Cardiac Physiology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
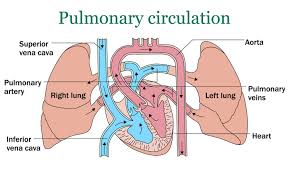
Pulmonary Circulation
The pathway that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the left atrium.
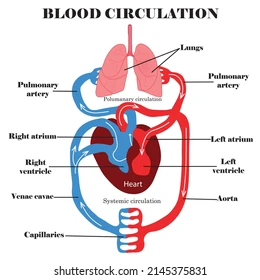
Systemic Circulation
The pathway that carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to body tissues and returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
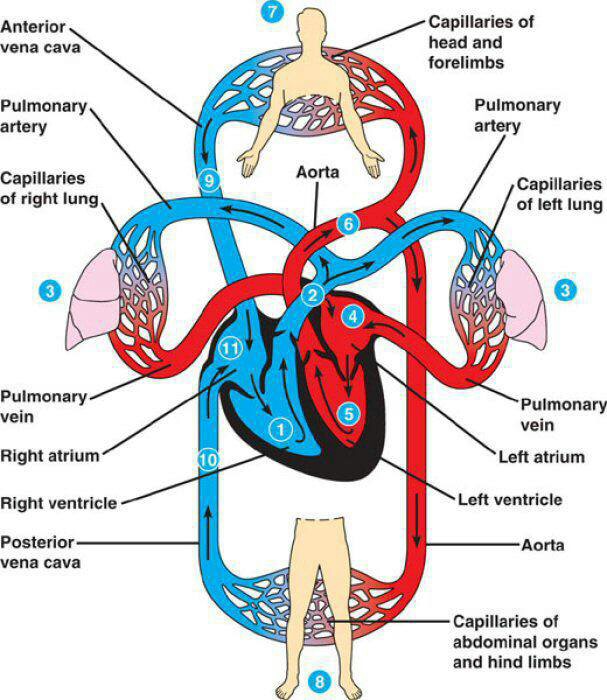
tricuspid blood flow
RA→RV
pulmonary blood flow
RV→pulmonary artery
mitral/bicuspid blood flow
LA→LV
aortic blood flow
LV→aorta
Cardiac Muscle Fibers
Intercalated discs with gap junctions allow rapid spread of electrical impulses and synchronized contraction.
Pericardial Sac
A double-layered membrane surrounding the heart; reduces friction and anchors the heart in place.
Blood Flow Pathway
Vena cavae → right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → mitral valve → left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta → body.
Chordae Tendineae
Fibrous cords that anchor AV valve leaflets to papillary muscles, preventing valve prolapse during ventricular contraction.
Fibrous Skeleton of Heart
Rings of dense connective tissue that support valves and prevent dilation during high pressure.
Systole
The contraction phase of the heart that pumps blood out of a chamber.
Diastole
The relaxation phase of the heart that allows chambers to fill with blood.
Atrial Systole
Atria contract, pushing blood into ventricles through open AV valves.
Ventricular Systole (First Phase)
Ventricles contract isovolumetrically; all valves closed, pressure rises.
Ventricular Systole (Second Phase)
Semilunar valves open, blood ejected into arteries.
Ventricular Diastole (First Phase)
Semilunar valves close, ventricles relax isovolumetrically.
Ventricular Diastole (Second Phase)
AV valves open, ventricles fill passively with blood.
Heart Pump Coordination
The right and left sides of the heart contract simultaneously, not sequentially.
Cardiac Cell Types
Autorhythmic cells (pacemakers) and contractile cells (muscle fibers that contract).
Pacemaker Potential Channels
Caused by “funny” Na⁺ channels (influx of Na⁺) and T-type Ca²⁺ channels (transient influx of Ca²⁺).
Autorhythmic Tissue Pathway
SA node → AV node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers.
SA Node
Primary pacemaker; sets heart rate around 70 bpm.
AV Node
Secondary pacemaker; sets heart rate around 50 bpm if SA node fails.
Bundle of His & Purkinje Fibers
Tertiary pacemakers; can set rate around 20 bpm if higher pacemakers fail.
Controlled Spread of Excitation
Ensures coordinated contraction — atria contract before ventricles.
Ventricle stimulation begins at the apex of the heart then continues to the base of the heart.
Effects on Heart Rate
Nerves and Horomones
Effects on Stroke Volume
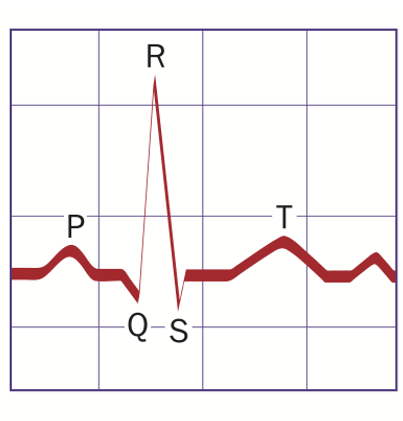
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
A recording of the heart’s electrical activity through electrodes on the skin.
P Wave
Atrial depolarization (atrial contraction).
