Unit 1 AP Psych
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Nature (Heredity)
refers to idea that our characteristics are passed down from parents through genes
Nurture (Environment)
our surroundings, upbringing, and life experiences influence who we become
Twin study
- identical = 100% of genes are shared = more similar in traits and behaviors
- fraternal = 50% of genes
- greater similarity in identical traits = strong genetic component to these traits and behaviors
- similarities are the same even with different environments
Adoption study
- examines whether adopted children = bio parents or adopted parents
- resembles more of their bio parents because genes (nature) > environment (nature)
Family study
- research method used to understand the genetic and environmental influences on a particular trait/disorder
- proband = trait
- examine family members of who has proband to see how prevalent it is
- trait is influenced by genetics = more common
Brain
- part of central nervous system
- command center responsible for processing info, making decisions, and controlling bodily functions
Spinal cord
- part of central nervous system
- long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue that extends from brainstem -> vertebral column
- transmits nerve signals between the brain and rest of the body
Peripheral nervous system
- network of nerves that connects the CNS to the rest of the body
- responsible for transmitting sensory info to the brain and carrying out motor commands to muscles and organs
Somatic nervous system
enables voluntary control of our skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system
- controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing functions such as heartbeat, digestion, and more
- operates on its own without conscious efforts
Sympathetic nervous system
- "Fight or Flight"
- arouses the body and expends energy
Parasympathetic nervous system
- produces the opposite effects, calming the body as it decreases your heart rate, blood pressure, increases digestion, decreases blood sugar
- rest + digest
Neuron
- a nerve cell
- basic building block of nervous system
- 100 billion neurons in a mature human brain
- plays key role in sending signals
Glial cell
- surround neurons and provide physical support for neurons to grow on
- provide structure, insulation, communication, and waste support
- 90% of brain
Dendrites
receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to cell body
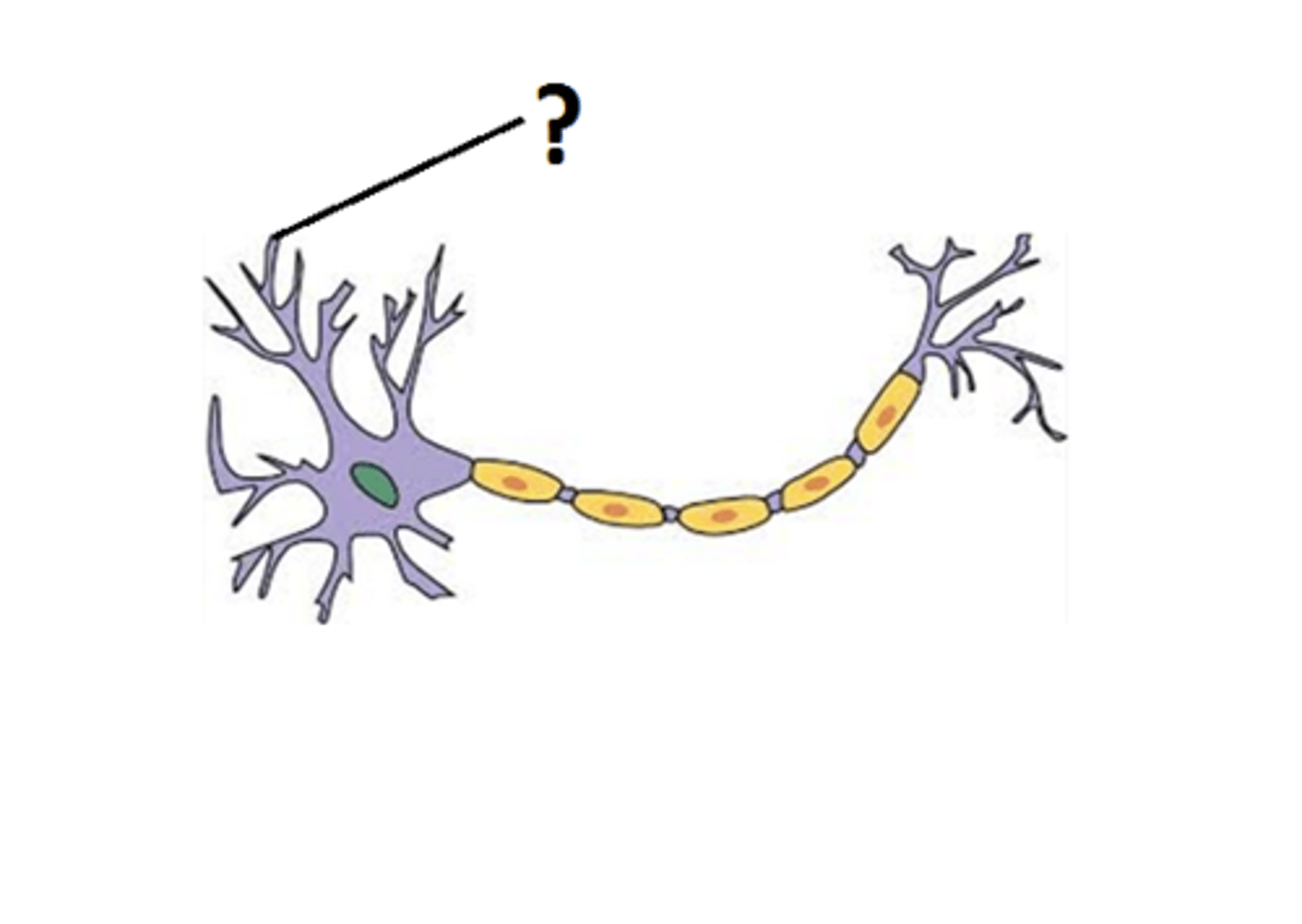
Nucleus
controls cell's activities and has genetic material
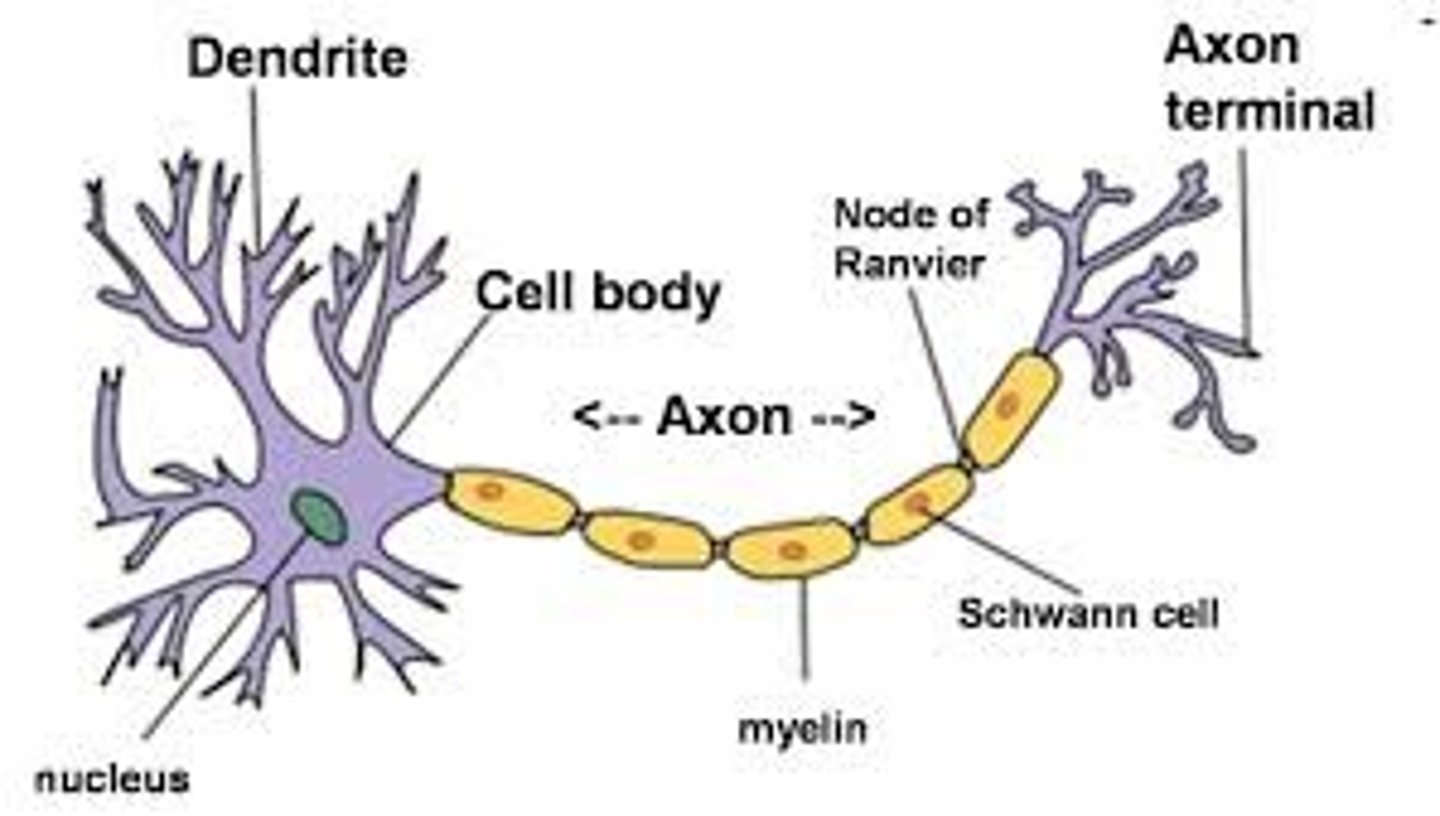
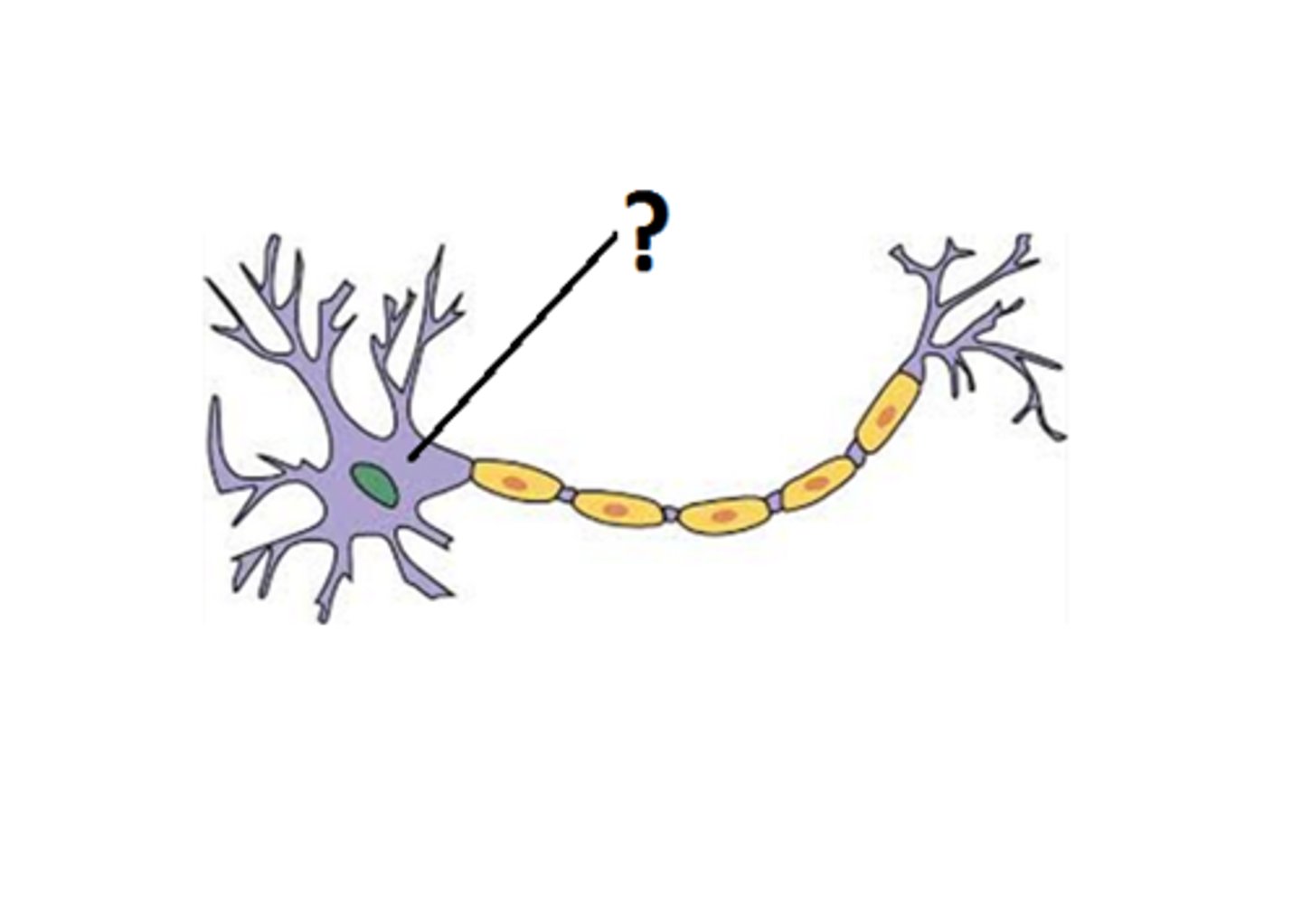
Cell body
provides energy
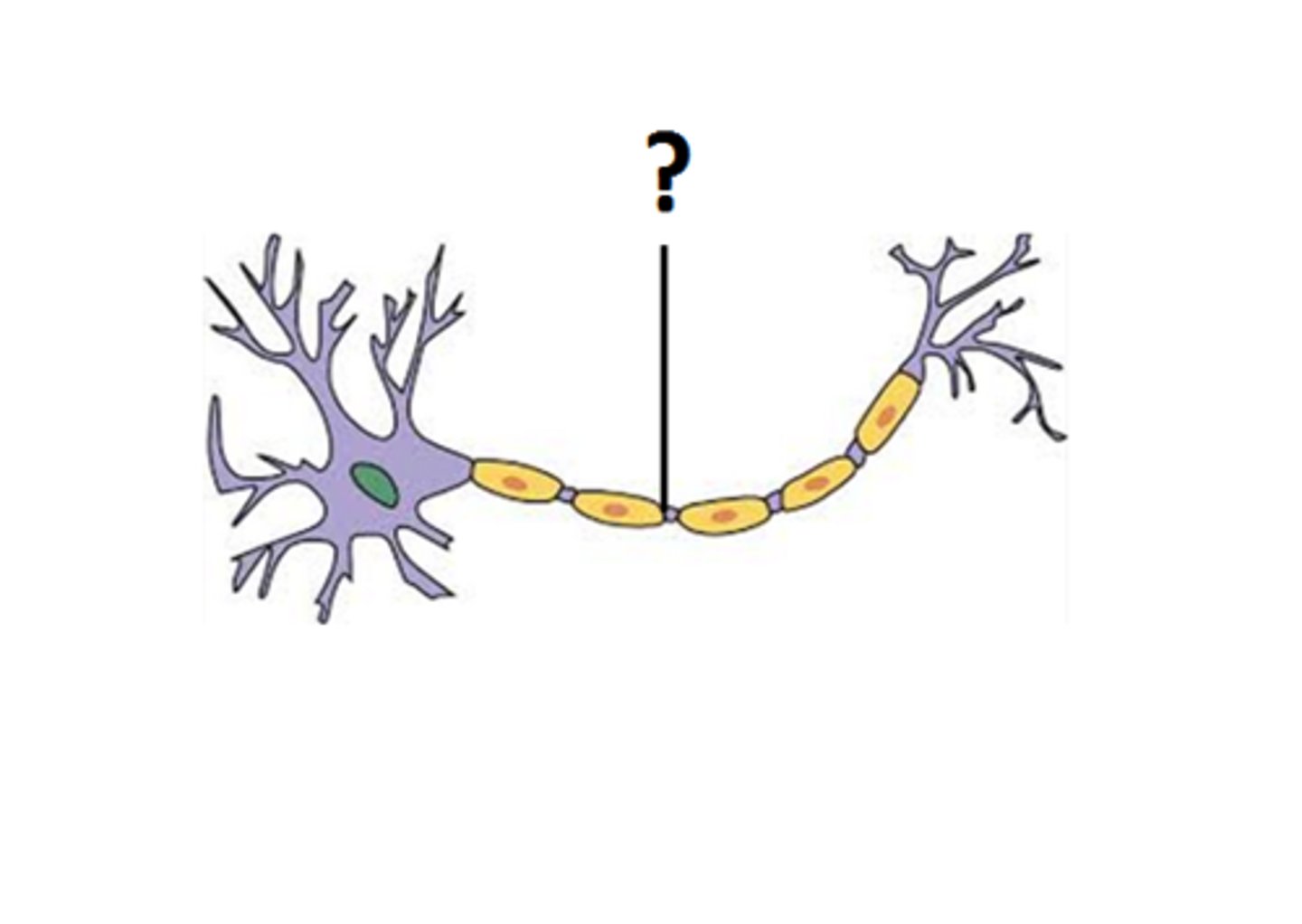
Axon
gets electrical messages away from cell body and goes to other cells
Axon terminal
transmits messages through neurotransmitters
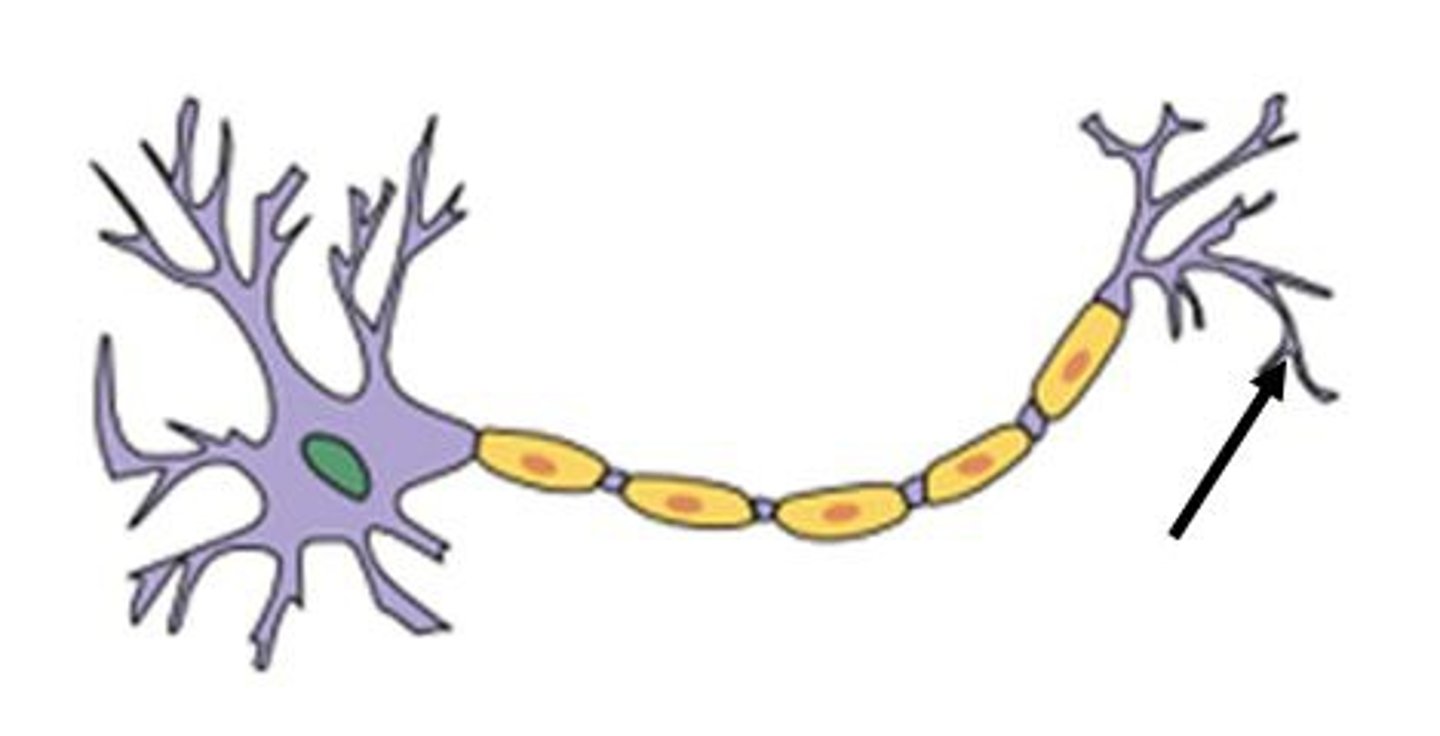
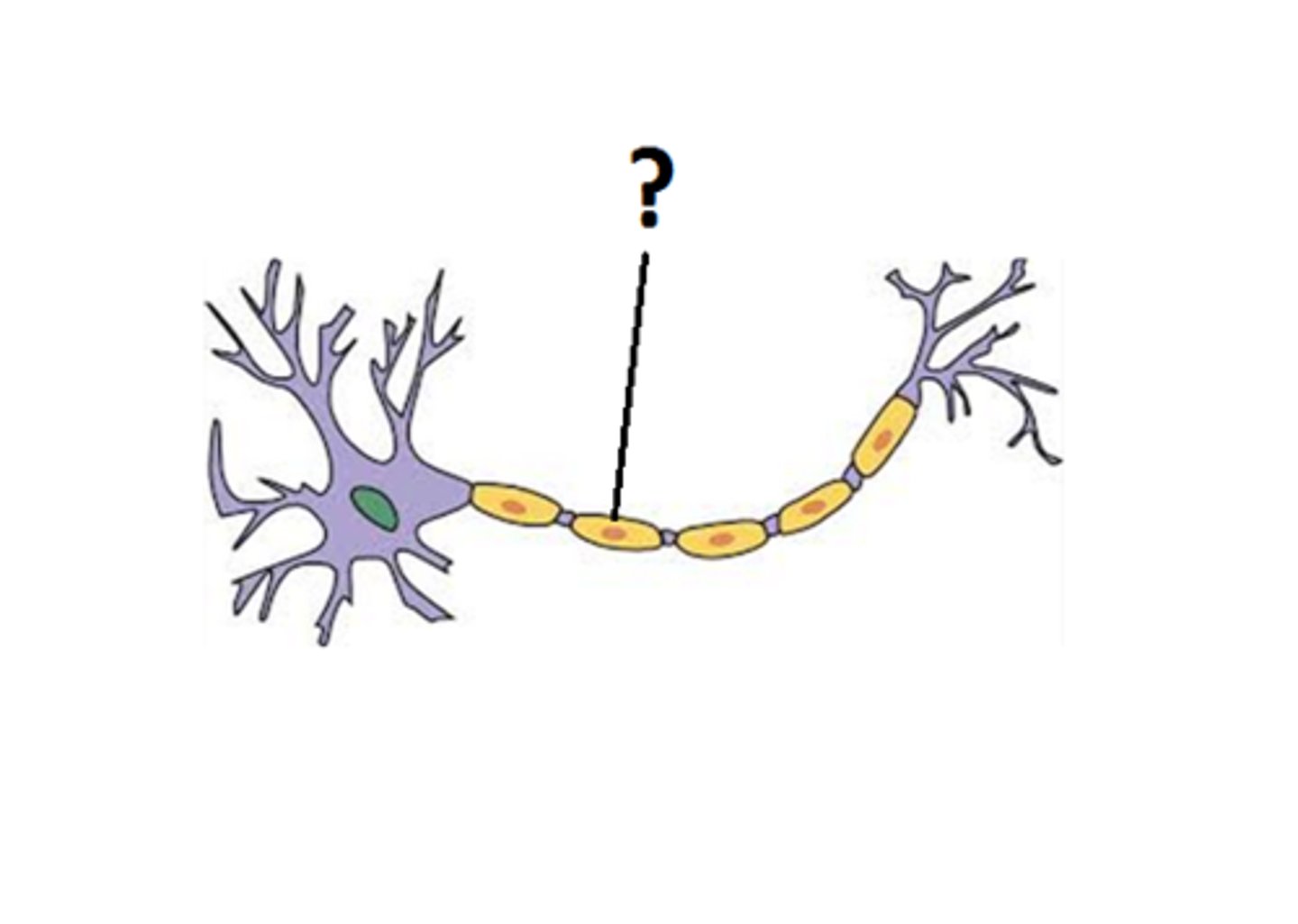
Myelin sheath
electrical impulses and transmits quickly and efficiently (speeding and transmission)
Sensory neuron
carries signals from sensory receptors to central nervous system
Motor neuron
carries signals from the brain to the muscle and glands
inter neuron
acts as relay stations between sensory input and coordinating motor system (translators)
Reflex arc
- includes sensory nerves that carry signals to spinal cord
- connects interneurons - transmit signals down the motor neurons to the muscles that triggered the reflex
