basic organic
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
application of IUPAC rules of nomenclature for systematically naming organic compounds
interpretation and use of general formula
simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series,
interpretation and use of structural formula
formula that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule
Interpretation and use of displayed formula
the relative positioning of atoms and the bonds between them
Interpretation and use of skeletal formula
the simplified organic formula shown by removing hydrogen atoms from alkyl chains leaving just a carbon skeleton and associated functional groups
Homologous series
a series of organic compounds having the same functional group but with each successive member differing by CH2 (definition is required)
functional group
a group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a compound
Alkanes
C–C, general formula Cn H2n+2
Alkenes
C=C double bond, general formula CnH2n, stem-2-ene depending on the lower number with the double bond
two double bonds: pent -2-diene
Alcohols
C–OH, general formula CnH2n+1, the bond to the OH group must always go to the O of the OH group
stem-1-ol when only one the OH functional group
1-hydroxy stem-2-ene
Haloalkenes
C–X where X i a halogen atom F, Cl, Br, I
General formula Cn H2n+1 X
Aldehydes
Carboxyl compound, contains C=O at the end of the carbon chain so attached to the first carbon is another hydrogen , counting starts from 1 at the functional group C=O for naming branches, general formula Cn H2n O
stem: al NO numbers as the functional group is always at the start e.g butanal
Ketones
Carbonyl compound C=O not at the end of the carbon chain, within the chain so C bonded to carbonyl group and the same C is bonded to another C
Stem-2-one depending where the =O position is
Carboxylic acid
Functional group C=O, C-OH at the end of the chain, Cn H2n+1 COOH OR Cn H2n O2 stem anoic acid no numbers as always in the same position , always start counting from 1 from the functional group
Presence of two functional carboxyl groups
At either end of the carbon chain pentane dioic acid
Cycloalkanes
Just like alkanes, hydrocarbon, saturated , Cn H2n unlike alkanes , every corner of closed shape is a carbon , cyclo stem e.g cyclobutane (square)
Naming esters
part after the oxygen double bond; suffix, count how many carbons, stemoate e.g. butanoate
part before oxygen single bond, the prefix, alkyl group count how many carbons e.g. methyl propanoate
alkyl group
of formula CnH2n+1) with one fewer H atoms than parent alkane group that gives the name e.g. alkyl group of methane is methyl, alkyl group of ethane is ethyl
aliphatic
