Lecture 4: Upper limb II: Scapular Muscles and Axilla
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
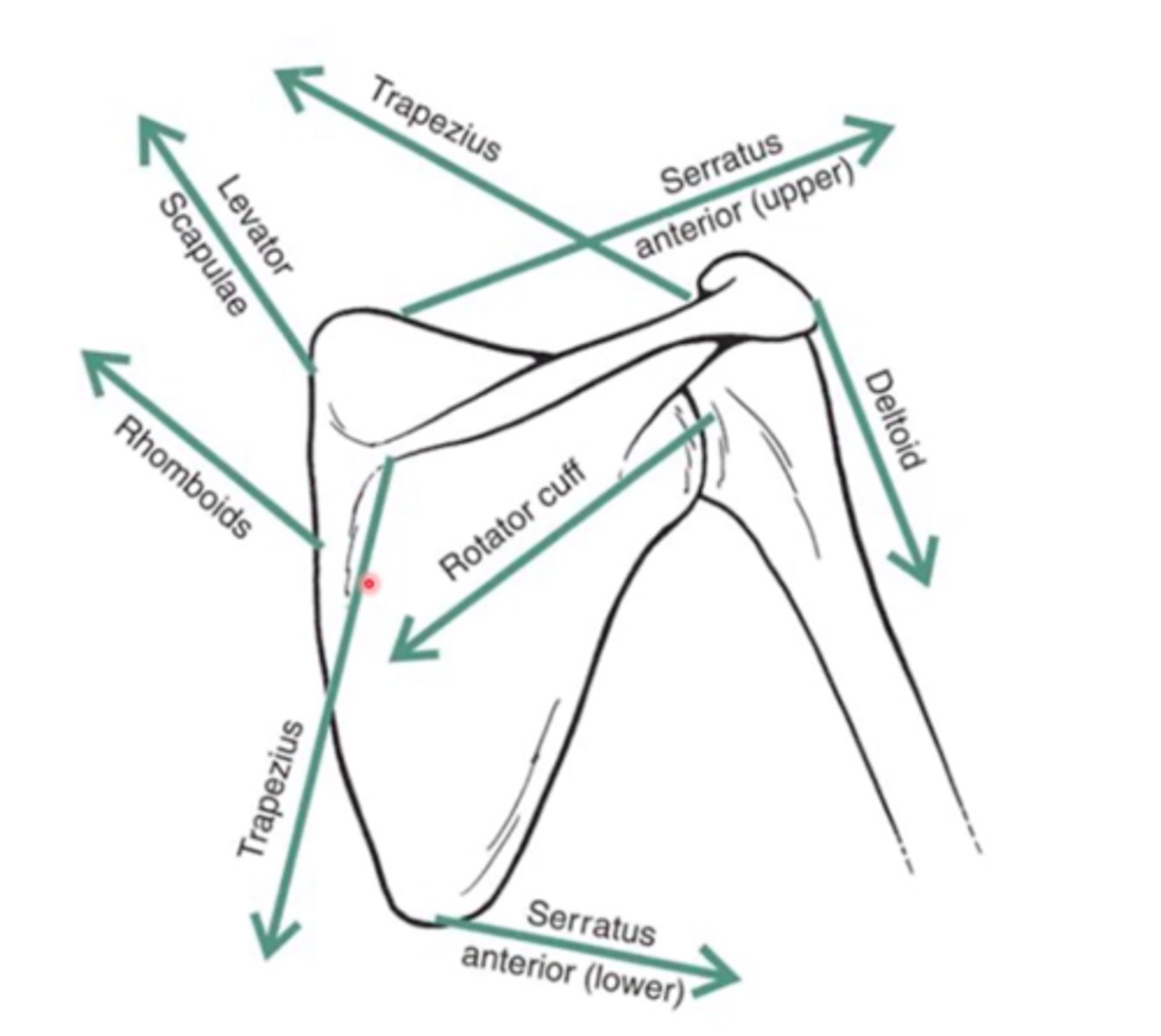
Scapular Muscles
deltoid
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
teres minor
teres major
subscapularis
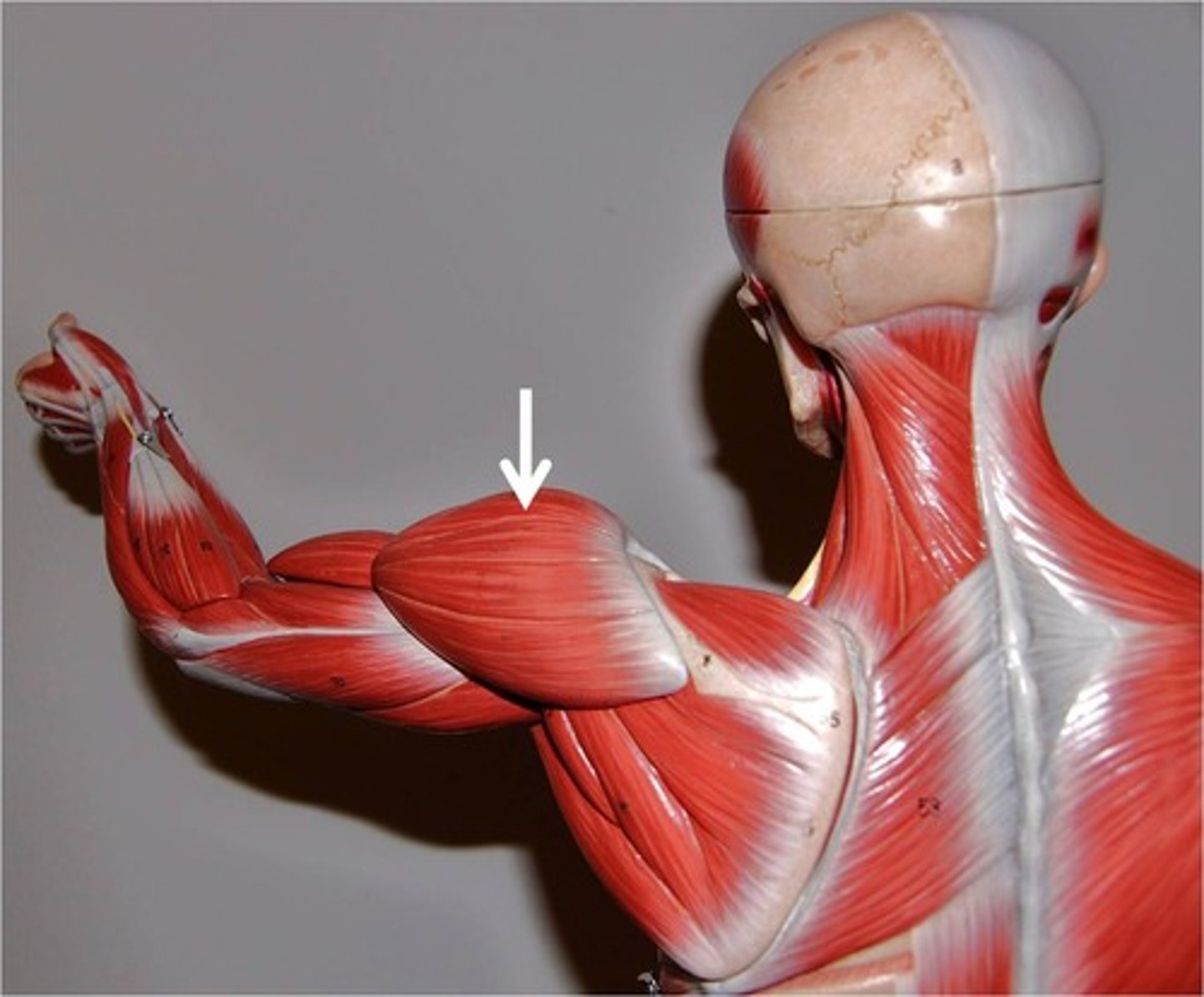
deltoid
Origin- lateral 1/2 of clavicle, acromion, scapular spine
Insertion- deltoid tuberosity
Innervation- axillary
Actions- abduction 15-90 can do everything BUT adduction
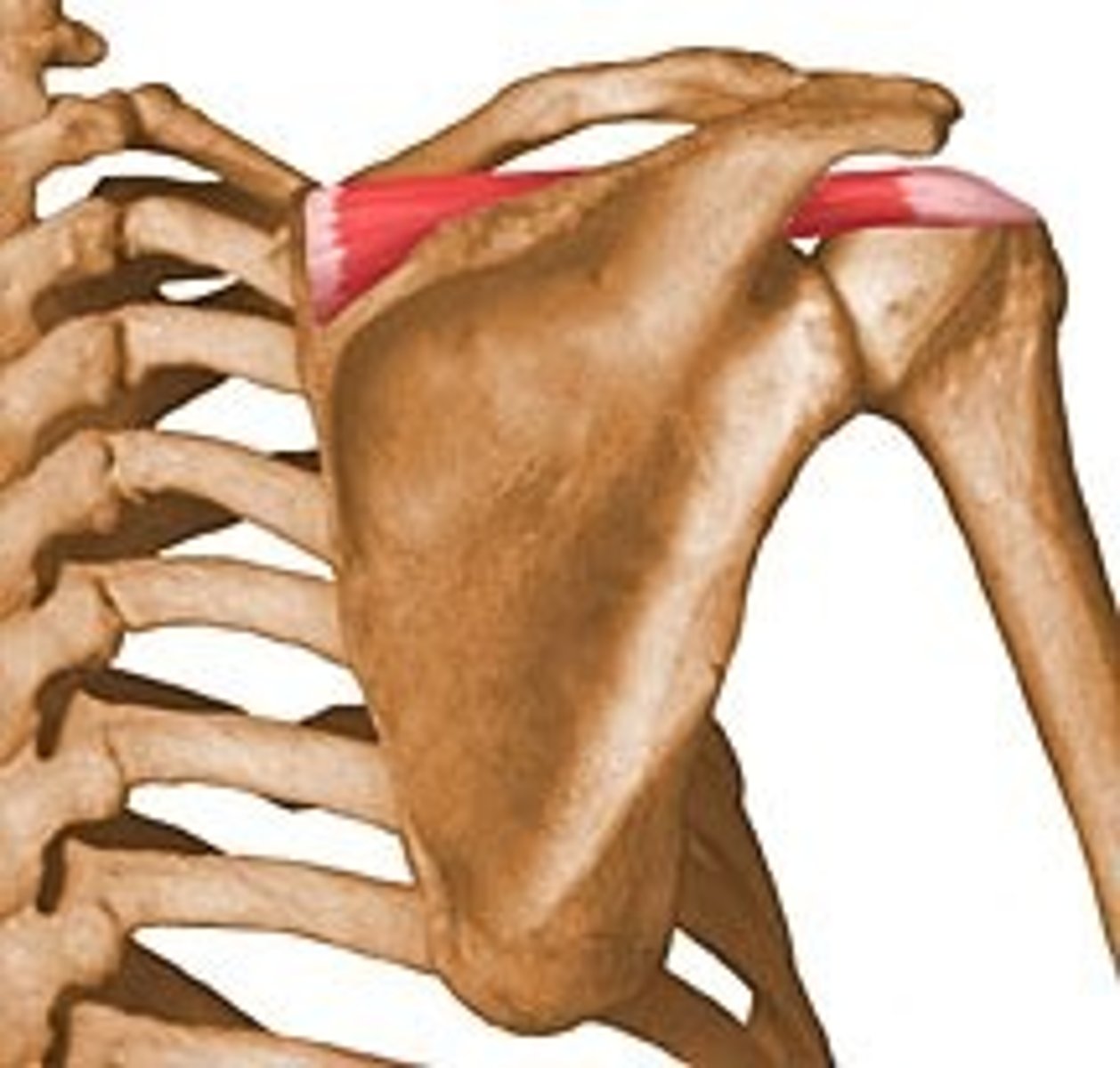
supraspinatus
Origin- supraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion- greater tubercle of humerus
Innervation- suprascapular
Actions-abduction 0-15*
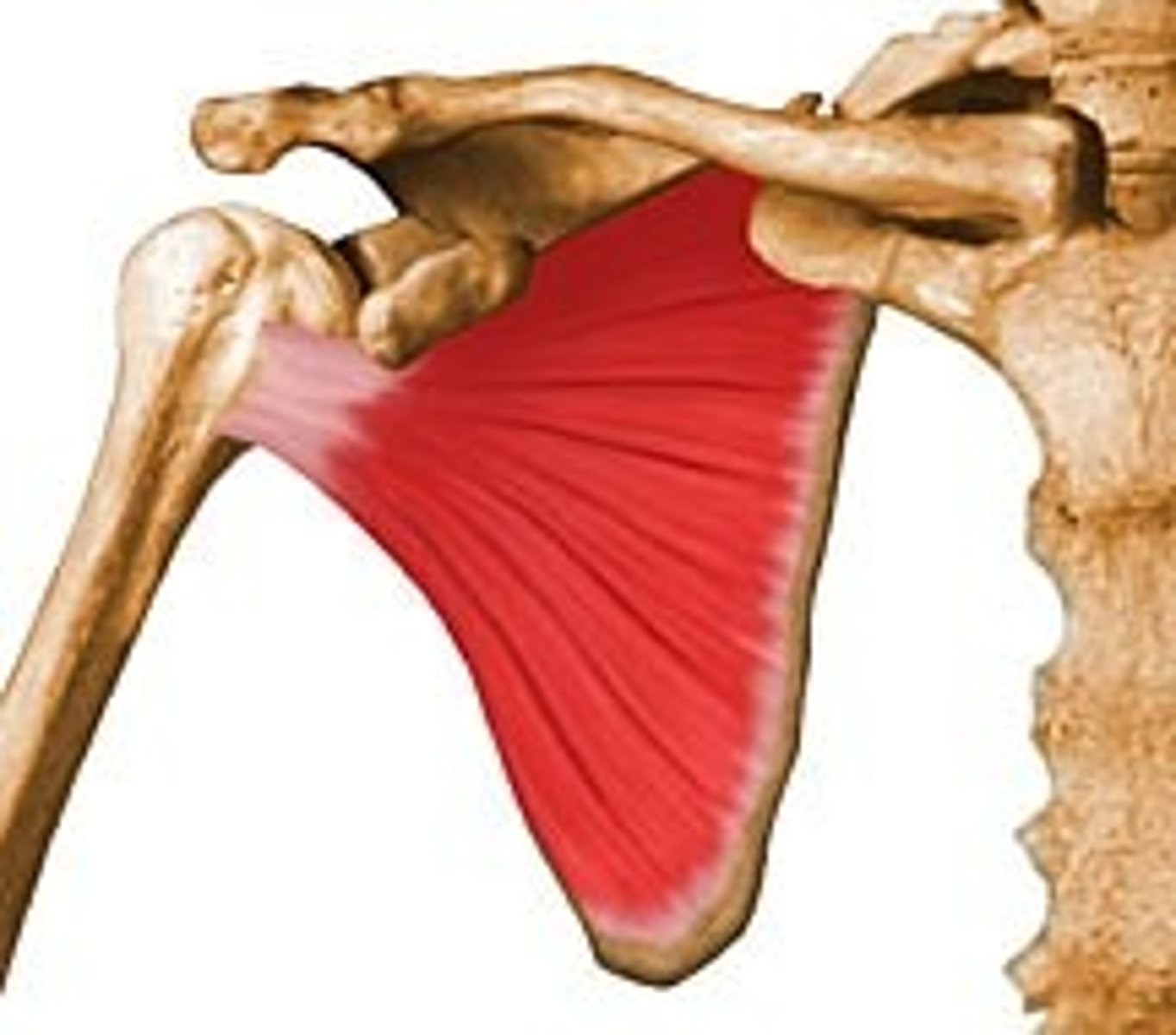
Infraspinatus
Origin- infraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion-greater tubercle of humerus
Innervation-suprascapular
Actions- lateral rotation, adduction
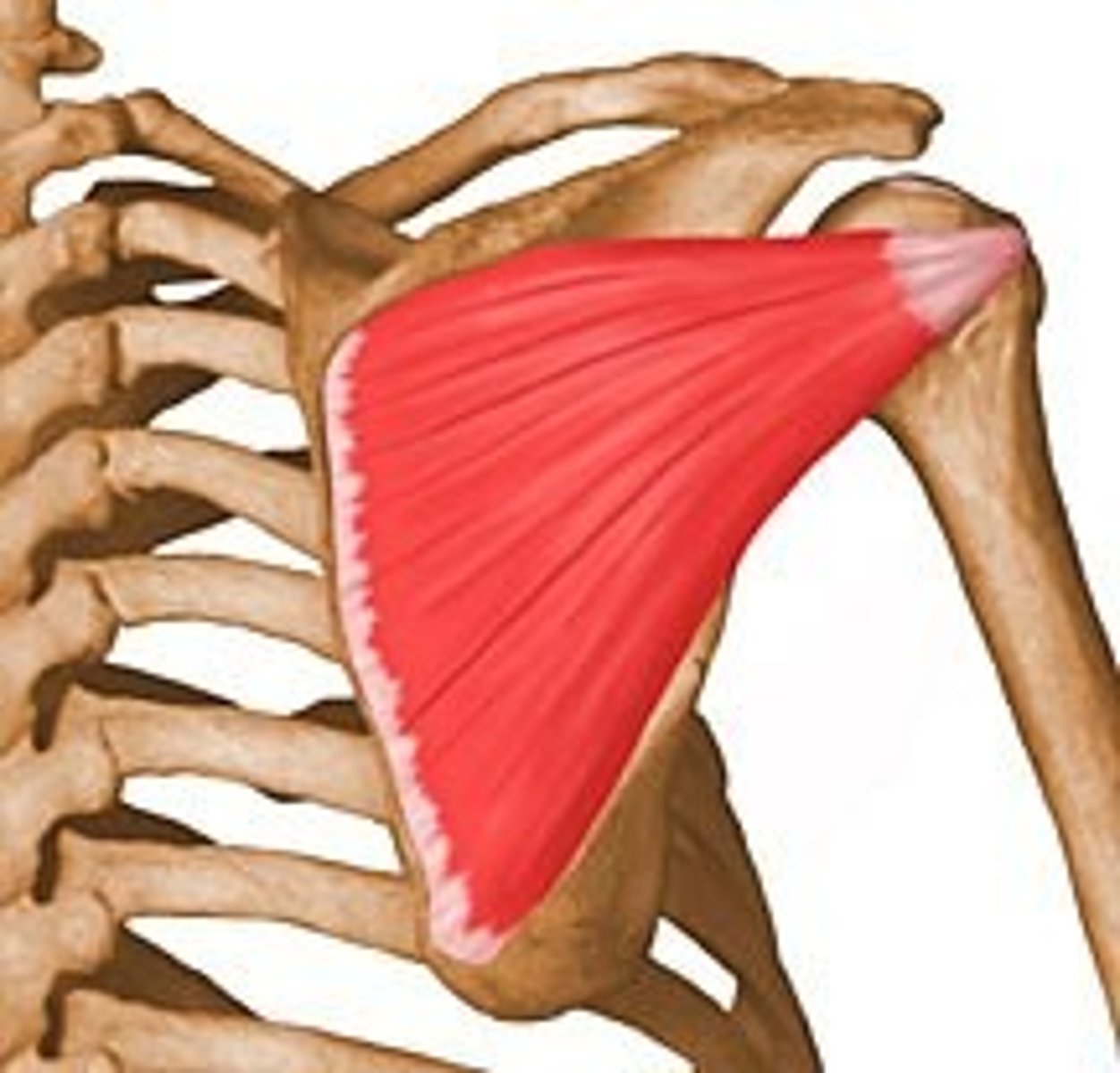
teres minor
Origin- lateral border of scapula
Insertion-greater tubercle of humerus
