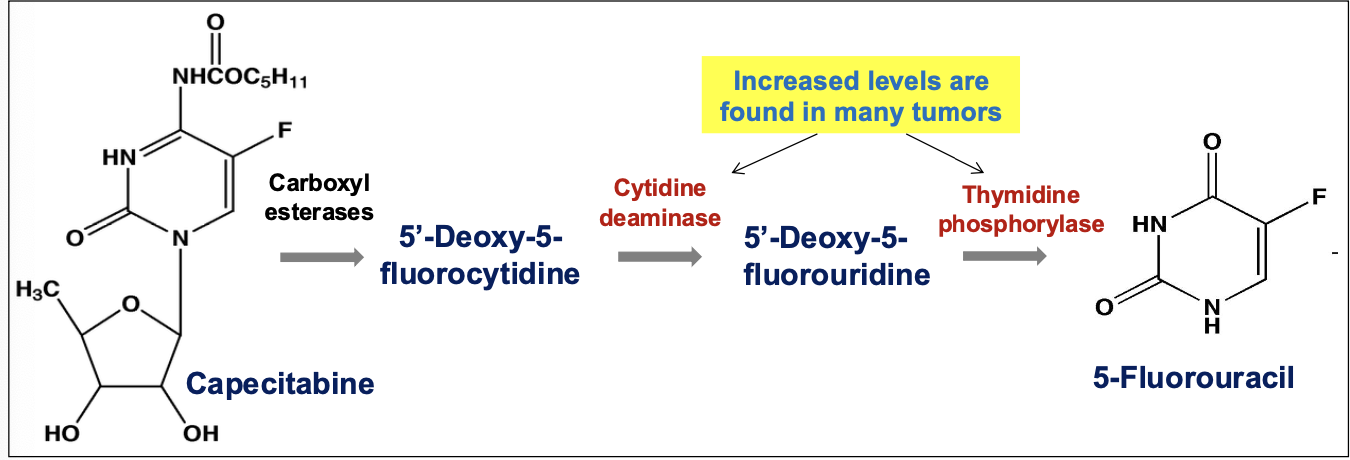
___ is an oral prodrug form of 5-FU?
Capecitabine
Metabolized to 5-FU
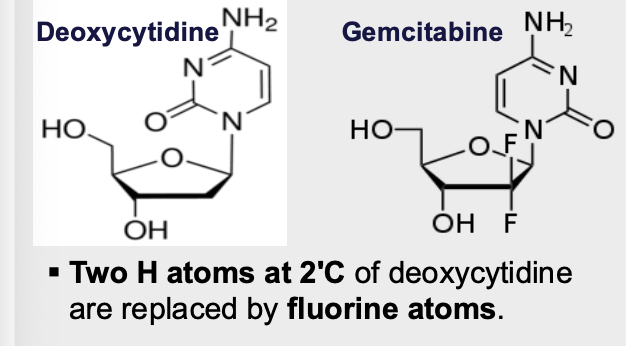
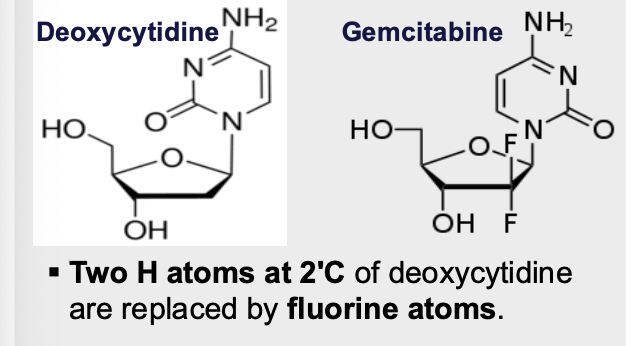
What are the structural features of gemcitabine?
2 H atoms at 2C of deoxycytidine are replaced by fluorine atoms
Looks like deoxycytidine
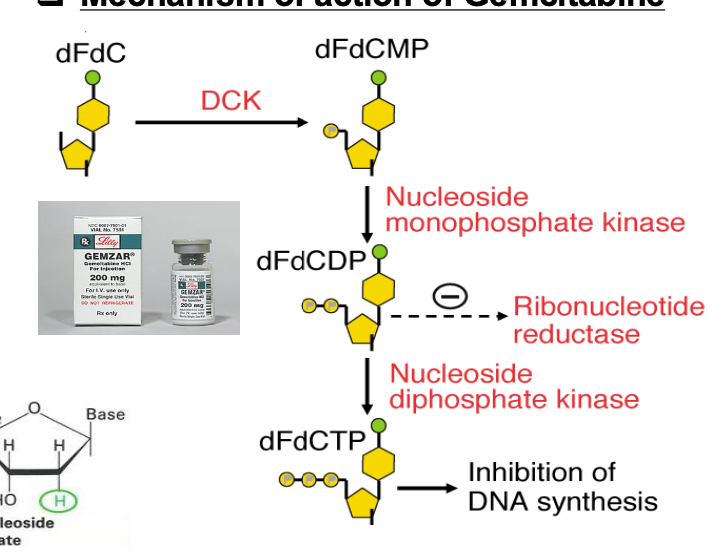
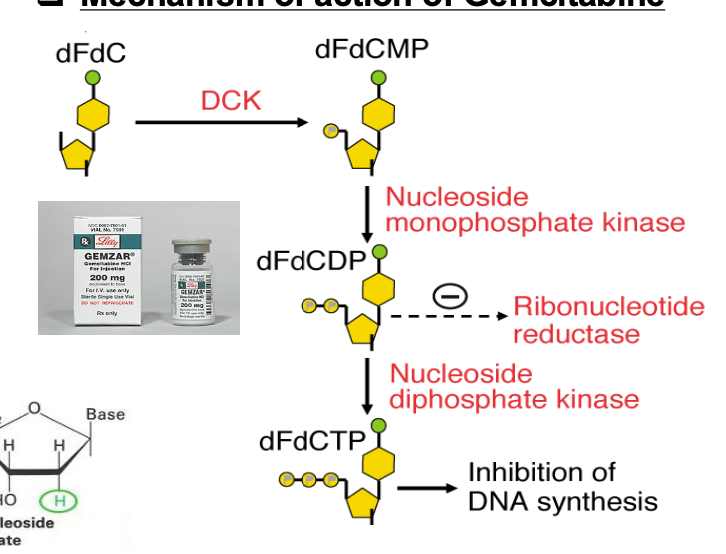
What is the MOA of gemcitabine?
