Unit 12: Misc Topics
1/246
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
247 Terms
Describe the architecture of an atom
The atom is the basic building block that makes up all matter
Protons (+) charge
Neutrons (neutral) charge
Electrons (-) charge
Protons and neutrons are in the center of the atom (nucleus)
Electrons orbit the nucleus in the electron cloud
How do you determine an atom's atomic number?
By the number of protons in the nucleus
How do you know if an atom carries a charge?
Neutral if # electrons = # protons
Positive if # electrons < # protons
Negative if # electrons > # protons
What is a charged atom called?
Positive: cation
Negative: anion
What is an ionic bond?
Involves a complete transfer of valence electron(s) from one atom to another\nThis leaves one atom with a (-) charge and the other with a (+) charge\nIonic bonds are common with metals, acids, and bases
What is a covalent bond?
Involves the equal sharing of electrons. The strongest type of bond.\nSingle: 1 pair shared\nDouble: 2 pairs shared\nTriple: 3 pairs shared
What is a polar covalent bond?
'in-between" type of bond.
Atoms share electrons, but the electrons tend to remain closer to one atom than the other.
This creates a polar molecule, where one area of the molecules is relatively positive, and the other is relatively negative.
What are Van der Waals forces?
A very weak intermolecular force that holds molecules of the same type together.
Electrons (-) are in constant motion. This creates a temporary partial (+) and (-) charges at different parts of the molecule at any given time. The net result is that electron-rich areas of one molecule will be attracted to electron poor areas of another molecule.
The weakest type of molecular attraction.
Dalton's Law
Law of Partial Pressures
The total P is equal to the sum of the partial P exerted by each gas in the mixture.
P = P1 + P2 + P3...
Examples of how Dalton's law can be used in the OR
Calculate the partial P of an unmeasured gas
Calculate the total P
Convert partial P to volumes %
Convert volumes % to a partial P
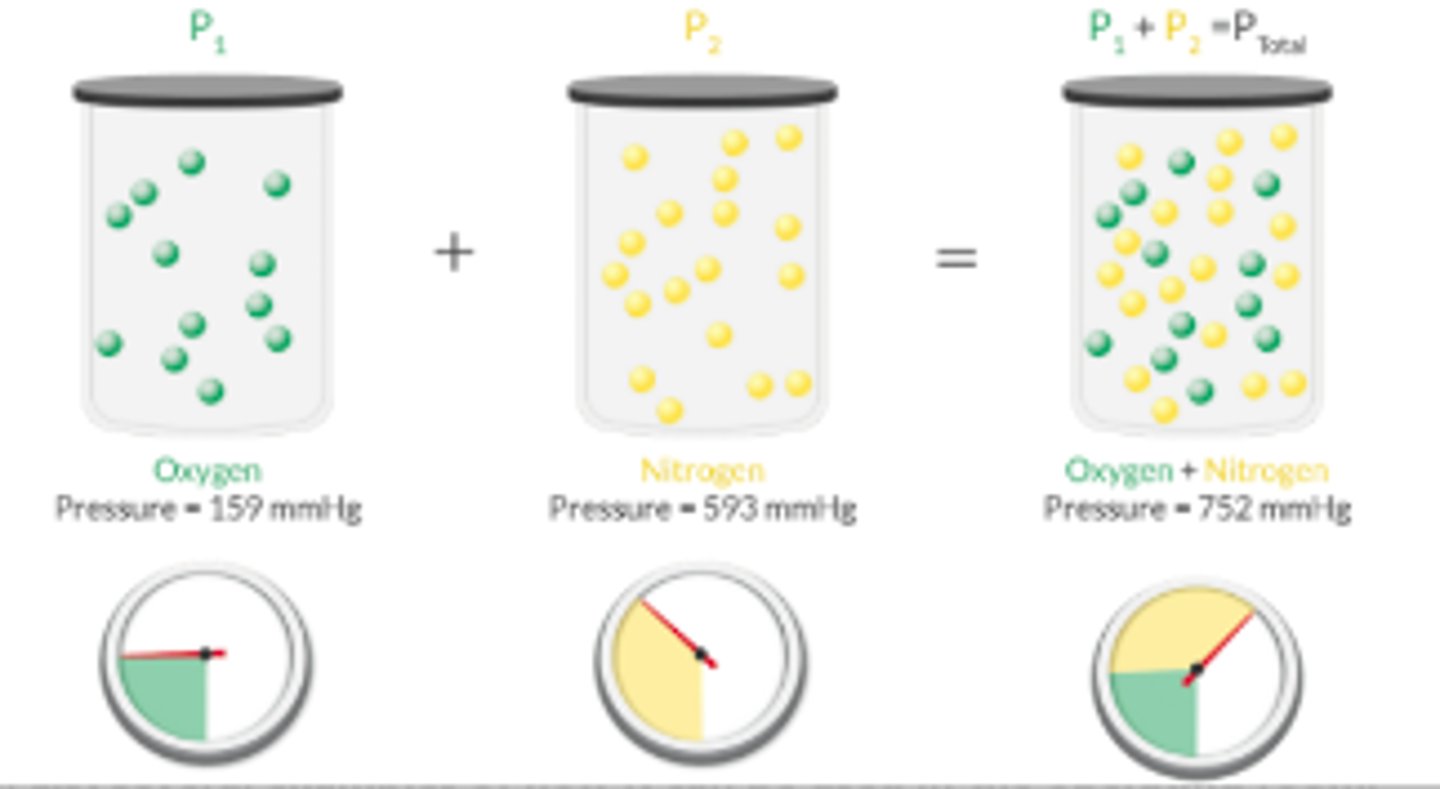
At sea level, the agent monitor measures the end-tidal sevo as 3%. What is the partial P of sevo in the exhaled tidal volume?
This is an application of Dalton's law of partial P.
partial P = volumes % x total P
Partial P = 0.03 x 760 mmHg
= 22.8 mmHg
What is atm at sea level?
760 mmHg
Define Henry's Law
At a constant T, the amount of gas that dissolves in a solution is directly proportional to the partial P of that gas over the solution.
The higher the gas P, the more of it will dissolve into a liquid.
↑ T = ↓ solubility
↓ T = ↑ solubility
How can Henry's Law be used in the OR?
Anesthetic emergence is prolonged in the hypothermic Pt
Dissolved O2 in the O2 carrying capacity equation (CaO2)
Describe Fick's Law of diffusion.
A transfer rate of gas through a tissue medium
Directly Proportional to:
-partial P difference (driving force)
-diffusion coefficient (solubility)
-membrane surface area
Inversely Proportional to:
-membrane thickness
-molecular weight
List clinical examples of Fick's Law of diffusion.
