Lecture 2--Chordates and Vertebrates
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the five characteristics shared by all chordates?
Notochord
Pharyngeal/gill slits
Endostyle
Dorsal hollow nerve tail
Post-anal tail
What are the two additional characteristics shared by all vertebrates?
Bilateral symmetry and closed circulatory system
What is the function of the notochord?
Provides support to body and facilitates movement/muscle contractions
What embryonic layer does the notochord originate from?
Mesoderm
What is the function of the pharyngeal slits?
Support gill structures and facilitate feeding mechanism
Where are the pharyngeal slits located in chordates?
Posterior to mouth
Which organ is the endostyle located in?
Pharynx
What is the function of the endostyle?
Moves food particles to GIT with cilia (lower vertebrates), becomes thyroid (higher vertebrates)
What is ontogeny?
Developmental history of an organism from fertilization
What is the process where a zygote rapidly divides?
Cleavage
What are the stages of zygote development?
Zygote → morula → blastula
What is gastrulation of the blastula?
Formation of gut, germ layers
What is neurulation of the blastula?
Formation of the neural tube
What are the three germ cell layers?
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
What does the ectoderm develop into?
Exoskeleton, skin, appendages, nervous system
What does the mesoderm develop into?
Organs, bone and cartilage, muscles, vasculature
What does the endoderm develop into?
Inner lining of organs, GI tract, respiratory tract, bladder, urethra, liver
What are the four types of tissue in the body?
Epithelium, connective tissue, muscle, nervous
What are the four types of epithelium?
Squamous, cuboidal, columnar, transitional
What is transitional epithelium?
Between squamous and cuboidal
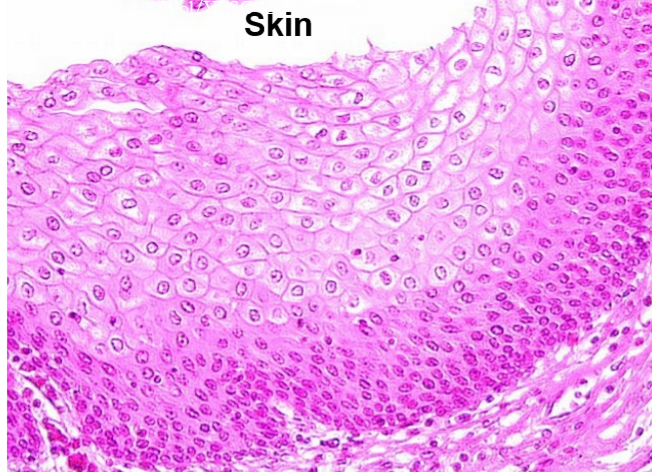
What type of epithelium is this?
Squamous
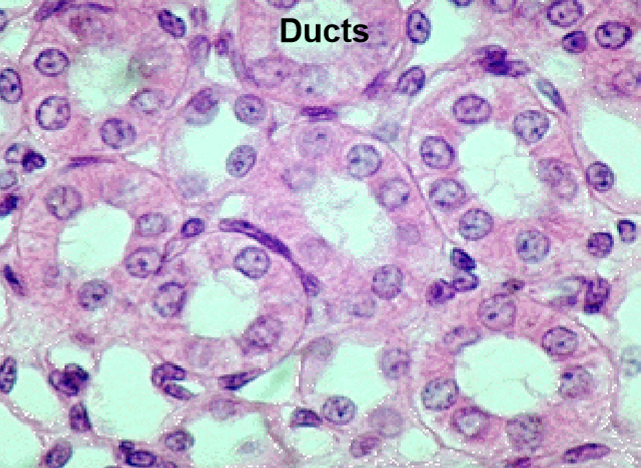
What type of epithelium is this?
Cuboidal
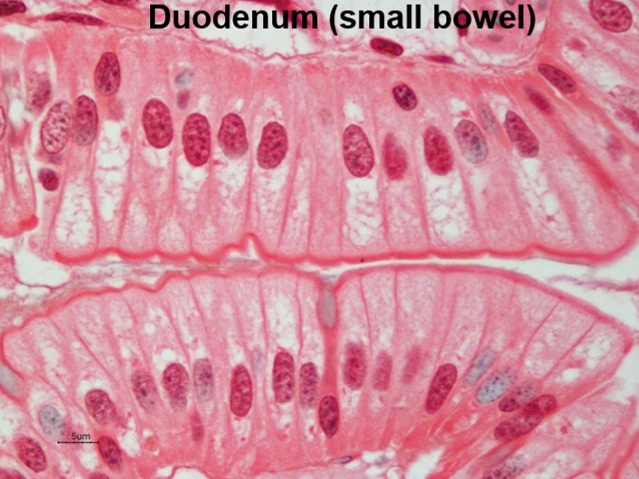
What type of epithelium is this?
Columnar
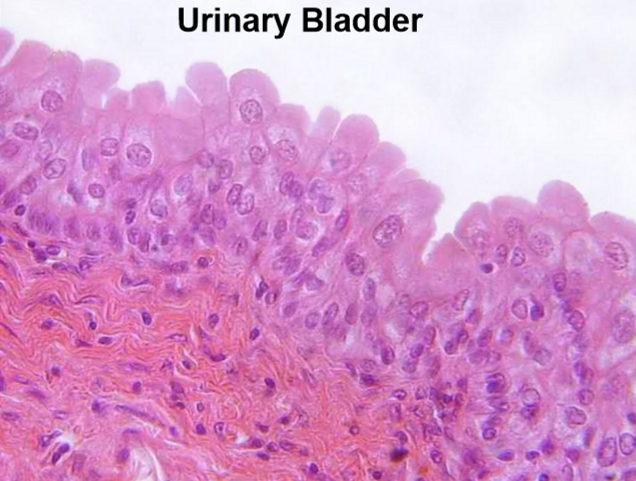
What type of epithelium is this?
Transitional
What do exocrine glands secrete into?
Ducts
What do exocrine glands secrete into?
Blood
What are the two types of connective tissue?
Bone and cartilage
What is phylogeny?
Course of evolutionary change within related groups/organisms
Vertebrates have all chordate characteristics plus:
Vertebral column (replaces notochord), cranium
What are agnathans?
Jawless vertebrates
What is a craniate?
Chordate with a head containing a brain, eyes, and sensory organs
What do agnathans have to draw in food/water?
Muscular pharyngeal pump
What is a gnathostome?
Chordate with a jaw
What is the benefit of gnathostomes having a jaw?
Removes prey size limitations
What is the type of gnathostome that has bony armor?
Placoderms
What is a placode?
Embryonic structure that gives rise to other structures
What are the two types of gnathostomes?
Chondrichthyes and teleostomi
What is the type of gnathostome that has a cartilaginous skeleton?
Chondrichthyes
What are the two modern groups of chondrichthyes?
Elasmobranch (sharks, rays) and holocephalans (chimaera)
What type of teleostomi contains ray-finned fishes?
Actinoptergii
What is a special feature of actinopterygii?
Otoliths
What type of teleostomi contains fleshy-finned fish and gives rise to tetrapods?
Sarcopterygians
What are amniotes?
All terrestrial vertebrates except Amphibia → embryos enveloped in extra-embyronic membranes
What are the two characteristics shared by all mammals?
Hair, mammary gland
What order of mammals contains egg-laying animals?
Monotremes
What order of mammals contains marsupials (early birth)?
Metatheria
What order of mammals contains placentals?
Eutheria