D103 Cell Migration (ALS 4, Video 7 and 8)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
when do cells migrate
during embryonic development
immune response
wound healing
cancer: metastasis
involves actin
components of cell migration
stress fibers: parallel bundles of f-actin
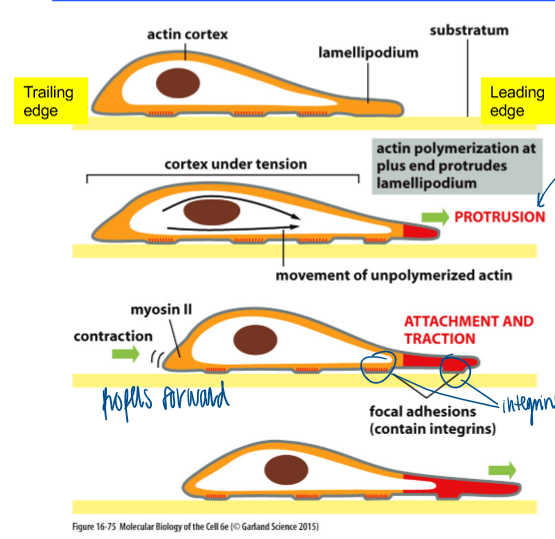
leading edge: branched actin
trailing edge
contractile actin fibers (stress fibers)
actin bundles are anchored to substratum
cell body is translocated
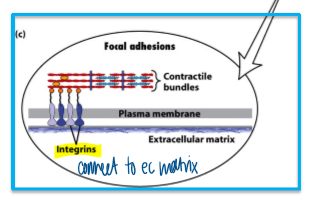
integrins connect to the ECM
leading edge
branched actin meshwork
front membrane is pushed out
steps of cell migration
membrane extension: enhanced actin mesh formation at the leading edge of the cell (protrusion)
formation of new attachment: dynamic attachment of cells to the substratum via focal adhesions (attachment)
cell body translocation: myosin-dependent constration at the trailing edge (traction)
breaking cell attachment; recycling of the membrane and attachment machinery
how can we study cell migration in tissue culture cells
wound healing assay
indicates cell migration, not directional migration
how is cell migration regulated
via small GTPases (Rho, Rac, and Cdc42)
found inside cytosol as a part of the signal transduction pathways for cytoskeleton structure
small GTPases function
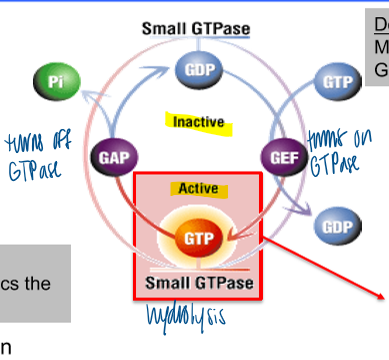
function as tightly controlled molecular timers
gtp binding portein with 2 different conformational states (GTP or GDP bound)
GAPs and GEFs
regulators of activation states
localization of GAPs and GEFs provides spatial regulation of GTPase activity
GAP: turns off GTPase
GEF: turns on GTPase
lipid anchored
transient association with the cytosolic leaflet of plasma membrane
GDI
prevents GTPase from associating with membrane
dominant active
mutant whihc mimics the GTP-bound state
dominant negative
mutant, which mimics hte GDP-bound state
can be locked in inactive state
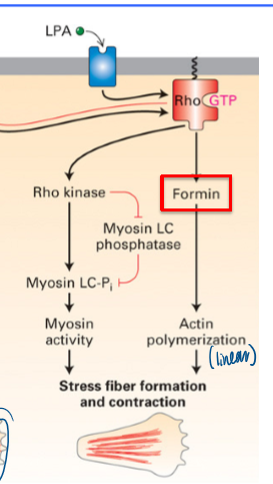
result of dominant active Rho
gain stress fiber formation and contraction
involves formin
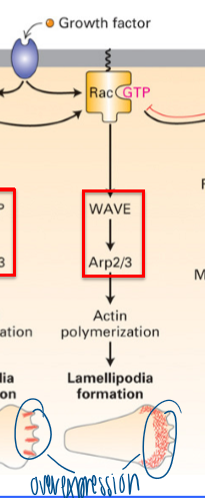
result of dominant active Rac
gain of lamellopodia formation
requires WAVE → Arp2/3
branched network
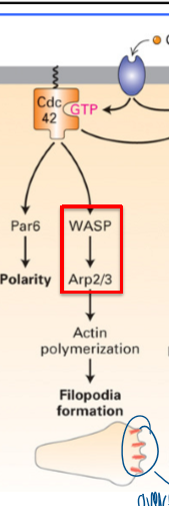
result of dominant active Cdc42
filopodia formation