Diffusion hypoxia
A pt w/COPD has a ↓ alveolar surface area + therefore has a slower rate of inhalation induction
Calculation of CO
Drug transfer across the placenta
Compare + Contrast Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's Laws
Boyle's: inverse relationship
-one variable ↑, the other ↓
-one variable ↓, the other ↑
Charles's + Gay-Lussac's: direct relationships
-one variable ↑, the other ↑
-one variable ↓, the other ↓
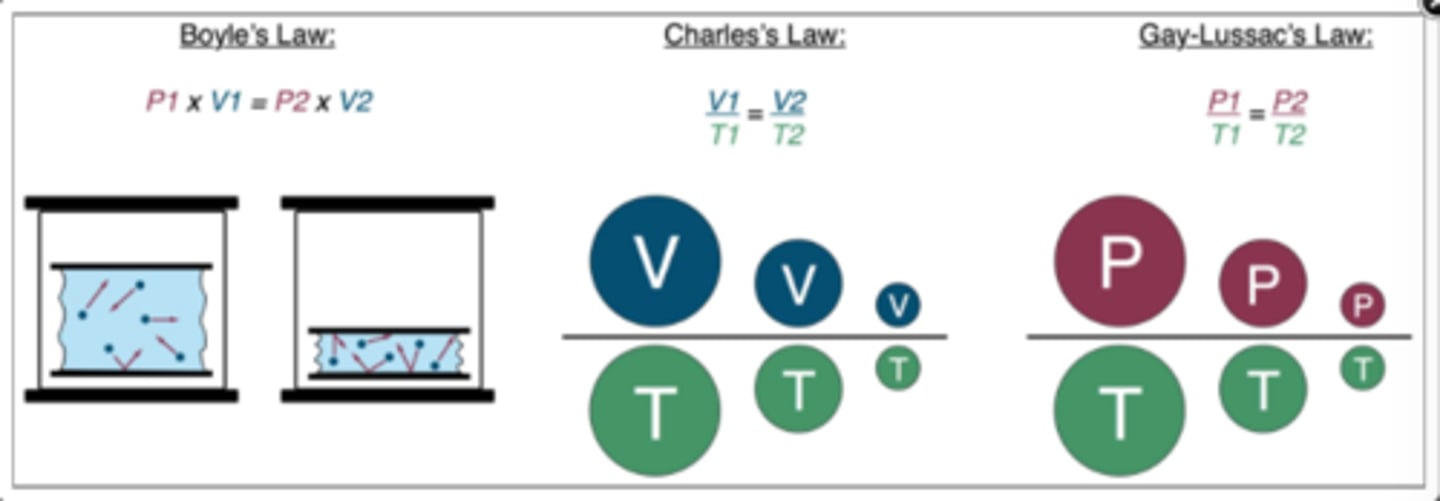
List several examples of how Boyle's Law can be applied in the OR
P x V
Diaphragm contraction ↑ Vt
Pneumatic bellows
Squeezing an ambulance bag
Using bourdon P gauge to calculate how much O2 is left in a cylinder
List an example of how Charles's Law can be applied in the OR
V / T
LMA cuff ruptures in an autoclave
List an example of how Gay-Lussac's law can be applied in the OR
P / T
O2 tank explodes in a heated environment
What is the fxn of the ideal gas law?
unifies all 3 laws into a single equation, where:
PV = nrT
P = Pressure
V = Volume
n = number of moles
r = constant 0.0821 L-atm/K/mole
T = Temperature
Define Ohm's Law
Current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance. We can adapt Ohm's law to understand fluid flow
current = voltage diff/resistance
- or -
Flow = P gradient / resistance
How is Poiseuille's Law r/t Ohm's Law?
It is a modification of Ohm's that incorporates vessel diameter, viscosity, and tube length
Q = 丌r⁴△P / 8ηL
How do △ in r affect laminar flow (x2, x3, x4, and x5)?
Altering the r exhibits the greatest impact on flow.
r = 1⁴: 1 x 1 x 1 x 1 = 1
r = 2⁴: 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16
r = 3⁴: 3 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 81
r = 4⁴: 4 x 4 x 4 x 4 = 256
How can we apply Poiseulle's Law to the administration of a unit of PRBCs?
We can deliver it faster if we:
-↑ the r w/a lg bore IV
-↑ the P gradient w/a P bag +/or ↑ the height of the IV pole
-↓ the η by diluting the blood with 0.9& NaCl +/or running it through a fluid warmer
-↓ the length by not using longer tubing than needed
What does Reynold's number tell you?
3 types of flow:
Re < 2000: laminar dependent on η
Re > 4000: turbulent dependent on density
Re 2000-4000: transitional
Re = (density x diameter x velocity) / η
Explain how understanding Reynold's number helps you treat status asthmaticus.
Pt suffers from ↑ a.w. resistance → ↑ turbulence + WOB
-can improve flow by having pt inhale lower density gas
-O2/helium mixture (heliox) improves Re by ↓ density
-the key is we convert turbulent flow to laminar flow
--Helium does not improve flow if it is already laminar
Explain Bernoulli's principal.
describes a relationship b/t the P and velocity of a moving fluid or gas
-if velocity is high, then the P exerted on the walls of the tube will be low
-if velocity is low, then the P exerted on the walls of the tube will be high
Discuss Bernoulli's principal in the context of a river.
when the river is wide, the water moves slowly. When it becomes narrow, the water moves much faster. This is bc the same V of water is moving through the wide + narrow parts of the river at any given time.
Slower water = higher P on bank
Faster water = lower P on bank
Explain Venturi effect.
Application of Bernoulli's principal. airflow in a tube moves past the point of constriction, the P at the constriction ↓, and if the P in the tube falls below atm P, then the air is entrained into the tube.
Adjusting the diameter of the constriction allows for control of the P drop + the amount of air that is entrained.
Examples of Venturi effect.
Jet ventilator
Venturi
Nebulizer
Explain the Coanda effect.
Describes how a jet flow attaches itself to a nearby surface + continues to flow along that surface even when the surface curves away from the initial jet direction.
Examples of Coanda effect.
Wall hugging jet of MR
Water that follows the curve of a glass
How do you calculate the Law of Laplace for a sphere?
T = (P x r) / 2
Ventricle: T = (P x r) / 2 x thickness
Ex: alveolus, ventricles, saccular aneurysm
How do you calculate the Law of Laplace for a cylinder?
T = (P x r)
Ex: blood vessels, Ao aneurysm
What is the yearly max for radiation exposure?
Non-pregnant: 5 rem
-eye + thyroid are most susceptible to injury
Pregnant: 0.5 rem or 0.05 rem/mothn
-fetus is most susceptible to injury
List 3 ways to protect yourself from radiation exposure.
Distance
Duration
Shielding
How can we apply the inverse square law to radiation exposure?
amount of exposure is inversely r/t the square of the distance of the source.
intensity = 1 / distance²
What is boiling point, + how is it affected by atm P?
T at which a liquid's vapor P = atm P
↑ P atm = ↑ boiling point
-ex: hyperbaric O2 chamber
↓ P atm = ↓ boiling point
-ex: high altitude
Define specific heat.
Amount of heat required to ↑ the T of 1 g of a substance by 1ºC
Define Vapor Pressure
in a closed container, molecules from a volatile liquid escape the liquid phase + enter the gas phase.
The molecules in the gas phase exert P on the walls of the container.
Define Vaporization
Process by which a liquid is converted to a gas. This requires energy (heat)
Define heat of vaporization
Number of calories required to vaporize 1mL of liquid
Explain latent heat of vaporization.
number of calories required to convert 1g of liquid to a vapor without a T change in the liquid. Let's apply this to what happens inside the vaporizer.
Apply latent heat of vaporization of anesthetic vapor inside of a vaporizer.
-Anesthetic liquid in the vaporizer exerts a vapor P inside the vaporization chamber. This means some of the agent exists as a liquid, and some exists as a gas.
-FGF over the anesthetic liquid, carrying away some of the agent that exists in the gas phase.
-this cools the remaining liquid, which reduces the vapor P of that liquid. Therefore, there are fewer anesthetic molecules that enter the gas phase.
-The net result is a ↓ in vaporizer output.
-Modern vaporizers compensate for this T △
Explain the Joule-Thompson effect in the context of gas cylinders.
A gas stored at high P that is suddenly released spaces from its container into a vacuum. It quickly loses speed as well as a significant amount of kinetic energy, resulting in a fall in T. This explains why an O2 cylinder that is opened quickly feels cool to the touch.
Conversely, rapid compression of a gas intensifies its kinetic energy, causing the T to rise.
What is an adiabatic process?
A process that occurs without gain or loss of energy (heat).
Ex: a very rapid expansion of a gas were there is no transfer of energy
What is critical T?
Highest T where a gas can exist as a liquid, regardless of the P applied to it.
Critical T + Gas Cylinders
N2O 36.5ºC (liquid in cylinder)
O2 -119ºC (gas in cylinder)
in the OR, only N2o + CO2 have critical T above room T.
