5- inorganic chem
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
what is the rate equation?
rate= k (A)^m (B)^n
what equation to calcualte activation energy from a graph
gradient x 8.314/1000
suggest two reasons why it is unlikely that a multi step mechansism reaction could happen in one step
the overall equation dosent match the rate equation
collision are unlikely with more then two species
what is the overall order of reaction
m+n
why would you use an excess of ____ ensure that the order with respect to ____ is effectively zero
becuase the change in concentration is small itll have effectively zero effect on the rate of reaction
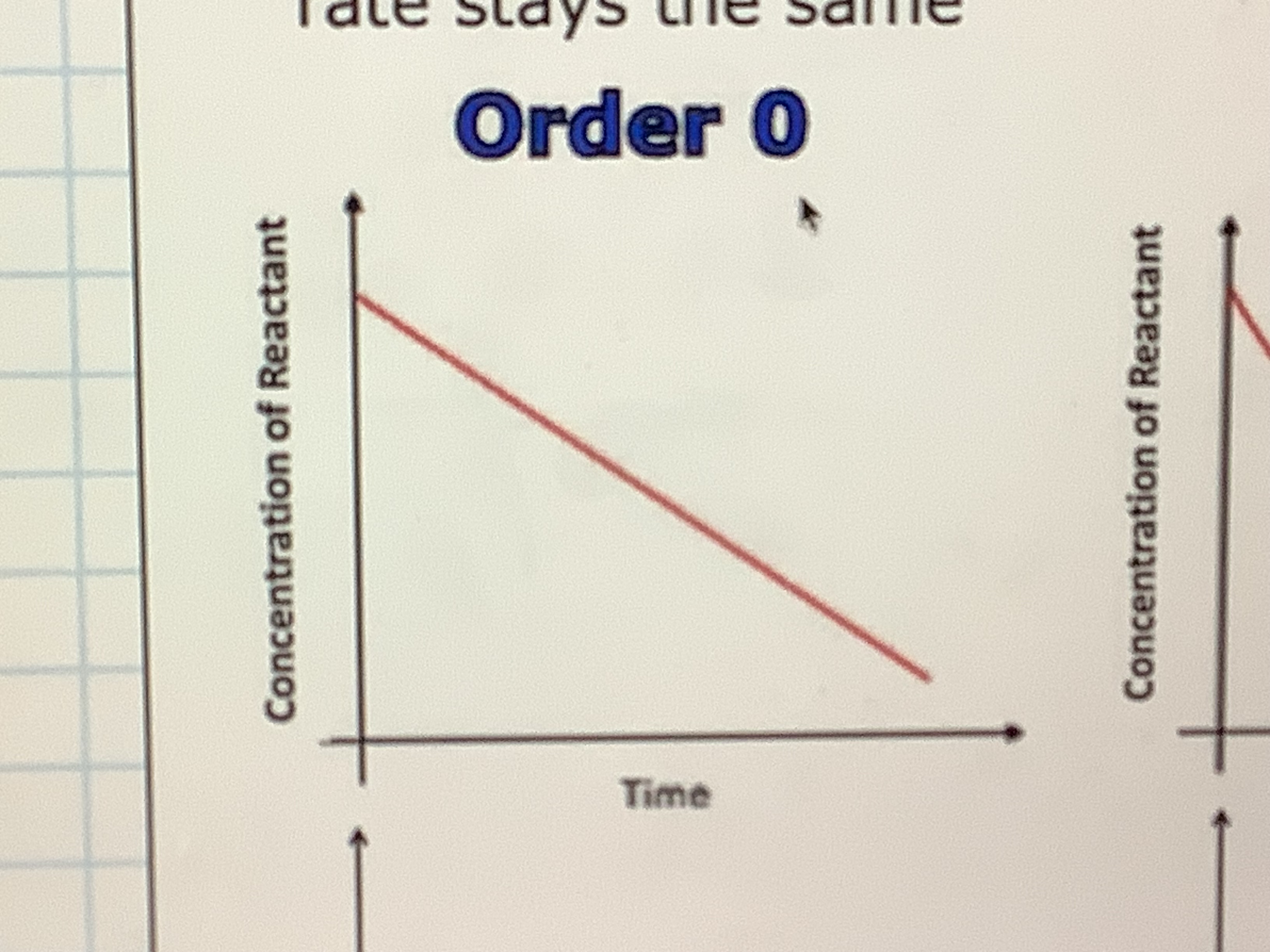
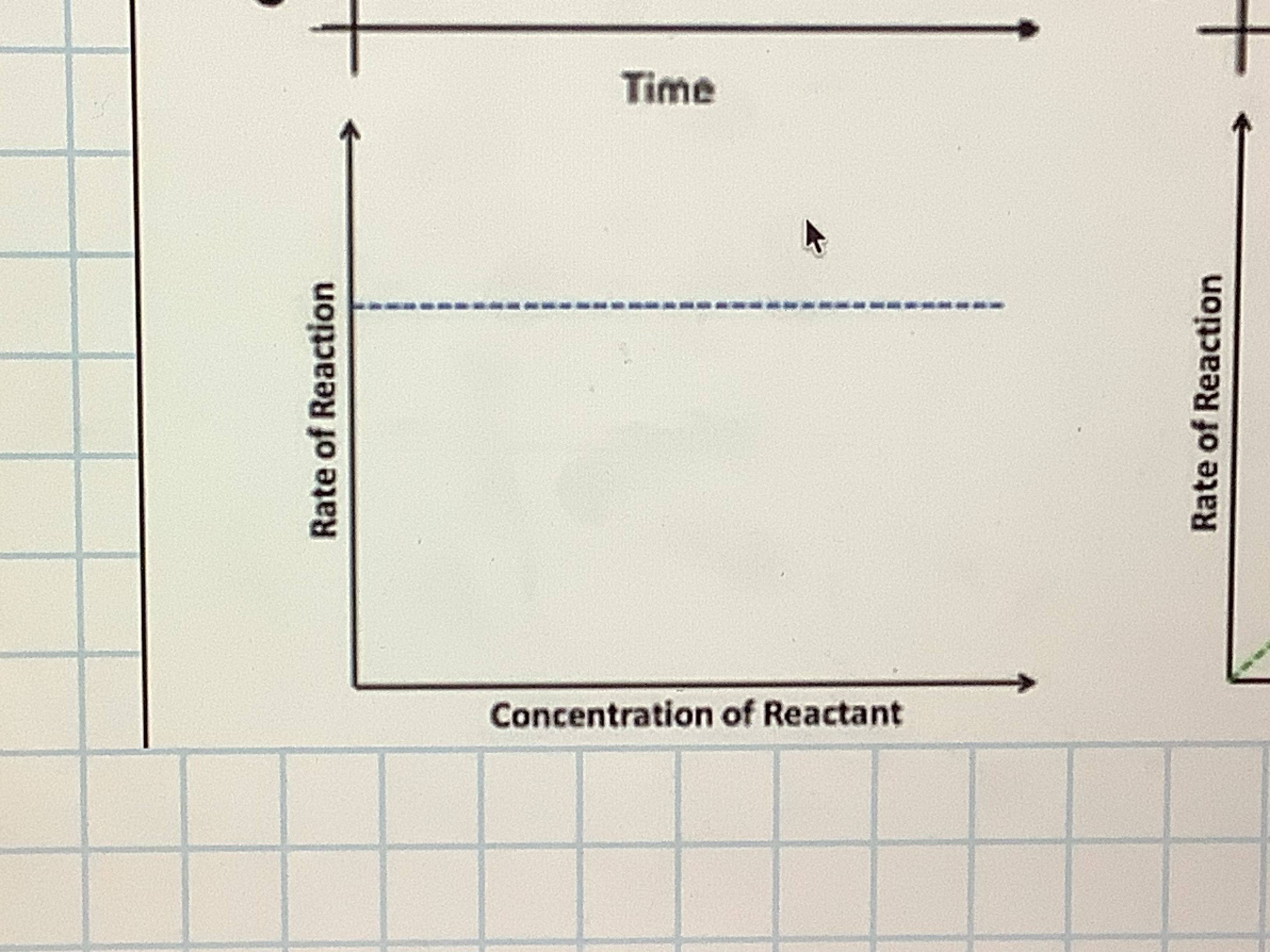
what does order 0 mean
the rate is unaffected by the concentration
