Biology: Organisation (Paper 1)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is a specialised cell?
A cell with a specific function
e.g nerve cells
Muscle cells
What is referred to as ‘the building blocks of life’?
Cells
How to form tissues organs etc
Cells > tissues
A group of similar cells working together for one function
Tissues > organs
A group of tissues working together for one function
Organs > Organ systems
A group of different organs working together to perform a function
Test for starch
Iodine solution
Blue - black positive
Refer to ‘iodine solution’ not ‘iodine’
Test for lipids
Sudan III Test
Sudan III stain solution
Fat is stained snd separated from substance
Bright red layer - positive
Test for sugars
Benedicts (reagent) test
Water bath at 75º
Wait 10 mins
Green / Yellow / Brick red positive\
Don’t boil mix for too long as starch will turn to sugars - false positive
Test for proteins
Biuret test
Purple positive
Hold test tube infant of white paper as purple result is hard to see
pH effect on Enzymes
Enzymes work best in their optimum pH level
If pH is too high or low
The hydrogen bonds in the active site
Break down and the active site loses its shape
It can no longer break down food
The enzyme had denatured
What can muscle tissue do?
Contract to bring about movement
What can glandular tissue do?
Release hormones and enzymes
What does epithelial tissue do?
Cover all parts of the body
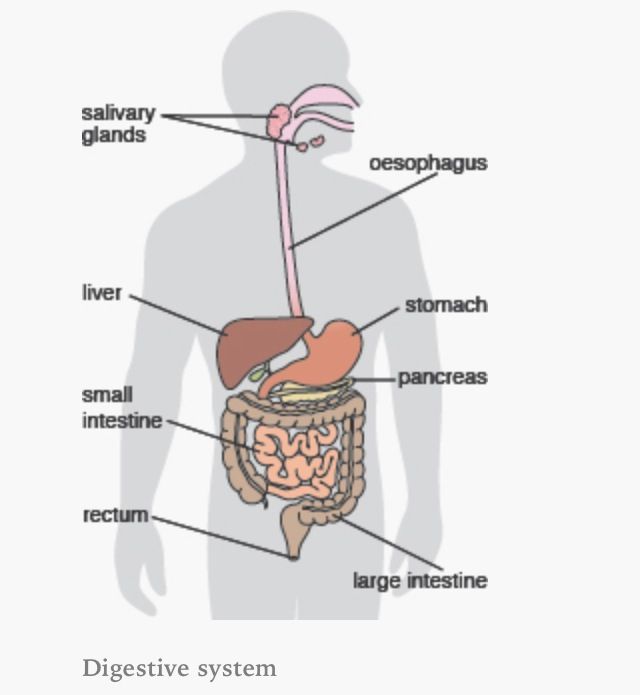
Label the Digestive system
How do Enzymes aid digestion
The enzymes pass out of the cells into the digestive system
They come into contact with food molecules
They catalyse the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into smaller soluble molecules
Properties of Enzyme Protease
Substrate | Products | Location |
|---|---|---|
Proteins | Amino acids | Small intestine Pancreas Stomach |
Properties of enzyme Lipase
Substrate | Products | Location |
|---|---|---|
Lipids (fats) | Fatty acids Glycerol | Pancreas Salivary gland Stomach |
Properties of enzyme Carbohydrase
E.g. Amylase
Substrate | Products | Location |
|---|---|---|
Carbs Starch | Sugars Glucose | Pancreas Small intestine Salivary glands |
What are the ….. for?
Cell membrane
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Cell membrane - controls what goes in & out
Ribosomes - protein synthesis
Mitochondria - Respiration for energy
Cytoplasm - Site of chemical reactions
Nucleus - Holds DNA
What is parastalsis?