What is Critical P?
minimum P required to convert a gas into a liquid at its critical T.
T conversion formulas
C = K - 273.15
K = C + 273.15
C = (F - 32) x 5/9
F = (C x 1.8) + 32
Define P
P = Force / area
↑ area = ↓ P
↓ area = ↑ P
P conversion factors
1 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 1 bar = 100kPa = 1033 cm H2O = 14.7 lb/in²
1 mmHg = 1.36 cm H2O
1 cm H2O = 0.74 mmHg
What is Avogadro's number?
1 mole of any gas is made of up 6.023 x 10^23 atoms
A mole of gas = the molecular wt of that gas in grams
If a molecule is diatomic (O2), you much account for both atoms
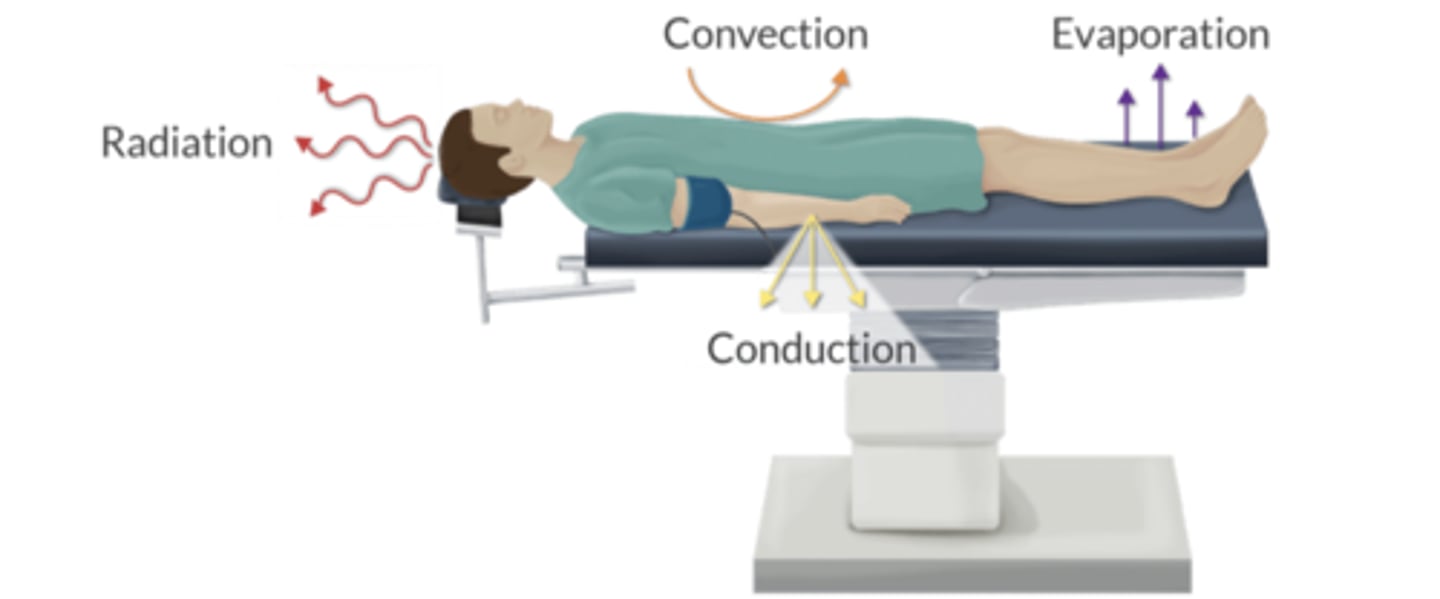
What are the 4 mechanisms of heat transfer? Rank them from most to least important.
Radiation ~ Infrared (60%)
Convection ~ Air (15-30%)
Evaporation ~ Water loss (20%)
Conduction ~ Contact (<5%)
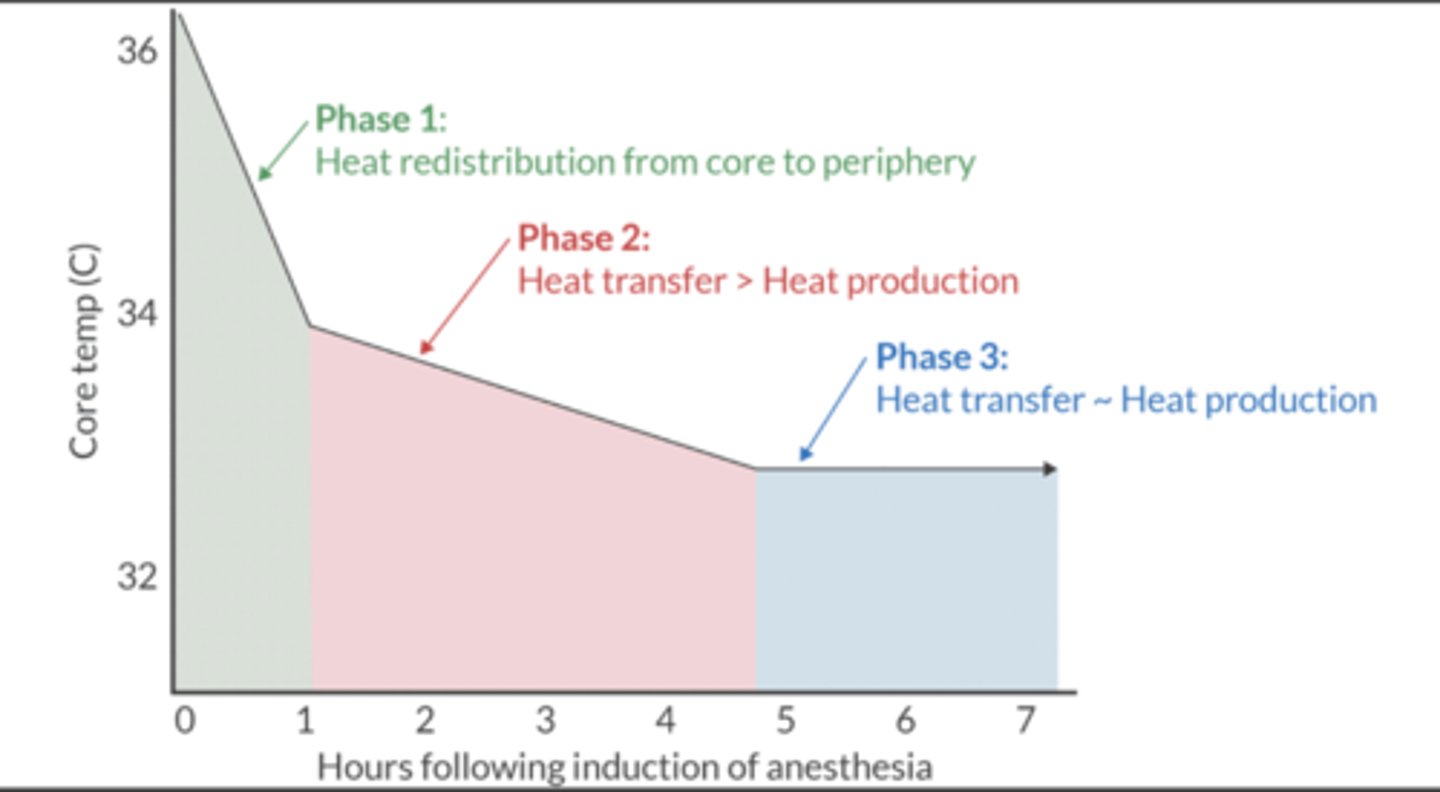
Explain the 3 stages of intra-op heat transfer.
When no attempts are made to maintain normothermia, heat transfer follows a triphasic curve.
