Neuro Physiology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Glial Cells
Non-excitable cells that support and protect the CNS and PNS
-Functions → protect, nourish, guide developing neurons, aid neural synapses
CNS
Where are these types of glial cells located?
-Oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, microglial cells, pericytes
PNS
What are these types of glial cells located?
-Satellite cells, Schwann cells
Neurons
Excitable cells that initiate and transmit electrical and chemical signals
-Synthesize, package, and release neurotransmitters
-Produce and conduct action potentials along the axon
CNS, metabolic, connective, capillaries, ionic, PNS, autonomic, astrocytes
Neuroglia of the CNS and PNS: Astrocytes and Satellite Cells
-Astrocytes
Star-shaped cells that are the largest and most common ___ neuroglia
Provides structural and ________ support in the nervous system
_________ tissue support to neurons
Forms end feet on ___________ in the BBB, role in molecule transport
Regulates _______ concentration of the ECF
-Satellite cell
Located in the ___
Surround sensory and ________ neurons and function to similarly to __________
ventricles, choroid, CSF, immune, antigen-presenting, health, plaques, debris
Neuroglia of the CNS and PNS: Ependymal Cell and Microglia
-Ependymal Cell
Line the ________ and central canal
Form the ______ plexus
Produce and circulate ___ for the brain and spinal cord
-Microglia
Function as resident _______ cells in the CNS
Exhibit both phagocytic and ______-________ functions
Also plays a role in maintaining overall brain ______ → find ______ and damages neurons / synapses to remove ______ and promote tissue repair
contractile, endothelial, tight
Neuroglia of the CNS and PNS: Pericytes
-_________ cells
-Surround __________ cells
-Help form and maintain _____ junctions of the BBB
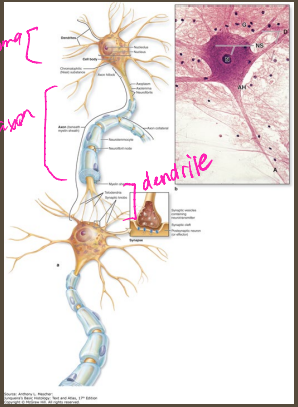
soma, away, impulses, multipolar
Neurons
-Make up functional units of the CNS and PNS
-Components:
____ → cell body
Axon → carries action potentials _______ from the soma
Dendrites → receive _________ from other neurons
-Classification → __________ (MC), bipolar, unipolar, or anaxonic
insulating, quickly, Ranvier, salutatory, location, oligodendrocytes, many, Schwann
Neurons and Myelin
-Myelin → fatty, _________ membrane that allows action potentials to travel more ________ (10x faster) along neurons
-Current is focused by nodes of ________, creating _________ conduction
-Different structure depending on location within the nervous system
CNS → _____________; ____ axons
PNS → ________ cells; one axon
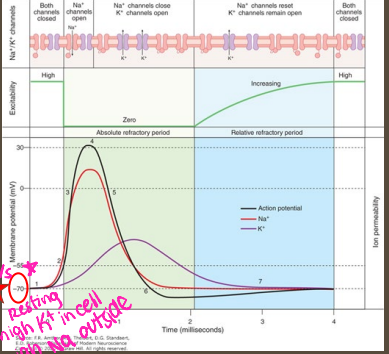
action potentials, axon, opening, sodium, unidirectionally, 70, 55
Neurons
-Communicate via generation of nerve impulses AKA _____ ___________
-Self-regenerative signals that propagate along the ____ to initiate some type of response
-Mediated by _________/closing of voltage-gated _________ channels
-Move ___________, one way only
-resting membrane potential is -__ mV, -__ mV is the all or nothing threshold
communication, synapse, activation, hormones, electrical, gap, directly, chemical, neurotransmitters, common
Neuronal Impulse Transmission