Diphosphate form (dFdCDP) - strong inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase - inhibits synthesis of dNDP from NDP
Triphosphate form: replaces dCTP during DNA replication - arresting DNA synthesis followed by tumor growth arrest and apoptosis
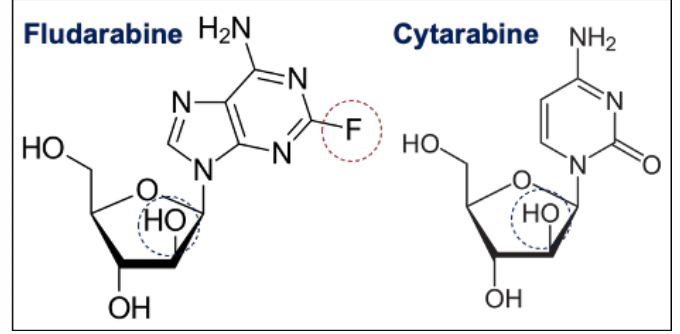
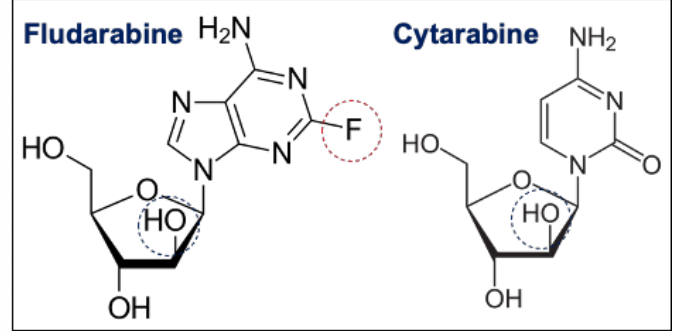
Fludarabine is a ______ analogue, whereas cytarabine is a ____ analogue. Both are DNA _____ inhibitors
Purine analogue, pyrimidine analog
DNA synthesis inhibitors - interferes with ribonucleotide reductase + DNA polymerase
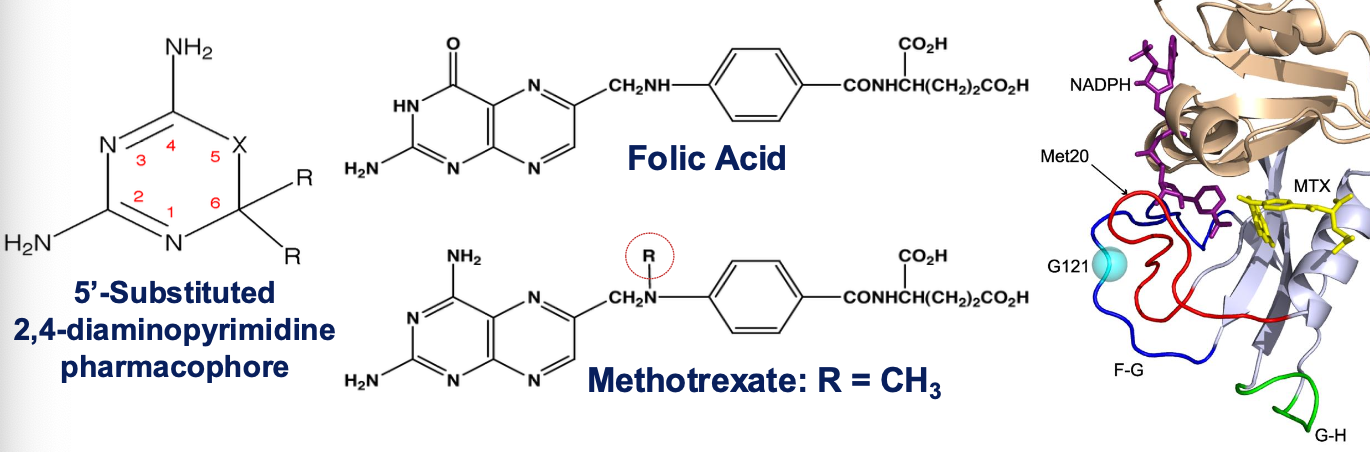