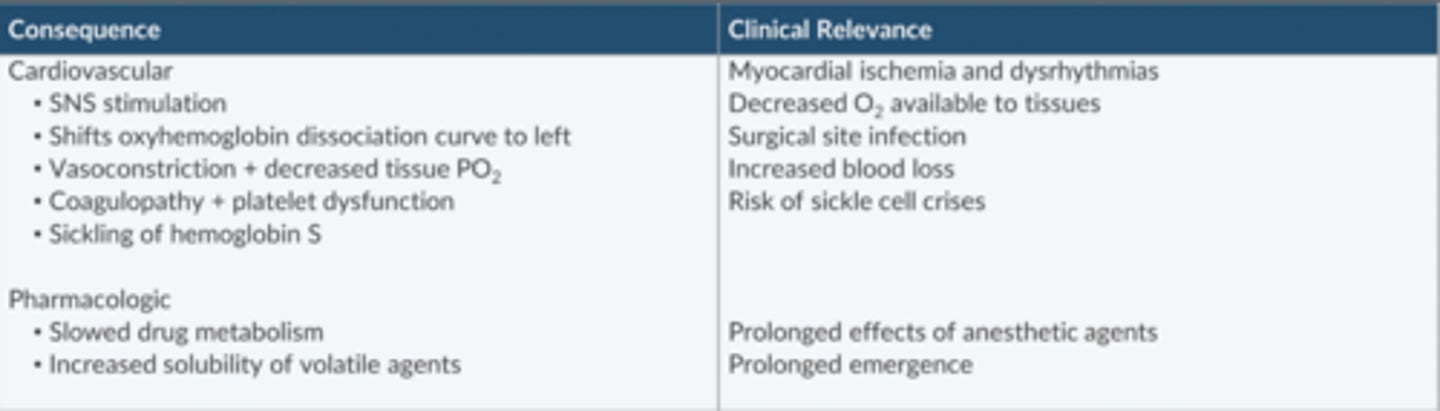
What are the consequences of peri-op hypothermia?
CV
-SNS stim
-Oxyhegb curve shifts L
-Vasoconstriction + ↓ tissue PO2
-Coagulopathy + Plt dysfxn
-Sickling of hgb5
Pharmacologic
-slowed drug metabolism
↑ solubility of volatile agents
Name 3 drugs that can be used to treat post-op shivering.
↑ O2 consumption 400-500%
↑ risk MI + infarction
Meperidine (kappa)
Clonidine (⍺2)
Precedex (⍺2)
When is hypothermia a good thing?
O2 consumption is ↓ 5-7% for every 1ºC ↓ in T
-cerebral ischemia
-cerebral aneurysm clipping
-TBI
-CPB
-Aox
-carotid endarterectomy
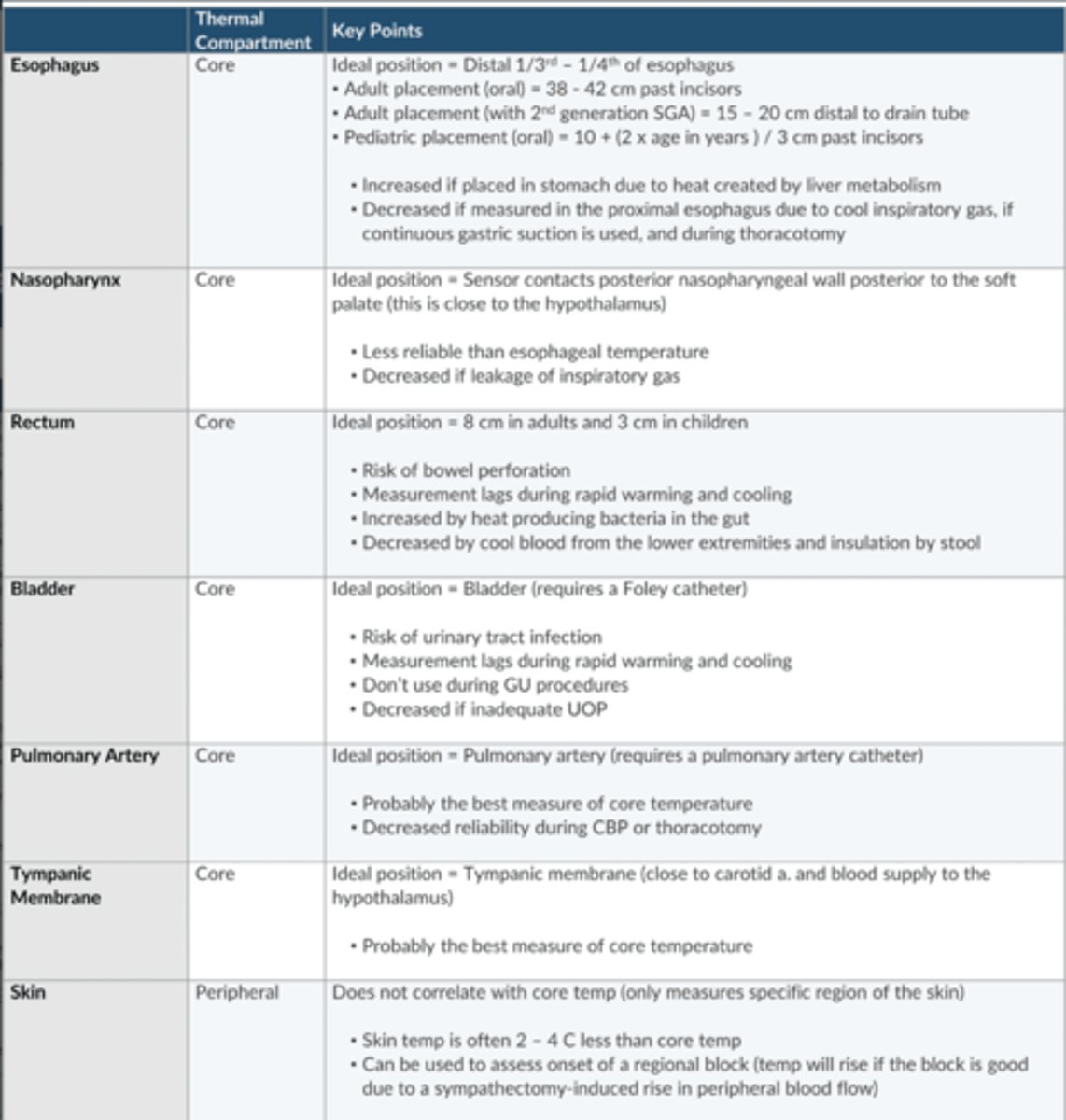
In which region of the esophagus should an esophageal T probe be placed?
Distal 1/3-1/4 of the esophagus
38-42 cm past the incisors
How does esophageal T probe misplacement affect the reading?
↑ is placed in the stomach 2/2 heat created by liver metabolism
↓ is placed in the proximal esophagus 2/2 cool inspiratory gas
Various sites of T measurement
Esophagus (core)
Nasopharynx (core)
Rectum (core)
Bladder (core)
PA (core)
Tympanic membrane (core)
Skin (peripheral)
What are the 3 ingredients required to produce a fire?
Fuel: ETT, drapes
Oxidizer: O2, N2O
Ignition Source: cautery, laser
Steps to take during an a.w. fire
1. Stop ventilation + remove ETT
-DO NOT squeeze bag to extubate: blow torch effect +/or push debris into the lower a.w.
2. Stop the flow of all a.w. gases
3. Remove other flammable material from the a.w.
4. Pour water or saline into the a.w.
5. If the fire isn't extinguished on 1st attempt, then use CO2 extinguisher
Steps to take after an a.w. fire
1. Re-establish ventilation by mask. Avoid supplemental O2 or N2O
2. Check ETT for damage - fragments may remain in the a.w.
3. Perform bronch to inspect for a.w. injury or retained fragments
What does "laser" stand for?
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
How is laser different from ordinary light?