Innervation-axillary
Actions-lateral rotation, adduction
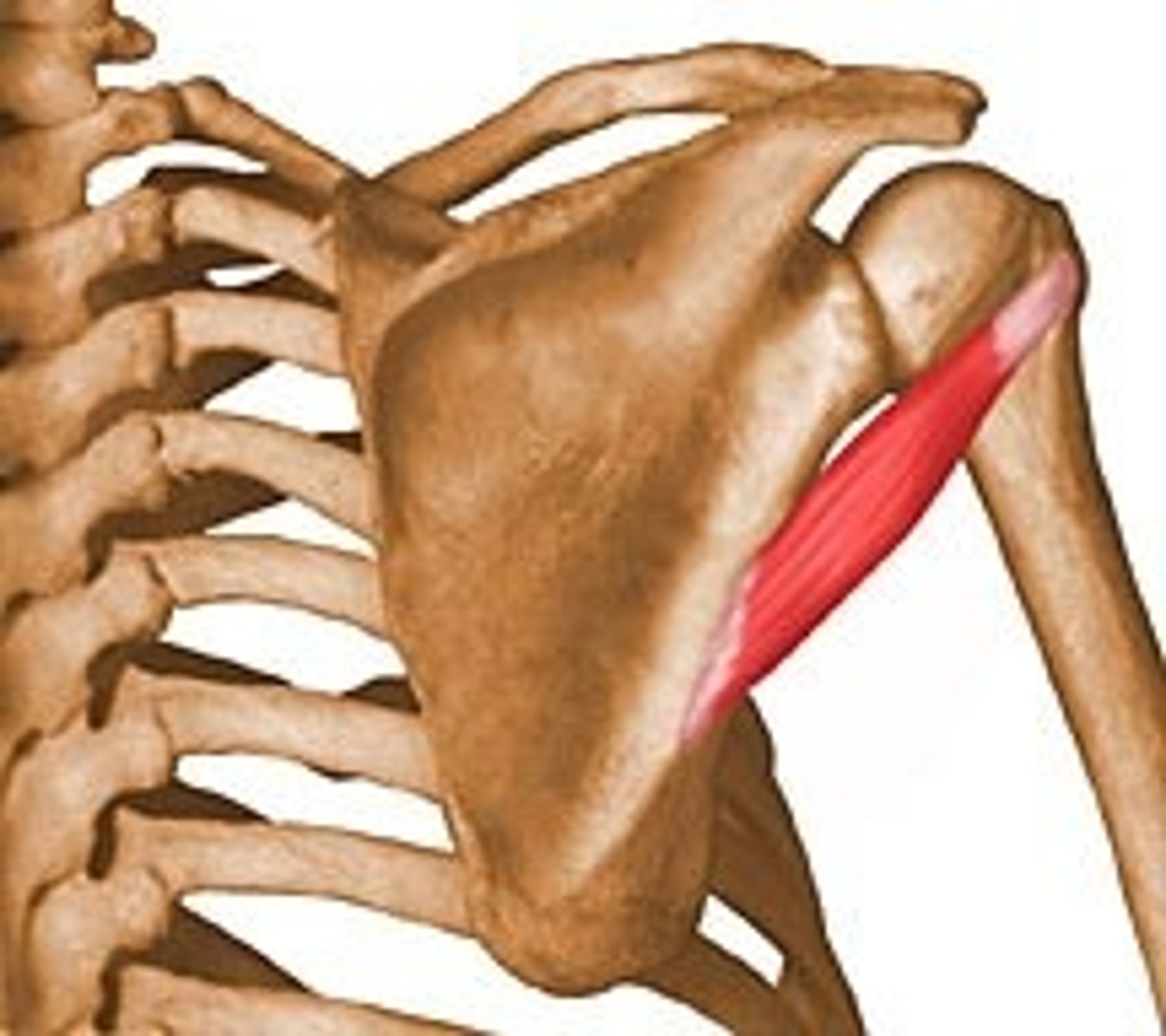
teres major
Origin- inferior angle of scapula
Insertion- intertubercular groove of humerus- medial lip
Innervation- lower subscapular
Actions- adduction, medial rotation
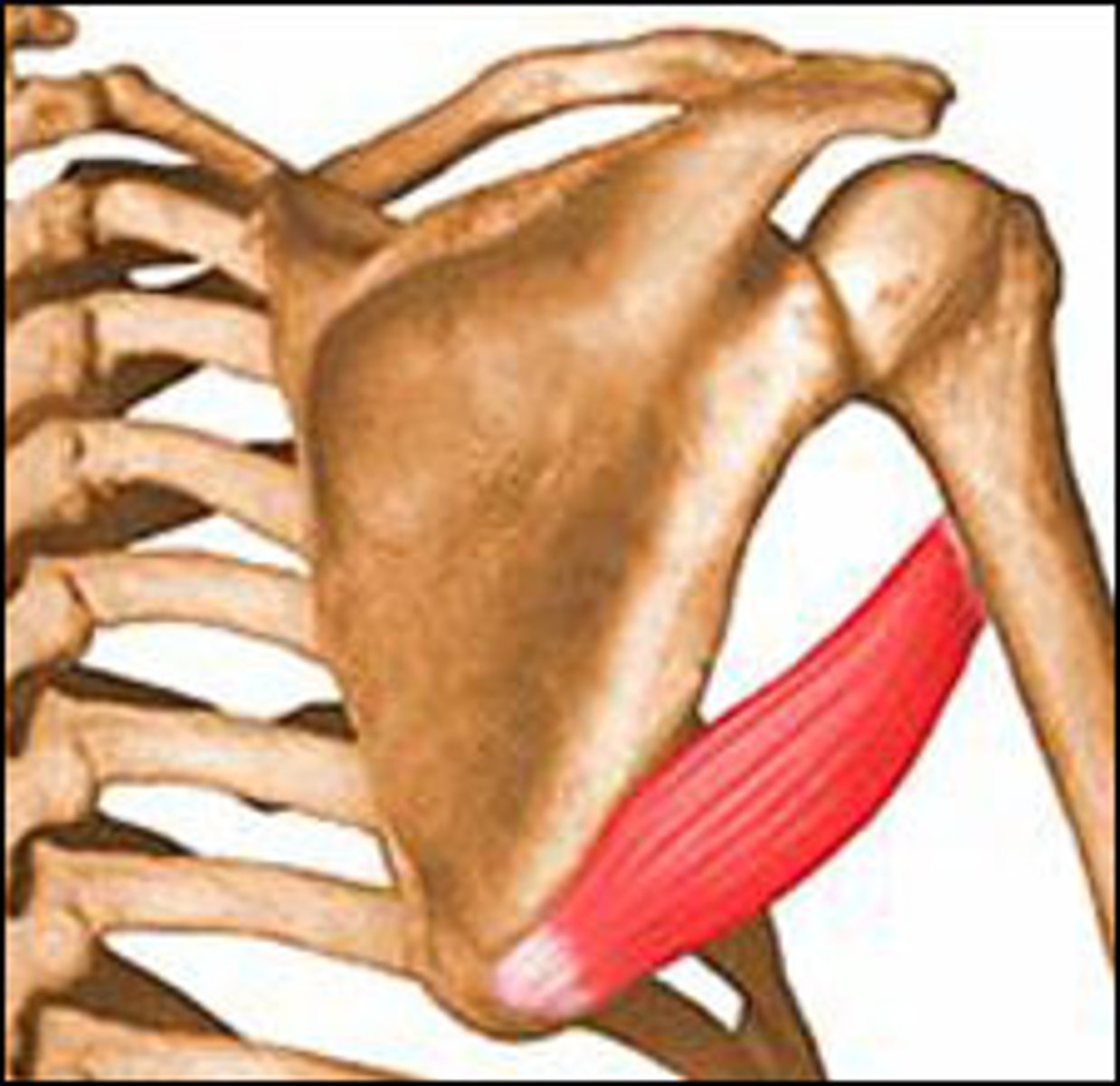
Subscapularis
Origin- subscapular fossa
Insertion-greater tubercle of humerus
Innervation-upper and lower subscapular
Actions- medial rotation, adduction
Movement in the Shoulder Joint
Abduction/ adduction
Flexion/ Extension
Medial Rotation/ Lateral Rotation
Circumduction
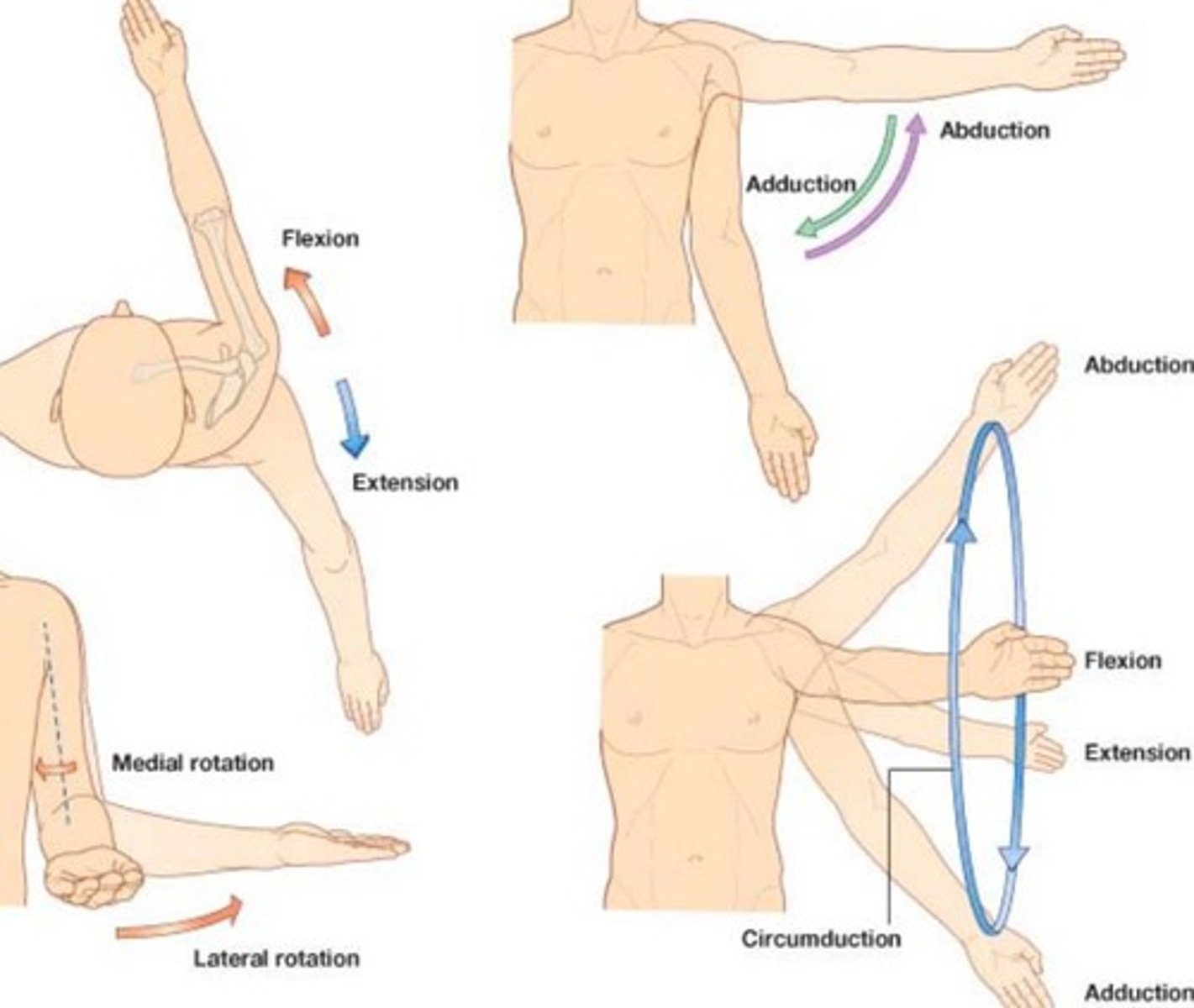
Joints that movement at Shoulder joint depends on
Glenohumeral joint movement
Sternoclavicular joint movement
Acromioclavicular joint movement
Scapular rotation
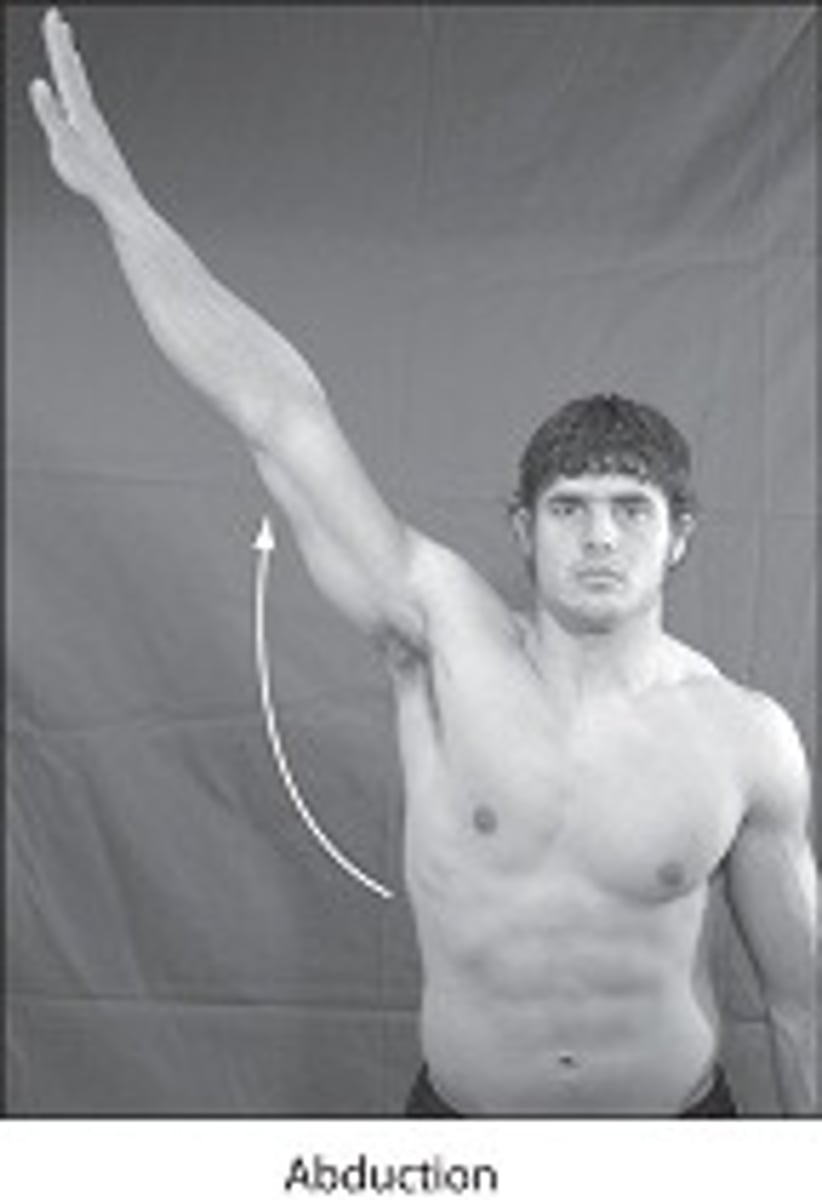
Abduction at the Shoulder Joint
pure abduction is limited to 90* by the acromion
Deltoid muscle is only effective in abduction AFTER initiation by the supraspinatus muscle.