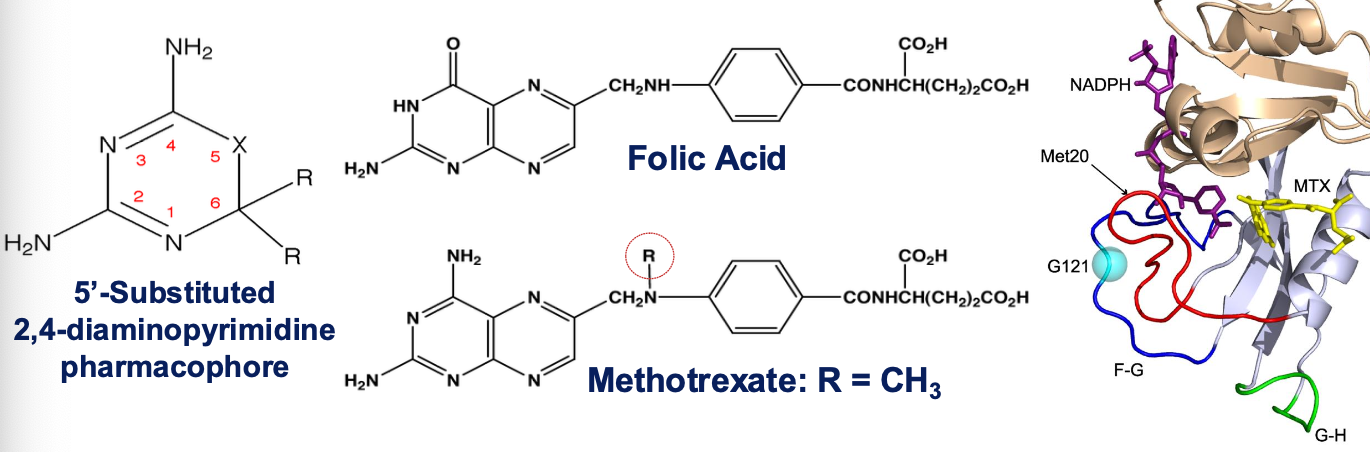
Methotrexate’s primary molecular target is ______, which is an enzyme essential for DNA synthesis and cell replication
Inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)
Inhibits DNA synthesis in S phase
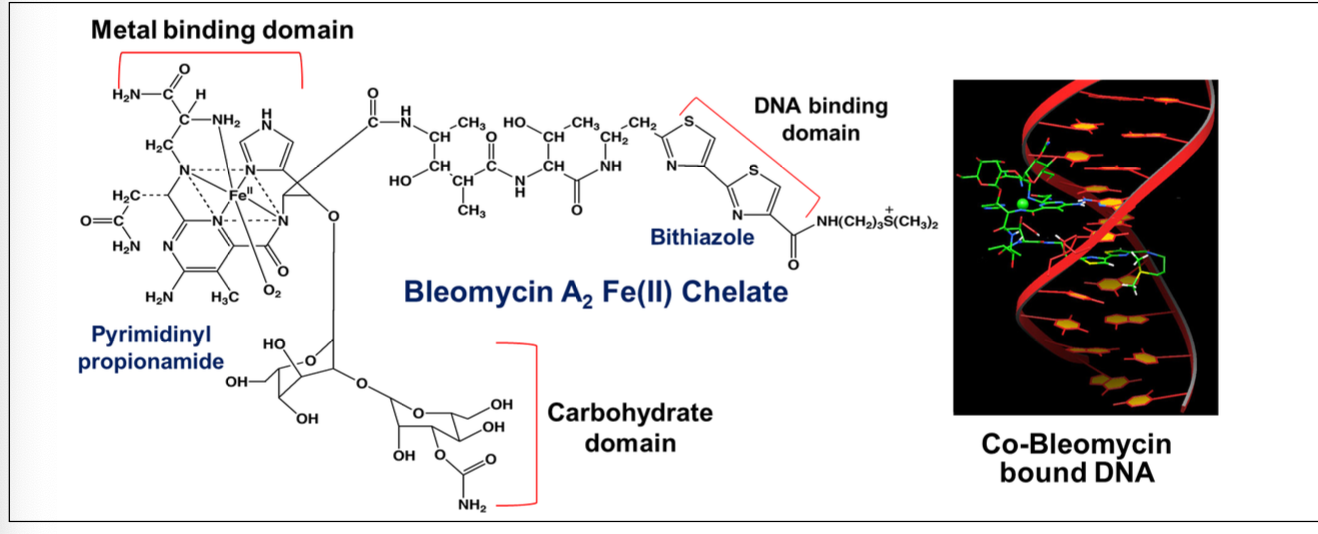
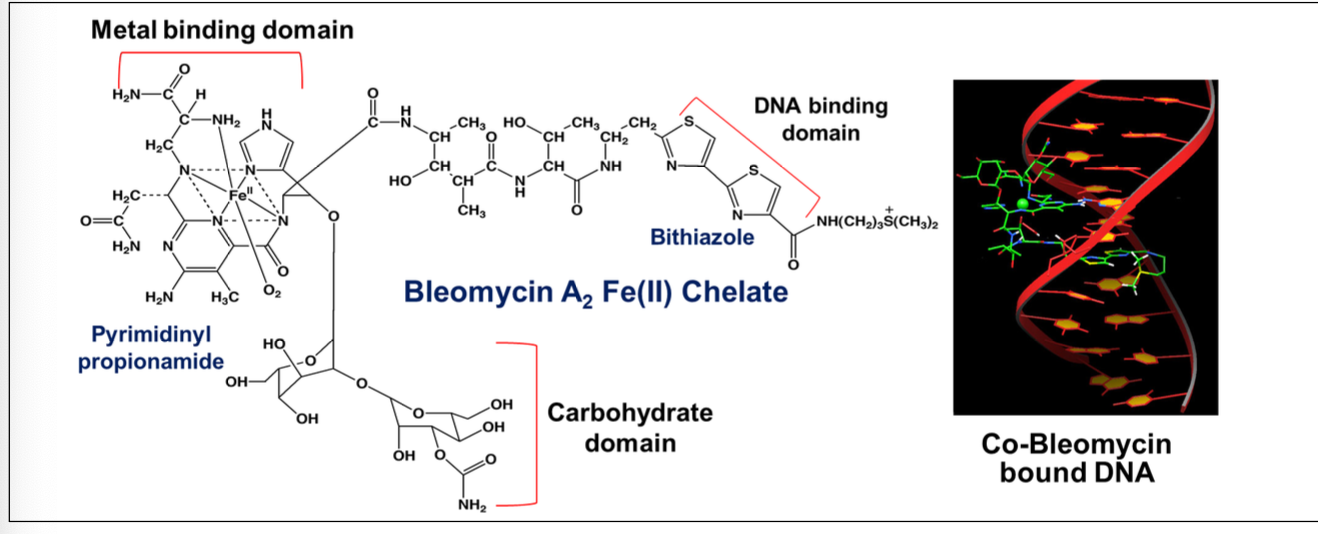
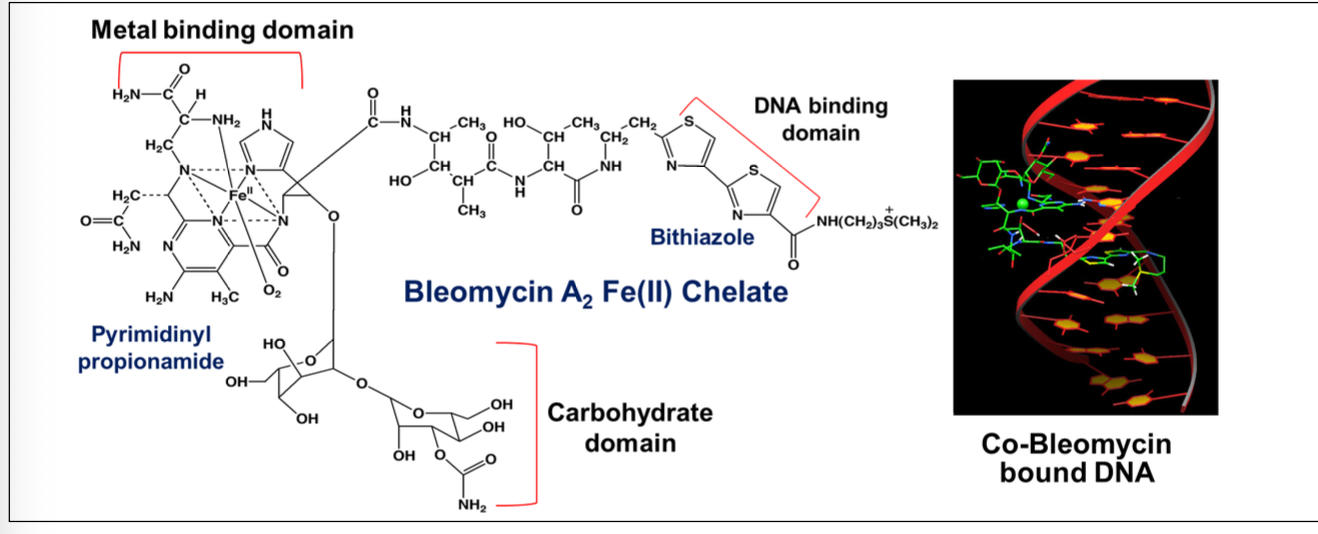
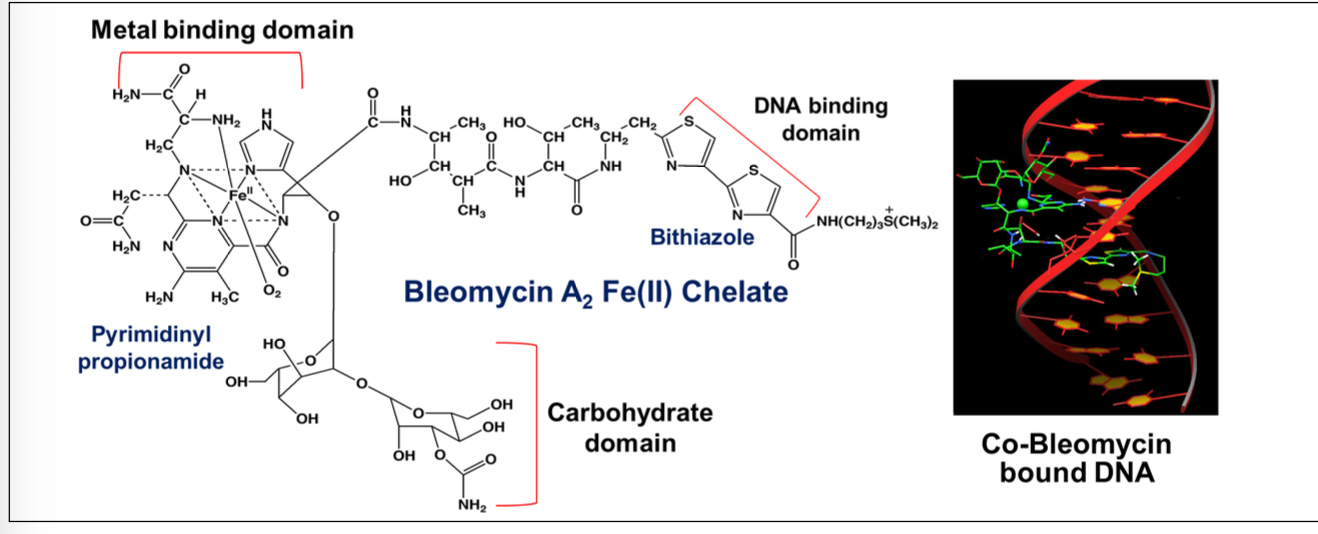
What is the MOA of bleomycin on DNA?
Forms a chelate with iron
Binds to DNA → causing generation of free radicals
Causes DNA strand breaks
What is the major side effect of bleomycin?