The squeezing action in oesophagus and intestines to put food through
What is the optimum pH and temp for enzymes?
pH 5-9
Optimum pH7
Optimum temp 37º
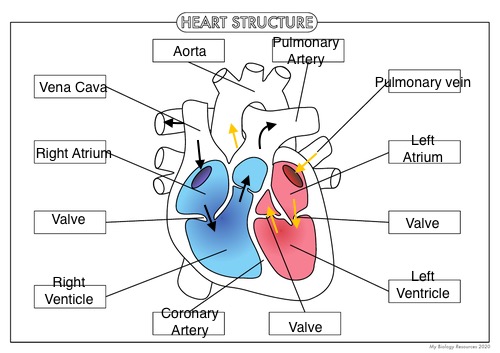
Label the heart
How is the small intestine adapted for absorption?
Villi, increased surfaced area
Large surface area (5m long)
Micro villi, increase surface area
Villi have thin membrane for a short diffusion path
Capillaries absorb nutrients
Rapid rate of diffusion
What is a single circulatory system?
Blood goes from heart to gills (for oxygen) to organs
Blood loses lots of pressure passing through gills and loses oxygen before getting to organs.
What is a double circulatory system?
Blood from heart to lungs for oxygen
Back to heart
Pumped around rest of body
Back to heart
Blood passes through heart twice which speeds up transport and increases oxygen
Properties of Arteries
High pressure blood
From heart to body
Thick wall and muscle
Elastic fibres which stretch and recoil in-between surges of blood
Properties of veins
Blood to the heart
Deoxygenated
Low pressure
Valves to prevent back flow
THin wall
Properties of capillaries
Substances from blood diffuse
E.g CO2 and glucose
What does the pulmonary artery do?
Pumps deoxygenated blood away from heart to lungs
What does aorta do?
Pumps oxygenated blood to body
What does the pulmonary vein do?
Pumps oxygenated blood into the heart to go to the body
What does the vena cava do?
Allows deoxygenated blood from body into the heart
What side has a thicker wall? Why?
Left side
Pumps blood to rest of the body so requires thicker muscular wall as the blood is pumped at a greater force
What is found in the blood?
Plasma - liquid
Red blood cells, white blood cells
Plateletes (tiny fragments of cells)
What does plasma transport?
Plasma transports CO2 from organs to lungs
Waste product urea from liver to kidneys to be excreted
Soluble digestion products e.g. glucose
What aaptations do red blood cells have?
Transport oxygen from lungs to body
Haemoglobin which carries oxygen (oxyhaemoglobin)
No nucleus (more room for haemoglobin)
Concave shape for larger surface area for more haemoglobin
White blood cells features
Make antibodies
Contain nucleus ( & DNA)
What are platelets for?
To help clot blood to prevent bleeding out.
Cardiovascular diseases
Coronary heart disease
Fatty deposits block coronary arteries. Arteries narrow which limits oxygen to heart
Statins reduce cholesterol which slows down build up of fat
Stent
Can cause liver problems
Leaky valves
Artificial increase blood clot risks
Gas exchange in lungs
Alveoli - large surface area, one cell thick, good blood supply, steep concentration gradient
Bronchi - tubes into lungs
Bronchioli - smaller tubes from bronchi
Trachea contain rings of cartilage preventing collapse
Cancer
uncontrolled growth and mitosis (tumour)
Benign tumour - contained a membrane, stay in one place
Malignant - cancer, spread
Alcohol - Mouth & throat cancer
UV light - skin cancer
Radon - Uncontrolled cell division
Non communicable
Can’t be passed on from person to person
Communicable
Passed on from person to person
What can HPV cause?
Cervical cancer
What polymer is amylase made of?
Amino acids
Evaluate the use of anti-clotting drugs
Advantage:
Only one per day
Tablet is easy to swallow / not painful
Disadvantage:
Could forget to take the drugs
Could still clot in the first week.
How does an enzyme work?
Lock and key theory
Starch / substrate binds to active site
Shape of active site and substrate are complementary
Bonds between the starch molecules are broken to produce smaller molecules
What is the difference between transpiration and translocation?
Transpiration - Removes water, only goes up
Translocation - Stores nutrients, goes up and down