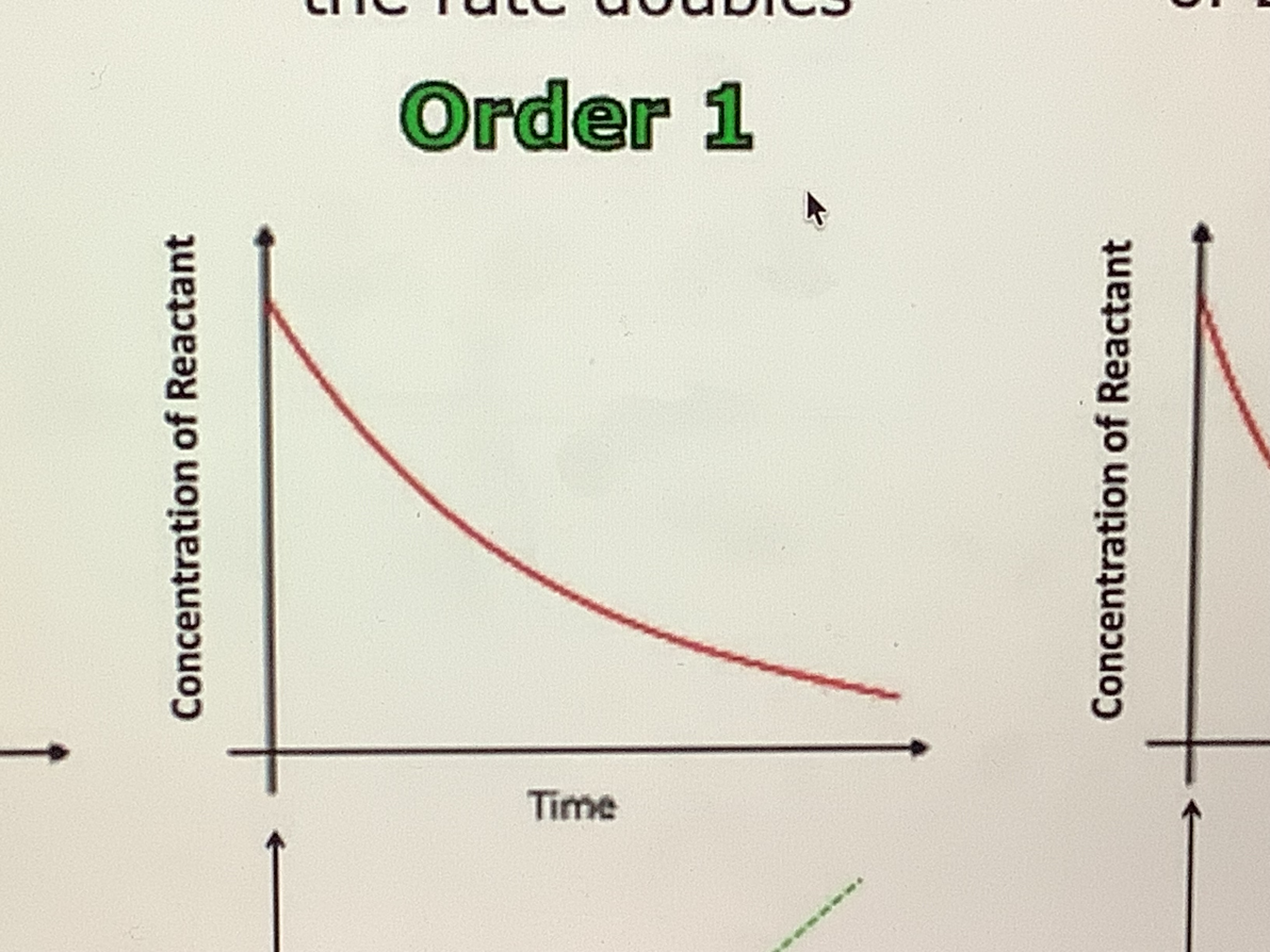
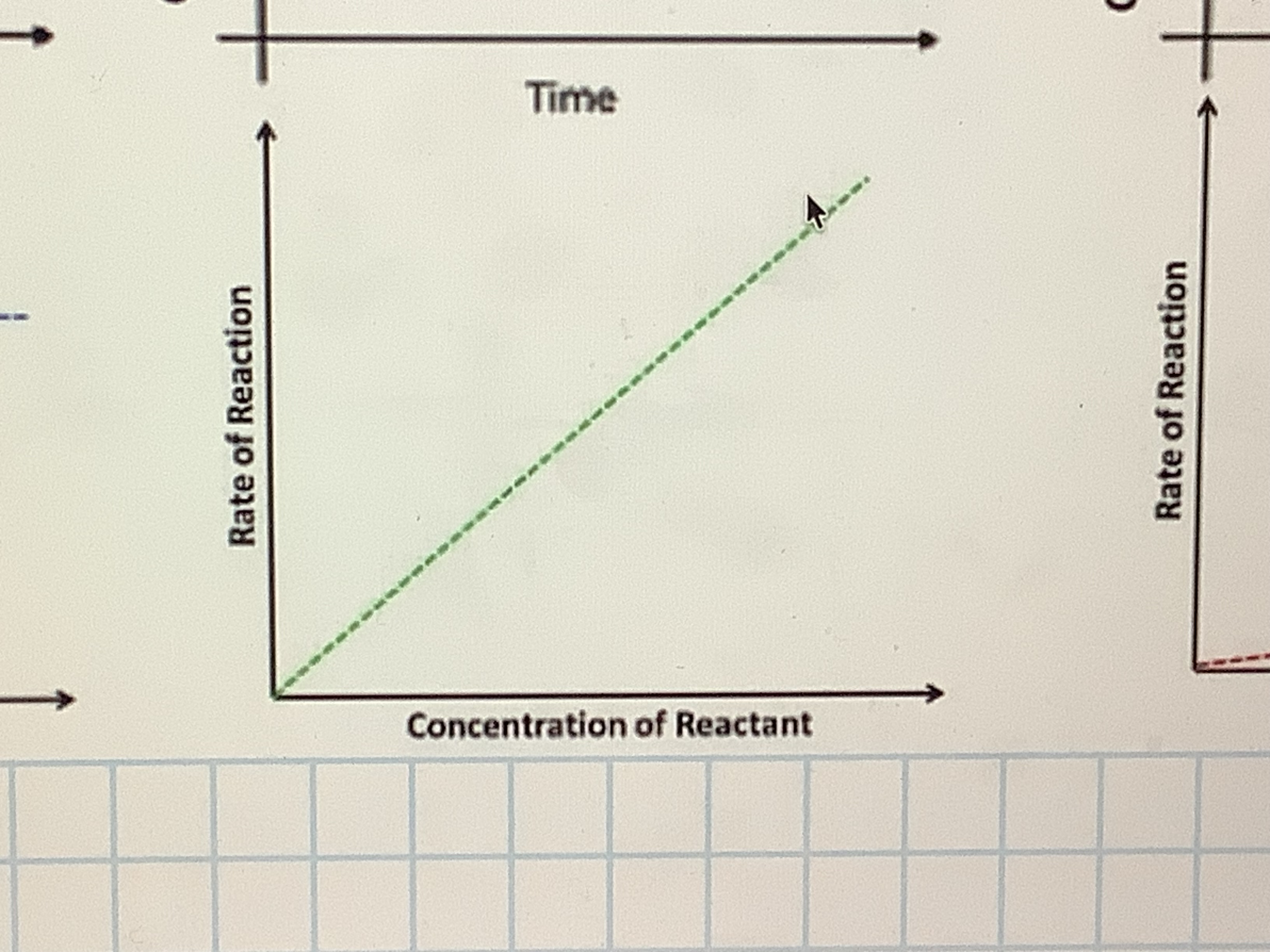
what does order 1 mean
the rate is direclty proportional to the concentration, when it doubles so does the rate
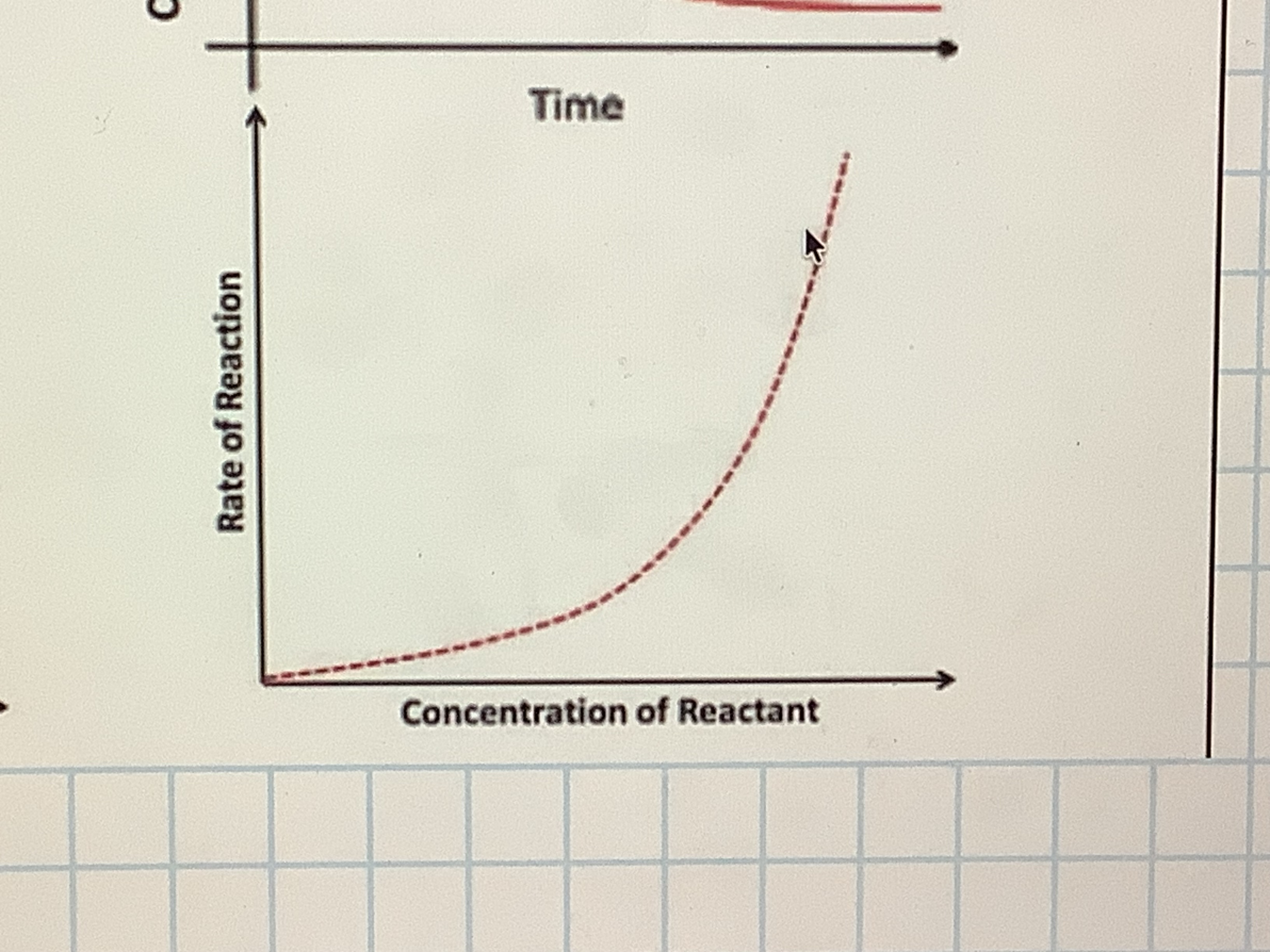
what does order 2 mean
rate is proportional to the concentration squared, if you double the concentration the rate will increase by a factor of 2²
what does half life mean
the time take for the concentration of a reactant to decrease by half
what is the equation for finding k when using half life of a first order reaction, concentration time graphs
k= ln 2/ half life
whats the equation that links rate, change in concnetration and change in time
rate = change in conc/ change in time
how to find k with order 0 using graphs
concentration time graph: gradient = k