requires WASP → Arp2/3
linear f-actin (filopodia) to establish polarity
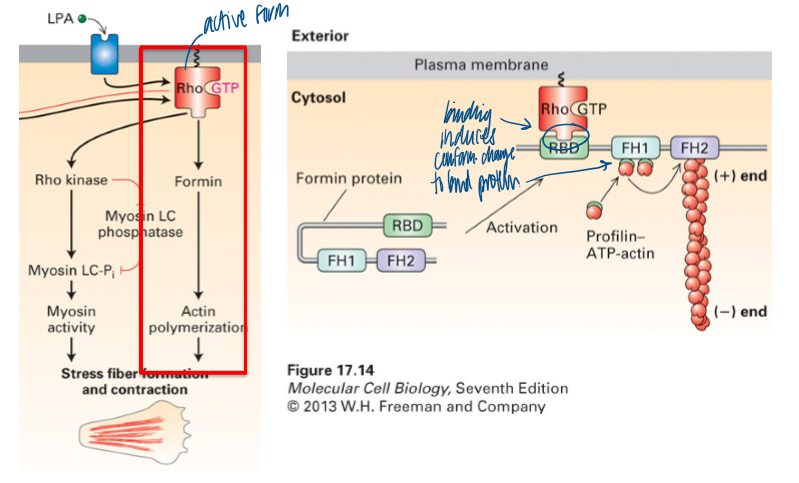
what does Rho activation lead to
formation of linear stress F-actin fibers
binding induces conformational change to bind protein
formin and myosin (via ROCK) are activated; stress fibers and contraction for movement
what does rac and Cdc42 activation promote
polymerization of f-actin structures
both use Arp2/3 for movement
activated via conformational change
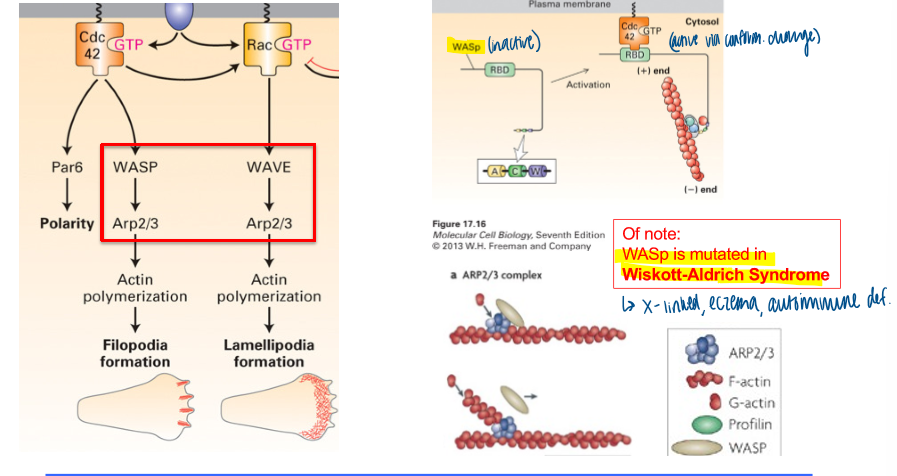
wiskott-aldrich syndrome
WASp is mutated
x-linked, causing eczema and autoimmiune def
what leads to directional cell migration
coordinated interplay between small GTPases
front: Cdc42 and RAC activation
rear: RHO activation
location of GEFs
dictates where F-actin polymerizes and how f-actin organized
listeriosis
caused by listeria monocytogenes
food poisoning, diarrhea, meningitis, pregnant women
bacteria in rapid movement
how does listeria move inside a “host” cell
actin-based motor/tail
without ActA, the bacteria cannot move inside a cell
ActA is necessary for bacterial motility; sufficient for motility
actin dynamics at leading edge in listeria
Rac1 (GTP) activates WAVE to activate Arp2/3
treadmilling actin network for migration in eukaryote; reuse building blocks and pushing plasma membrane forward
ActA of listeria activates the Arp2/3 complex (WASp independent)
intrinsic property of actin
polymerization/depolymerization that depends on the cytosolic conc of g-actin atp
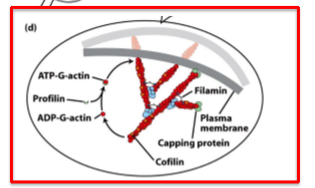
thymosin, profilin, cofilin
regulation of actin binding proteins
actin binding protein control organization and dynamics
formin, arp complex, capping protein, toropomyosin
nucleating factors
formin and ARP complex
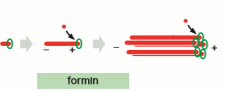
formin
nucleates assembly and remains associated with the growing + end
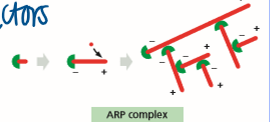
ARP complex
nucleates assembly to form a web and remains assorted with the - end
thymosin
binds subunits; prevents assembly
profilin
binds subunits; sppeds elongation by promoting ADP/ATP exchange
cofilin
binds adp-actin filaments; accelerates disassembly
destabilizes - end
gelsolin
severs filaments and binds to + end
capping protein
prevents assembly and disassembly at + end
