1. PCR
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
GENOME- DEFINITION
total of all genetic material in an organism
INTRONS AND EXONS
DNA that makes up chromosomes consists of billions of base pairs
but coding regions of DNA that determine protein structures, only make up around 2% of that DNA
EXONS- coding regions
INTRONS- large, non coding regions of DNA
if these are found in genes they are removed from mRNA after transcription, before it is translated
DNA/GENE SEQUENCING
analyse individual strands of DNA or individual genes
gives order of bases that codes for a particular protein in cell
can also be used to identify diff species of living organism
DNA PROFILING
analyse patterns in non-coding areas of DNA and use them to identify individuals
PCR USES- LIST
polymerase chain reaction used for:
genotyping
cloning
mutation detection
sequencing
forensic science, to identify criminals
test paternity
PCR USES
PCR adapts natural process of DNA replication in cells, enabling us to produce larger samples from tiny traces of biological materials
when tiny sample of DNA is increased using PCR to produce a large enough sample for analysis (amplification)
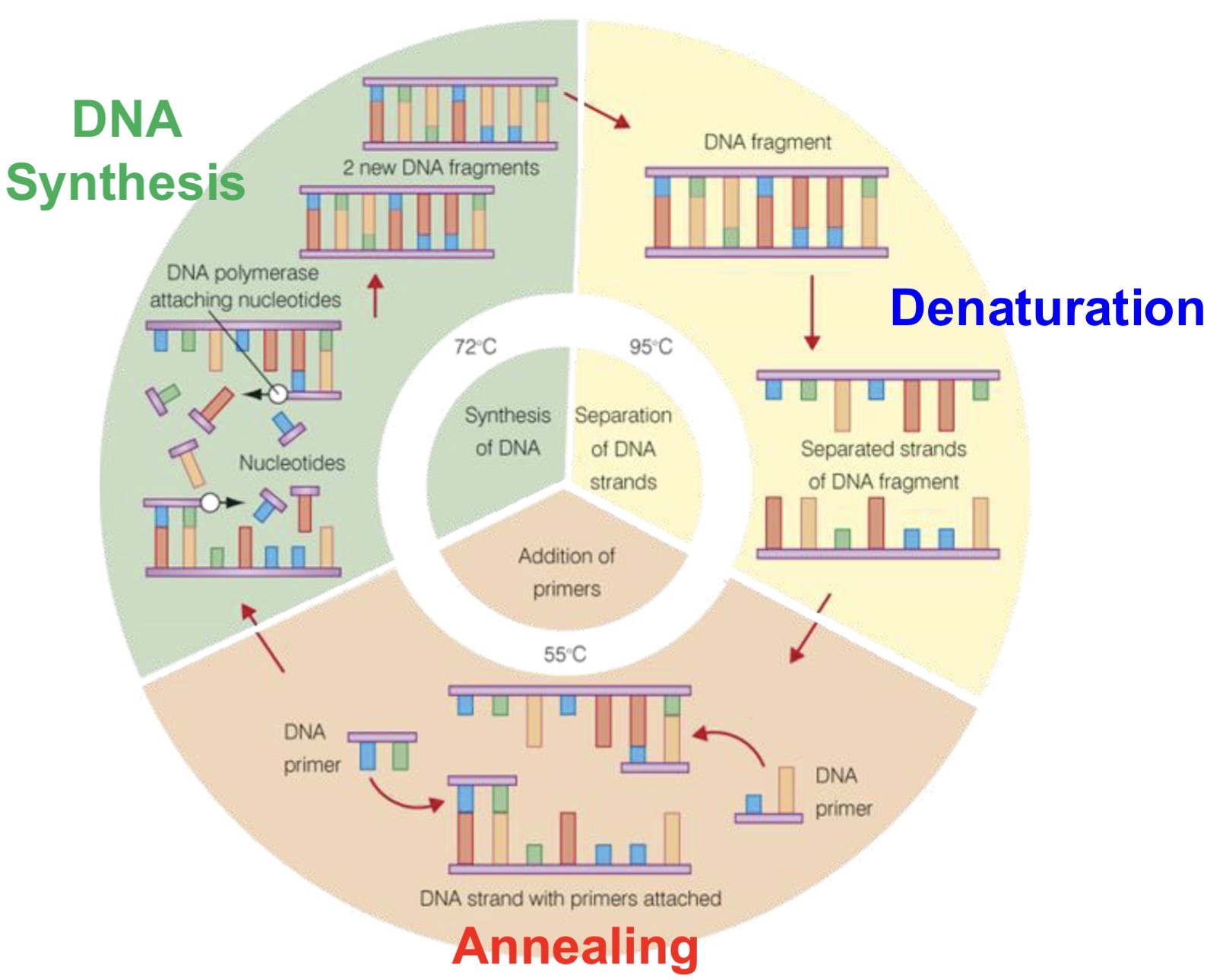
DEVELOPING PCR- ISSUE
to separate DNA strands in PCR the sample DNA needed to be heated to around 90-95°C
but DNA Polymerase is needed and would be denatured by a temp this high
DEVELOPING PCR- SOLUTION
enzymes from a thermophilic bacterium that lives in hot springs is used
enzymes in this bacterium are not denatured at high temps changes needed to allow for DNA replication
PCR- REQUIREMENTS
DNA sample
HEAT STABLE DNA POLYMERASE- enzyme that joins DNA nucleotides together
DNA NUCLEOTIDES - Consisting of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate, and either an A,T,C or G base
PRIMERS
Thermal Cycler machine
PRIMERS
short chain of DNA nucleotides- have a base sequence complementary to the ends of the DNA fragments
mark where DNA fragment is to be extended/built/amplified
PCR- STEPS