Pulmonary fibrosis - impaired lung function
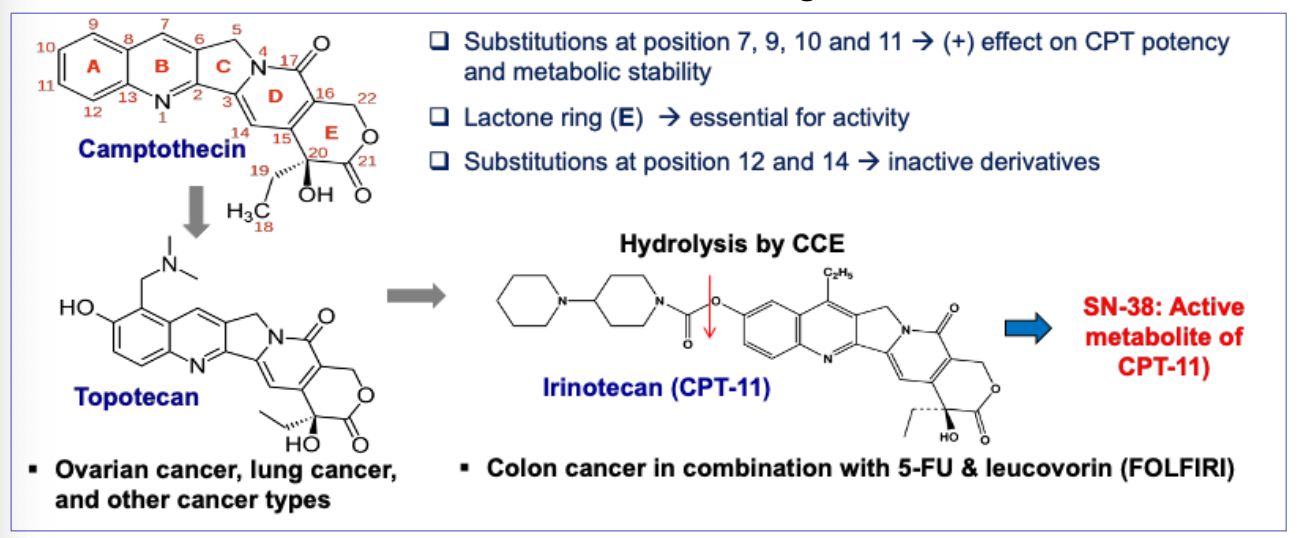
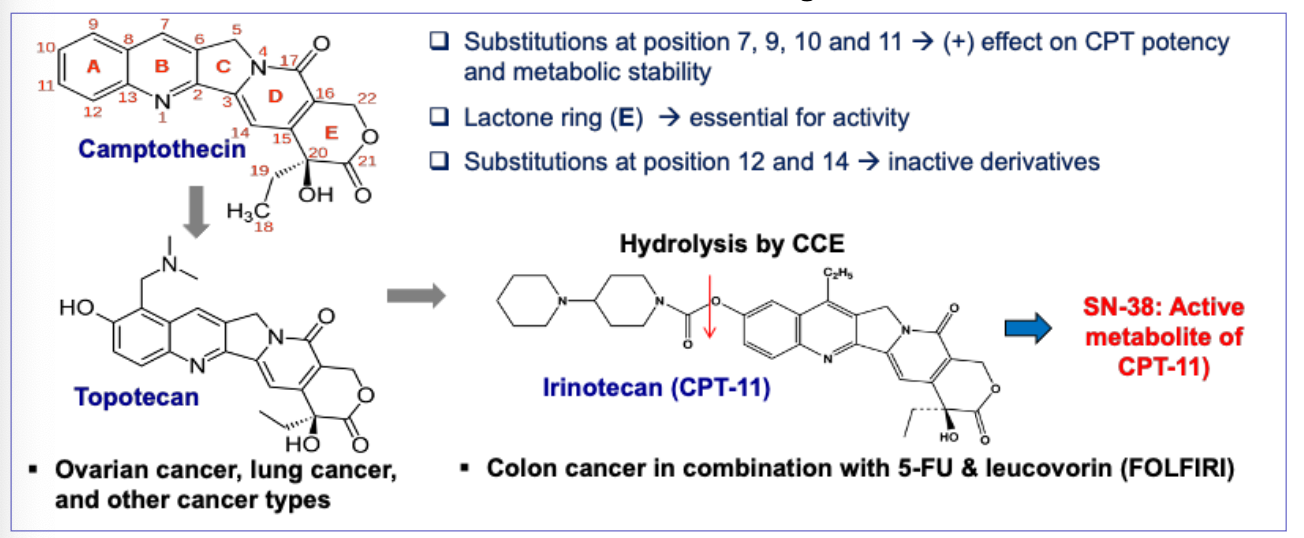
What is the MOA of irrinitecan?
Prodrug - converted to active 7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin by a carboxylesterase-converting enzyme (CCE)
Topoisomerase I inhibitors
Stabilizing covalent DNA topoisomerase I cleavable complex - prevents DNA replication
Converts into lethal double stranded DNA damage
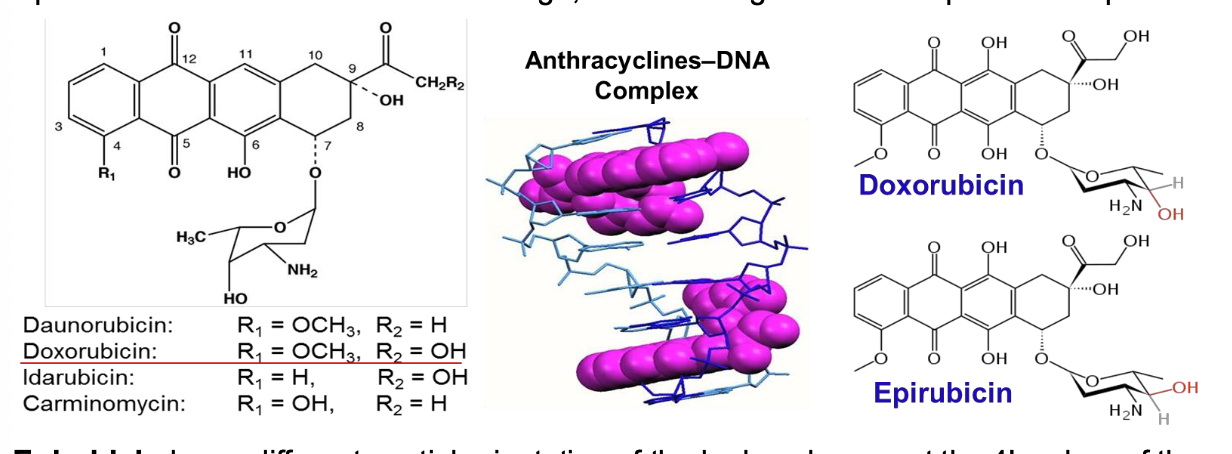
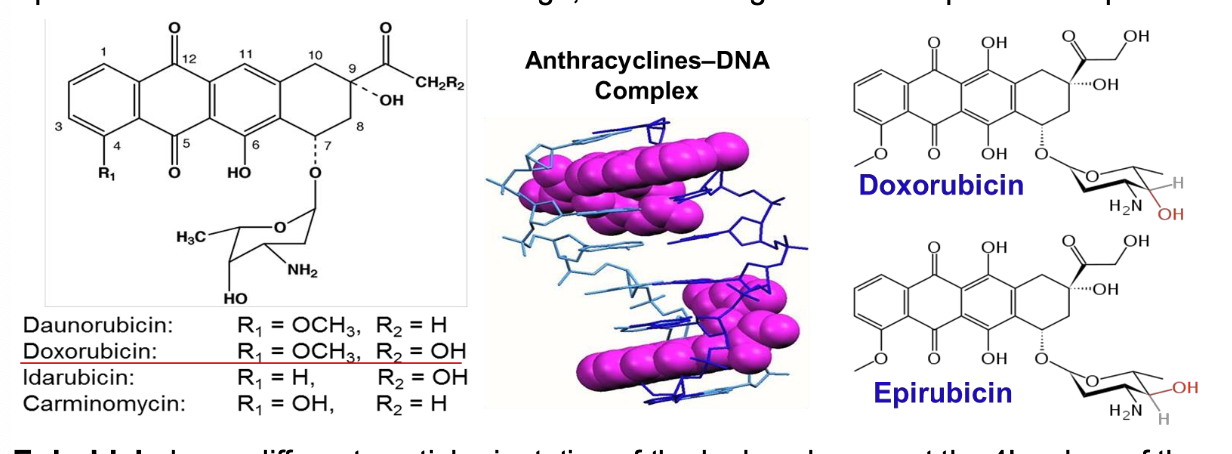
What is the MOA of doxorubicin on DNA? What is the target?
