W2 and W4 - Paranasal Sinus, Brain Vasculature
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
BBB (Blood Brain Barrier)
the brain capillary specialization that restricts the movement of certain molecules from the bloodstream into surrounding neural tissue
therefore, a healthy BBB prevents a sig. amount of CM into brain tissues during CM studies
Main Vessels that Supply the Brain
internal carotid arteries (ICA)
vertebral arteries
Venous System
SVC → Brachiocephalic vein → Subclavian vein → IJV, EJV, vertebral vein
Bifurcations from the Aortic Arch
Brachiocephalic (RT)
RT subclavian → RT vertebral
RT common carotid → RT ICA and ECA
LT common carotid → LT ICA and ECA
LT subclavian → LT vertebral
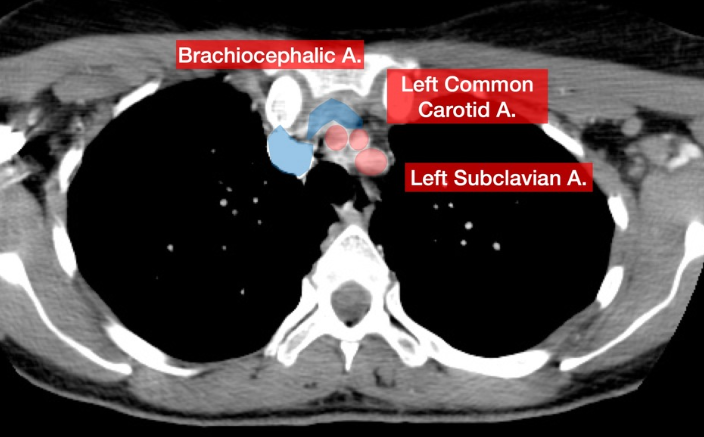
pathway of the L/R vertebral arteries
vertebral arch → transverse foramina → foramen magnum → L/R vertebral arteries unite to form the basilar artery
Anterior and Middle Vasculature is supplied by
ICA
common carotid artery bifurcation level
C4/5
external carotid artery supplies the
face, scalp, neck, tongue