Abduction over 90* requires scapular rotation

Lateral Rotation at the Shoulder Joint
tilting of the scapula such that the inferior angle moves away from the vertebral column
Glenoid cavity tilts upwards via serratus anterior and trapezius
Medial Rotation at the Shoulder Joint
tilting of the scapula such that the inferior angle moves towards the vertebral column
Glenoid cavity tilts downward via the rhomboid major and minor, pectoralis minor, levator scapulae and trapezius
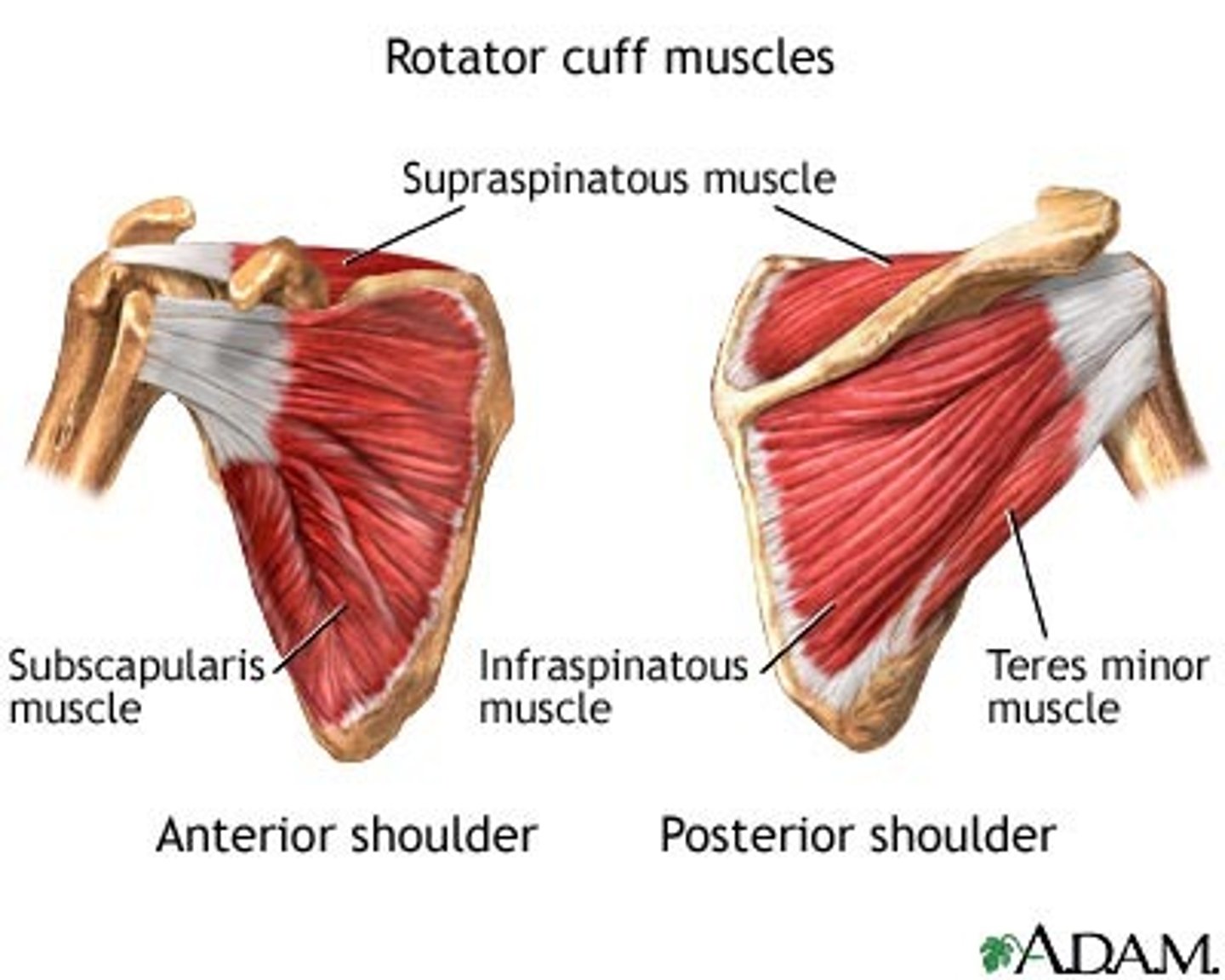
Rotator Cuff (SITS muscles)
- no major ligaments
-supported by the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles
major role in stabilizing the head of the humerus during shoulder movements
acts in rotation of the humerus
Tendinous insertions of:
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
Inflammation of the rotator cuff
most often involves the supraspinatus tendon and the overlying subdeltoid bursa; both structures can be compresses in the small spaces between the acromion and the humerus
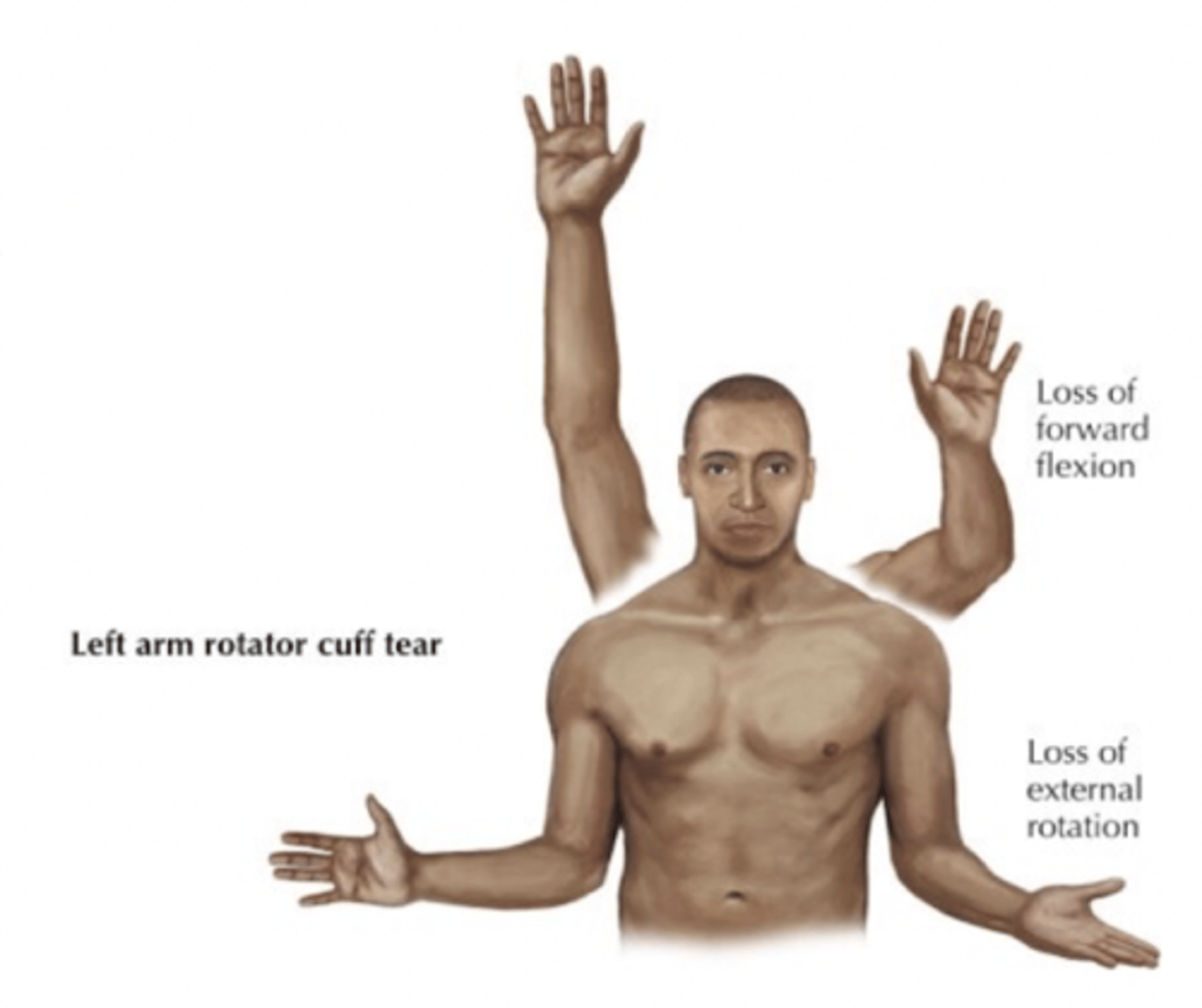
Shoulder Dislocation