- more involuntary
Reflex arc process (step 1)
detection by sensory neurons
- specialized nerve endings in your skin, the sensory receptors, detect the stimulus
Reflex arc process (step 2)
signal transmission to the CNS
- receptors trigger an electrical signal in a sensory (afferent neuron)
- acts like a one-way street, carrying the message from your hand to spinal cord
Reflex arc process (step 3)
processing in the CNS
- crucial shortcut
- sensory neuron delivers to interneuron with the spinal cord
- interneuron acts as a simple processing center
Reflex arc process (step 4)
activation of motor neurons
- interneuron passes the signal directly to a motor neuron (efferent neuron)
Reflex arc process (step 5)
response execution
- motor neuron carries command away from spinal cord to effector, part of body that responds
Action potential
neuron will fire, sending electrical signal down the axon
Stimulus threshold
minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a particular response
All-or-nothing principle
neuron will either fire all the way or nothing at all
Depolarization
occurs when neuron's membrane potential becomes less negative due to the influx of sodium (Na+) ions, bringing it closer to the threshold for firing an action potential
Refractory period
- period where action potential isn't possible
- potassium channels reopen and sodium channels close gradually returning neuron to its resting potential
Resting potential
- electrical charge of a neuron that is ready to fire
- negative charge
Reuptake
chemical messengers are taken back up into the sending neuron to be used again
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- chronic disease that affects CNS, brain, spinal cord, optic nerves