Monochromatic (single wavelength)
Coherent (oscillates in the same place)
Collimated (exists as a narrow parallel beam)
What is the difference b/t a long and a short wavelength laser? + clinical consequences
Long Wavelength:
-absorb more water + do NOT penetrate deep into tissue
-cornea is at risk
Short Wavelength:
-absorbs less water + penetrates deeper into tissue
-retina is a risk
What color goggles must be worn for each type of laser?
CO2 = Clear
Ruby = Red
Argon = Amber
Nd:YAG = Green
Discuss the flammability of ETT in the context of laser surgery on the airway.
Most ETT are flammable (PVC, red rubber, silicone)
Laser reflective tape is no longer advised
-Smarter to use laser resistant ETT (is NOT laser proof! Cuff is not resistant)
-many resistant tubes have 2 cuffs (proximal: dye, + distal)
-resistant tubes do not ↓ risk of fire when cautery is used.
The cuff is the most vulnerable component
Fill cuff with Saline (dye optional).
-helps absorb the thermal energy
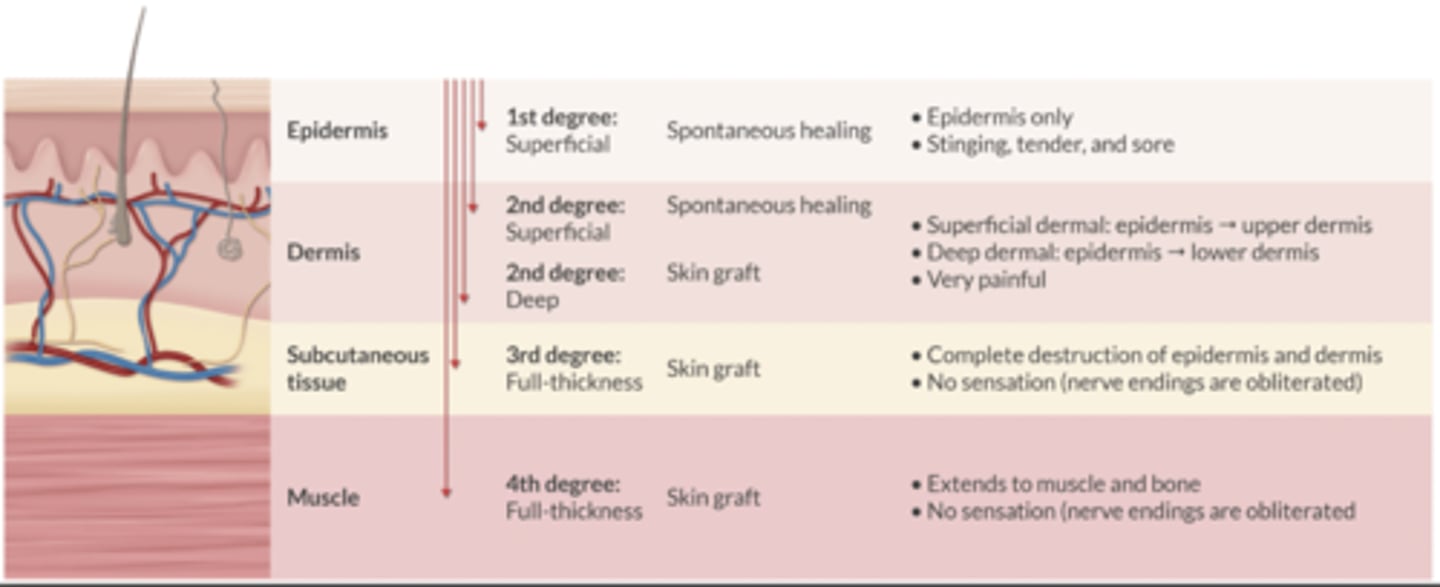
Describe the 4 degrees of burns. Which require a skin graft?
1st Degree: superficial
-Spont healing
2nd Degree: superficial
-Spont healing
2nd Degree: deep
-Skin graft
3rd Degree: full-thickness
-Skin graft
4th Degree: Full-thickness
-Skin graft
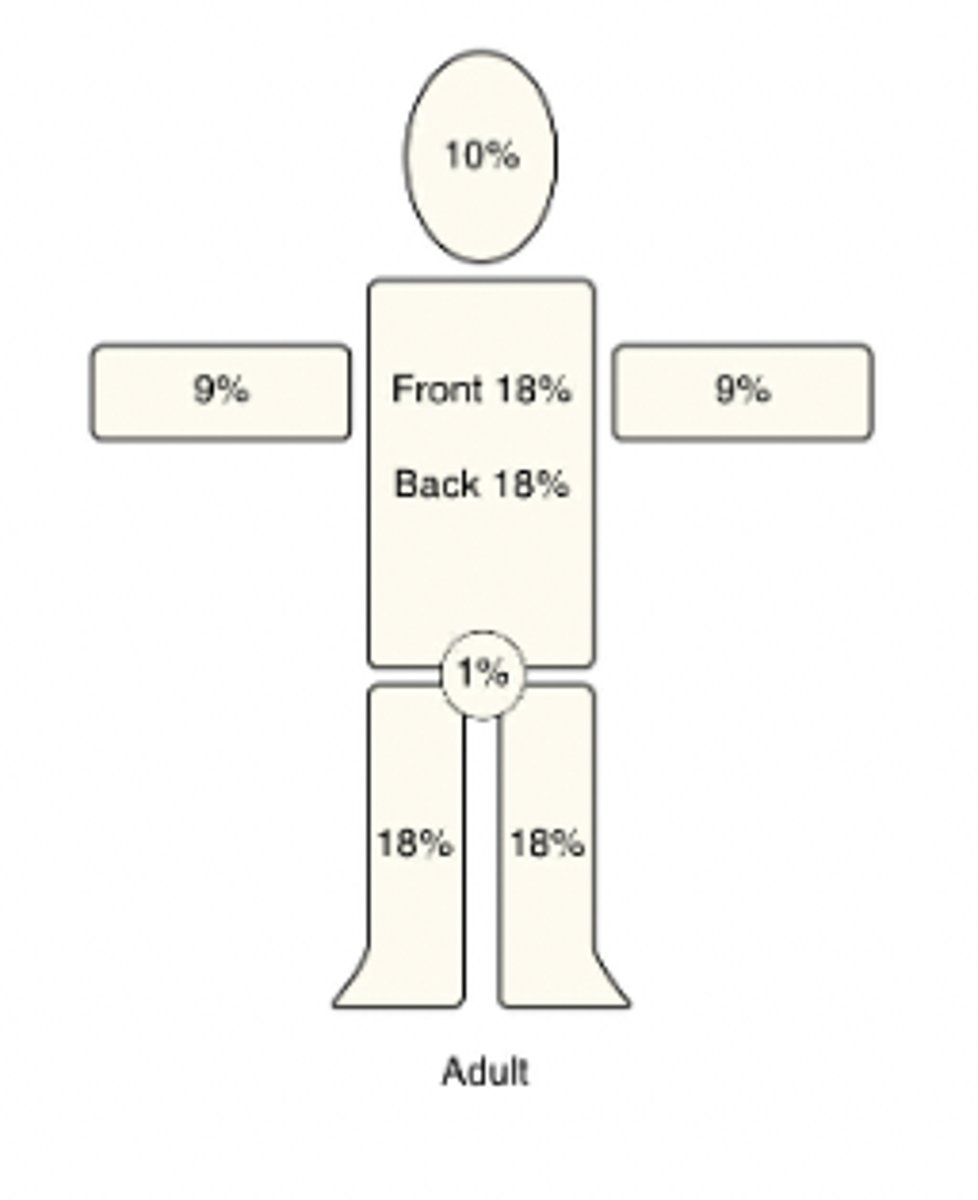
Describe the Rule of 9s + how it applies to an adult
Burn severity is a fxn of depth + fraction of TBSA consumed
-TBSA is divided into areas representing 9% (or multiples of 9%)
-Due to rounding, the numbers do not = 100
-This concept if important for calculating fluid requirements
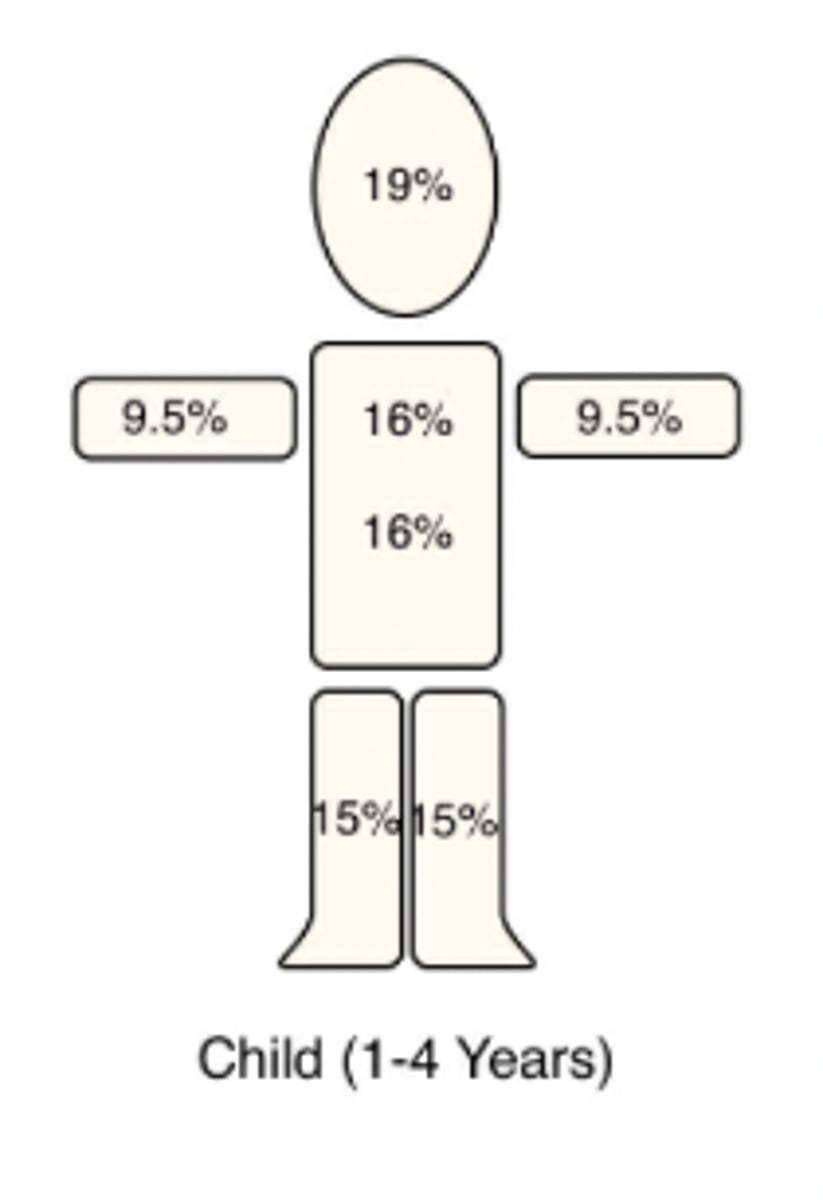
How is the Rule of 9s different for children?
The child's head is 19% of TBSA (9.5% front + 9.5% back)
As a general rule, for every year >1 y/o up to 10 y/o, you can ↓ head SA by 1% + ↑ each leg by 0.5%
Describe the consequences of the capillary leak that occurs after a burn.
Greater w/major burn, inhalation injury, or delay in resuscitation
Consequences
-↑ microvascular permeability → edema formation
-loss of protein-rich IST fluid → ↓ plasma onc P → edema
-loss of IV volume → hypovolemia + shock
-Hypovolemia → hemoconcentration
Why are fluid requirements higher in the first 24 hours after a burn?
Fluid shifts + edema formation are the greatest in the first 12 hours and begin to stabilize by 24 hrs.
-avoid albumin in 1st 24hrs; lost to IST space
-hemolysis is common in initial stage, however, profound hypovolemia → hemoconcentration