rate concentration graph: y intercept = k
how to find k with order 1 using graphs
concentration time graph: k= l2/ h.lL
rate concentration graph: gradient = k
initial rate
the instantaneous rate of a chemical reaction at t=0
what are pros and cons of continous monitoring
pros: more accurate
cons: more work to monitor several reactions over some time. Takes longer to process results
what are pros and cons of the clock method
pros: quick and simple to carry out easy to process 1/t
cons: only gives an approximation of the initial rate, need to choose quantities carefully
What is the shape of an order 0 graph showing time concentration
What would a graph look like for order 0 showing concentration and rate of reaction
What would a graph showing order 1 for conenctration and time
Order 1: concentration/ rate of reaction
Order 2: concentration/ time
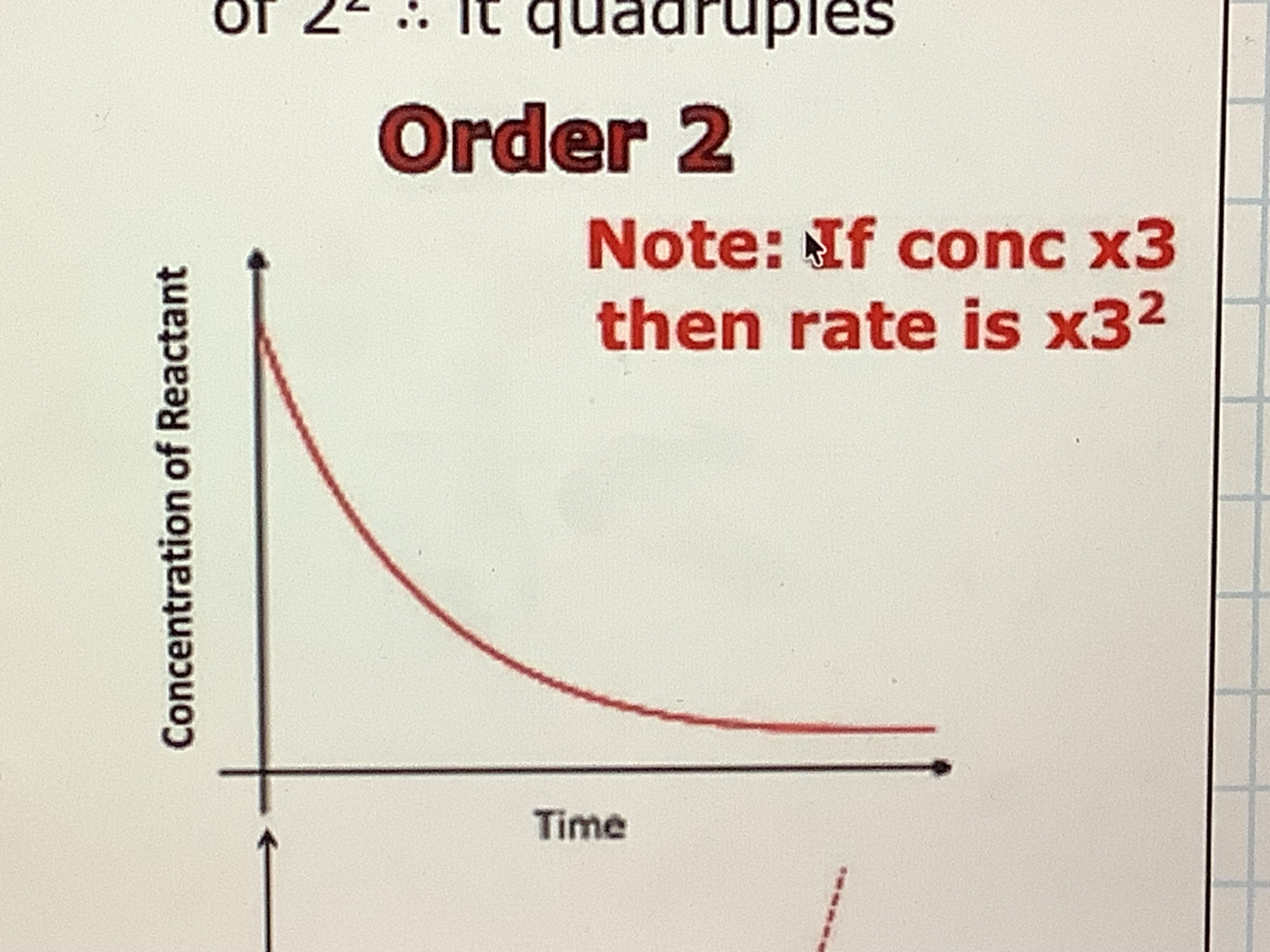
Order 2 : concentration/ rate of reaction
lattice enthalpy
the energy change that accompanies the formation of one mole of ionic compound from gaseous ions under standard condidtions
standard enthalpy change of formation
the enthakpy change that happens when one mole of an element is formed from its constituent elements under standard conditions
enthalpy change of atomisation
the enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of gaseous atoms forms from the element in its standard states
firs ionisation energy
the energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions
electron affinity
the enthalpy change that takes place when one electron is added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form on mole of gaseous 1- ions