- autoimmune disorder where body attacks itself, damaging protective coating of neurons (myelin sheath)
Myasthenia gravis
- chronic autoimmune disorder where antibodies destroy antibodies block or destroy many of muscles receptors sites for neurotransmitters to acetylcholine receptors
- muscle weakness
Excitatory message
- cause neurotransmitters to fire off the message -> passed along to the next cell
- to release
Inhibitory message
- block the chemical message from being passed along any further
- to block
Dopamine
- excitatory
- pleasure + rewards -> feel motivated, satisfied, excited
- responsible for many addiction
TOO MUCH - addiction to feel pleasurable
TOO LITTLE - parkinson's disease and depression
Seratonin
- inhibitory
- happiness + feeling good
- regulate mood + feel calm + focused + emotionally stable
TOO MUCH - hallucinations
TOO LITTLE - depression + mood disorders + OCD
Norepinephrine
- excitatory
- "Fight or Flight"
- increases bodily arousal
TOO MUCH - anxiety
TOO LITTLE - depression + mood disorders
Glutamate
- excitatory
- several receptors -> memory, cognition, mood-recognition
- most abundant
TOO MUCH - overstimulation (migraines + epileptic seizures)
TOO LITTLE - insomnia, concentration problems + mental exhaustion
GABA
- inhibitory
- calms + relaxes people
- increases sleepiness + decreases anxiety
- reduces heart rate, blood pressure, breathing
TOO MUCH - overly sleepy + normal functioning impaired
TOO LITTLE - anxious + insomnia
Endorphins
- inhibitory
- alleviate pain, lower stress, improve mood + well being
- pleasurable activities (exercise)
TOO MUCH - ignoring all pain + risk injury
TOO LITTLE - significant pain
Substance P
- excitatory