-rising hob in the first few days suggest inadequate volume resuscitation
-consider transfusion if Hvt < 20 (healthy pt) or Hct < 30 (pre-existing cv dz)
Describe the Parkland formulas for resuscitation in burn patients.
1st 24hrs:
-Crystalloid = 4mL x TBSA % x kg (1/2 1st 8 hrs, then 1/2 next 16hrs)
-Colloid = none
2nd 24hrs:
-Crystalloid = D5W @ normal maintenance rate
-Colloid = 0.5mL x TBSA % x kg
Describe the Modified Brooke formula for resuscitation in burn patients.
Differences from Parkland bold
1st 24hrs:
-Crystalloid = 2mL x TBSA % x kg (1/2 1st 8 hrs, then 1/2 next 16hrs)
-Colloid = none
2nd 24hrs:
-Crystalloid = D5W @ normal maintenance rate
-Colloid = 0.5mL x TBSA % x kg
What is an acceptable UOP in a burned pt? Is this different in children or pts who've suffered a high voltage electrical injury?
Adult = > 0.5mL/kg/hr
Child = > 1mL/kg/hr
High Voltage = > 1-1.5mL/kg/hr
Myoglobinemia + Burns
Result of extensive m damage following high voltage electrical injury.
nephrotoxic
-needs to be flushed out of the body
Why is the burn patient at risk for abdominal compartment syndrome?
-What is the diagnosis and treatment of this complication?
May result from aggressive fluid resuscitation
Intra-abd HTN: IAP > 20 mmHg or > 12 mmHg + evidence of organ dysfxn
Tx: NMB, sedation, diuresis, abd decompression
Discuss the clinical considerations for the pt w/CO poisoning
-CO binds to Hgb w/an affinity 200x that of O2
-shifts oxyhgb curve to the left (left = love), which impaired offloading of O2 to tissues
-Oxidative phosphorylation is impaired
-Blood cherry red appearance
-SpO2 NOT accurate
-SpO2 may give falsely elevated result
-Tx: 100% FiO2 or hyperbaric O2
Discuss the use of NMB in the Burn Pt
Up-regulation of exntrajunctional R begins after 24 hrs
-Sch safe w/in first 24 hrs
-Sch lethal ↑ K after 24 hrs
-NDNMB dose should be increased 2-3 fold
Describe the physiologic changes that accompany electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
Initial: ↑ PNS activity during tonic phase (lasts ~15s)
Secondary: ↑ SNS activity during clonic phase (lasts several minutes)

Discuss absolute contraindications to ECT
Recent MI (<4-6 months)
-most common causes of death: MI + dysthymias
Recent intracranial Sx (<3 months)
Recent CVA (<3 months)
Brain tumor
Unstable C-spine
Pheochromocytoma
Discuss relative contraindications to ECT
Pregnancy
Pacemaker/ICD
CHF
Glaucoma
Retinal detachment
Severe pulmonary dz
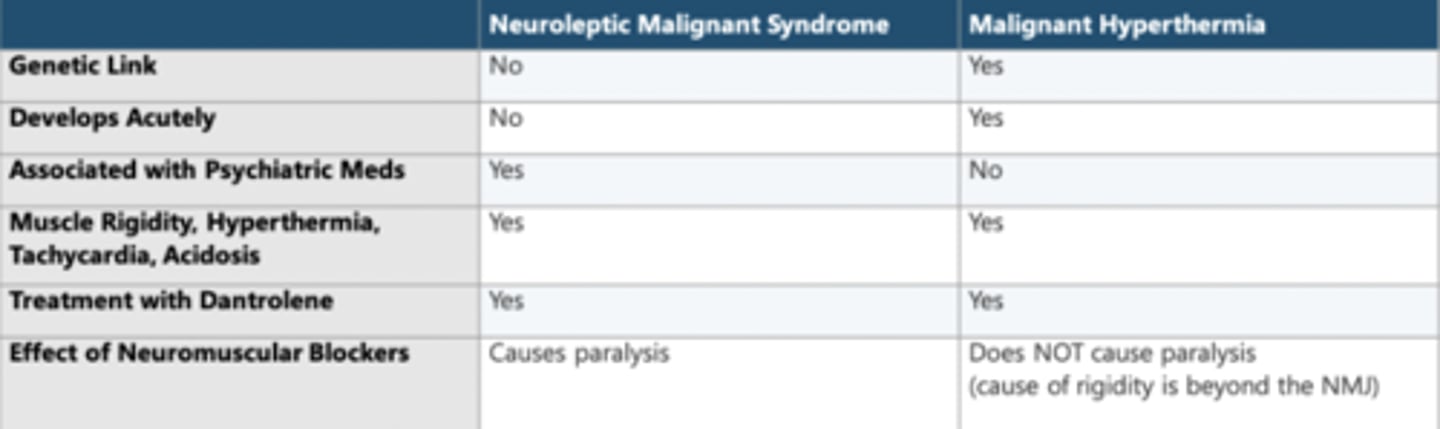
Compare neuroleptic malignant syndrome with malignant hyperthermia.