-Neurotransmission is the process by which ___________ occurs within the nervous system. It occurs at a _______, which is a space between the pre-synaptic neuron and post-synaptic target
-Mediates many effects including __________ of muscle contraction and secretion of __________ from glands
-2 mechanisms:
_________ synapses → utilizes ___ junction channels, pre-synaptic current flows ________ into post-synaptic neuron
________ synapse → utilizes _____________, much more ______ than electrical synapses in mammalian nervous system
depolarization, calcium, cleft, post-synaptic, neuron, muscle, junction
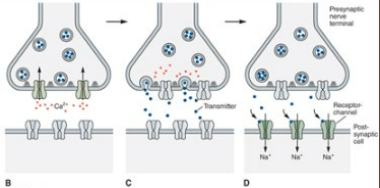
Chemical Synapse Impulse Transmission
-Transmission Process
____________ of pre-synaptic nerve terminal by _________ → release of neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters diffuse across the _____ → binding and activation of receptors on the _____-________ target
-CNS → presynaptic axon and another ________
-PNS → neuron and target _______/gland cell
Often called a _________
signal, GABA, serotonin, modulatory
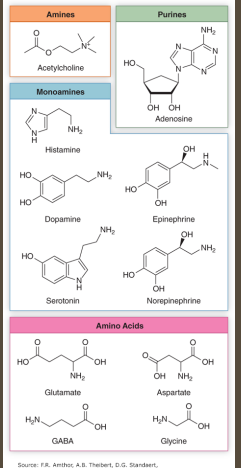
Neurotransmitters
-Molecules that carry a ________ from one nerve to another nerve or cell type
-Important NTs → glutamate, ____, acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and ________
-Properties → excitatory, inhibitor, __________. Short or long-lasting time course
excitatory, dopamine, reward, motor, motivation, mood
Dopamine
-Monoamine
-_________ and inhibitory → receptor dependent
-Acts on ___________ receptors (D1-D5)
-Very important in the _______ system
-Functions → regulates ______ control, reward and ____________ pathways, prolactin inhibition, and _____ regulation
modulatory, adrenergic, attention, stress, hormonal, rate, glucose
Norepinephrine and Epinephrine
-Catecholamine; ______________
-Acts on _________ receptors (alpha and beta) → binds to both, but one usually has a higher affinity
-Functions
Norepinephrine → _________, arousal, ______ response, autonomic regulation
Epinephrine → mainly ___________, mediating fight-or-flight responses (heart ____, BP, _______ mobilization)
modulatory, 5HT, mood, appetite, GI
Serotonin
-Monoamine
-___________
-Acts on ___ receptors, which can be inhibited by a lot of different substances
-Functions → ______ regulation, sleep-wake cycle, ________, pain perception, __ motility
excitatory, nicotinic, acetylcholinesterase, somatic, sympathetic, PNS
Acetylcholine
-Amine
-________ and modulatory, acts on muscarinic and _________ receptors
-Degraded by ______________ in the nerve terminal
-Location/Roles → NT of ________ efferent neurons, utilized by ___________ preganglionic neurons (adrenal medulla and sweat glands)
-Major NT of the ___
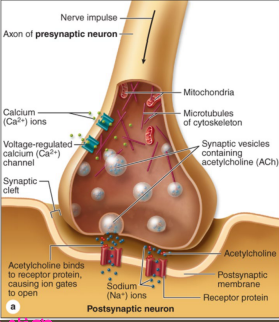
ligand, neuromuscular, autonomic, excitatory
Cholinergic Receptors: Nicotinic Receptors
-_______ gated ion channels
-Locations → skeletal muscle at the ____________ junction, ________ ganglia (SNS and PNS)
-5 sub-types
-Always __________
g-coupled, CNS, parasympathetic, inhibitory, heart, excitatory
Cholinergic Receptors: Muscarinic Receptors
-_-_________ protein receptors
-Locations → ___ and _____________ effector organs
-Excitatory and ___________ (receptor dependent)
M2 (_____) → inhibitory, hyperpolarize