- pain signals to the brain
- reacting to pain when we get hurt (inflammation + regulate mood)
TOO MUCH - chronic pain
TOO LITTLE - reduced sensitivity to pain
Acetylcholine
- excitatory
motivation, arousal, attention, learning, memory
- important for REM sleep
- regulating cardiac contraction, activating muscle action
TOO MUCH - severe muscle spasms
TOO LITTLE - alzheimers + dementia
Psychoactive drugs
- chemical substances that alter mood, behavior, perceptions
- affect brain chemistry by altering affects of neurotransmitters
Agonist
occupy receptors and activate them
Antagonist
occupy receptors and block neurotransmitters from activating them
Reuptake inhibitor
block the reuptake of neurotransmitters
Stimulant
- speed up body's functions
- sense of increased energy, mental alertness, and forced wakefulness
EX - caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamine
Depressant
- lower neural activity + slow body functioning
- affects hippocampus -> memory under the influence
- affects GABA -> slow reactions
- affects dopamine -> happy
EX - alcohol, benzodiazepines -> slow CNS, barbituates -> reduce anxiety
Hallucinogens
- psychedelic
- drugs that cause hallucinations + distort people's perception of reality
EX - LSD -> lights are "fluffy", marijuana, mushrooms, opioids
Opioids
- produced from opium reduce neuro-transmission + temporarily lesson pain + anxiety
EX - morphine, codeine, oxycontin
Tolerance
- brain will readjust its chemistry to counteract effects of drugs
- user finds effects of same dose of drug diminish over extended use or they need more of a drug to have same effect
Addiction
compulsive, uncontrollable, craving for drug
Withdrawal
- symptoms associated with discontinuing a drug
