Impulse Decomposition
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Representation of the Discrete-Time Signal x[n] using Impulses
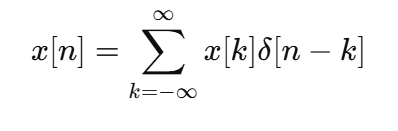
It produces a shifted impulse response h[n - k]
What happens when an LTI system is applied to δ[n - k]
Convolution Sum Formula
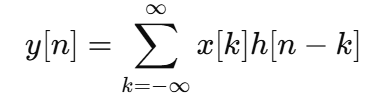
When the input has short duration (few nonzero samples).
When is direct convolution by summing shifted impulse responses most effective?
Write the input as a weighted sum of shifted impulses.
First step in direct convolution?
x[k]h[n - k]
What is the output corresponding to x[k]δ[n - k]
By summing all weighted, shifted impulse responses.
How is the final output obtained in direct convolution?
y[n] = x[n] + (1/2)x[n - 1]
The system equation for the two-path multipath channel
The impulse response of the system equation for the two-path multipath channel
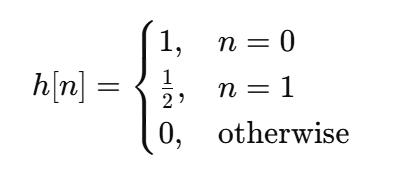
Example 2.1
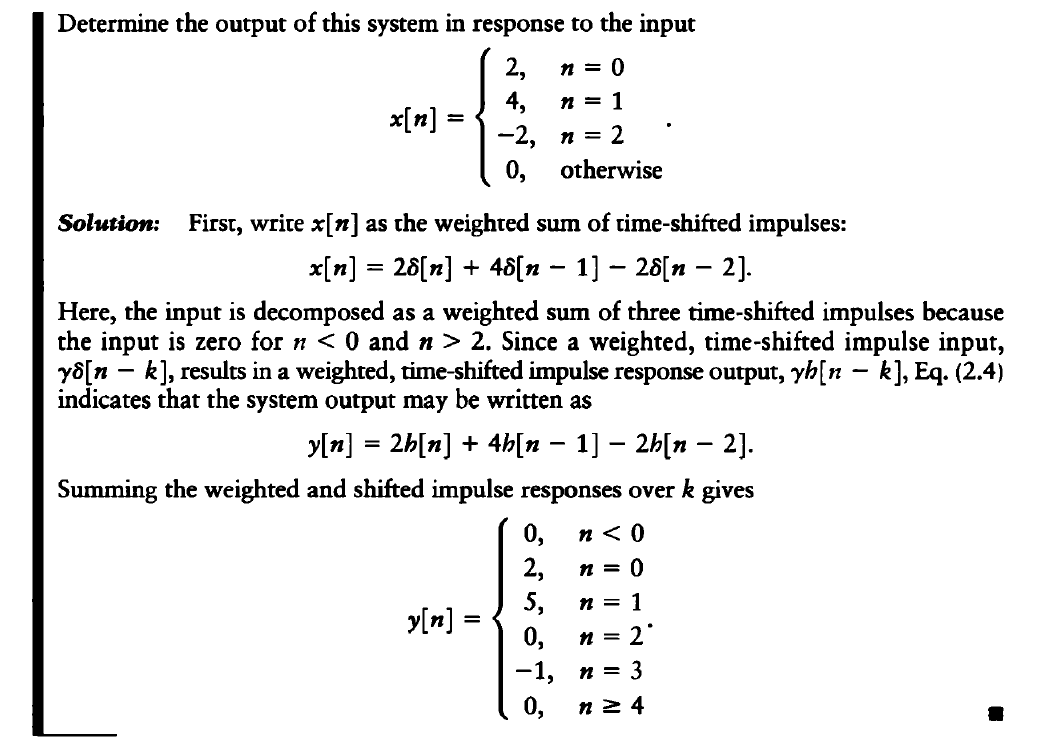
It requires summing many shifted impulse responses for each n
Why is direct convolution inefficient for long signals?
w_n[k] = x[k]h[n - k]
What is the intermediate signal used in convolution evaluation?
Because n is treated as a constant during summation over k
Why is n written as a subscript in w_n[k]?
Expression of the output using the Intermediate Signal
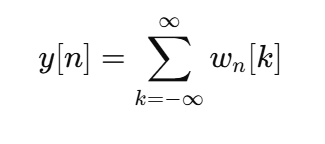
Because h[n - k] = h[-(k - n)], which involves reflection in k
Why is the impulse response reflected in convolution?
Reflect about k = 0, then shift by n
What are the two operations applied to h[k] inreflect-and-shift convolution?
Shifted to the left
If n < 0, how is h[n - k] positioned?
Shifted to the right
If n > 0, how is h[n - k] positioned?
When the nonzero portions of x[k] and h[n - k] do not overlap
When is w_n[k] = 0 for all k?
Because the mathematical form of w_n[k] changes only when overlap changes.
Why do we analyze convolution over intervals of n?
The start or end of overlap between x[k] and h[n - k]
What determines the boundaries between intervals of n?