NMS is caused by dopamine depletion in the basal ganglia + hypothalamus
Causes: DA antagonists or w/d from DA agonists
Tx: Bromocriptime, dantrolene, supportive, ECT
What is the etiology and Tx of Serotonin Syndrome?
Occurs when there
s excess 5-HT activity in the CNS + PNS.
Key drug interactions ↑ risk:
SSRI + Meperidine
SSRI + Fentanyl
SSRI + Methylene Blue
What are the determinants of intraocular pressure? What's the normal value?
Relatively noncompliant compartment containing:
-choroidal BV
-aqueous fluid volume
--humor produced by ciliary process (posterior chamber)
--humor reabsorbed by the canal of Schlemm (anterior chamber)
-extraocular m tone
Normal 10-20 mmHg
Intraoccular perfusion P = MAP - IOP
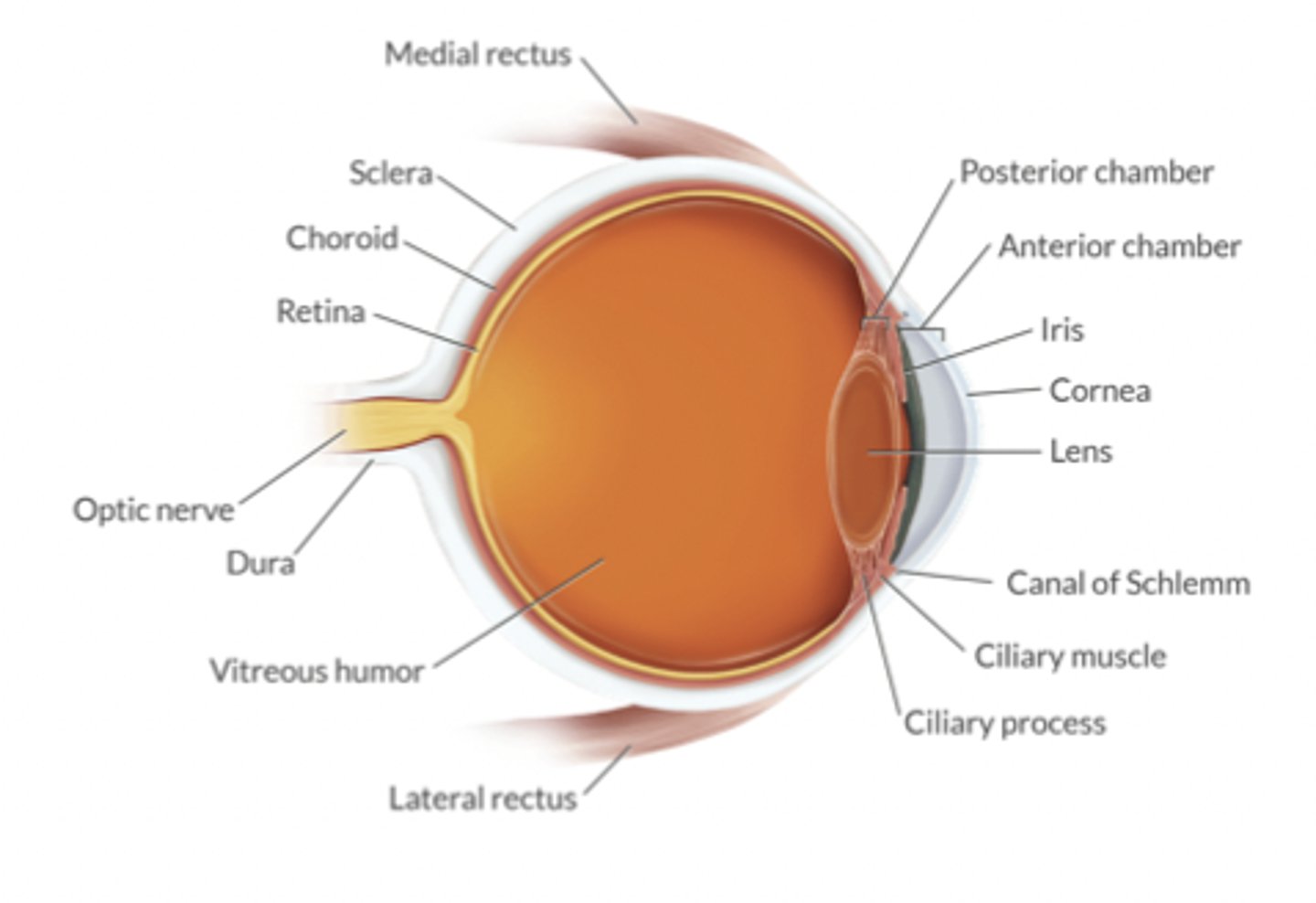
What factors reduce IOP?
Hypocarbia
↓ CVP
↓ MAP
VA
N2O
NDNMB
Propofol
Opioids
Benzos
Hypothermia
What factors increase IOP?
Hypercarbia
Hypoxemia
↑ CVP
↑ MAP
DL/intubation
Straining/coughing
Sch
N2O (if SF6 bubble in place)
Trendelenburg
Prone
External compression by facemask
+/- Ketamine
-causes rotary nystagmus + blepharospasm (avoid)
What is the difference between open and closed angle glaucoma?
Chronically elevated IOP that → retinal a compression
Open: sclerosis of the trabecular meshwork. impairs aqueous humor drainage.
Closed: closure of the anterior chamber. creates mechanical outflow obstruction.
Which drugs reduce aqueous humor production?
Acetazolamide ↓ by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase
Timolol: non-selective BB
Which drugs increase aqueous humor drainage?
Echothiophate: irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor, promotes drainage via canal of Schlemm
-can prolong duration of Sch + ester-type LA
What is strabismus correction? What unique considerations apply to the anesthetic management of these pts?
Corrects misalignment of extra ocular m + re-establish the visual axis.
-↑ risk PONV
-↑ risk of activating the oculocardiac reflex (afferent CN 5 + efferent CN 10)
What pt populations benefit from a TAP block?