M3 (smooth muscle, glands) → __________, depolarize
inhibitory, GABA, abundant, excitability, sedation, anxiety
GABA
-Amino acid
-_________
-Acts on ____ receptors (A and B)
-Most _________ inhibitory NT in the brain
-Functions → reduces neuronal _________, promotes ________, motor control, and ______ reduction
-Brainstem required
excitatory, CNS, ionotropic, glutamate, common, learning, most
Glutamate
-Amino acid
-Excitatory → most abundant _________ NT in the ___
-Acts on __________ (NMDA, AMPA, kainate) and metabotropic ___________ receptors
-Most _________ NT in the brain
-Functions → synaptic plasticity, memory, __________, excitatory signaling in ____ brain circuits
Glutamate
Learning, memory, primary excitatory NT in the CNSA
Acetylcholine
Muscle contraction (NMJ) / autonomic nervous system (CNS)
GABA
Main inhibitory NT in brain, reduces neuronal excitability/stress
Dopamine
Motor control, reward, motivation, mood
Norepinephrine
Arousal, attention, stress response
Epinephrine
Similar to norepi, effects in spinal cord, thalamus, hypothalamus
Serotonin
Mood, sleep, appetite, pain regulation, modulates other NTs action
Histamine
Wakefulness, arousal, attention, inflammatory response
afferent, stimuli, sensory, CNS, unipolar
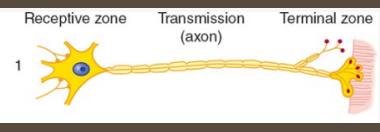
Sensory Neurons
-_________; enable perception of _______ outside the CNS
-Transmit _______ information from receptors in the skin/eyes/ears to ___ for processing
-Receptor → sensory neuron → CNS
-Typically _______ and often myelinated
efferent, movement, motor, muscles, multipolar
Motor Neurons
-________; facilitate ____________/physiologic responses
-Transmit _____ commands from CNS to _________ or glands to elicit a response
-CNS → motor neuron → effector tissue
-Typically __________ and heavily myelinated
voluntary, skeletal, conscious, acetylcholine
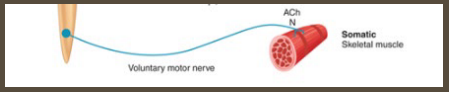
Somatic Neurons
-Function under _________ control, typically innervates _________ muscle
-Enable __________ perception/movement
-Utilize _____________ at neuromuscular junction
involuntary, respiration, neurotransmitters, homeostasis
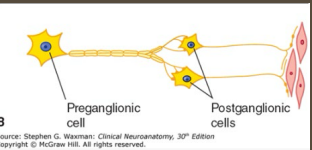
Visceral Neurons
-Control the ___________ or unconscious activity of glands
-Regulates cardiac muscle and most smooth muscle (___________ and digestion)
-Various _____________ utilized (Ach, norepi) depending on pathway
-Functions to maintain _______________
excitatory, norepinephrine, sweating, inhibits, close, responses, emergencies
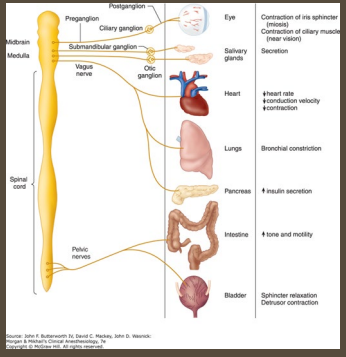
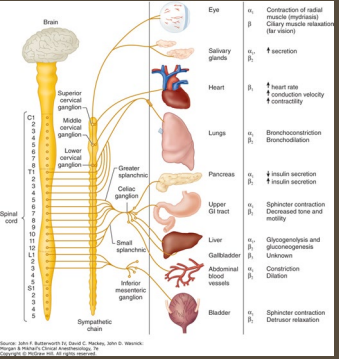
Sympathetic Nervous System
-”Fight or flight”
-Generally _________ → the primary NT is _____________
Increases heart rate and BP, bronchodilation, mydriasis, and stimulates ___________
_______ digestion and urination
-Ganglia _____ to the CNS
-Controls body __________ during __________ and excitement
opposes, acetylcholine, decreases, increases, effector, homeostasis
Parasympathetic Nervous System
-Rest and digest
-________ sympathetic nervous system
Primary NT is ___________
__________ HR and BP, bronchoconstriction, and miosis
__________ peristalsis and salivation, promotes digestion and urination
-Ganglia near ________ organs
-Maintains ______________