Chapter Four: Other Tissues
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Muscle Tissue
Has the general function of movement. Contains skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle
Skeletal Muscle Description
Long, cylindrical, multinucleated cells; obvious striations
Skeletal Muscle Function
Voluntary movement; locomotion; manipulation of the environment; facial expression
Skeletal Muscle Location
In skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally to skin
Skeletal Muscle Photomicrograph
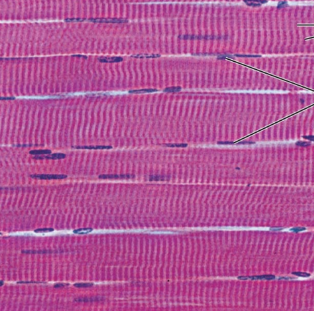
Cardiac Muscle Description
Branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigitize at specialized junctions (intercalated discs)
Cardiac Muscle Function
As it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control
Cardiac Muscle Location
The walls of the heart
Cardiac Muscle Photomicrograph
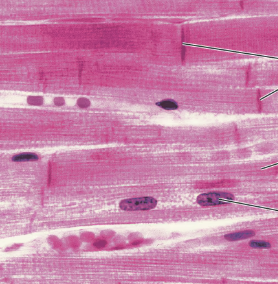
Smooth Muscle Description
Spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets
Smooth Muscle Function
Propels substances or objects along internal passageways; involuntary control
Smooth Muscle Location
Mostly in the walls of hollow organs
Smooth Muscle Photomicrograph
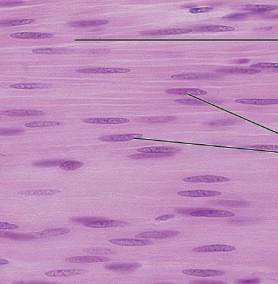
Nervous Tissue Overview
Main tissue of the nervous organs including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Contains two types of cells (neurons and neuroglia)
Nervous Tissue Description
Neurons are branching cells; cell processes that may be quiet long extend from the nucleus-containing cell body; also contributing to nervous tissue are nonconducting supporting cells, neuroglia
Nervous Tissue Function
Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands) that control the activity of the effector organs
Nervous Tissue Location
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Nerve Tissue Photomicrograph
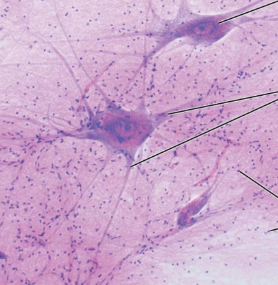
Good Regenerators of Tissues
Bone, Areolar/dense irregular CT, Blood, Epithelia
Mediocre Regenerators of Tissues
Smooth Muscle and Dense Regular CT
Poor Regenerators of Tissues
Skeletal muscle, tendons, ligaments, cartilage
Almost no regeneration of Tissues
Cardiac muscle and nervous tissue