(a compound containing carbon and hydrogen joined together in straight chains, branched chains or non-aromatic rings), can be saturated or unsaturated
Straight chain hydrocarbon
contains one continuous carbon chain only with no branches (this includes shorter carbon chains, doesn’t include branches of other atoms such as O)
Branched chain hydrocarbon
contains a shorter side bonded to a longer continuous carbon chain
Alicylic hydrocarbon
an aliphatic compound contains carbon atoms arranged in non-aromatic rings with or without side chains, pic is not a benzene ring as it is missing the third double bond
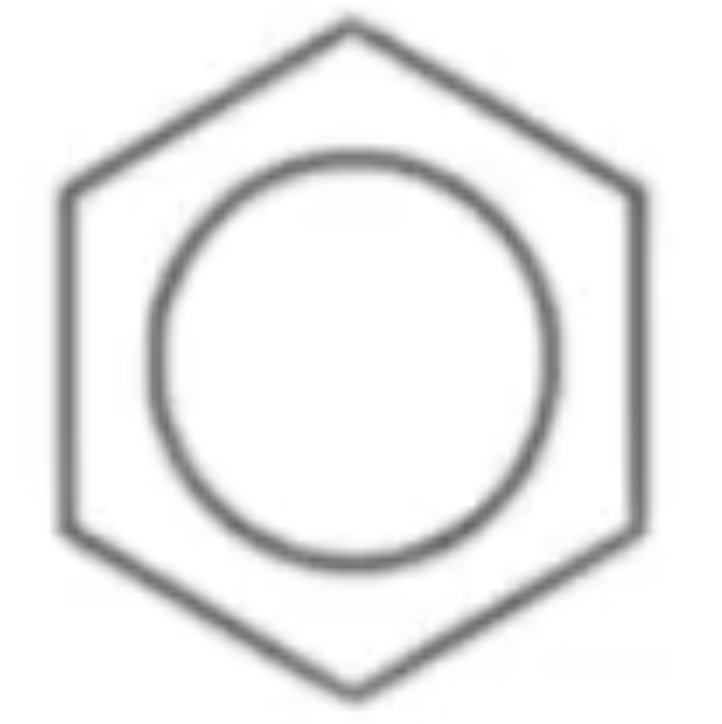
Aromatic
an unsaturated hydrocarbon compound containing a benzene ring
Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon
single carbon–carbon bonds only) and unsaturated (the presence of multiple carbon–carbon bonds, including C=C, C C / and aromatic rings
use of the general formula of a homologous series to predict the formula of any member of the series
explanation of the term structural isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae), isomerism occurs when two or more organic molecules have the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms
the different types of covalent bond fission
Covalent bonds can be broken by homolytic or heterolytic fission
Homolytic fission
a covalent bond is broken with each bonding atom receiving one electron from the bonded pair, forming two radicals
Heterolytic fission
a covalent bond is brown with one bonding atom receiving both electrons from the bonded pair forming two oppositely charged ions
the term radical
a species with an unpaired electron) and use of 'dots' to represent species that are radicals in mechanisms
a 'curly arrow' in a mechanism
as the movement of an electron pair, showing either heterolytic fission or formation of a covalent bond
reaction mechanisms show how a reaction takes place using diagrams
EQ
from the revision resources on SharePoint done all the basic organic chem worksheet apart form page 4, struggling with this one
systematic name for benzene ring
ends in benzene, put all alkyl groups and everything
For structural formula
When there’s an alkyl group, 2- methyl
The (CH3) goes before the second carbon
CH3 (CH3) CH CH2 CH2 CH3
When there’s a carboxylic acid at one end and at the other end a C=O
The functional groups present are carboxylic acid and Kentone not aldehyde
Molecular formula of CYCLOHEXENE
Cn H2n for cylcohexane
Then take two off due to the double bond in hexene
Check skeletal formulae for but-2-ene and other alkanes and that
Structural formula of a haloalkane that has 1 so 1-chlorobutane
As there is a 1 the Cl would go at the very end of the formula