usually occurs in the anterior and inferior direction because the joint capsule is reinforced superiorly, anteriorly and posteriorly by the rotator cuff tendons but NOT Inferiorly.
-can damage the axillary artery and nerve
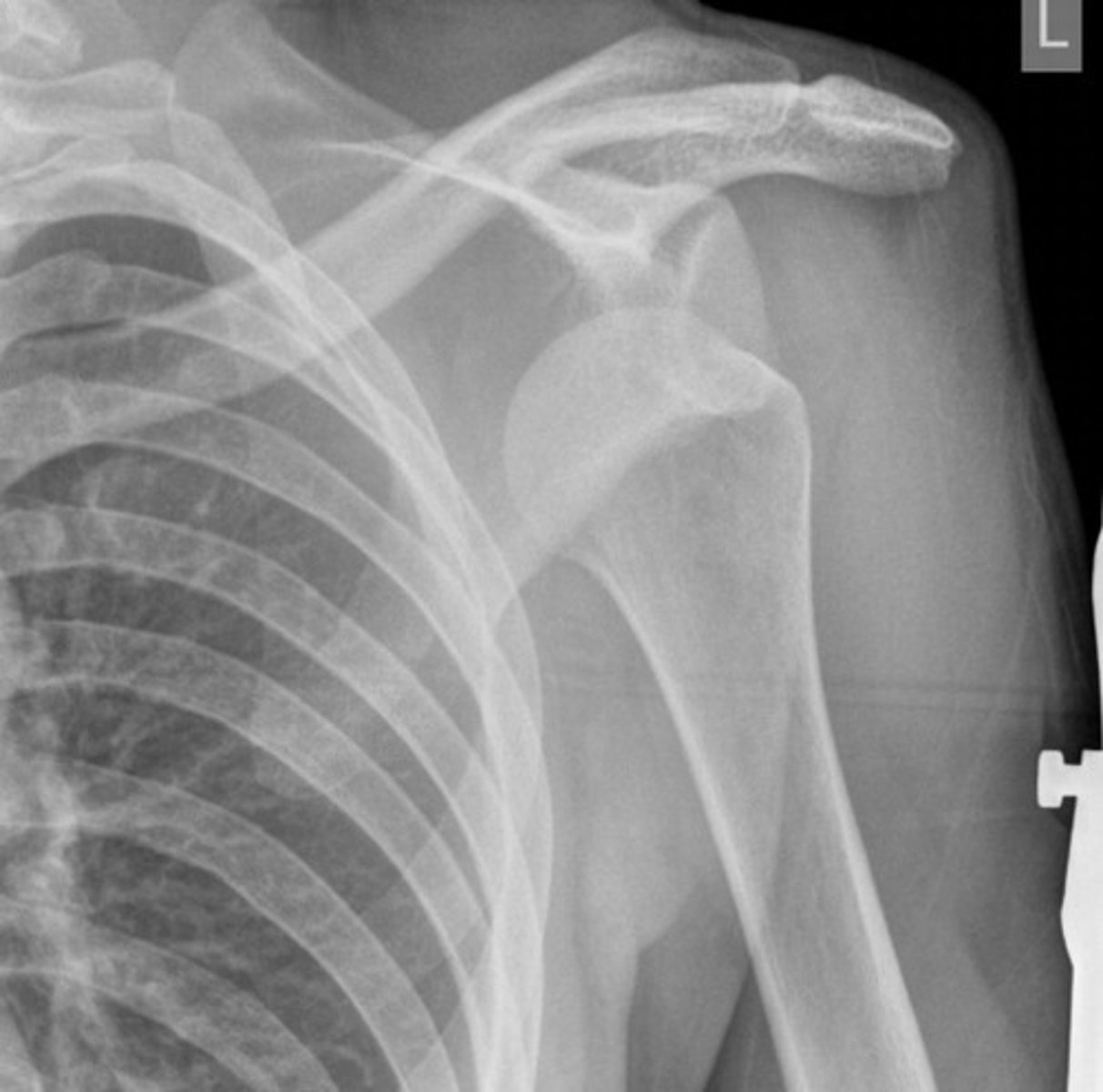
Upper Limb Muscle Testing
Deltoid: resisted abduction of arm at 90*
Supraspinatus: resisted initial abduction
Infraspinatus and teres minor: resisted lateral rotation
Subscapularis: resisted medial rotation or lift off test
Rotator Cuff (especially supraspinatus): inverted soda can test
Impingement test
AXILLA
Boundaries, Contents, Axillary Artery
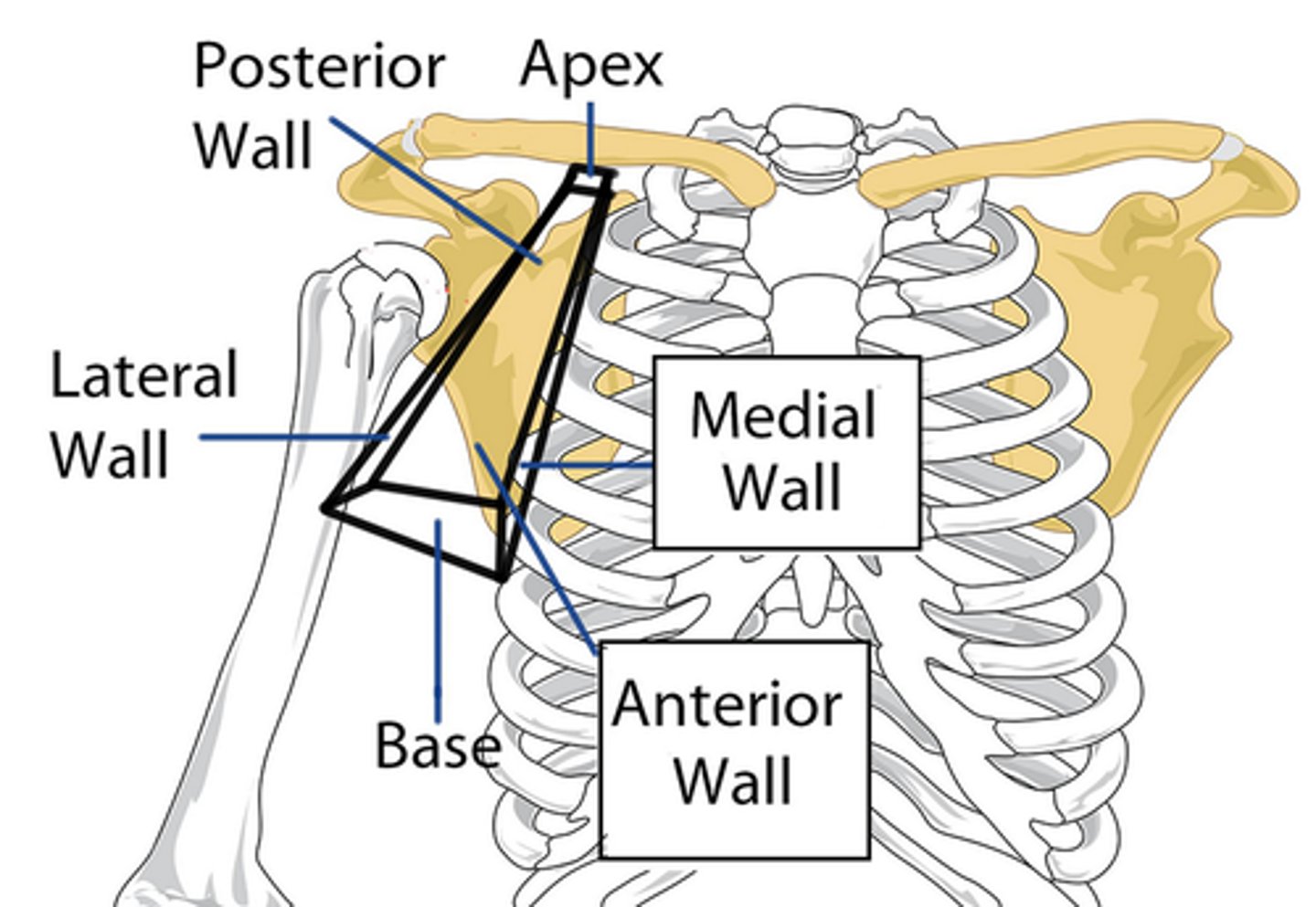
Axilla boundaries
Anterior, Posterior, Medial, Lateral
Axilla anterior boundary
Clavicle and pectoral muscles
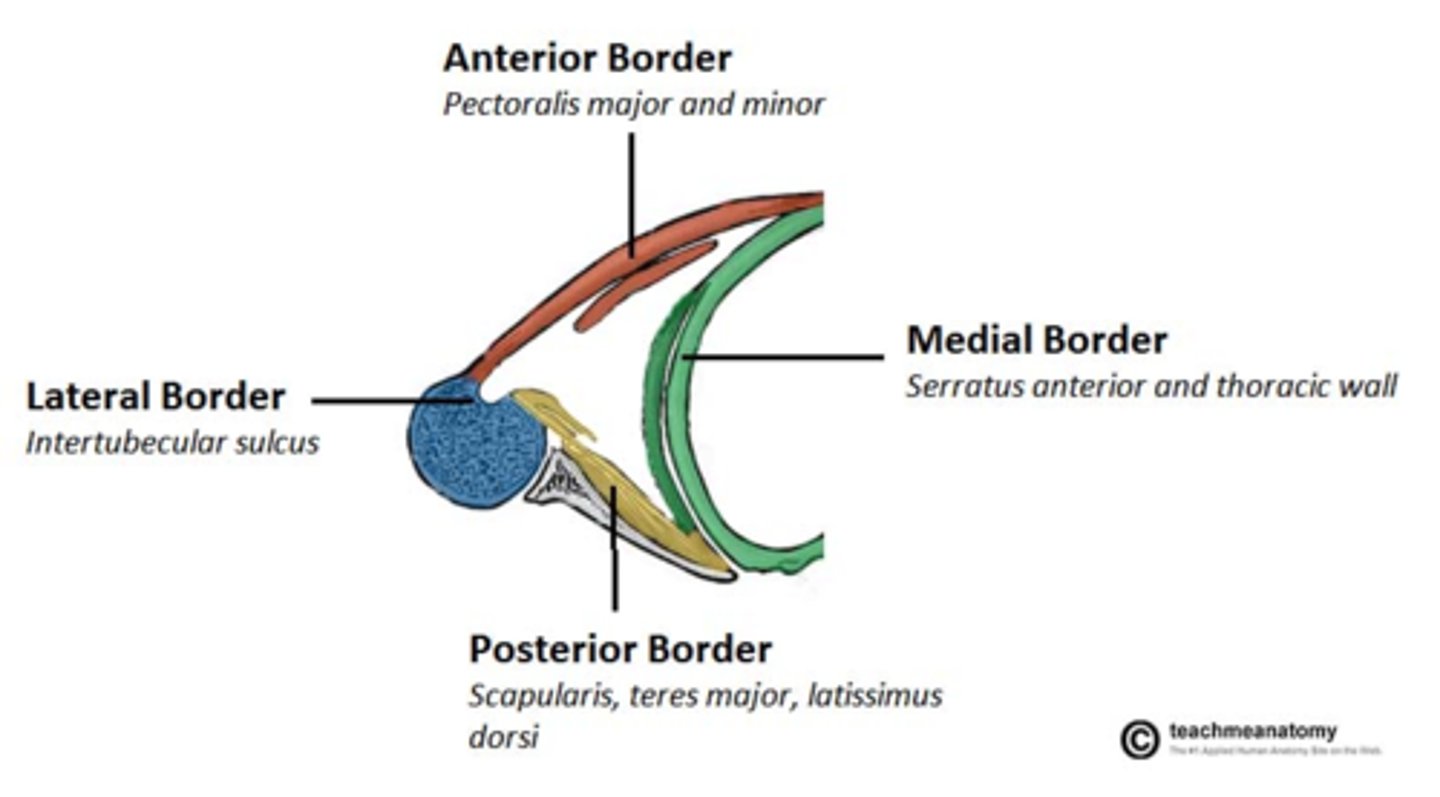
Axilla posterior boundary
scapula and subscapularis muscle
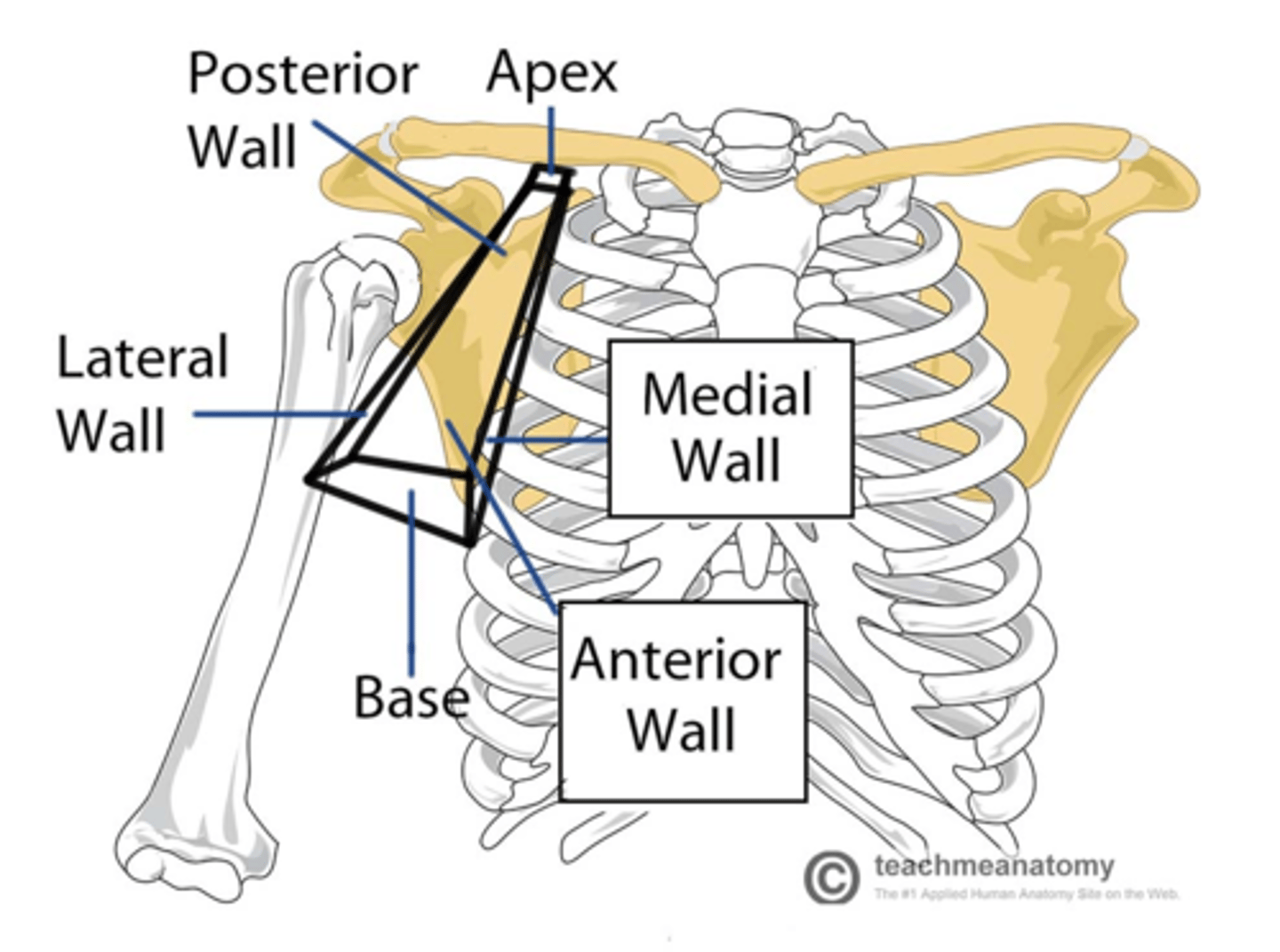
Axilla medial boundary
Serratus anterior muscle
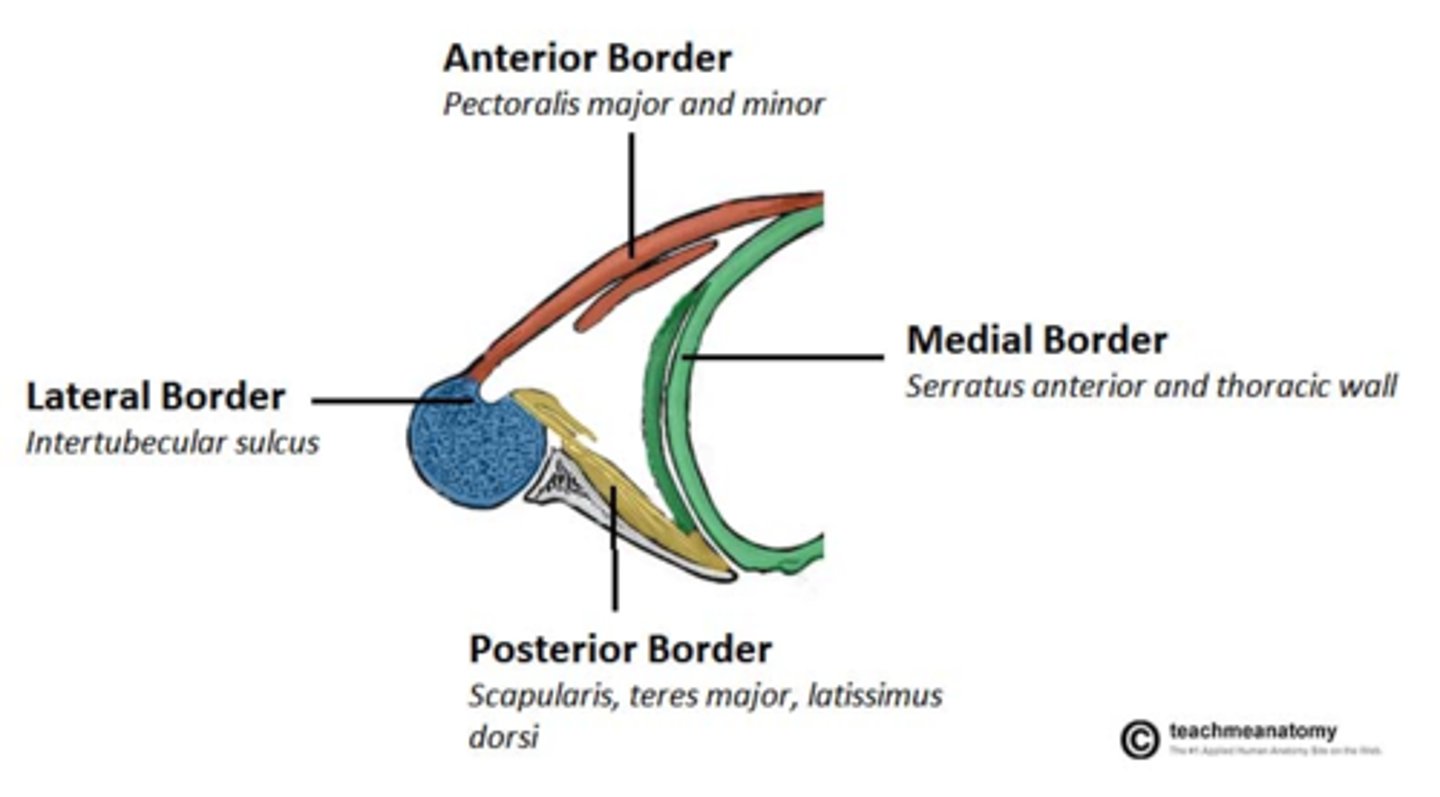
Axilla lateral boundary
humerus
Axilla Contents
Axillary Artery
Axillary vein
Brachial plexus