- include cravings, pain, tremors, anxiety, depression
Medulla
- responsible autonomic functions
- don't consciously control
INJURED - death b/c controls vital life functions
Cerebellum
- muscle control, balance + movement
INJURED - walking, imbalance, uncoordinated movements, susceptible to alcohol, vertigo (dizziness)
Reticular activating system (RAS)
- voluntary movement, eye, learning, cognition, emotion
INJURED - loss of consciousness, irreversible coma, sleep issues
Brain stem
lower part of the brain, connecting the cerebrum with the spinal cord and regulating vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and consciousness
Limbic system
bordering the brain stem, responsible for behaviors related to emotions, motivation, encoding of memories, and olfaction (our sense of smell)
Brain's reward center
- group of interconnected brain structures that are involved in motivation, pleasure, addiction
INJURED - loss of interest in activities, lack of motivation, addiction
Thalamus
- sensory info from eyes -> occipatal lubes/skin -> parietal lobes
- emotions processed
- senses NOT SMELL
INJURED - tingling, numbness, motor impairments, hypersensitivity, chronic pain, vision loss, light sensitivity
Hypothalamus
- survival drives + homeostasis + reproduction
- alerts body
INJURED - can't tell when hungry, over-eating, gaining weight + sleepyness
Pituitary Gland
- master
- endocrines system's most influential gland
- works with hypothalamus -> regulate growth, controls other glands
INJURED - not producing enough hormones (fatigue, memory, mood changes, sexual dysfunction
Hippocampus
- turning info short term -> long term
- recalling events
INJURED - won't be able to retain info and convert short -> long term