Displayed and structural formula of cypcohexane
Definition of homologous series
Series of compounds with the same functional group, each successive member differing by CH2
Explanation of increasing BP of cycloalkanes
More carbon atoms in the ring, more electrons, more area of contact, stronger London forces, more energy needed to break IMF
Draw the structural isomer of an alkene
Number of carbon atoms, the cycloalkane of it as it is also CnH2n
Define the term hydrocarbon
Compound containing carbon and hydrogen only
Type of hydrocarbon a benzene ring is
Unsaturated
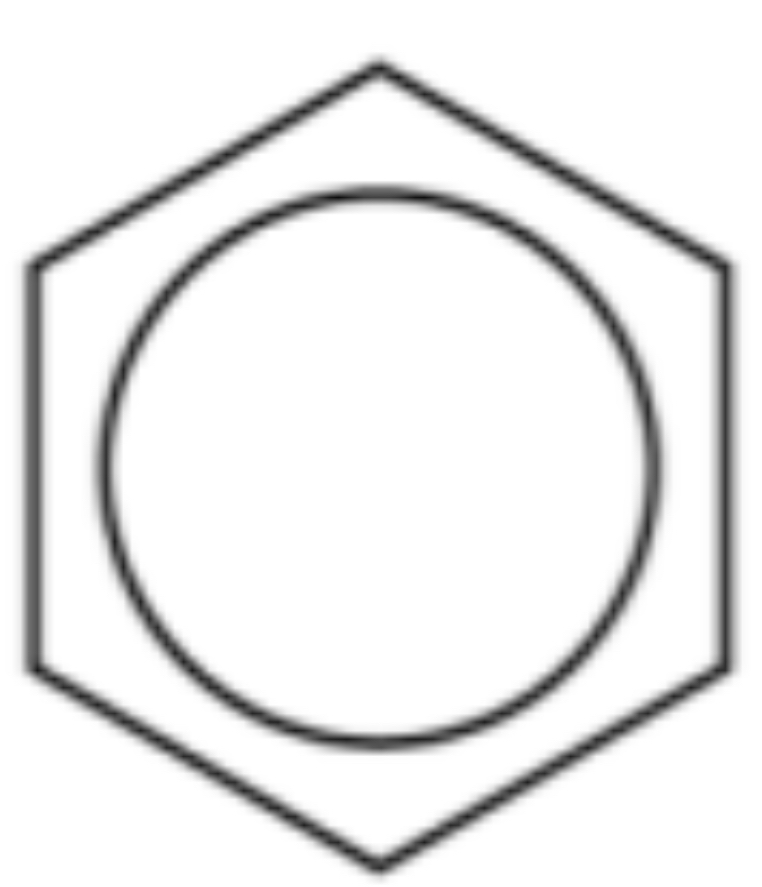
Name the compound, empirical formula
Benzene, CH
Deduce the general formula for alcohols
Cn H2n+2 O
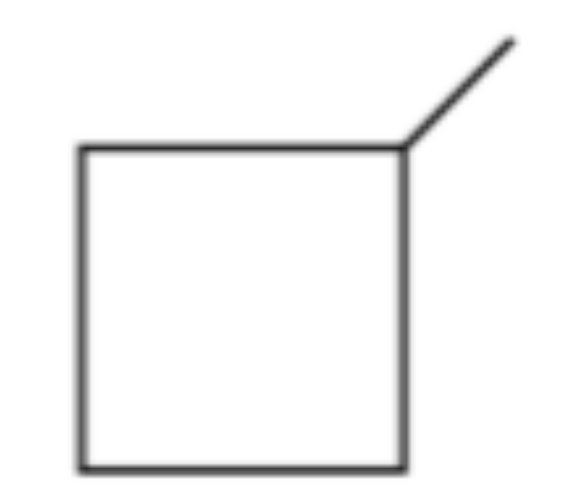
Aliphatic, molecular formula C5 H10
Which type of organic mechanism will have an atom economy of 100%
Addition because it only has 1 product
Are the compounds structural isomers
No because they have different molecular formulae
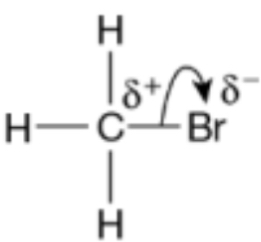
When UV light is used the C-Br bond fission is homolytic, describe what happens to the bonding electrons when the C-Br bond undergoes homolytic fission
Each atom joined by the bond receives one bonding electron
When the C-Br bond breaks homolytically the name given to the type of particle produced
Radicle
The type of particle produced when the C-Br bond breaks heterolytically
What does a curly arrow represent
Movement of a pair of electrons
Use curly arrows and partial charges to show the breaking of the C-Br bond via heterolytic fission on the displayed formula
Bromine is more electronegative
Homologous series in which methyl butanoate belongs
Ester
All possible structures of the compound C4 H8 O
Elimination vs substitution vs addition
Elimination: water is produced or something
Substitution: one atom or group is replace by another
Addition: one product is made by adding two reactants
Explain why alcohols have a higher BP than alkanes
Alcohols have hydrogen bonds, Alkanes have London forces , hydrogen bonds in alcohols are stronger than London forces in alkanes, more energy required to break hydrogen bonds than London forces
All of question 4b in revision resources on share point
Explain what is meant by heterolytic fission
Breaking of a covalent bond where one of the bonding atoms receives both electrons from the bonded pair of electrons
Naming esters with alkyl branches
ETHYL 4-METHYL (branch) METHANOATE
so without the branch it would be ethylmethanoate additional branch goes in the middle of the name
Counting starts from 1 at the carbon attached by a double bond to an O, C=O
For methyl groups
Bi for 2
Tri for 3
Tetra for 4