critical regulators of f-actin in skeletal muscle cells (CapZ and tropomodulin)
sarcomeres
capped f-actin that cannot depolymerize (f-actin binding proteins)
bipolar filaments of myosin 2
motor domain of myosin
in all myosins
binds atp
bind f-actin
tail of myosin
unique to each myosin
tropomyosin
occupies the same site on f-actin as myosin → myosin cannot bind, muscle cannot contract
troponin
ca²+ sensing protein complex
muscle contraction in presence of Ca2+ and ATP
troponin undergoes conformational change
displaces tropomyosin
myosin can bind to f-actin because tropomyosin no longer blocks the myosin binding site
myosin “walks” towards the f-actin + end
where does the ca2+ come form during skeletal muscle contraction
action potential opens the voltage-gated ca²+ channel to release ca2+ to cytosol → binds to troponin → moves tryptomyosin → contracts
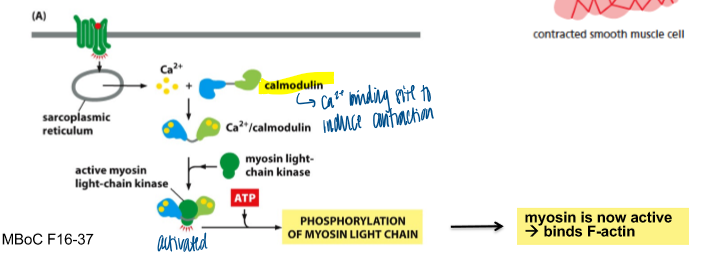
smooth muscle and Ca2+
sheets fo elongated spindle-shaped cells
cells have a single nucleus
contractile filaments without sarcomere organization
contain specialized forms of actin and myosin
ca2+ dependent contraction involves calmodulin, not troponin
focal adhesions
connecting a cell's actin cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix (ECM), allowing cells to adhere to their environment and sense mechanical forces
how were actin and focal adhesions visualized in this cell in the video
express G-actin with GFP tag; express vinculin with RFP tag
bc it was in a video, both structures are dynamic and require tagging for imaging
regulators of contractile actin bundle in trailing edge
formin
f-actin bundling proteins, myosin
rho
focal adhesion components
regulators of this branched actin org
WASP/ Arp2/3
profilin and cofilin
Rac and Cdc42
GTPS is commonly used as GTP analog that cannot be hydrolyzed. which of the following conditions does the addition of gtps mimic
gtp hydrolysis = gtp → GDP and Pi
thus activation of GEF to create the activated GTP
which of the following proteins is most upstream in the pathway that is activated by the bac chemoattractant
upstream = earliest
rac gef bc it must be activated first to do anything
why are f-actin capping protein critical for muscle contraction
prevent f-actin dynamics at both ends
titin
positions bipolar myosin fiber
nebulin
f-actin stabilizer