3.1.3.7 - Forces between molecules
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Permanent dipole-dipole forces
In substance made of molecules with permanent dipoles, will be weak electrostatic forces of attraction between
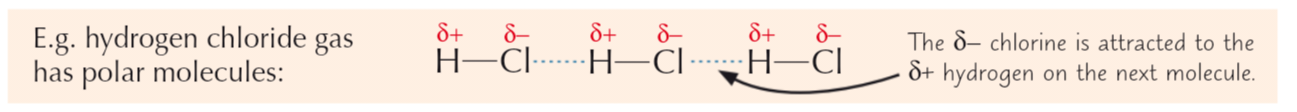
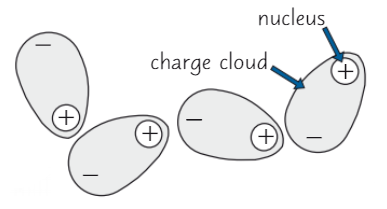
Van der Waals forces
Electrons in clouds always moving quickly
At any moment, electrons are likely to be more one side than the other - at this point, atom has temporary dipoleTemp dipole can cause another temp dipole in opposite direction on neighbouring atom - dipoles attracted to each other
2nd dipole can cause dipole on 3rd atom
Because electrons constantly moving, dipoles being created/destroyed all the time
Overall effect = atoms attracted to each other
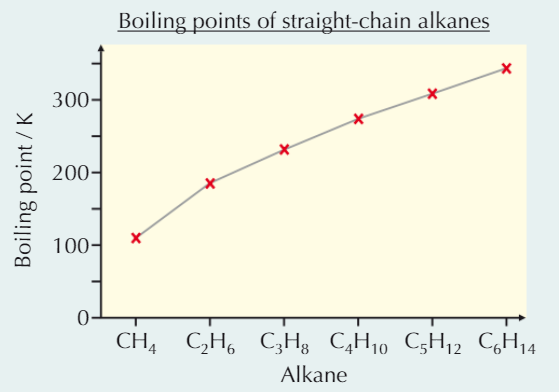
Stronger Van der Waals forces = (higher/lower) boiling point
HIGHER
Larger molecules → larger electron cloud → stronger VdW
Molecule shape affects VdW strength
Long, straight molecules lie closer together than branched → closer molecules = stronger VdW
When boiling, need to overcome intermolecular forces
Stronger intermolecular forces → more energy → higher BP
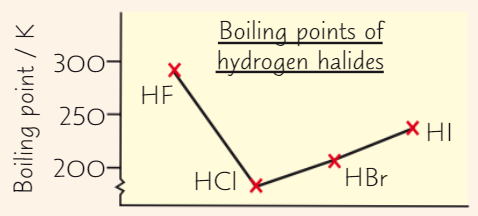
Hydrogen bonding only happens when hydrogen is covalently bonded to ___
Fluorine, nitrogen or oxygen
How does hydrogen bonding form?
F, N, O very electronegative → attract bonding electrons away from H atom
Bond is polarised
→ H has such high charge density (because it’s small) that H atoms form weak bonds with LP on F, N, O
Molecules with hydrogen bonding usually contain ___ groups
-OH or -NH
Water + ammonia both have H bonding

Substances with hydrogen bonds have ___ melting and boiling points
HIGHER
Because of extra energy needed to break hydrogen bonds