Intercalate into double helical DNA to inhibit DNA/RNA synthesis
Prevents replication of rapidly growing cancer cells
Topoisomerase II inhibitors: Anthracyclines
Stabilizes the topoisomerase II complex after it has broken the DNA chain
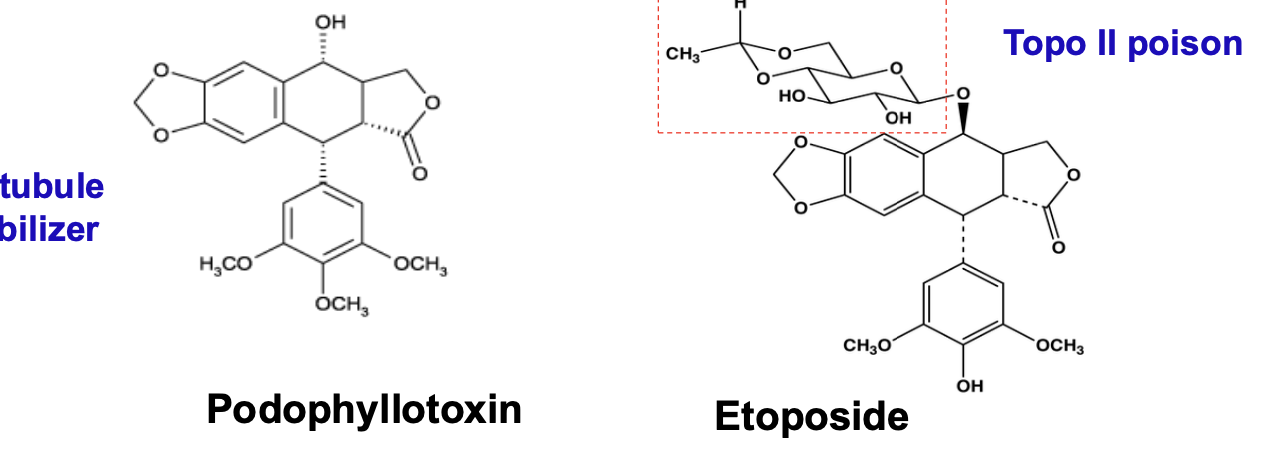
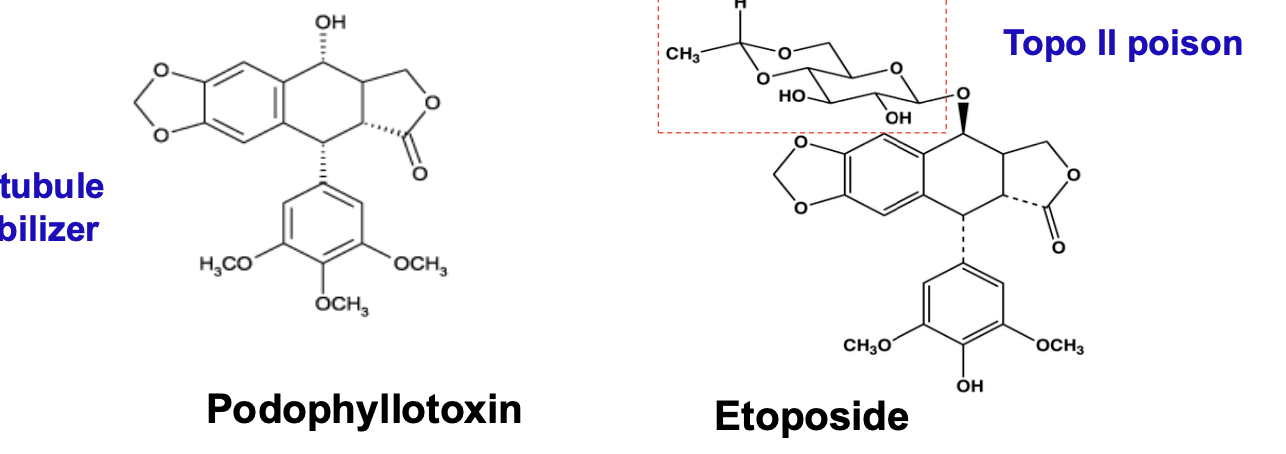
What is the MOA of etoposide?
Does not bind directly to DNA
Stabilizes a covalent intermediate form of the DNA topiosomerase II complex
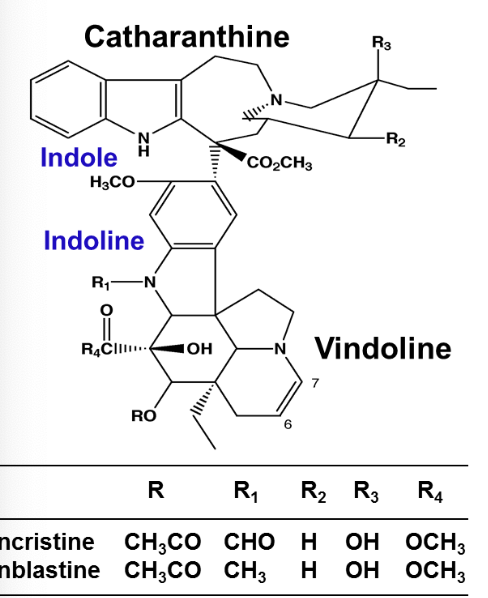
What is the MOA of vinblastine?
Mitotic spindle poisons that block the polymerization of tubulins into microtubules
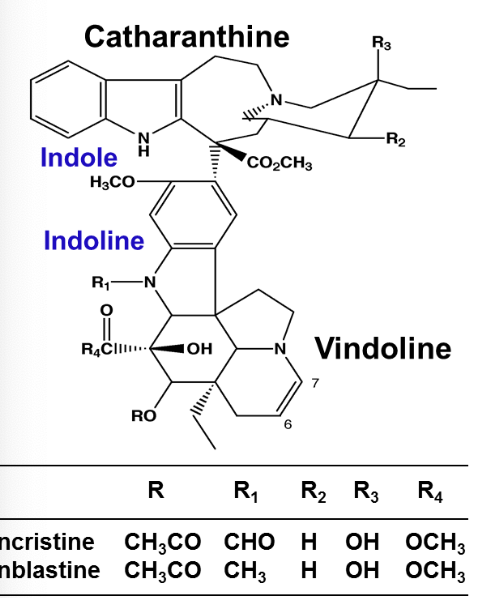
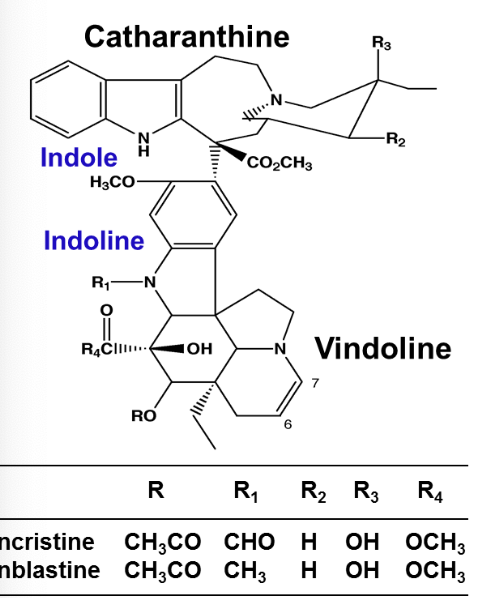
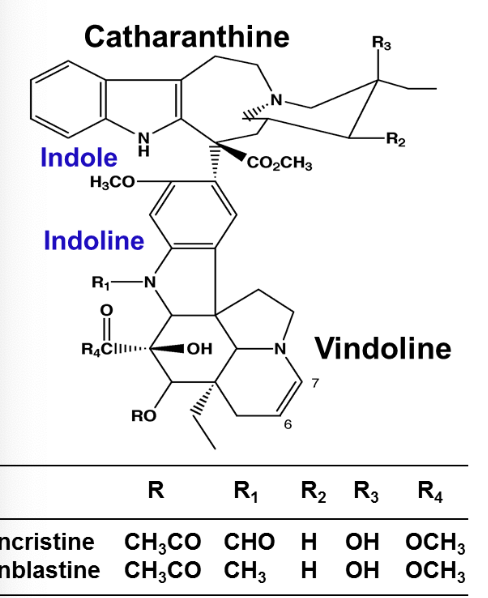
Vinblastine is comprised of 2 multi ringed units:
Indole containing (catharanthine)
Indoline moiety (vindoline)
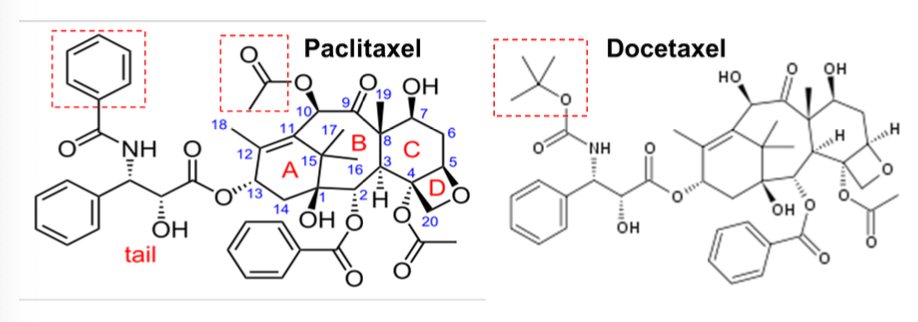
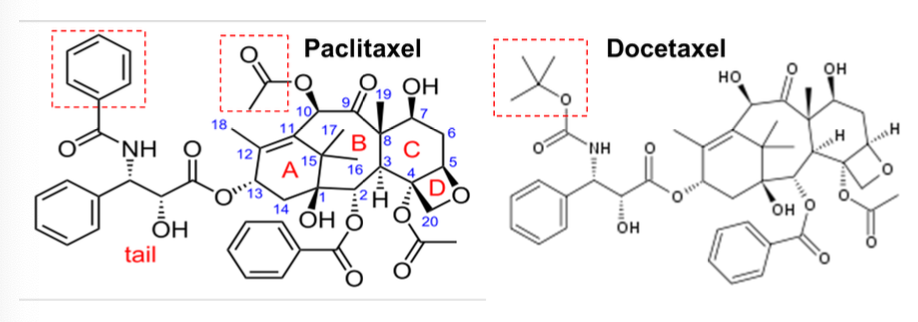
MOA of paclitaxel?