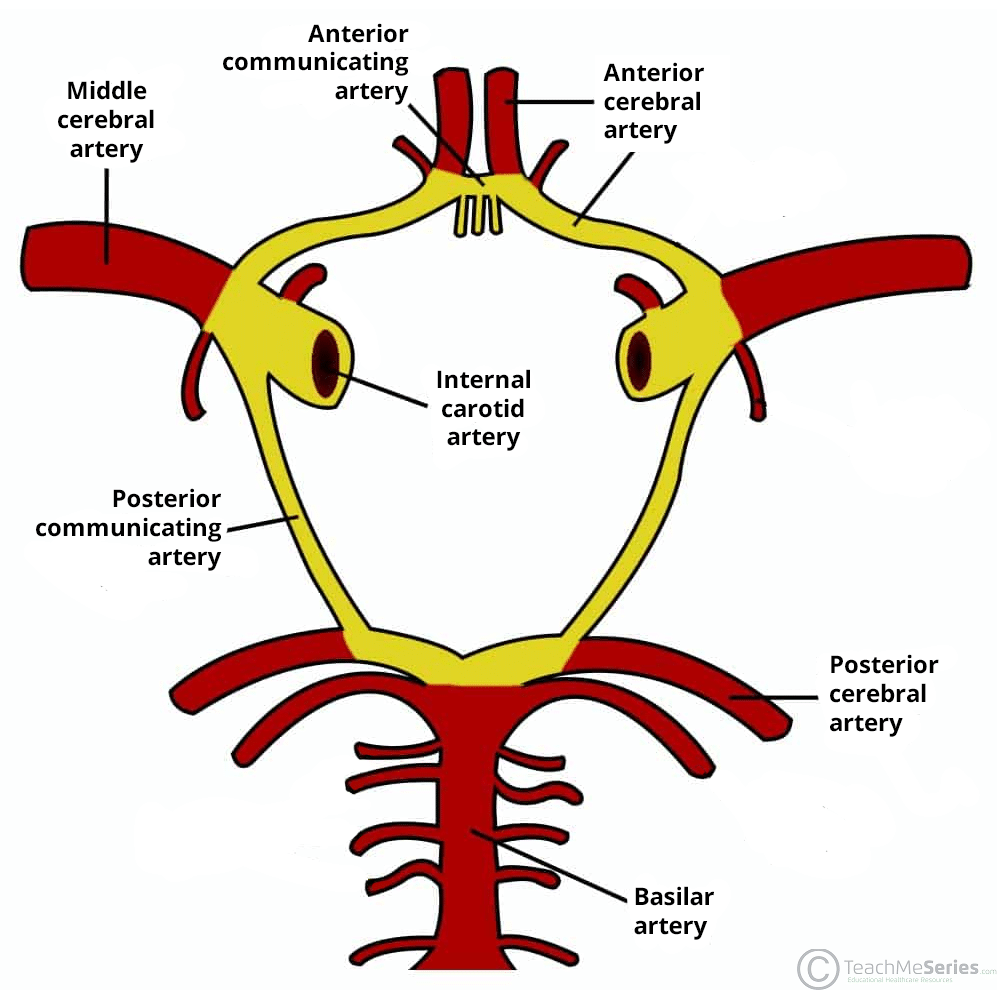
main branches of the internal carotid artery
L/R ophthalmic arteries
L/R anterior cerebral arteries
L/R middle cerebral arteries
what structures does internal carotid artery supply
brain lobes, orbital structures
Anterior CA supplies the
ant. frontal lobe, medial parietal lobe
Middle CA supplies the
lateral surface of the cerebrum, insula, ant/lat temporal lobes, basal nuclei
largest CA
posterior brain vasculature is supplied by the
basilar artery
pontine vessels
part of the post. brain vasculature
small branches that supply the pons
posterior brain vasculature main branches
post/inf cerebellar artery
ant/inf cerebellar artery
sup cerebellar artery
post cerebral artery
circle of willis (COW)
formed by the ant/post CAs, ant/post communicating arteries, and ICA
important collateral pathway allowing blood flow between the cerebral hems in the event of arterial blockage
dural sinuses
where all venous blood from the head drains into before getting emptied into the internal jugular veins
types of dural sinuses