standard enthalpy change of solution
the enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of compound is completely dissolved in water under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of hydration
the enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of isolated gaseous ions is dissolved in water forming one mole of aqueous ions under standard conditions
entropy
a measure of the dispersal of energy in a system, the more disordered a system , the greater the entropy
symbol: S
units: J K-1 mol -1
the number of wats a system can be arranged , higher entropy= more ways it can be arranged
entropy calculation
△S = ∑S products - ∑S reactants
gibs free energy calc
△G = △H - (T x △S )
temp is in kelvin
JK mol-1
how do we know if a reactioin is feasible
△G negative = feasible
∆G>0
-△S on a graph
gradient
temp becomes feasible on a graph
when line goes through x
△H on a graph
y intercept
dynamic equilibrium
can be only set up in a closed system
the rate of the forward reaction = rate of the reverse reaction
the amount of reactants and product appear to stay the same
le chateliers principle
states that when a system in dynamic equilibrium is subjeted to a change, the reaction will shift to minimise the change
temperature effect on equilibrium
increase: shift in endo direction
decrease: shift in exo direction
pressure effect on the equilibrium
increase: shift side with least moles of gas
decrease: shift side with most moles of gas
concentration effect on equilibrium
increase (x): shifts to the side without x
decrease (x): shift to side with X
kc
standard equilirbium constant
kc equation
𝐾𝑐=[𝐶]𝑐[𝐷]𝑑////[𝐴]𝑎[𝐵]𝑏
kc effect on equilibrium
if kc is small it will shift to the left
if kc is big it will shift to the right
Kp
used for gaseous equilbria when we know the partial pressure of the gases in the system
partial pressure
the contribution made by a gas towards the total pressure in a system
Kp equation
p(C)c p(D)d `/// (A)a p(B)b `
partial pressure equation
partial pressure = mole fraction x total pressure P
mole fraction equation
moles (A)/ total moles in mixture
what happens to the Kp value when the temp is increase ( -ve)
forward reaction is exothermic
this means that the equilitbim will shift to the left
this means that the denominator will increase and the numerator will decrease
Kp will therefore decrease