Mitotic spindle poisons that block the depolymerization of microtubules into tubulins
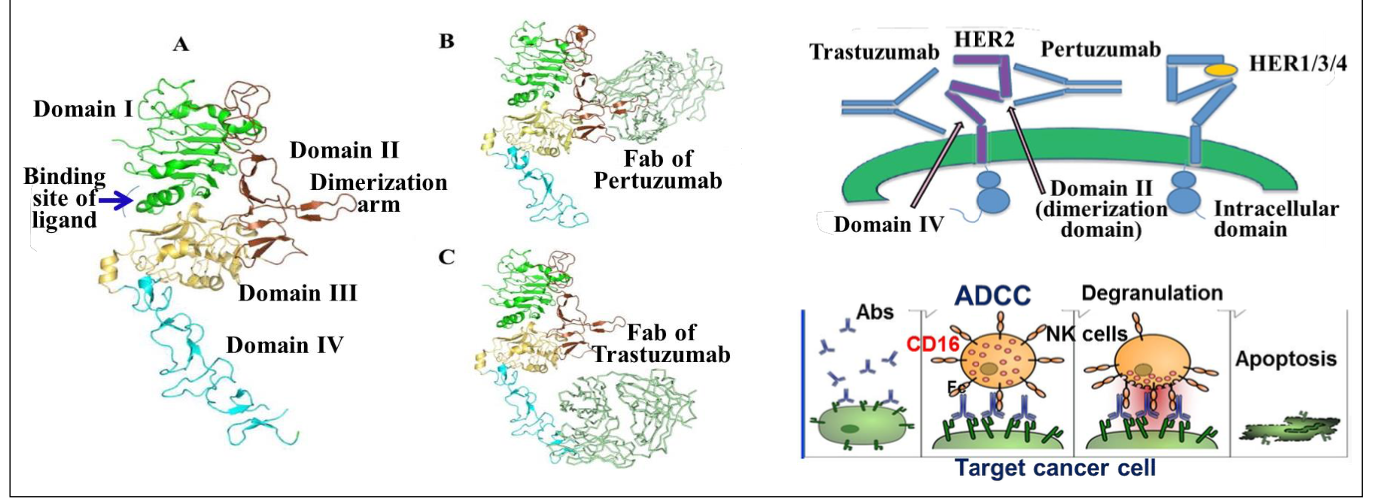
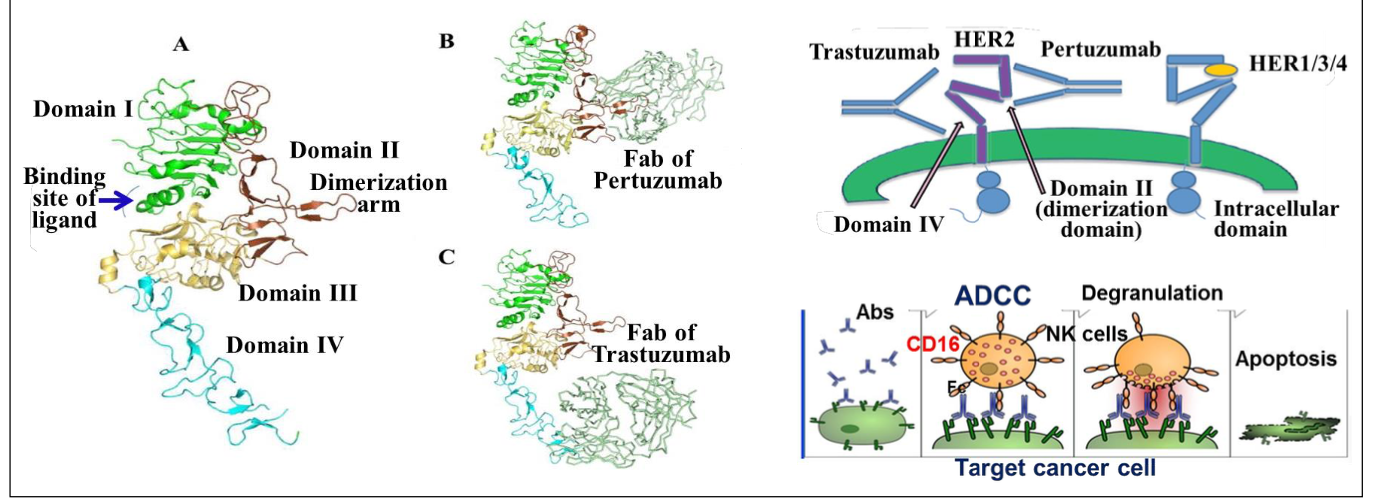
What is the MOA of trastuzumab?
Hepceptin - Humanized Anti-HER2 Mabs
Binds Her2 subdomain IV - inhibits HER2 activation
Induces antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) - destroys cancer
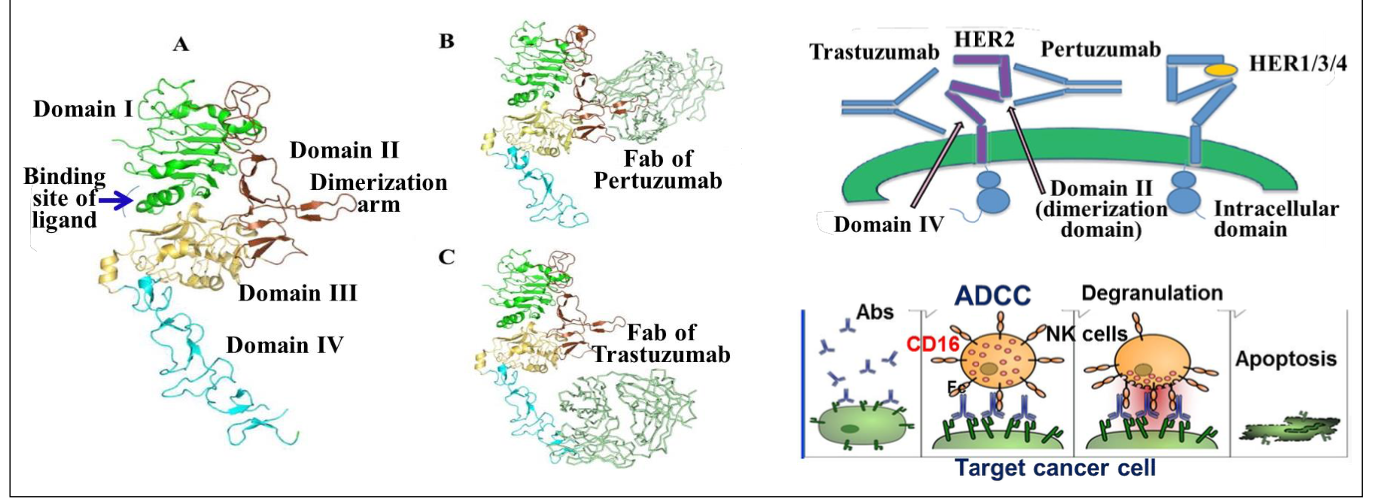
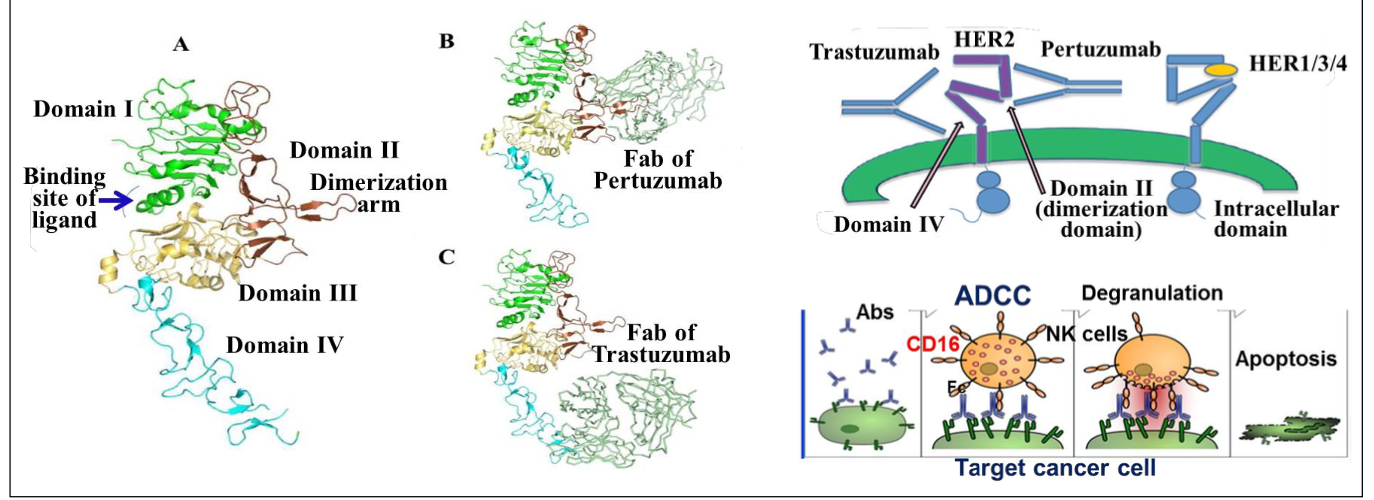
What is the major clinical uses of trastuzumab?