Long head of the biceps brachii muscles
Short head of the biceps brachii muscles
Coracobrachialis muscle
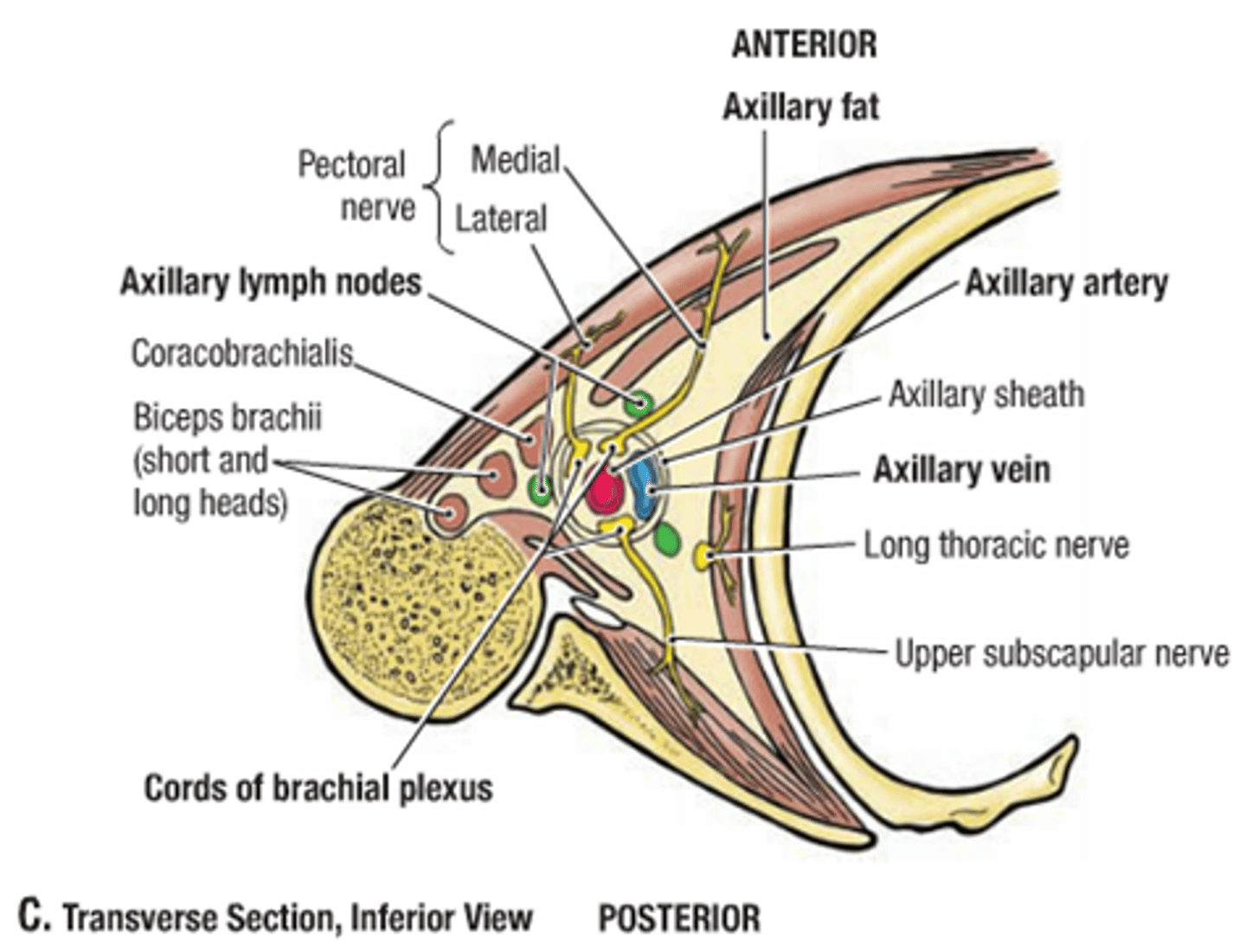
Axillary Artery
artery that carries oxygenated blood to the axilla (armpit) area
Axillary vein
accompanying vein of axillary artery,located medial & superficial to axillary artery
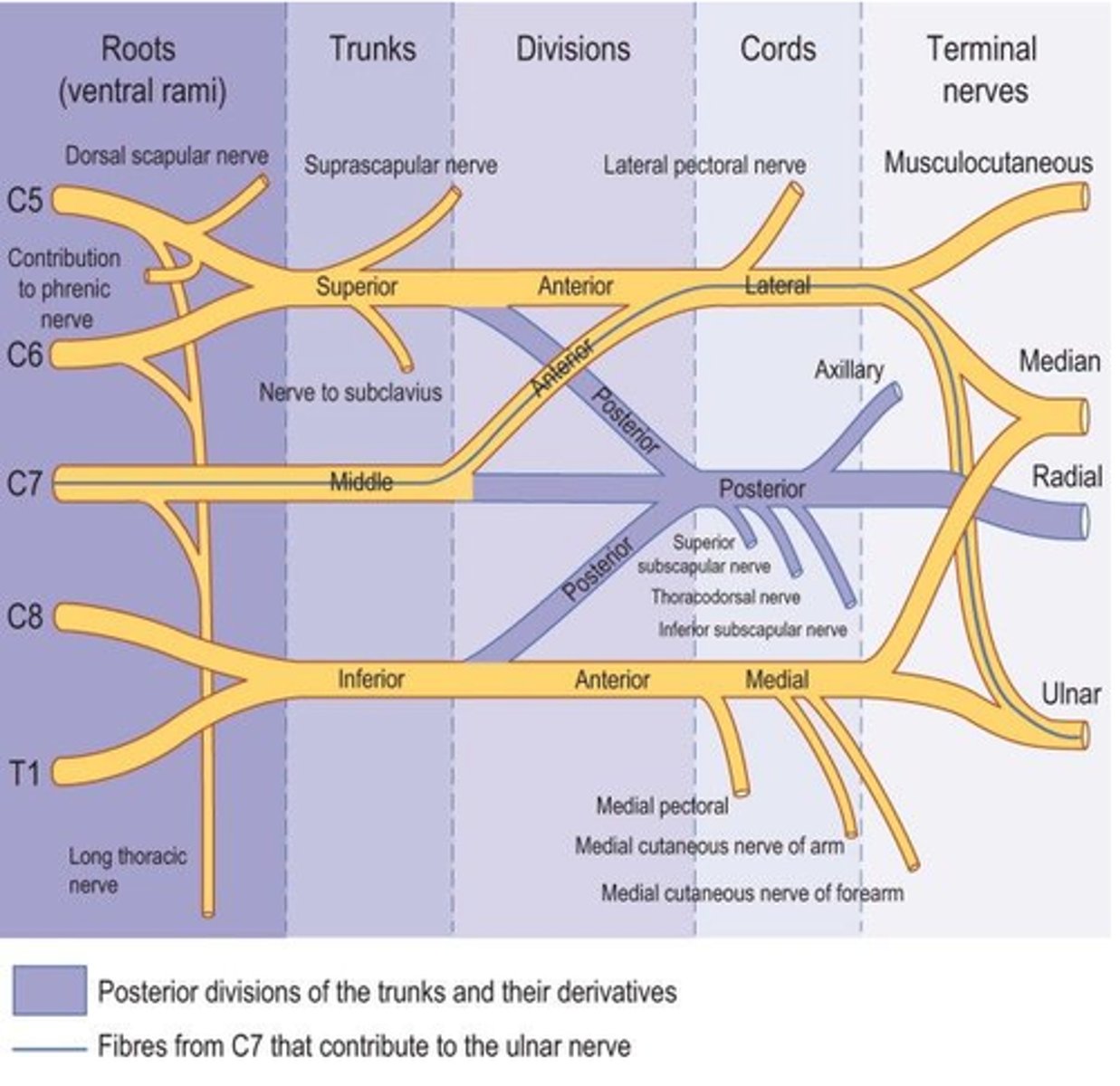
Brachial Plexus
network of interlacing nerves found in the upper arm area
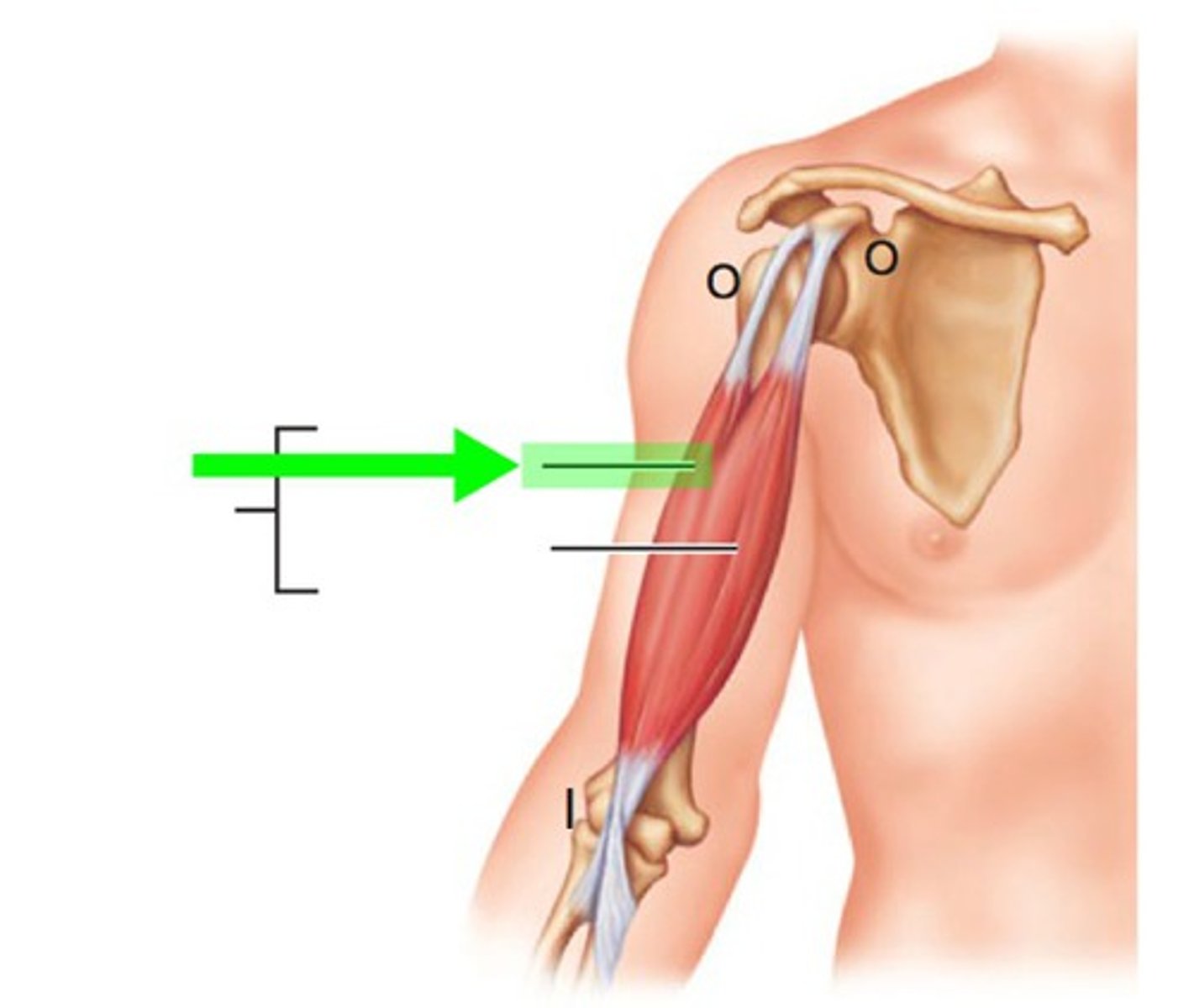
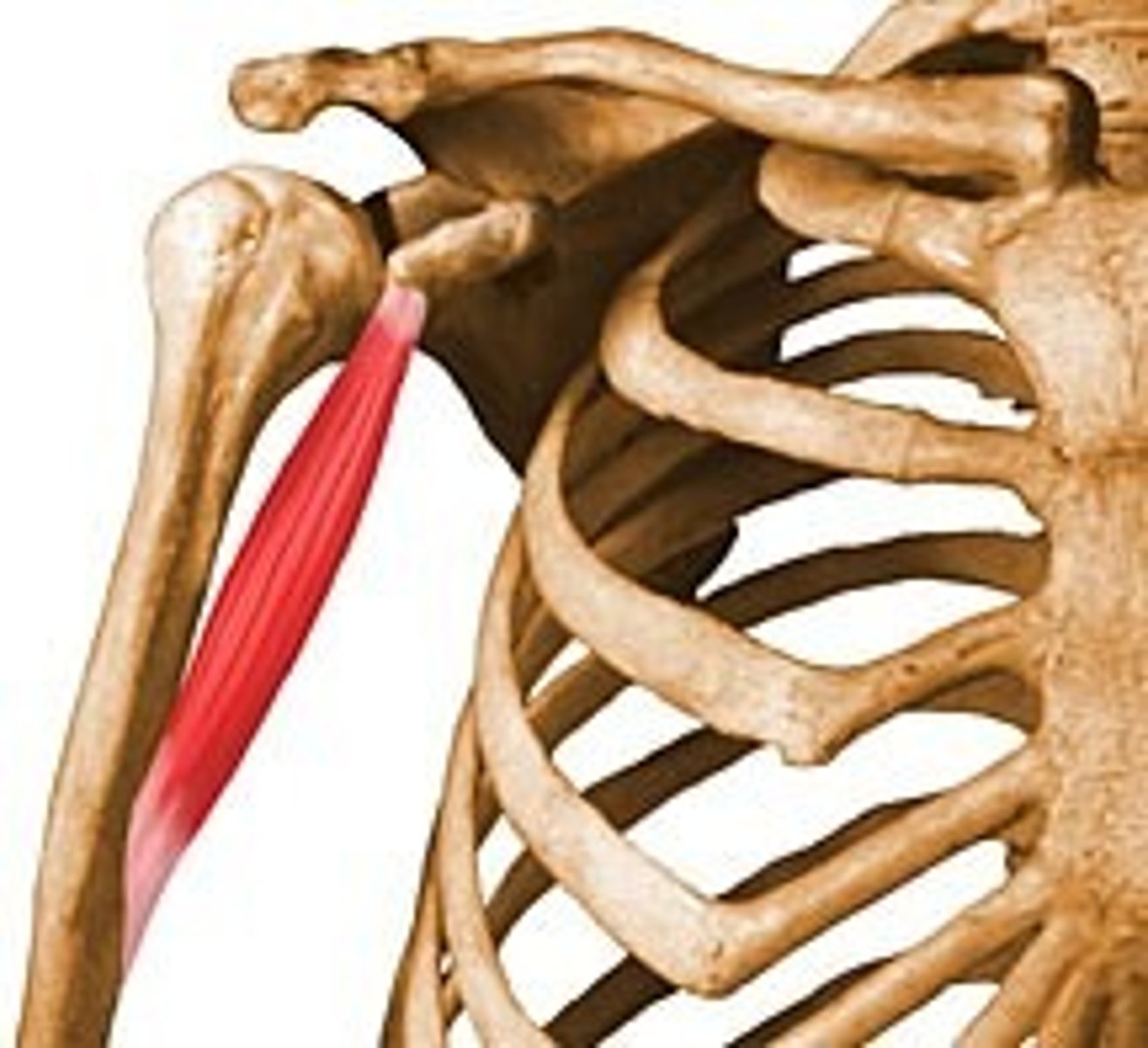
Long head of the biceps brachii muscles
origin: supraglenoid tubercle
insertion: radial tuberosity
movement: flexes elbow, supinates forearm, flexes shoulder
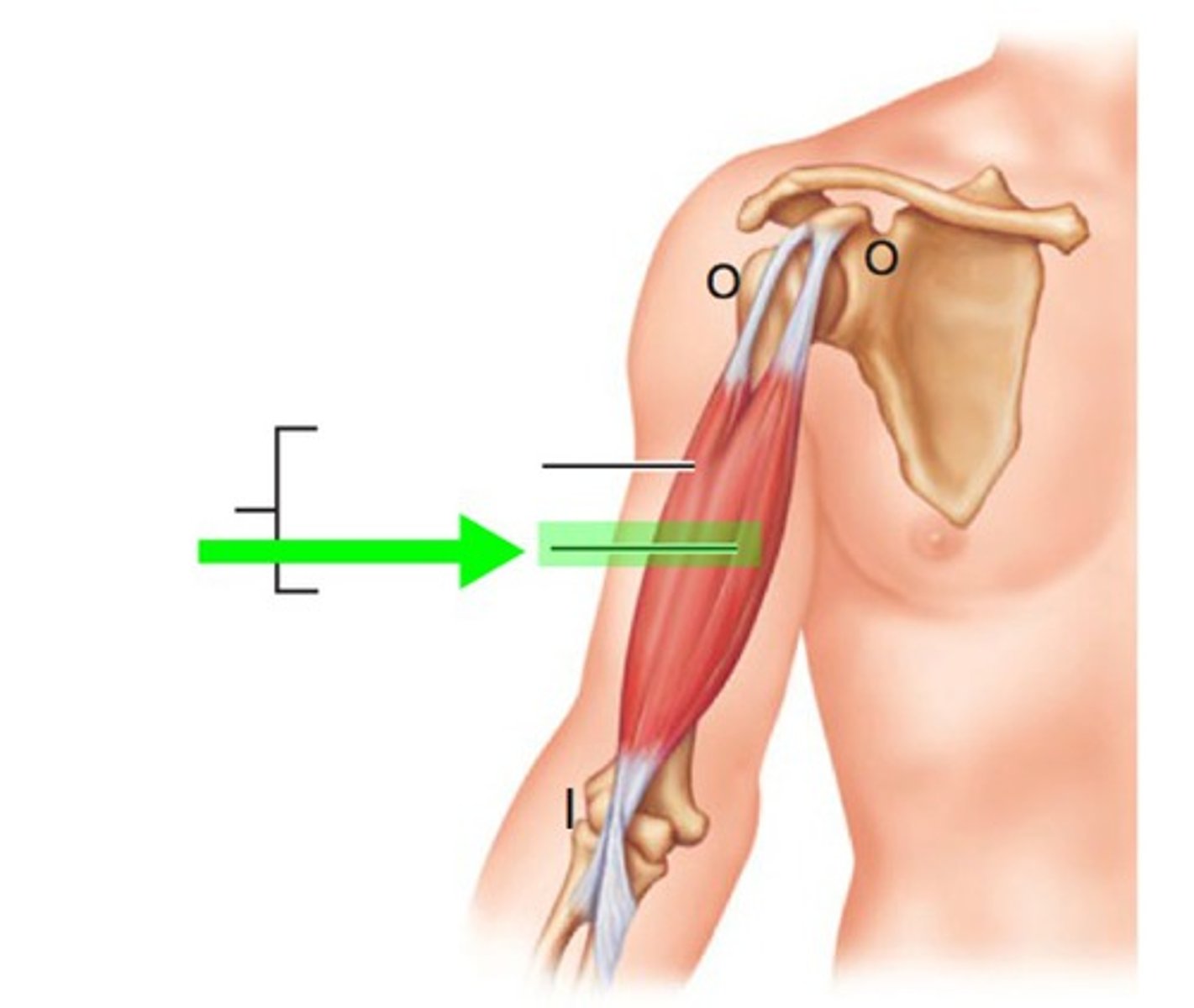
Short head of the biceps brachii muscles
origin: coracoid process
insertion: radial tuberosity
movement: flexes elbow, supinates forearm, flexes shoulder
Coracobrachialis muscle
flexion, adduction, horizontal adduction, diagonal adduction
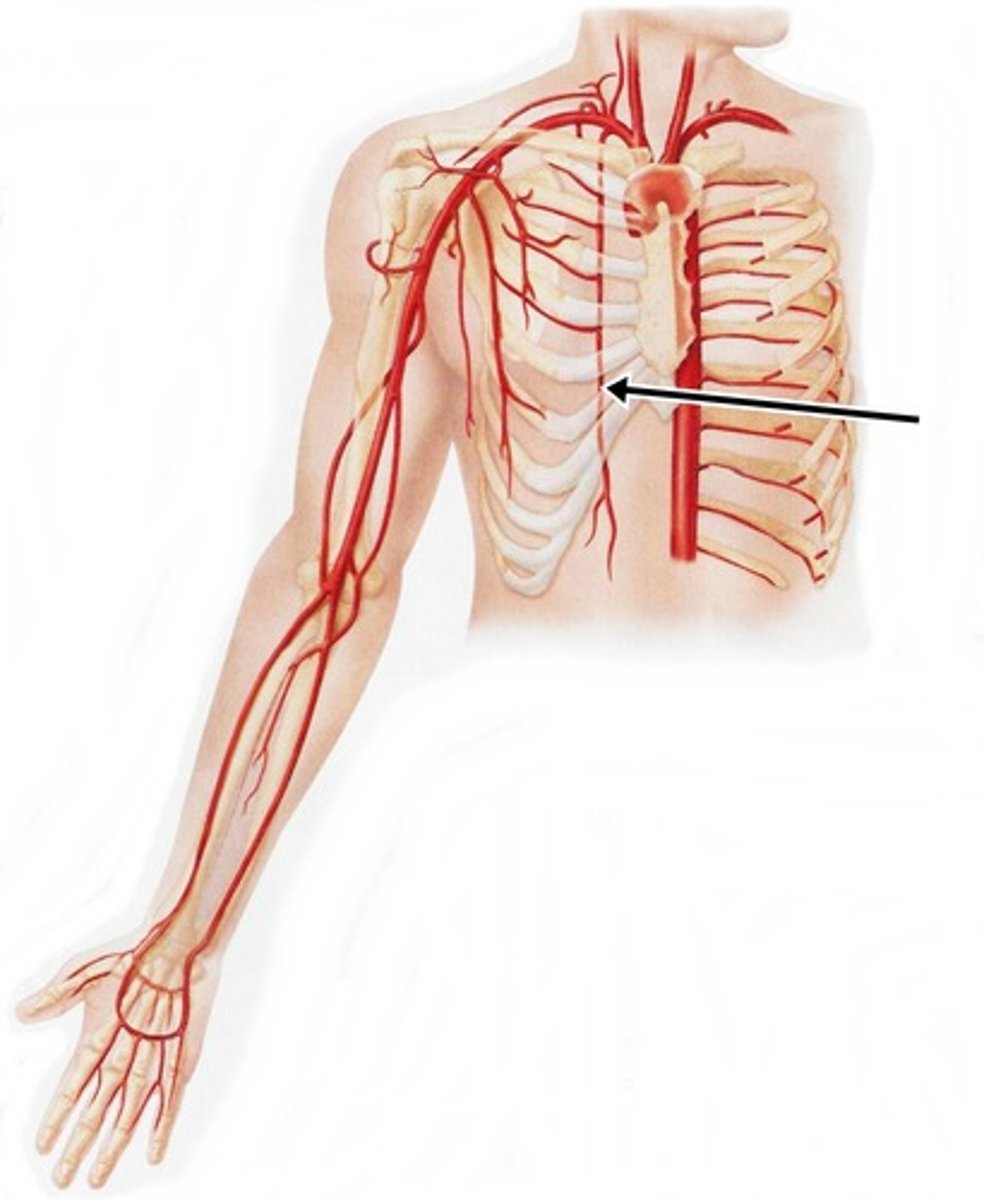
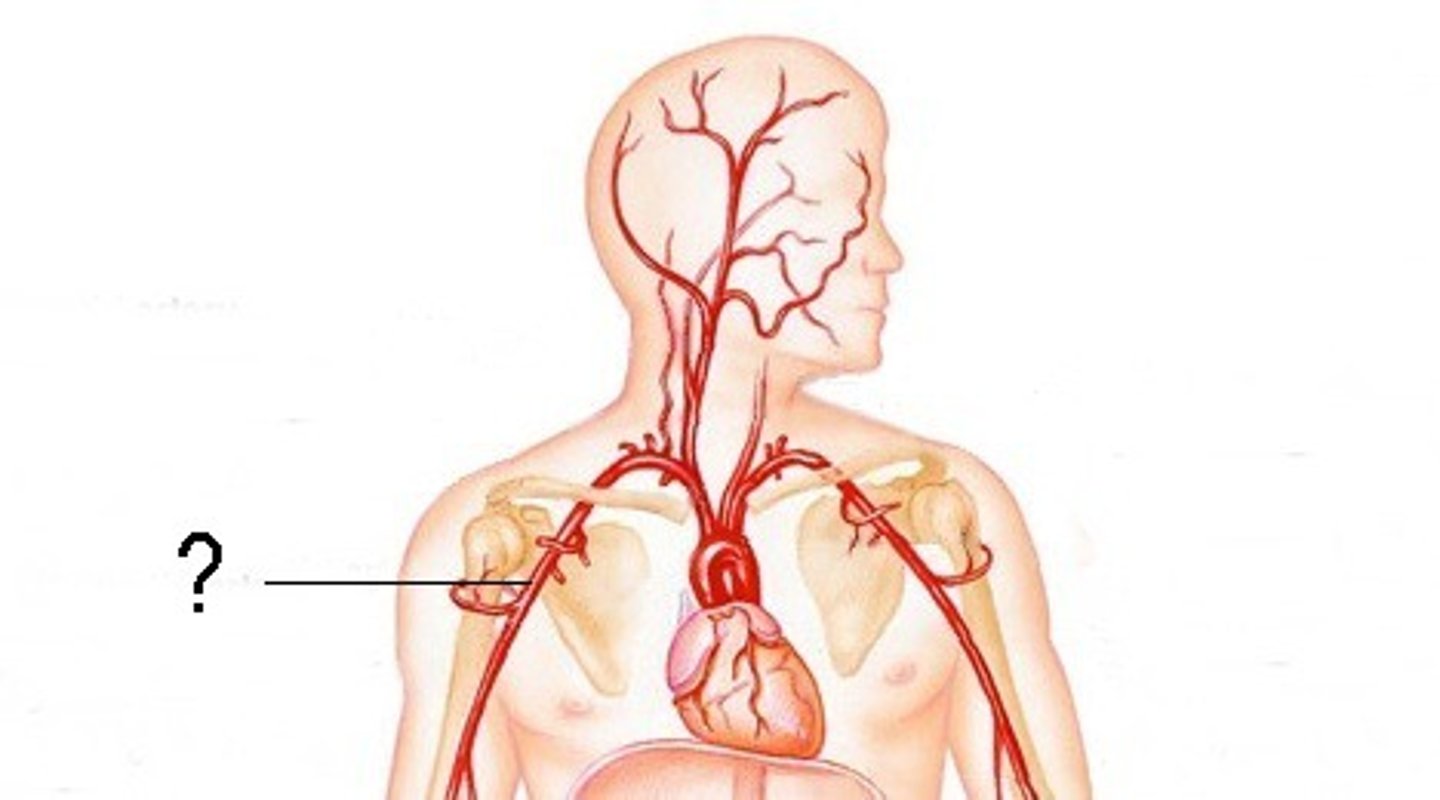
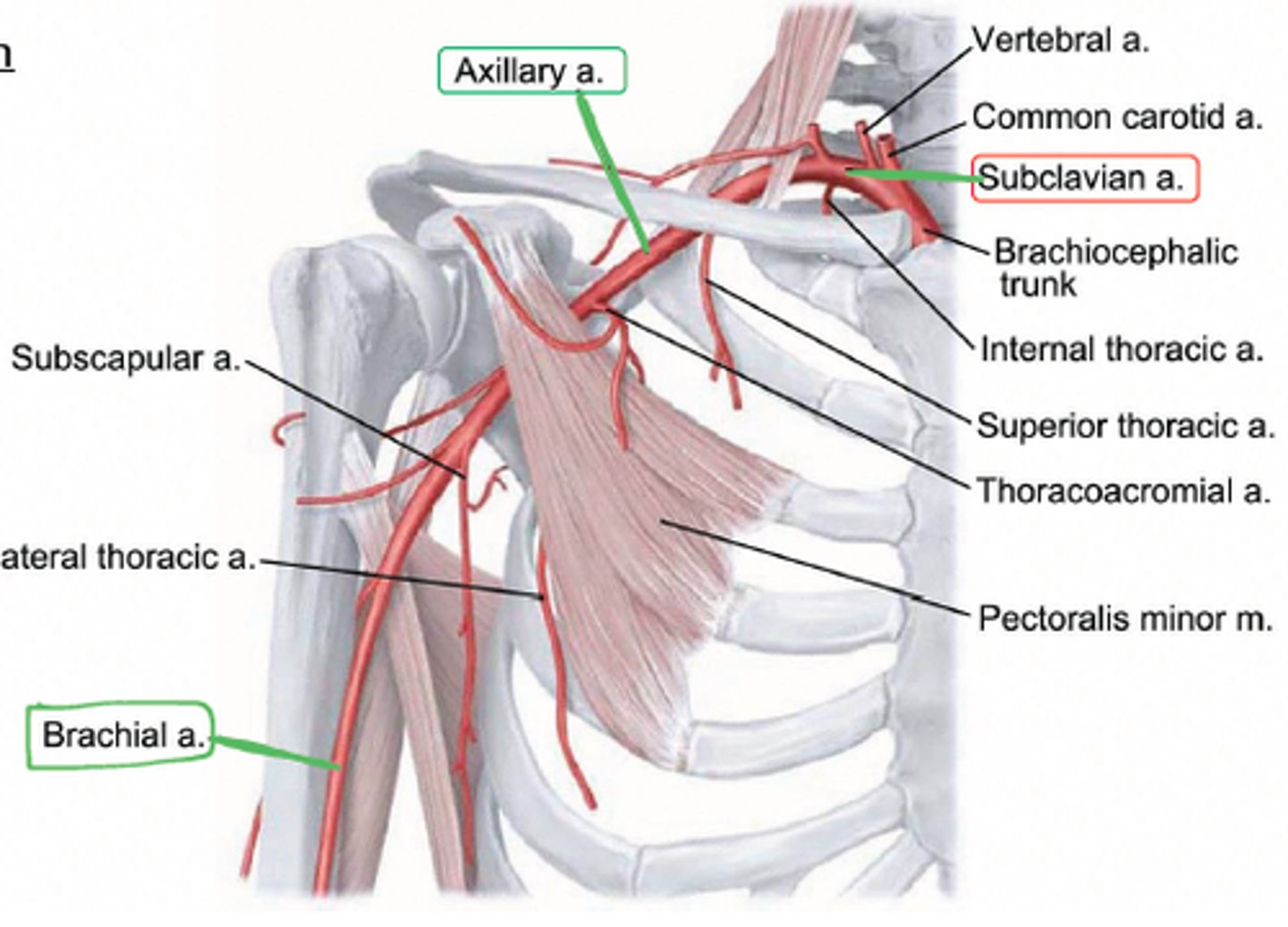