-unilateral PNB targets n of anterior and lateral abd wall
-abd procedures (gen, GYN, uro) that involve T9-L1 distribution
-Bilateral blocks req for a midline incision or laparoscopic Sx
Describe the anatomy required to perform a TAP block
Superficial to deep:
-Subq tissue
-External oblique m
-internal oblique m
-transverse abdominis m
-peritoneum
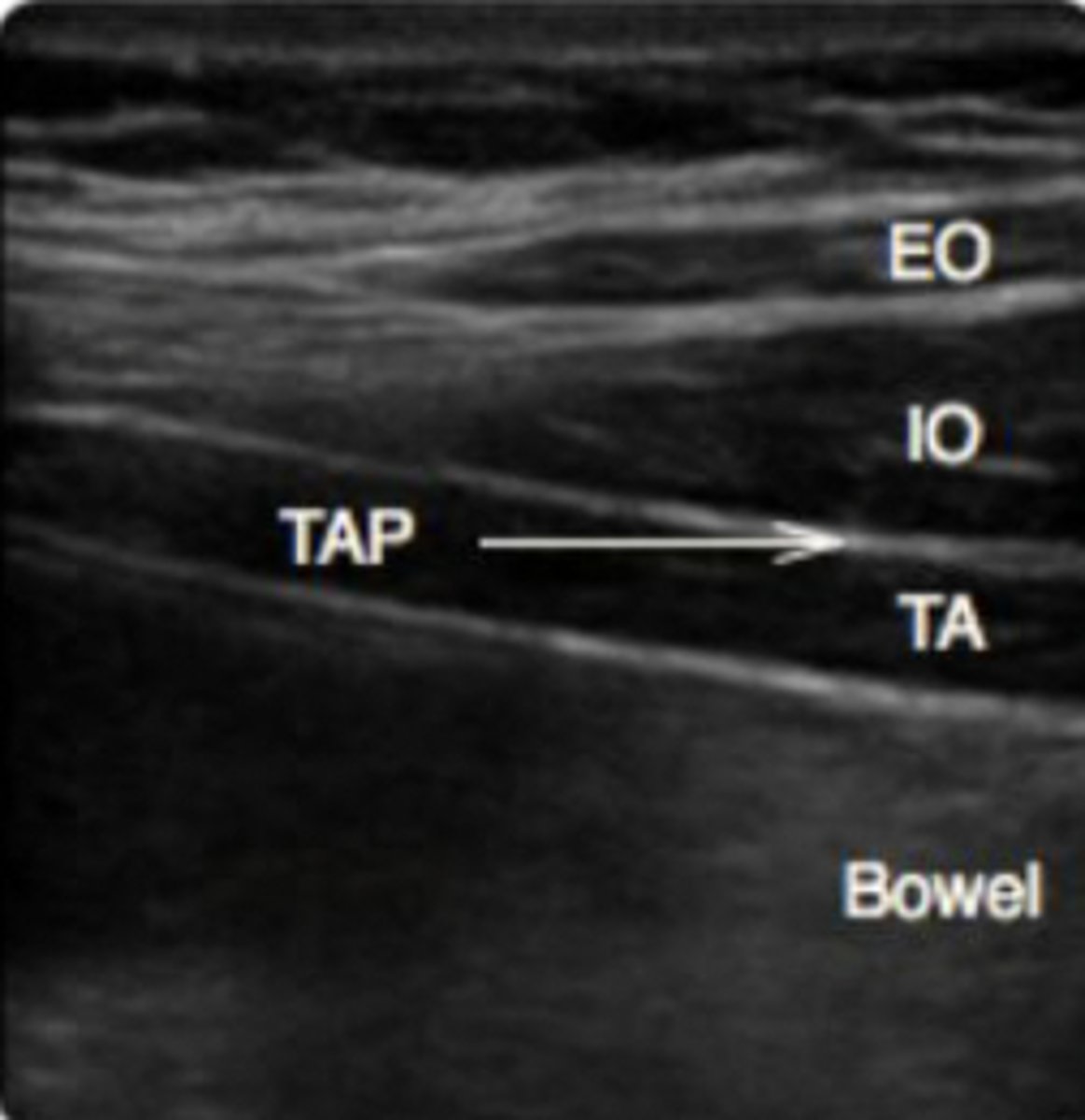
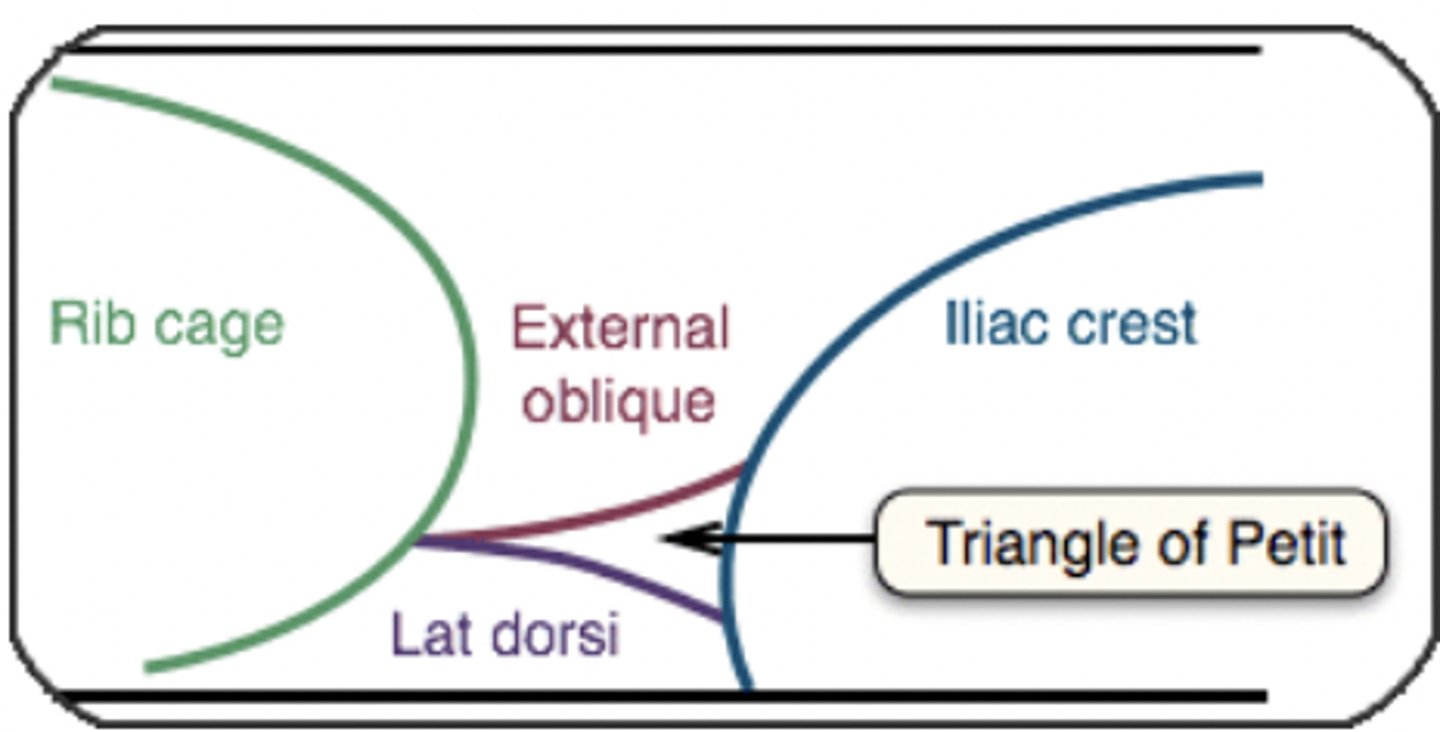
Describe the landmarks required to perform a TAP block
Form triangle of Petit:
-External oblique m
-Latissimus dorsi m
-iliac crest
Define allodynia + give an example
Pain 2/2 a stimulus that does not normally produce pain
Ex: Fibromyalgia
Define dysesthesia and give an example
Abnormal + unpleasant sense of touch
Ex: burning sensation from diabetic neuropathy
Define neuralgia + give an example
Pain localized to a dermatome
Ex: Herpes zoster (shingles)