Before/after surgery with HER2 + metastatic breast cancer
Her2 positive metastatic stomach or gastroesophageal junction cancer
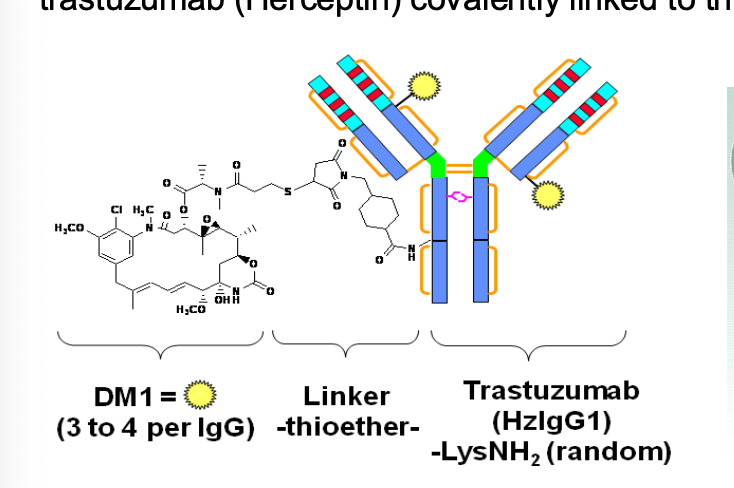
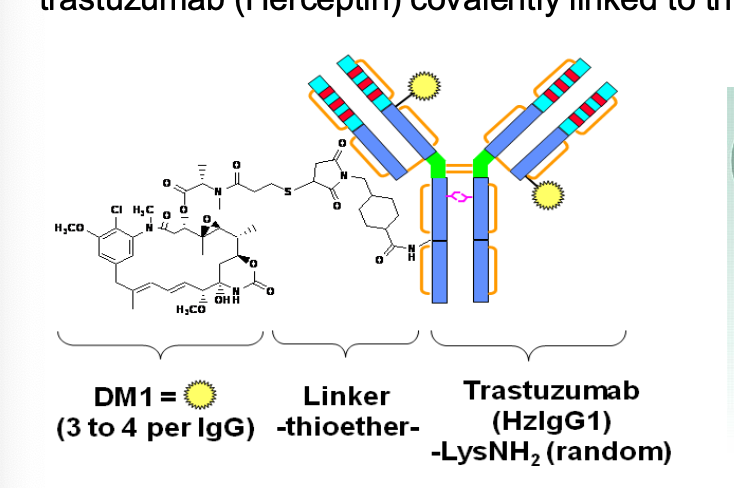
What is the difference between trastuzumab and trastuzumab emtansine?
Trastuzumab Emtansine is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN)
COVALENTLY LINKED to the cytotoxic agent maytansine (DM1)
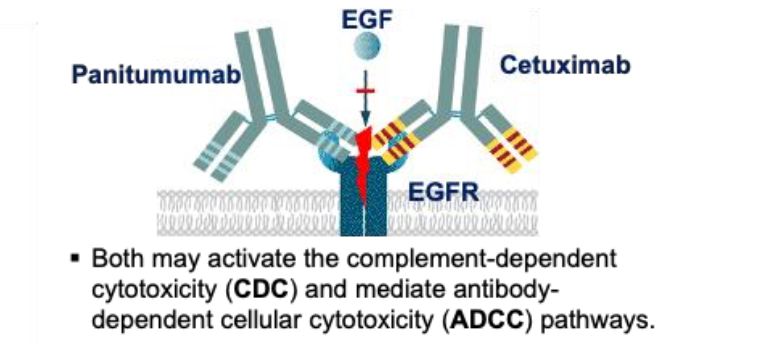
What two monoclonal antibodies inhibit cancer growth by blocking the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)?
Cetuximab and Pantumumab
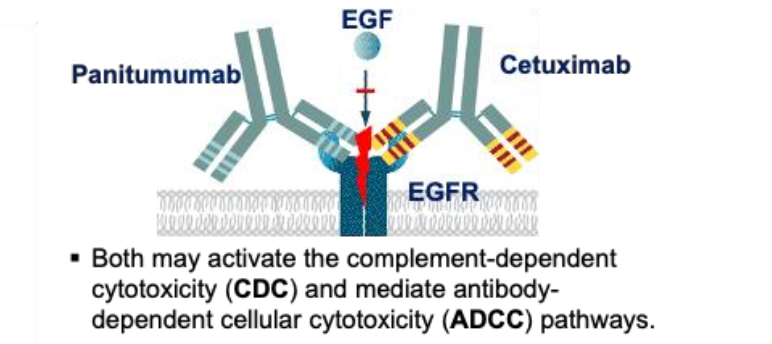
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that slows tumor growth by blocking what?
Inhibits VEGF
Decreases the blood supply to the tumor and slows tumor growth
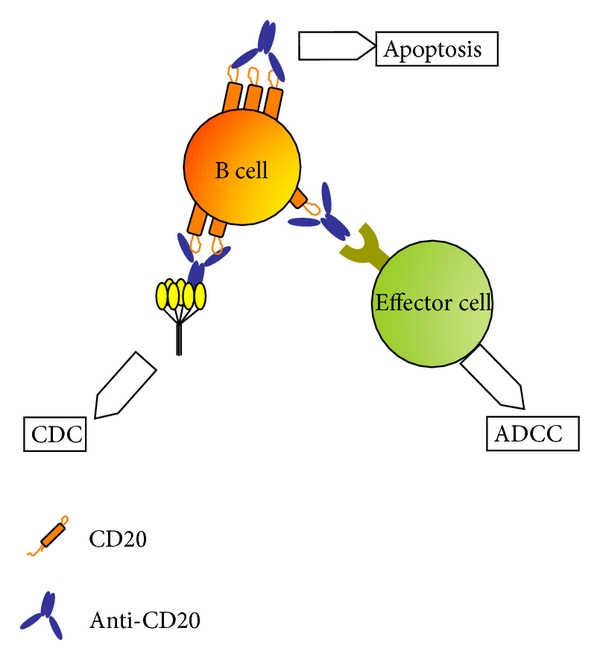
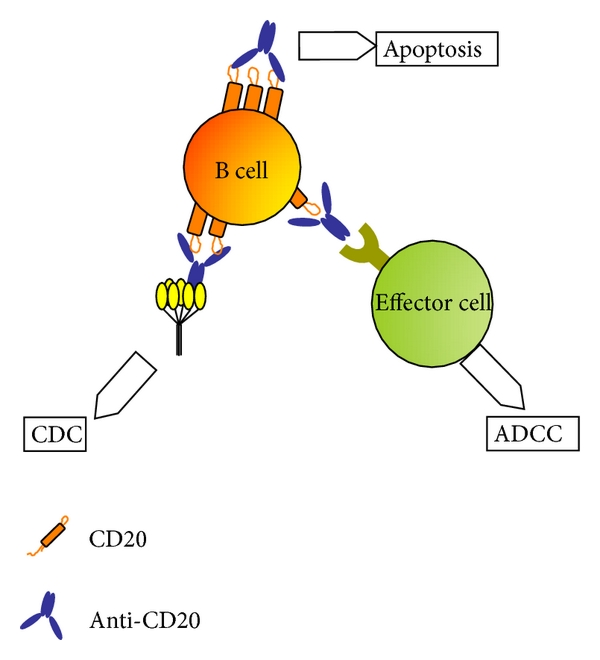
What 2 drugs are monoclonal antibodies that target and eliminate B cells by binding to CD20 protein?