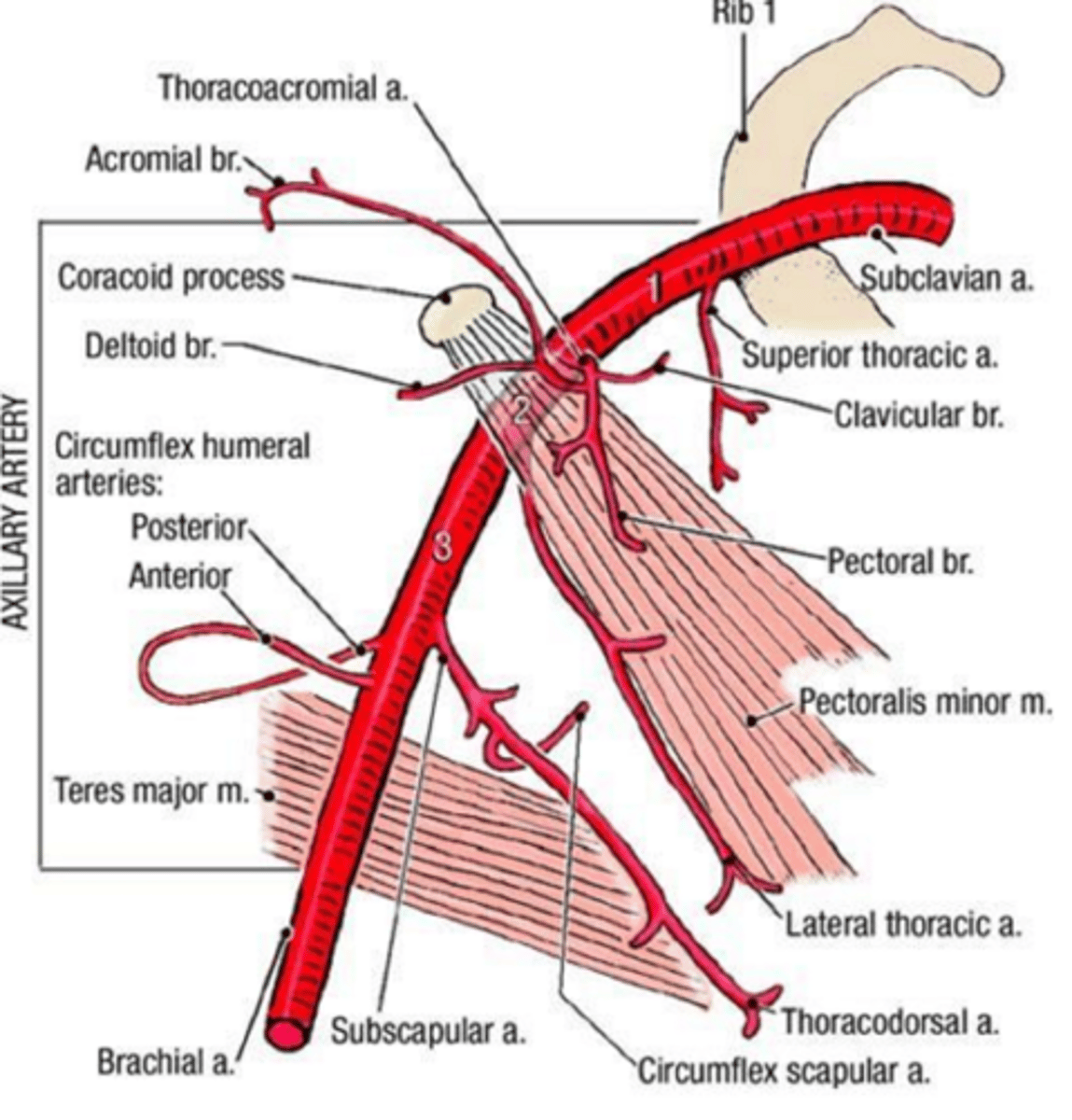
Axillary Artery; break down
divided into 3 parts by the pectoralis minor muscle
extends from the first rib to the inferior margin of teres major muscle
Axillary Artery: part 1
I. proximal to the pectoralis minor muscle
II. superior thoracic artery to the 1st/2nd intercostal spaces (small)
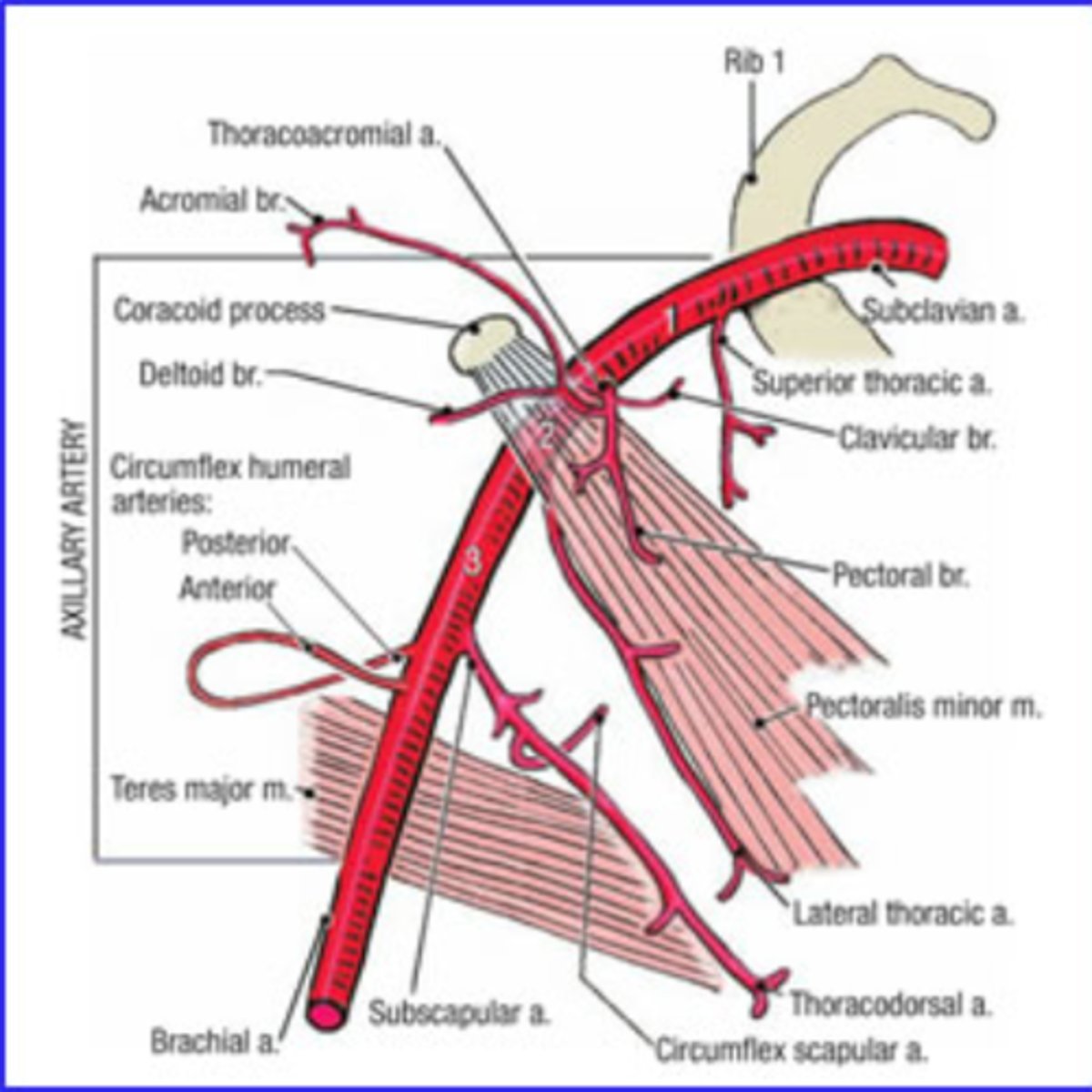
Axillary Artery: part 2
I. distal to the pecoralis minor muscle
II. thoracoacromial trunk with branches to shoulder, acromion, deltoid, clavicle, and pectoralis
III. lateral thoracic artery (highly variable) to breast and lateral chest wall
Axillary Artery: part 3
I. distal to the pectoralis minor muscle
II. anterior humeral circumflex artery (sometimes absent)
III. posterior humeral circumflex artery (usually larger than its anterior partner)
IV. subscapular artery (largest branch of the axillary artery) divides into the thoracodorsal and circumflex scapular arteries.
brachiocephalic trunk
The first large artery arising from the aortic arch. It carries oxygenated blood to the neck, head, and right forelimb.