Amygdala
- emotions + survival responses, afraid, "fight or flight"
- large + scary
INJURED - very little emotion + flat affect
Corpus callosum
- connects + communication between hemispheres
INJURED - impossible for left and right to communicate with each other
Occipital iobe
- processing distance, depth, perception, color, object, face, cognition, memory formation
INJURED - blindness, blind spots, visual distortions
Temporal lobe
- processing info related to hearing + auditory memory
INJURED - difficult to understand language + process what's heard, deafness
Parietal lobe
- touch, pressure, temperature, pain
INJURED - recognize difficulty by touch, pain, pressure, vibration
Frontal lobe
- decision making, judgement, problem-solving, personality, planning, language, reasoning
INJURED - personality changing, judgement, inability to solve problems
Cerebral cortex
- outer layer of the brain cerebrum, involved in complex functions such as thought, memory, awareness, language, and consciousness
- divided by left and right hemispheres
Specialized areas of the brain
- located on the cerebral surface, responsible for complex processing that goes on between the arrival of input in the primary sensory cortices and the generation of behavior
Prefrontal cortex
- most forward part of the frontal lube, complex cognitive behavior like planning, decision making, personality expression, social
INJURED - lack of impulse, impaired judgement, change in personality + bx
Motor cortex
- control voluntary movements
INJURED - paralyzed, lose control over movements
Somatosensory cortex
- detects sensory info -> temp, texture, pain
INJURED - numbness + difficulty feeling pain
Broca's area