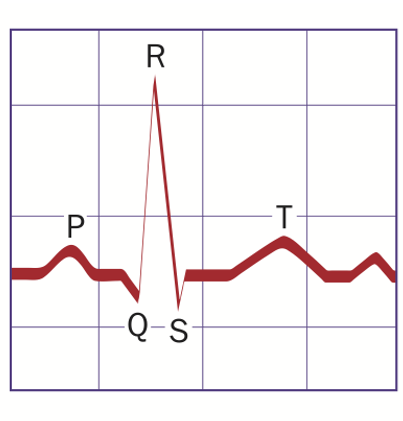
QRS Complex
Ventricular depolarization (ventricular contraction).
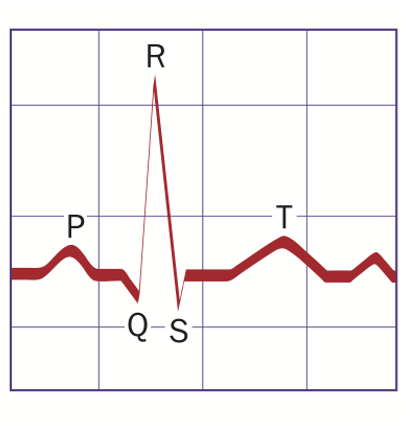
T Wave
Ventricular repolarization (ventricular relaxation).
Cardiac Output (CO)
CO = Heart Rate (In BPM) × Stroke Volume (in mL/beat).
Stroke Volume (SV)
The volume of blood ejected by one ventricle per beat.
Intrinsic Control of SV
Determined by venous return and Frank-Starling mechanism (greater stretch → stronger contraction).
Extrinsic Control of SV
Controlled by sympathetic stimulation, which increases contractility.
Frank-Starling Law
The greater the stretch of cardiac fibers, the greater the stroke volume.
Preload
The degree of stretch of the ventricle before contraction; related to venous return.
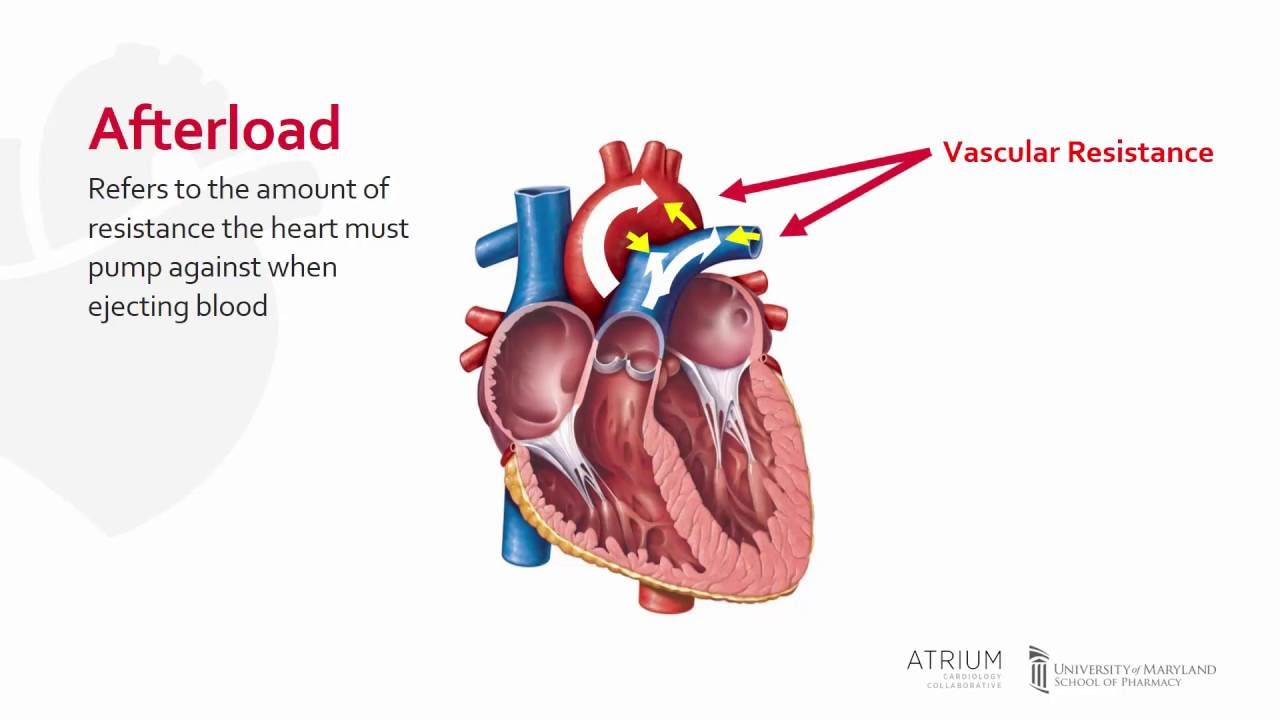
Afterload
The resistance the ventricle must overcome to eject blood (arterial pressure).
Heart Failure
A condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s metabolic needs.
Autorhythmic Cells
Pacemaker cells of the heart
Generate action potential due to unstable membrane potential.
Slow depolarization with Na and Ca influx until reaching action potential.