MCAT flashcards Physics
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Heat of transformation
The amount of heat required to change the phase of a substance, calculated by the equation q=ml, where q is heat, m is the mass of the substance, and L is the heat of transformation for that substance. The heat of transformation corresponding to the solid-liquid phase change is called the heat of fusion; that corresponding to liquid-gas is called the heat of vaporization.
Sound level
The loudness of a sound, measured in decibels (dB) and denoted by . given by the equation shown. I is the intensity of the sound and Io is a reference intensity of 10^-12.
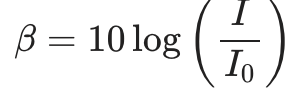
Noncenservative force
A force that dissipates mechanical energy from a system. As such, the energy dissipated depends on the path taken from initial to final position. Examples include friction, air resistance, and viscous drag
Conservative force
a force that does not cause dissipation of mechanical energy from a system. As such, the work performed is independent of the path taken.
Conservation of mechanical energy
states that when only conservative forces act on an object and work is done, energy is conserved and described by the equation: Change E= change U+ change K=0
Doppler effect
When a source emitting a sound and a detector receiving the sound move relative to each other, the perceives frequency f’ is less than or greater than the actual frequency emitted f, depending on whether the source and detector move toward or away from each other:
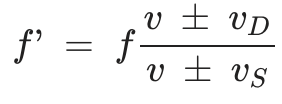
Convection
form of heat transfer where a heated fluid transfers energy by bulk flow and physical motion over another object, or cooled fluid absorbs energy by the same means.
Zeroth law of thermodynamics
states that two objects that are in thermal equilibrium with a third object are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
Snell’s Law
equation describing the angle of refraction for a light ray passing from one medium to an other , given by n1 sin theta1= n2 sin theta2, where n represents the index of refraction in each medium
Law of reflection
states that when light waves strike a medium, the angle of incidence theta i is equal to the angle of reflection theta r.
Total internal reflection
the condition in which the incident angle of light traveling from a medium with a high /n/ to a medium with a low n is greater than the critical angle theta _c. this results in all of the light being reflected and none of it being refracted.
Elastic potential energy
The energy associated with stretching or compressing a spring, calculated by the equation, and given in joules.
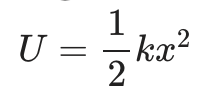
index of refraction
ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light though a medium, given by : n=c/v
Dispersion
the phenomenon observed when white light is incident on the face of a prism and emerges on the opposite side with all its wavelengths split apart, forming the visible spectrum. This occurs because lamda is related to the index of refraction by the expression
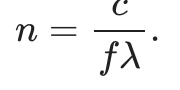
Newton’s Third Law
states that if one object exerts a force on another, the other object exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction; the law of “action and reaction”
Newton’s First Law
States that if no net force acts on an object, its velocity is constant
Frictional Force
An antagonistic force that points parallel and opposite in direction to the direction of movement of an object. Related to a coefficient of friction and the normal force: Static friction:
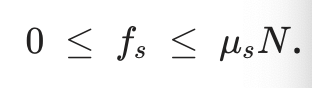
Torque
a force creating rotation about an axis: measured as the lever arm ( the distance between the fulcrum and the applied force) times the magnitude of the force times the sine of the angle between them:
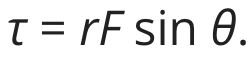
Rotational equilibrium
state where the sum of the torques acting on a body is zero, giving it not net angular acceleration. An object may be in rotational equilibrium, translational equilibrium or both
Thermal expansion
delta L=alpha L change of T
volume expansion
Delta V= beta V delta T
Heat gained or lost(phase change):
q=ml
Entropy and heat
delta S=Qrev/T