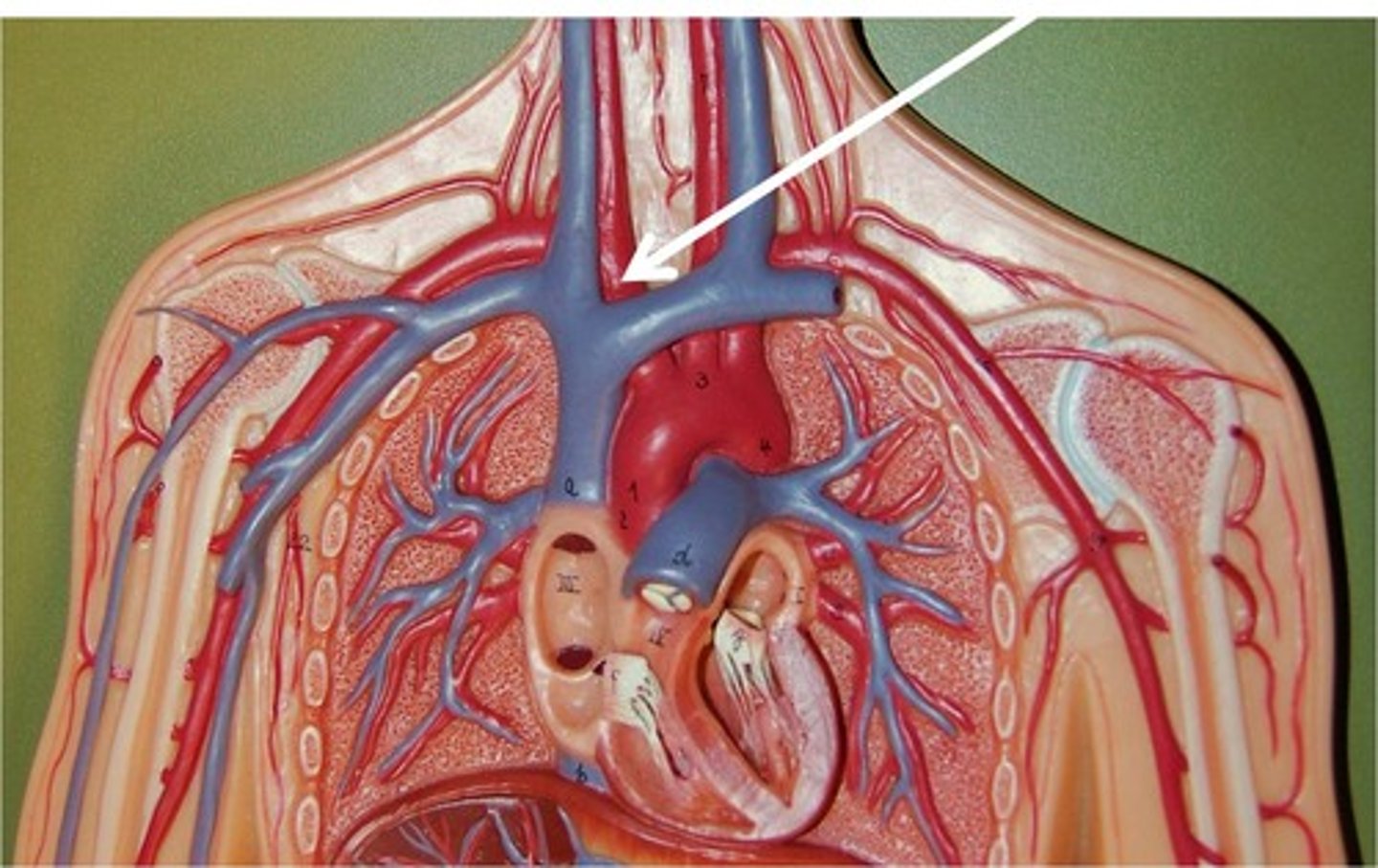
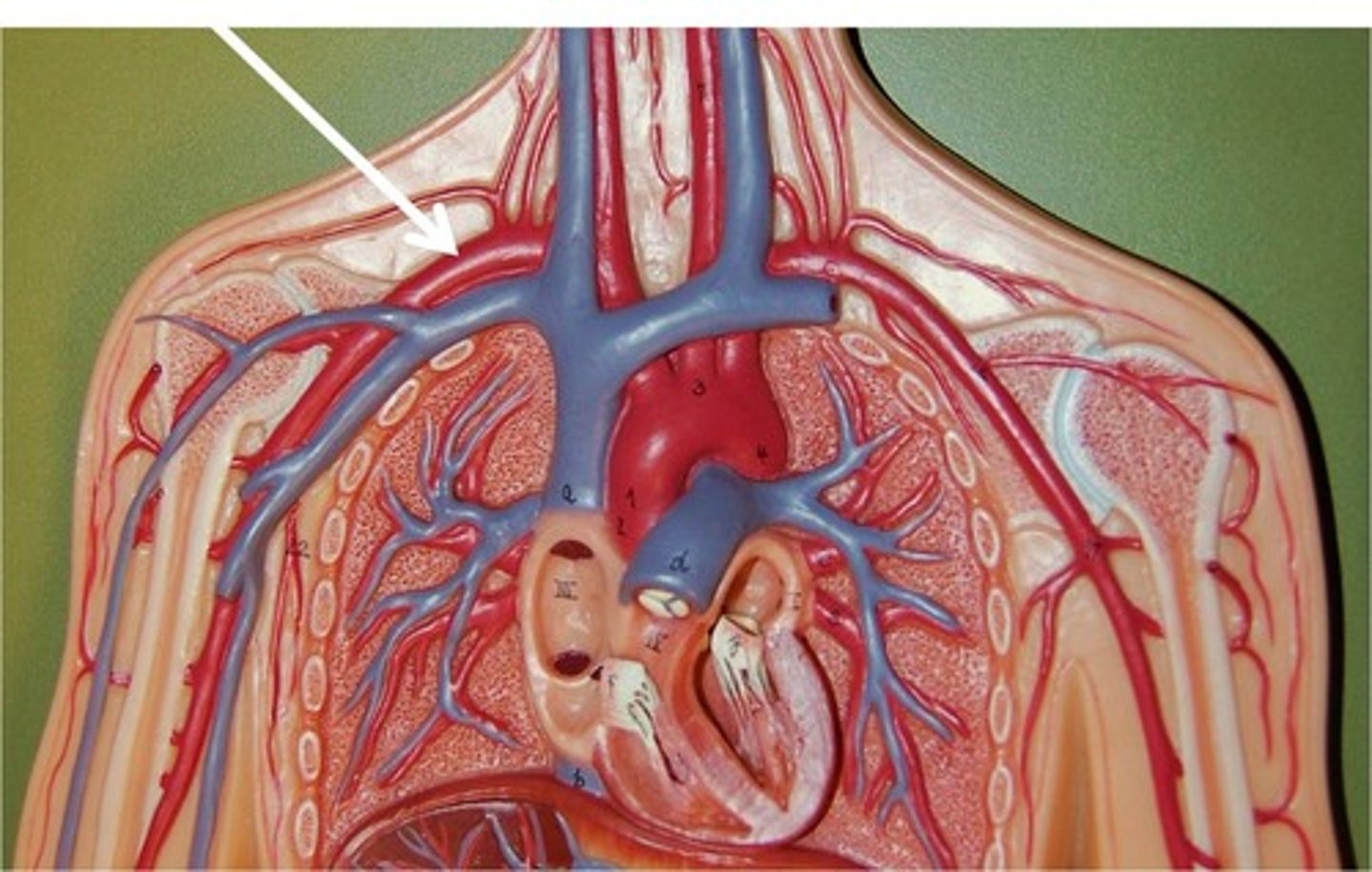
subclavian artery
Both a left and right, blood vessels that supply blood to the shoulders and upper limbs.
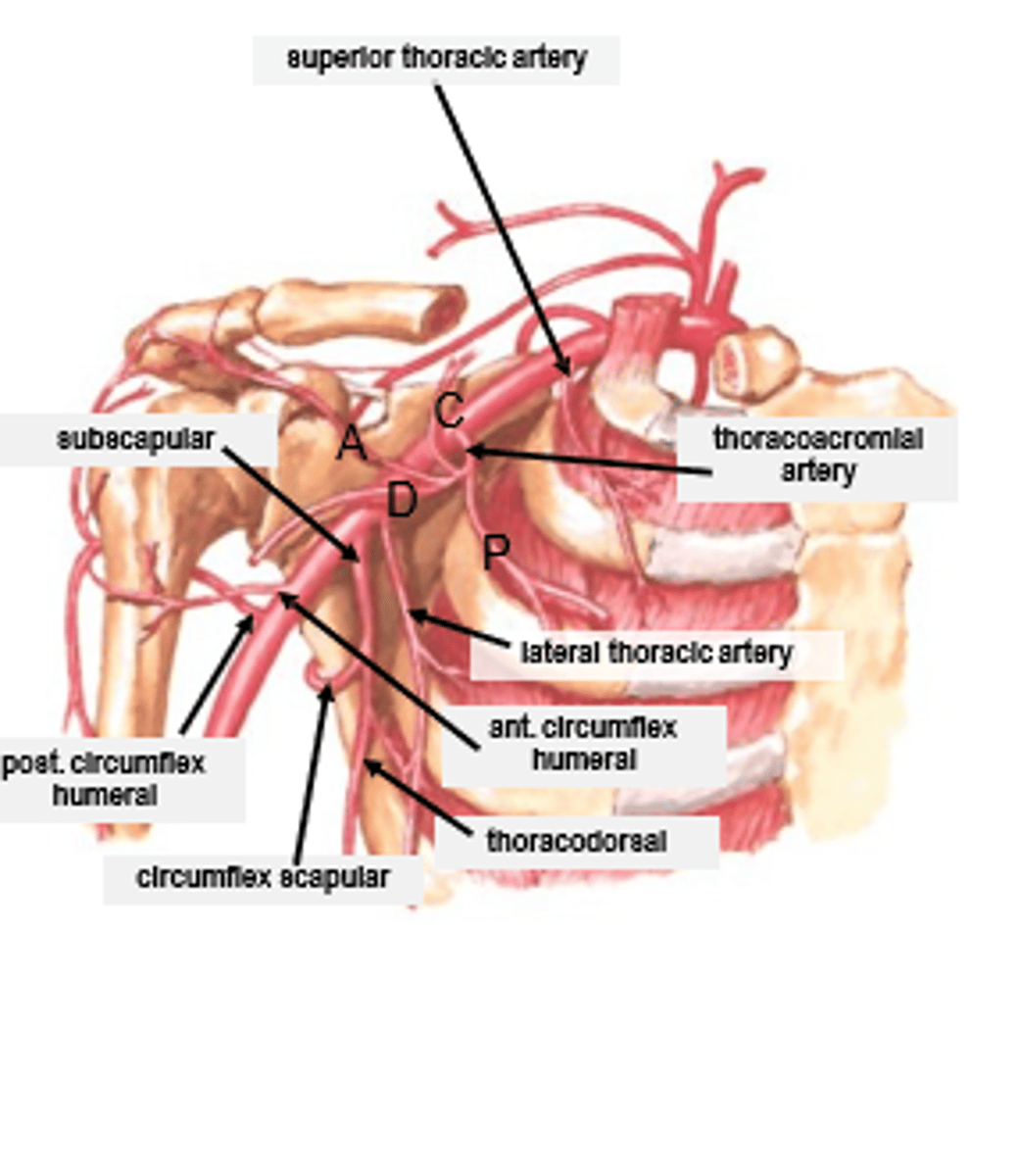
superior thoracic artery
first branch of axillary artery
supplies 1st and 2nd intercostal spaces
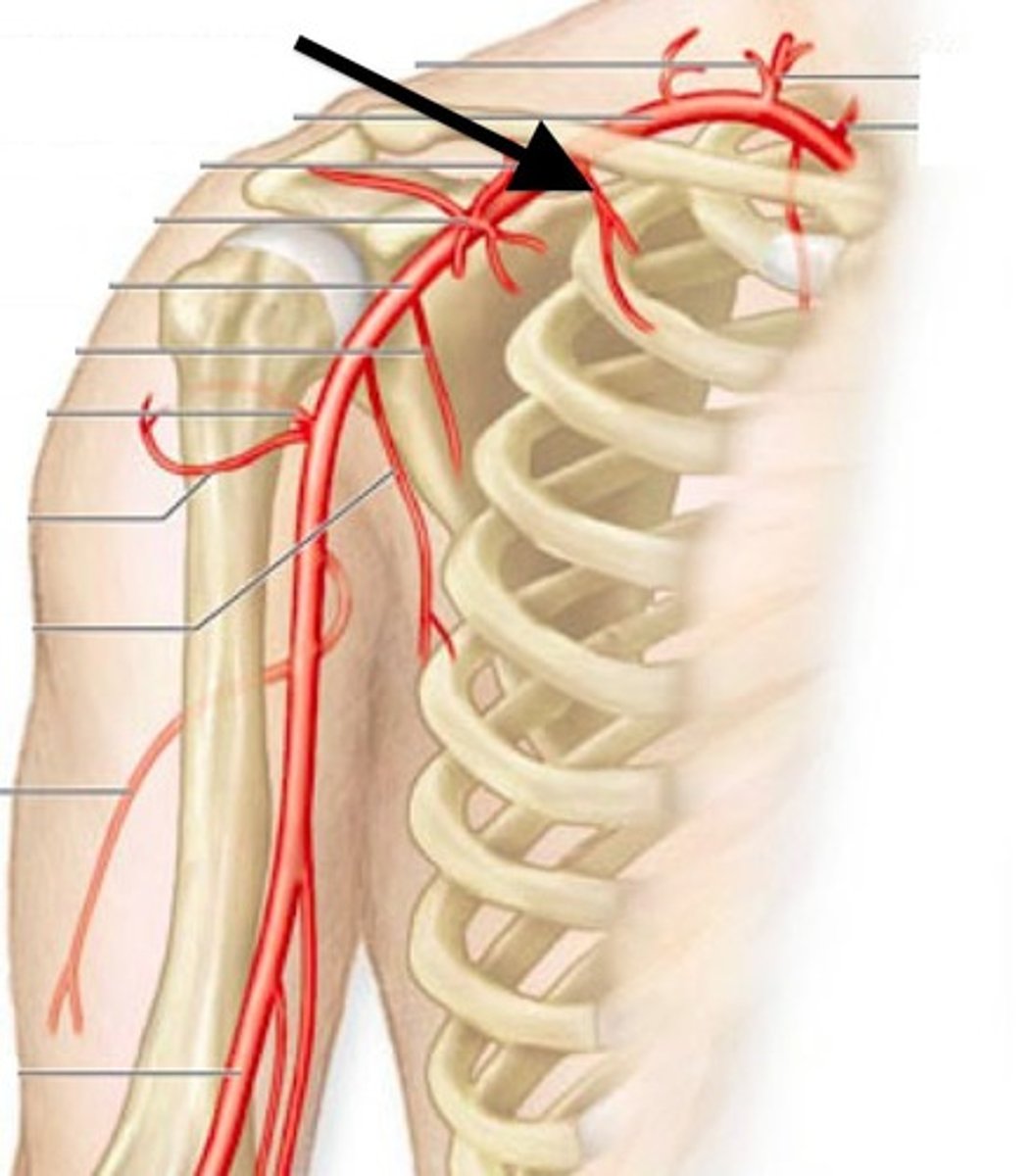
thoracoacromial artery
supplies superior shoulder and pectoral regions
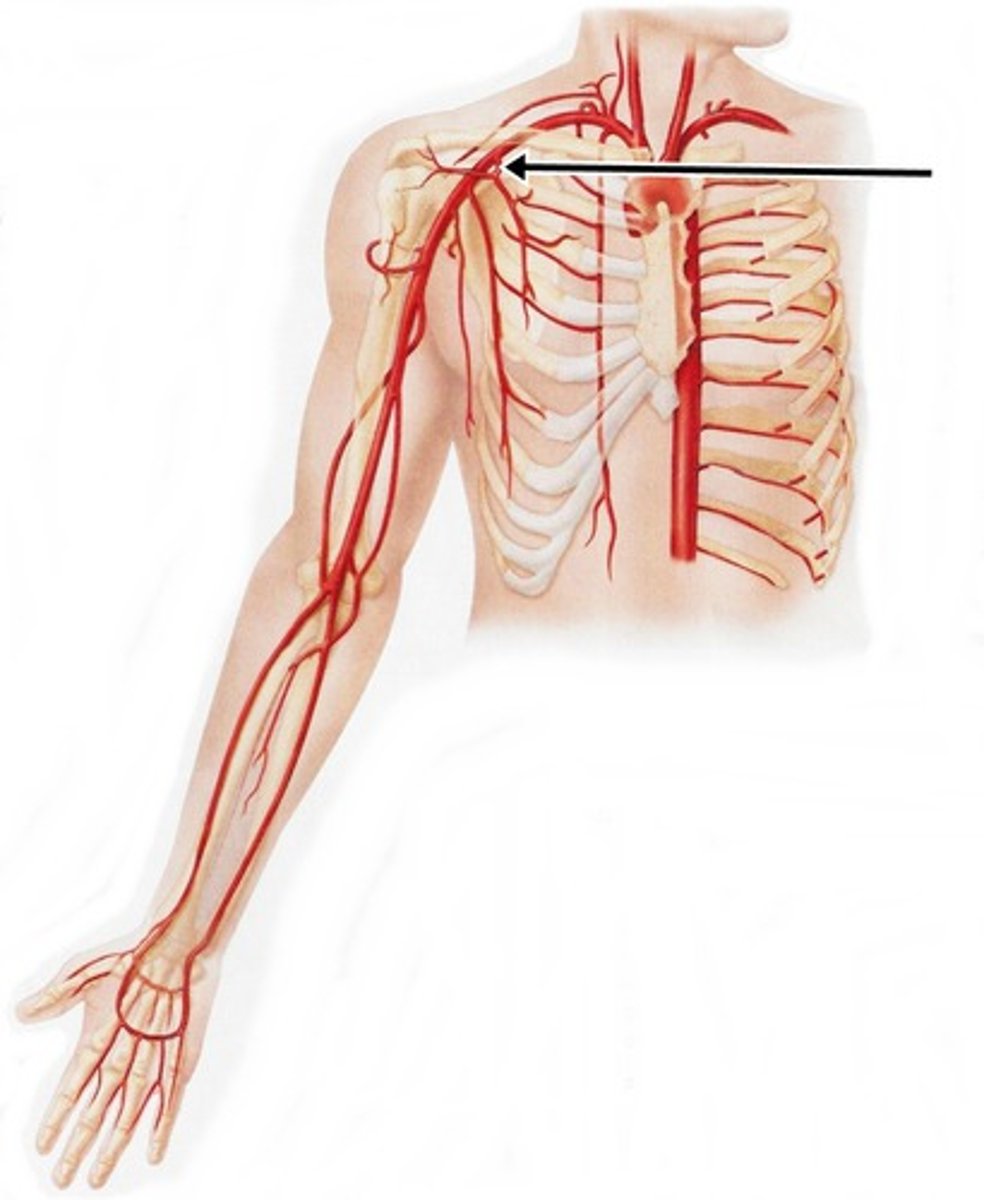
subscapular artery
serves scapula and dorsal thorax (upper back muscles)

anterior circumflex humeral artery
Origin: axillary (this is smaller then the one opposite to it)
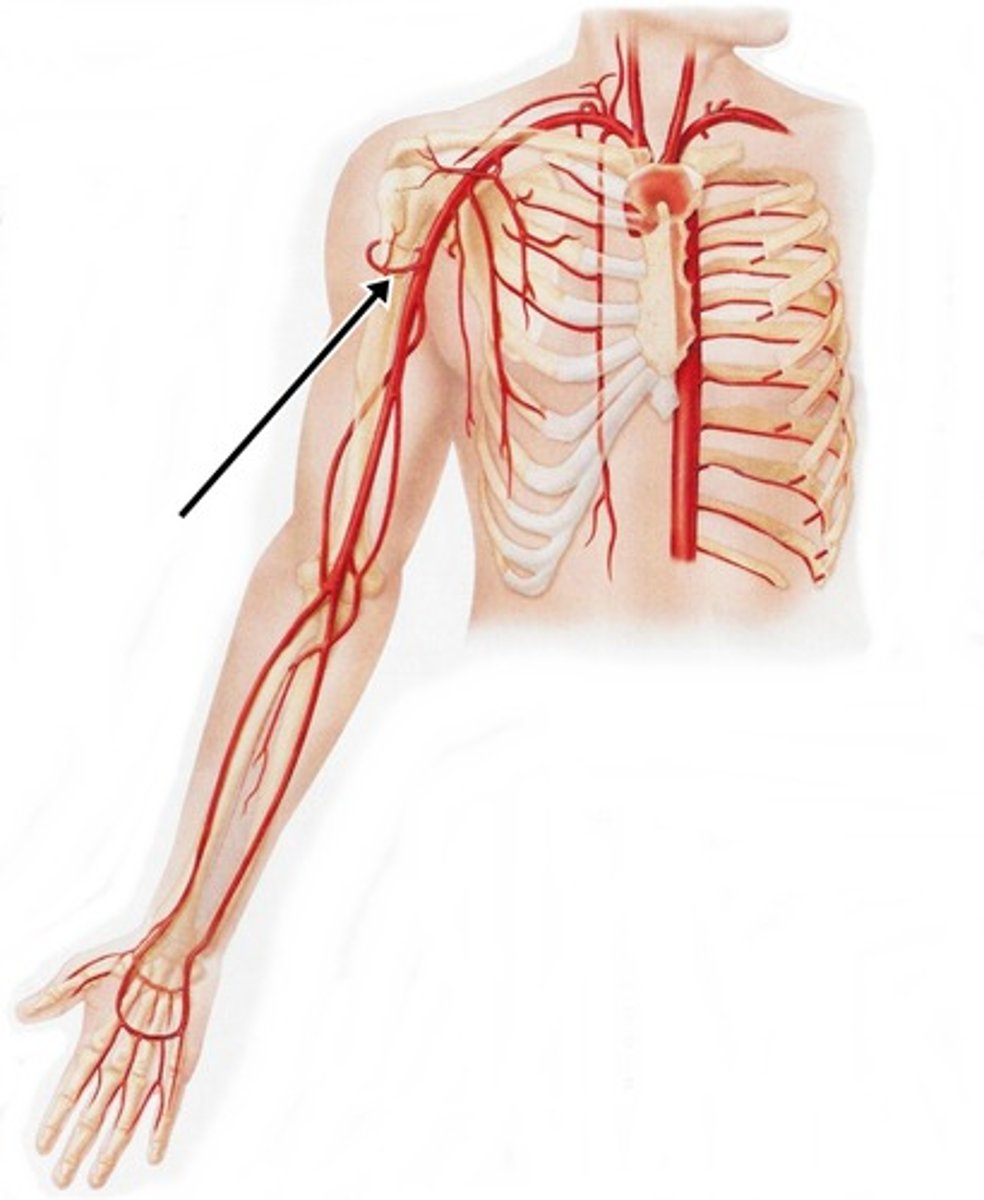
