Forces and motion
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Forces and motion
Last updated 12:49 PM on 5/30/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
1
New cards
What is Newton’s second law?
↳ An object will accelerate in response to a resultant force
2
New cards
What is terminal velocity?
↳ the constant velocity a falling object reaches when friction is equal to it’s weight
3
New cards
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic deformation?
↳ Elastic-the object goes back to it’s original shape once forces are removed
↳ Inelastic-the object does not go back to it’s orignial shape/size once the forces are removed
4
New cards
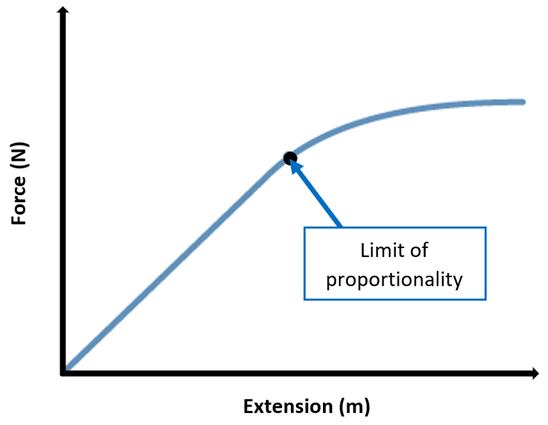
What is the limit of proportionality?
↳ Point where the object no longer obeys Hooke’s law (the force required to stretch or compress a spring is proportional to the distance the spring is stretched)