superior sagittal
inferior sagittal
straight
transverse
sigmoid
cavernous
petrosal sinus (sup, inf)
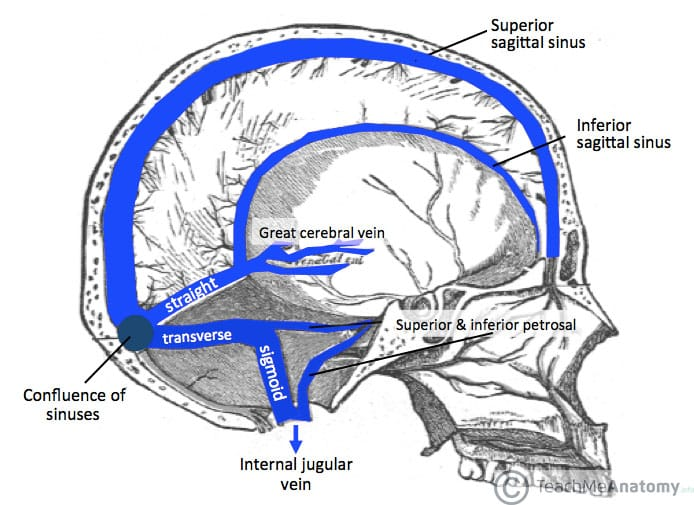
superior sagittal sinus drainage
confluence of sinus
inferior sagittal sinus pathway
joins with the great cerebral vein to form the straight sinus
straight sinus drainage
transverse sinus
transverse sinus drainage
sigmoid sinus
sigmoid sinus pathway
joins the jugular bulbs, exits the skull thru the jugular foramina and descends down as the internal jugular veins
cavernous sinus
drains into sup and inf petrosal sinuses
petrosal sinuses drainage
sigmoid
torcular herophili / confluence of sinuses
junction of the superior sagittal, straight, and transverse sinuses
cavernous sinus receives blood from
the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins
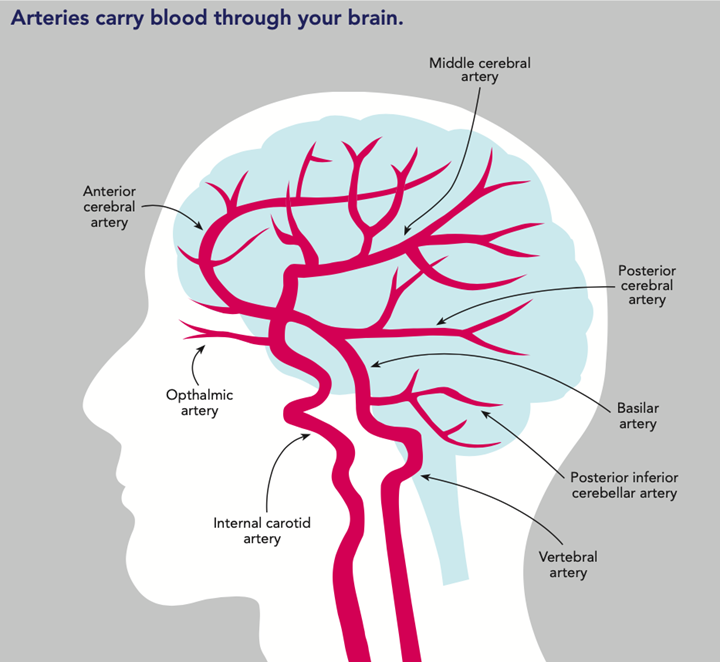
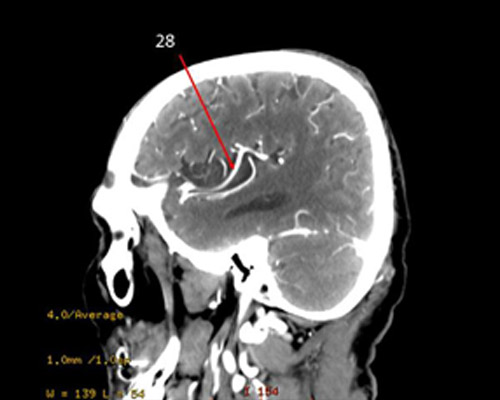
middle CA
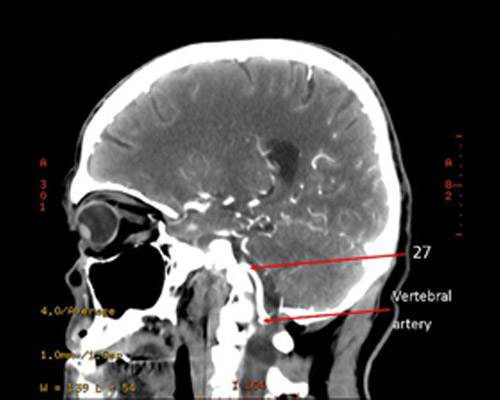
27?
27 = basilar
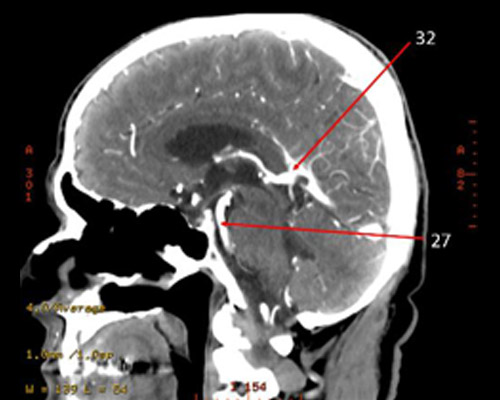
32?
32 = posterior CA
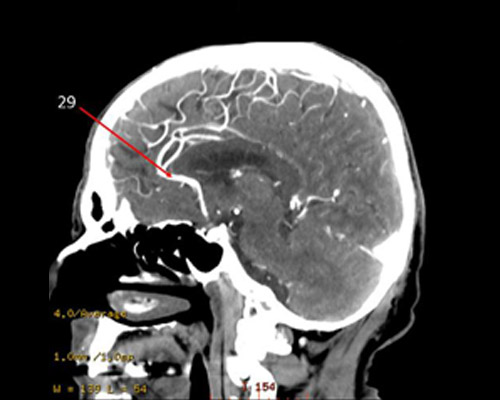
29?
anterior CA