posterior circumflex humeral artery
Origin: axillary (this is bigger then the one opposite to it)
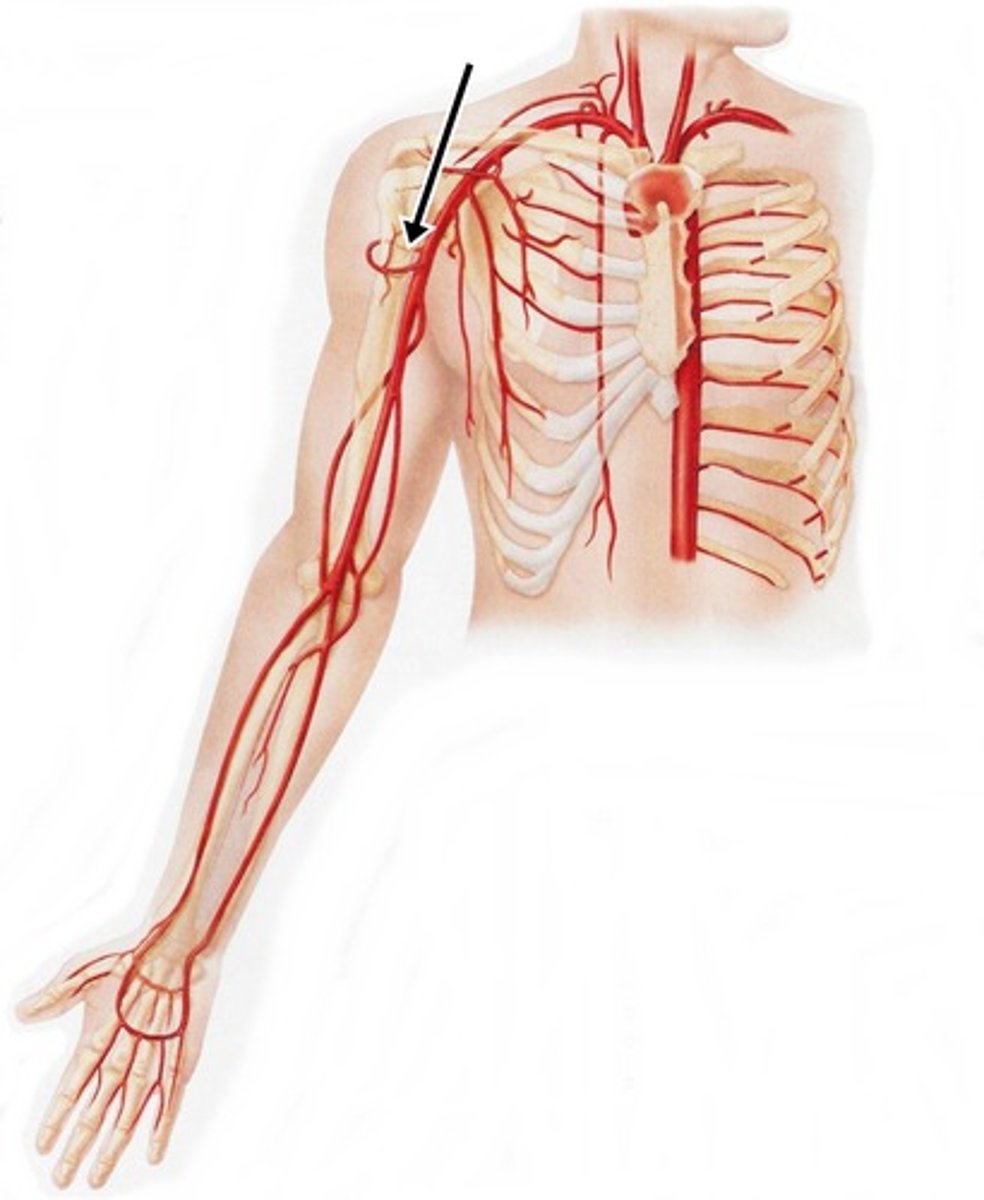
circumflex scapular artery
Originates as a branch of the subscapular artery, which is a branch of the axillary artery
Leaves the axilla through the triangular space to enter the posterior scapular region
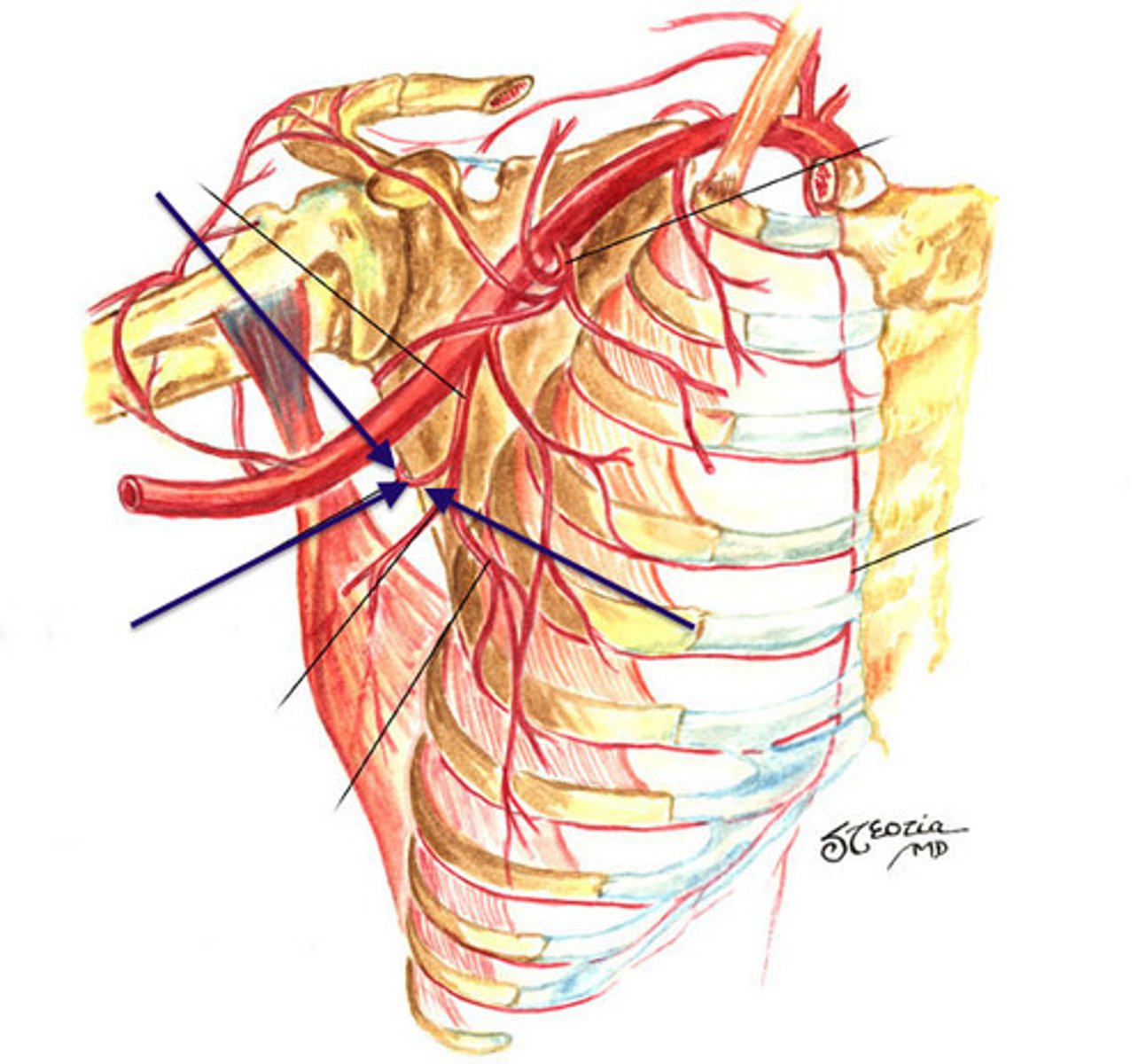
brachial artery
The major vessel in the upper extremity that supplies blood to the arm.
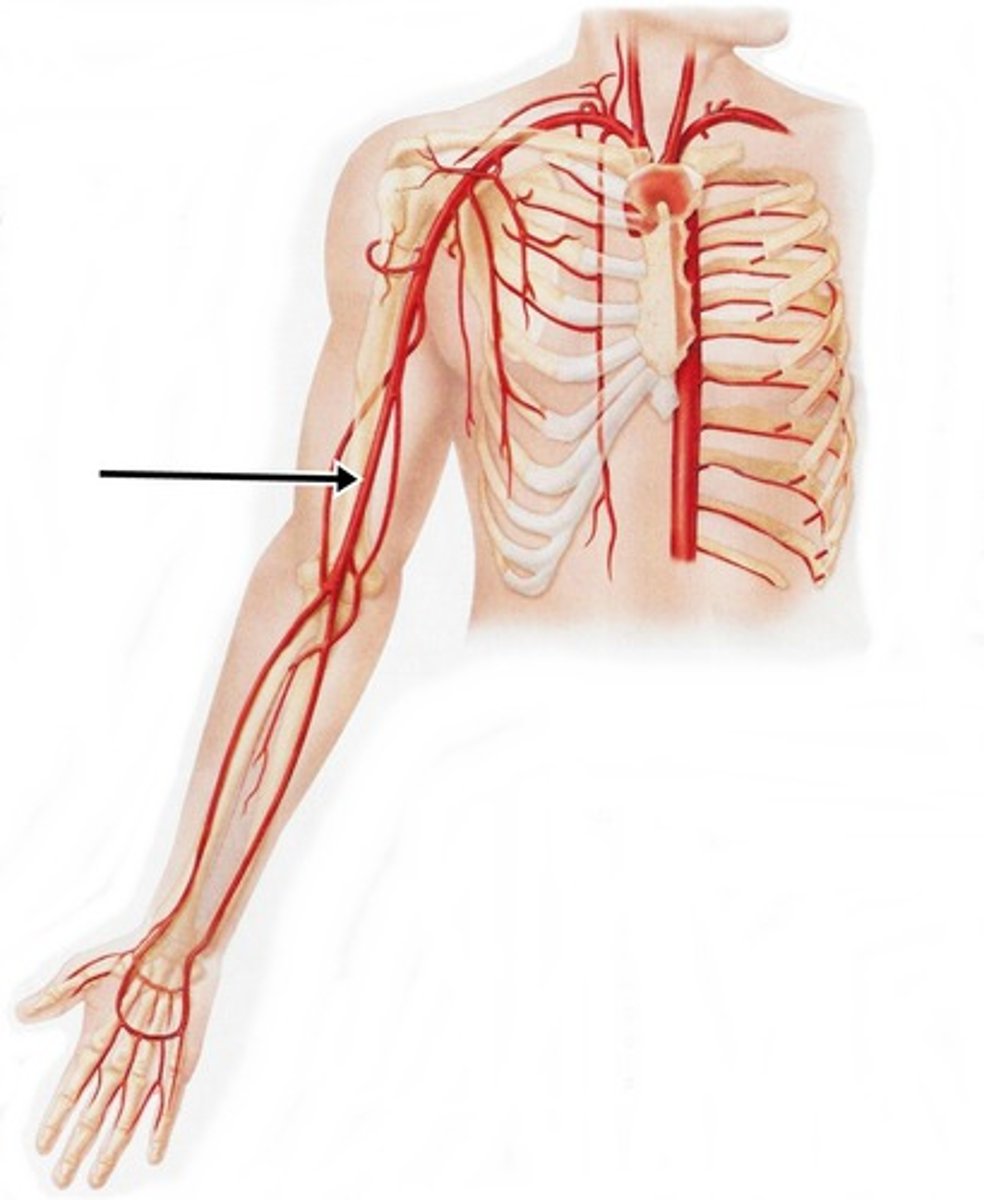
lateral thoracic artery
serves lateral chest wall
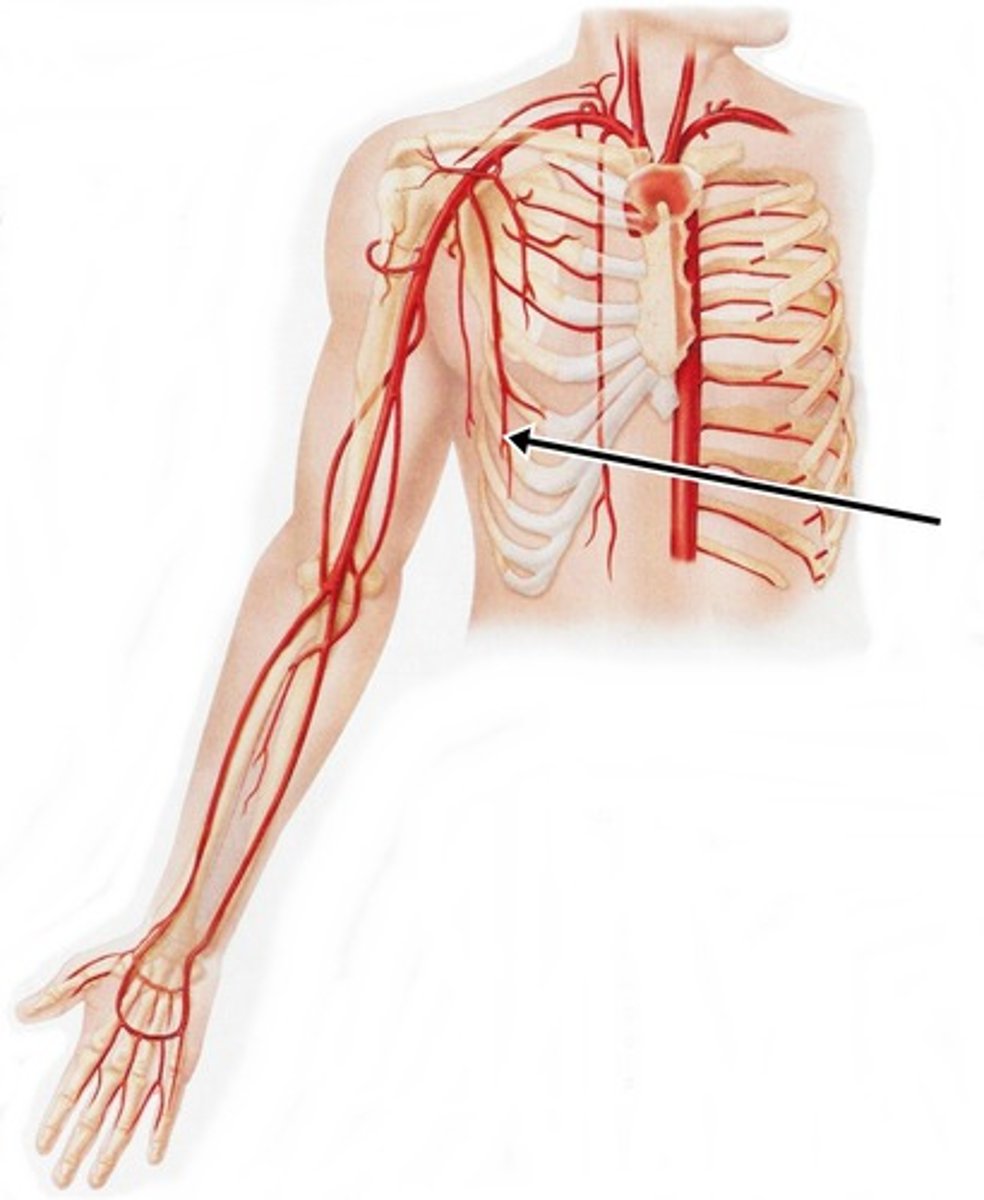
internal thoracic artery
branch of subclavian artery; supplies costal and sternum