Rotator cuff tears
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
what is the etiology for a R/C tear
-compression
-tensile overload
-macro trauma
compression
-decreased subacromial space OR
-decreased GH joint stability resulting in humeral head migration
tensile overload
-overuse/repetitive activities overload the tendon
-athletics that overload/overuse the R/C (especially supraspinatus)
macro trauma
-forces exceed the strength of the tendon resulting in a tear (FOOSH, sudden ECCENTRIC load)
-often occurs in older people who already have compression of subacromial space
FOOSH is
-often the MOI for a R/C tear
-R/C tries to prevent adduction (eccentric overload)
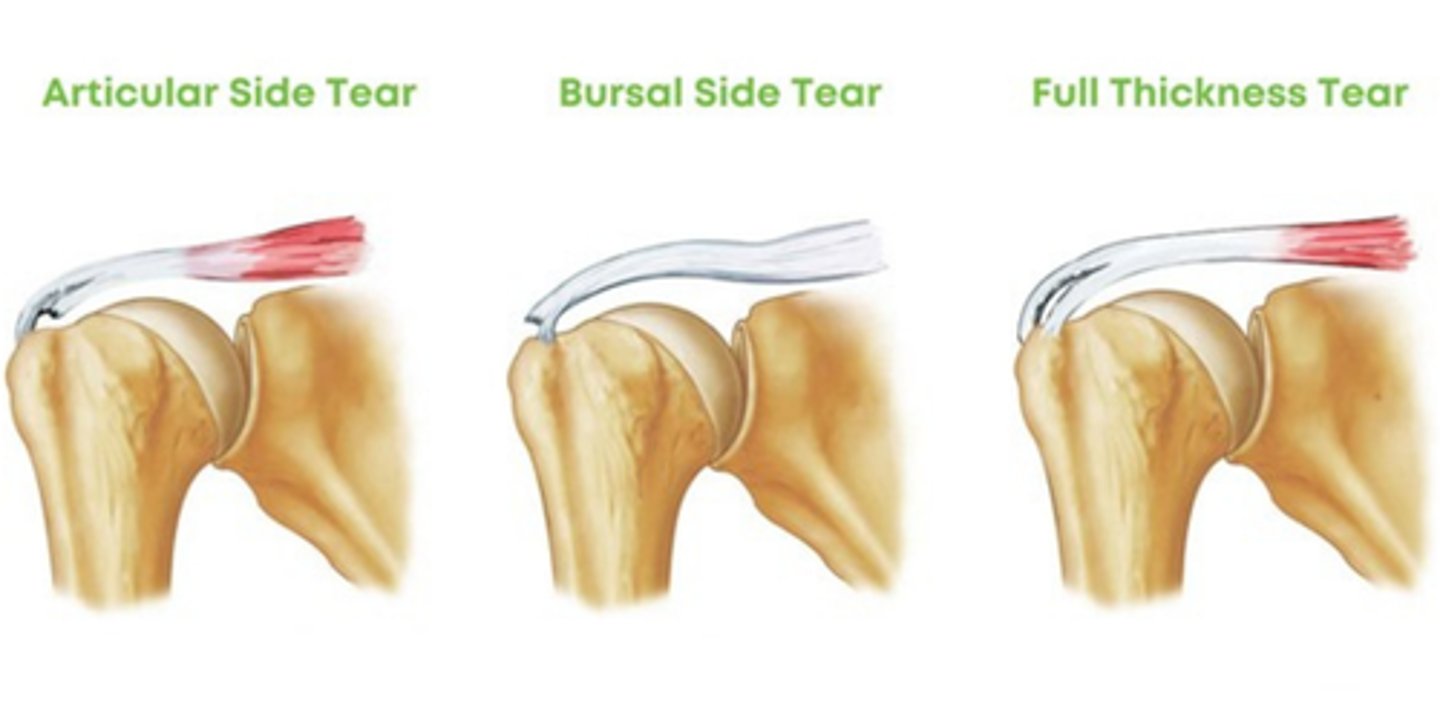
Classification of rotator cuff tears
-full vs partial thickness
-bursal or articular
-size of tear
-tendons involved
-shape of tear
-retraction
-tissue quality
full thickness rotator cuff tear
-tear extends completely through the tendon
-can range from small (1cm) to massive (5cm)
Where can rotator cuff tears occur
-bursa
-articular surface of humeral head
What constitutes a small tear
- < 1 cm
What constitutes a medium tear
-1-3 cm
what constitutes a massive tear
- > 5cm
shape of the tear is important to
-the surgeon
what is retraction
-how retracted the muscle is from the attachment point
tissue quality is
-very important
-decreased quality tissue is not as strong and repair is fragile
what tendons may be involved in R/C tears
-supraspinatus
-infraspinatus
-teres minor
-subscapularis
What muscle/tendon is always involved
-supraspinatus
what clinical findings will you see with a R/C tear
-insidious (degenerative), acute (injury or overuse) sxs
-pain
-weakness
-loss of shoulder ROM
-painful arc (60-120)
-pain w/ specific resisted tests of involved R/C muscle
-atrophy of muscles
-pain to palpation
-palpable defect
Where would a pt experience pain to palpation w/ a R/C tear
-pain at insertion
How would you palpate a defect (rent sign)
-palpate R/C tendons anterior to the margin of the acromion
-IR and ER the humerus
-observe and palpate for a defect of more than one finger width
What special tests can you do for R/C tear
-drop arm (supraspinatus)
-external rotation lag sign (infraspinatus)
-empty can test (supraspinatus)
-full can test (supraspinatus)
-specific R/C MMTs
-Hawkins Kennedy (painful w/ tear and impingement)
Who are candidates for surgical repair
-full thickness tears
-partial thickness tears that are unresponsive to conservative tx
surgery can be delayed up to _______________ with no significant change in outcomes
-3 mos
-any longer could be detrimental
full thickness tears and surgery
-symptomatic large, full thickness tears, esp in younger pts
-older pts w/ significant disability
-symptomatic small full thickness tears depend on pain and response to conservative tx
surgical techniques
-open RC repair
-arthroscopic surgical repair
Open RC repair
-more complex tears
-tears obstructed by delt
- > 5cm incision in anterior shoulder, remove delt from humerus to gain access
-longer recovery time
arthroscopic repair
-camera and cutting instrument
-2 small incisions to locate and repair tear
-smaller tears and tears w/ unobstructed view
Post surgical rehab is based on
-extent of tear (minimal or massive_
-strength and extent of repair
General precautions for post surgical rehab
-no active GH motion for 4-6 wks (can do passive)
-no elevation past 70 degrees for 4-6 wks
-avoid wb thru UE (will push humeral head into acromion)
-avoid carrying wt w/ UE (no more than 15 lbs 1st year)
-limit activities w/ fall risk
-BRODY AND HALL pg 778-779
non-operative rehab is
-very similar to post op rehab
In general in non-op rehab early mobilization
-is encouraged as opposed to sling and iimmobilization
In non-op rehab the pt will follow the ___________ phases but may progress more quickly
-same
pts long term precautions will
-depend on extent of the tear
a delay of surgery up to 3 mos has
-no effect on outcome
age influences outcomes
-negatively
number of tendons injured affects outcome of
-pts undergoing conservative tx but
-not surgery
subacromial decompression at the time of surgery influences the outcome
-positively