Rituximab
Ofatumumab
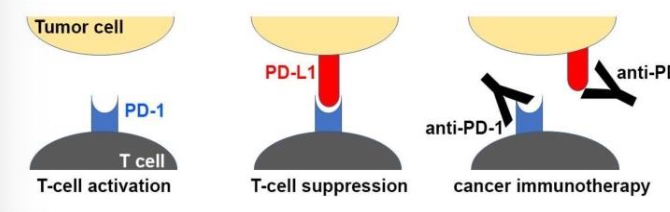
Pembrolizumab and nivolumab both function as ____ checkpoint inhibitors by blocking the _____ receptor, a protein on T cells that normally helps prevent T cells from attacking other cells in the body (Cancer cells)
Checkpoint Blockade - Programmed death (PD-1) receptor
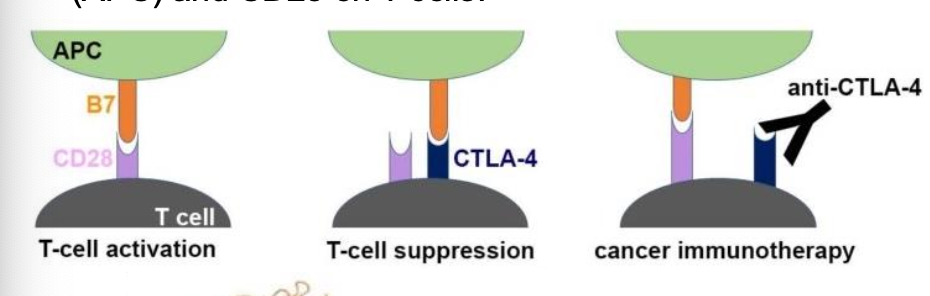
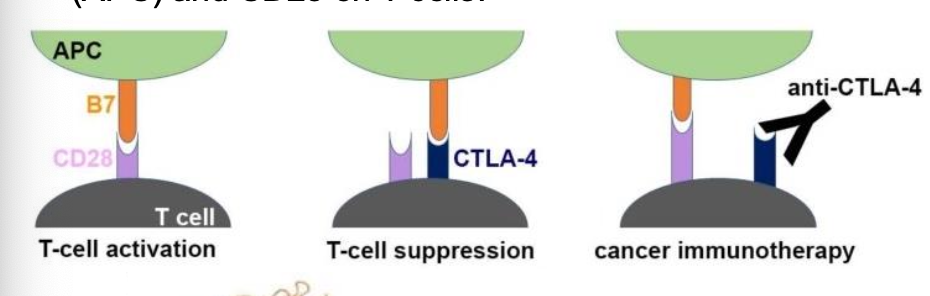
Ipilimumab functions as ____ a checkpoint inhibitor by blocking the _____ receptor, a protein on T cells that normally helps prevent T cells from attaching other cells
CTLA-4 inhibitor
Blocks the CTLA-4/B7 interaction
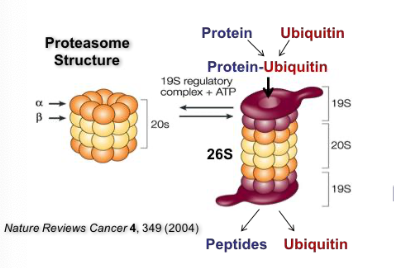
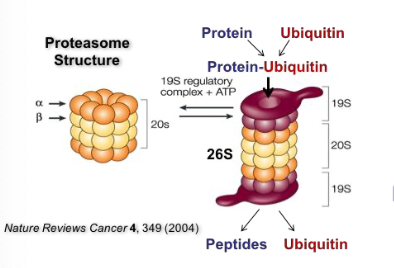
What does bortezomib target?
Proteasome inhibitor
Interacts with hydroxyl group of the threonine activate site of the 26S proteasome
Competitive, yet reversible inhibitor
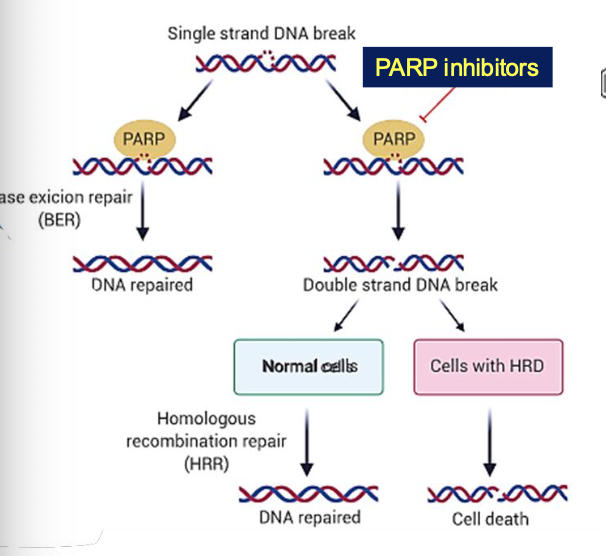
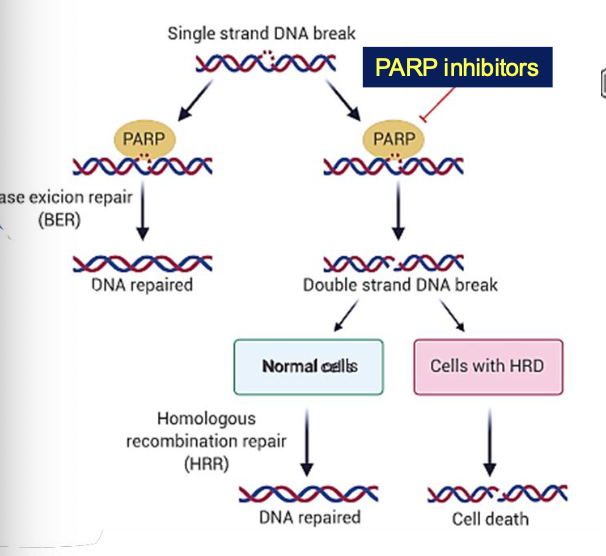
MOA of Olaparib?
PARP inhibitors - treatment for BRCA deficienct cancer
This enzyme plays a crucial role in DNA repair
PARP inhibitors - accumulation of DNA damage - cell death
List GnRH agonists and antagonist?
Agonists: Leuprolide, Goserelin, Triptorelin, Histrelin
Antagonist: Degarelix
reduces testosterone levels more quickly
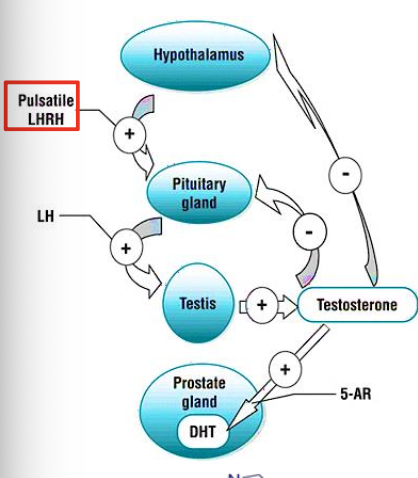
What is the MOA of abiraterone and flutamide?
Abiraterone: suppresses production of androgens - inhibits CYp17A1 - decreases testosterone
Flutamide: Nonsteroid antiandrogens - antagonist of androgen receptor