- speech production, command center, muscle movements
INJURED - difficulty with speech while comprehension is fine
NOT SPEECH IMPEDIMENT
Wernicke's area
- comprehension of speech, can say words easily but make no sense
INJURED - sounds normal and grammatically correct, but makes little sense
Aphasia
difficulty saying words
Split-brain procedure
severs callosum, structure that connects the 2 hemispheres of the brain
Split-brain purpose
reduce severe epilepsy symptoms
Split-brain cortex specialization
2 halves of brain - hemispheres have different function + abilities
work together to help think + feel
Contralateral hemispheric organization
brain is cross-wired:
- left body = right side of brain
- right body = left side of brain
Functional plasticity
move functions from a damaged area of the brain to other undamaged areas
Structural plasticity
actually change its physical structure as a result of learning
MRI
- detailed pic of soft tissues + brain
- frequent imaging test of brain + spinal cord
- high definition of one moment
fMRI
- blood flow + different parts of brain
- blood flow shows areas of brain that are working hardest (appear brighter)
- control actions + abilities
- movie + still photographs that show activity
EEG
- measures electrical activity
- find changes in brain activity that aid in diagnosing brain conditions (seizure, epilepsy, brain tumors, brain damage etc.)
Lesion
- destroys tiny clusters of normal/defective brain-cells
- brain areas are relevant for certain tasks by recognizing deficiencies in performance caused by lesion in a specific region
Case study (involving brain research)
in-depth study into 1 person who has a unique brain injury to look out the relationship between the behavior and the brain