Anatomy Unit 3 Cardiovascular System
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
what are the 3 components of the cardiovascular system?
blood
blood vessels
the heart
what are the 2 circuits of the cardiovascular system? describe their function
pulmonary circuit: transports blood to and from lungs
systemic circuit: transports blood to and from the rest of the body
what are the formed elements of blood? what percentage of blood do they make up?
makes up 45% of blood
erythrocytes (RBC)
leukocytes (WBC)
thrombocytes (platelets)
describe the appearance, shape, functions, and life span of red blood cells
appearance:
atypical (no DNA, no nucleus)
appears red
shape: disk-shaped with an indent in the center
increases surface area, allowing more O₂ to bind to it
functions: (carries out tasks using enzymes)
facilitates the transport of O₂ and CO₂
contains iron and a protein called hemoglobin
life span: 120 days
describe the function of white blood cells
defends and protects the body from foreign invaders
uses blood as a way to move from bone marrow to the rest of the body
less common than RBC
describe the appearance and function of platelets
appearance:
covered with many proteins to allow materials to stick (sticky)
not true cells (cell fragments)
function:
clots to prevent blood loss
what are arteries? describe the location and functions of arteries
muscular blood vessels
located deep to skin
functions:
carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body
changes diameter as needed
has higher pressure (how pulse is taken)
what are arterioles?
small arteries that connect to capillaries
what are veins? describe the location and functions of veins
flexible vessels with thin walls
located closer to the surface of the skin
functions:
carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart
transports CO₂, O₂, and other waste products
pumps blood at lower pressure: uses valves to prevent backflow
what are venules?
small veins near capillaries
describe the location, functions, and appearance of capillaries
located everywhere
functions:
site of exchanges (O₂, nutrients, and waste)
connects arteries to veins
appearance:
has a single layer of simple squamous endothelium
connected with tissue
what is vasoconstriction? what can it help with?
narrowing or constriction of blood vessels; making the opening smaller
can help stabilize/raise blood pressure, reduce heat loss, send more O₂ or nutrients to organs, protect the body against blood loss
what is vasodilation? what can it lead to?
opening of blood vessels
can lead to increased blood flow and decreased blood pressure
what is the heart and what does it do (generally)?
muscular 2-part pump that forces blood throughout the body
what does the left side of the heart do?
sends blood at high pressure to all parts of the body (except lungs)
what does the right side of the heart do?
pumps blood at a lower pressure through the lungs
where is the heart located?
in the thoracic cavity; between the pleural cavities and in the mediastinum
surrounded by pericardial sac
what is the base of the heart? where is it located?
the attached base where the great veins (aorta, vena cava) connect to the superior end of the heart
located posterior to the sternum
what is the apex of the heart?
inferior pointed tip
what are atria? describe its appearance
superior superficial chambers of the heart
appearance: when not filled with blood, each atrium deflates and becomes a lumpy, wrinkled flap (called auride)
what are ventricles?
inferior chambers of the heart
what are the 2 types of pericardium?
visceral pericardium (inner layer)
parietal pericardium (outer layer)
where is the pericardial cavity located? what does it contain?
located between parietal and visceral layers of the heart
contains pericardial fluid
what does the parietal sac do? what is it made of?
surrounds and stabilizes the heart
made up of fibrous tissue
what is the pericardium? describe its functions
double lining of the pericardial cavity
functions:
protects the heart and greater vessels
releases fluid to lubricate the heart to reduce friction
what are sulci?
deep groves within the heart
what are the 3 layers of the heart? describe them
epicardium (outer layer)
serous layer
areolar connective tissue
myocardium (middle layer)
cardiac muscle tissue
coordinates and controls heartbeat
endocardium (inner layer)
simple squamous epithelium
describe the location, appearance, and connections of cardiac muscle tissue
found in the myocardium
appearance:
single, central nucleus
branching interconnections between cells
intercalated discs
desmosomes: allow for strong & connected contractions
gap junctions: allows ions to pass through (allowing muscle to contract)
what are coronary arteries and veins generally?
the blood vessels of the heart
what are coronary arteries? describe their location and function
larger vessels located along the surface of the heart and branch off into smaller vessels & capillaries
function:
system of vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to heart muscle tissue (myocardium)
what are coronary veins? describe its function
function: collects deoxygenated blood from heart muscle tissue (myocardium) and takes it to the right atrium
what does coronary artery/vein blockage lead to?
cardiac infraction: death of cardiac muscles due to diminished blood flow
cardiac ischemia: malfunction of muscles due to lack of oxygen (can lead to infraction)
what are the 3 types of heart diseases?
coronary artery disease (CAD)
angina pectoris
myocardial infarction (MI or AMI)
what is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
when coronary circulation is partially/completely blocked by atherosclerotic plaque (fatty deposit)
plaque narrows vessel wall
what is angina pectoris?
when the workload of the heart increases, causing temporary ischemia
painful during exercise; comfortable at rest
what is myocardial infarction (MI or AMI)?
when cardiac cells die from a lack of oxygen
usually diagnosed by EKG and blood studies
consequences depend on the site and nature of the circulatory blockage
what are the treatment options of CAD and MI/AMI?
Risk Factor Modification
stop smoking, high blood pressure treatment, lower cholesterol diet, stress reduction, increased exercise
drug treatment
surgery
describe the non-invasive/invasive surgical treatments of CAD and MI/AMI
non-invasive
atherectomy
angioplasty/stents
invasive
coronary artery bypass surgery
what are the functions of heart valves?
facilitates pumping action
keeps blood flowing in correct direction
what are the 4 heart valves and what do they connect?
tricuspid valve (AV)
connects RA and RV
pulmonary valve (SL)
connects RV and pulmonary artery
bicuspid/mitral valve (AV)
connects LA and LV
aortic valve (SL)
connects LV and aorta
what is the interatrial septum?
‘wall’ that separates the atria
what is the interventricular septum?
‘wall’ that separates the ventricles
where does the right atrium receive blood from?
2 great veins
superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
where does the superior vena cava receive blood from? where does it transfer blood to?
receives blood from:
head
neck
upper limbs
chest
transfers blood to the right atrium
where does the inferior vena cava receive blood from? where does it transfer blood to?
receives blood from:
trunk
viscera
lower limbs
transfers blood to the right atrium
what is the coronary sinus? where is it located?
where the coronary veins bring deoxygenated blood from the heart to the right atrium
describe the interatrial septum, posterior & anterior wall of the right atrium
interatrial septum & posterior wall
smooth surface
anterior wall
prominent muscular ridges called pectinate muscles
what is foramen ovale? describe its function and where it is found
function:
oval opening that connects the 2 atria of the fetus, since lungs are still developing
closes within 3 months of birth
found only in the right atrium of newborns (3 months or younger)
fossa ovalis (small depression in the heart wall) appears after foramen ovale closes
describe the internal surface of the right ventricle
has trabeculae carnaea (muscular ridges)
has papillary muscles
describe the location and function of the tricuspid valve
found in the right ventricle
goes from RA to RV
function:
connects to chordae tendineae
opening and closing controlled by papillary muscle
where does the left atrium receive blood from?
left and right pulmonary veins
what is auscultation?
listening to heart & lung sounds
heart sounds:
“lub” AV valves closing
“dub” SL valves closing
heart murmur (unusual sound)
lung sounds:
airflow
what is a heartbeat?
single contraction of the heart in sequence
atria contracts first
ventricles contract second
& repeats
what is a cardiac cycle?
series of pressure changes within the heart due to the movement of blood
what is diastole?
when the ventricles are relaxed in the cardiac cycle
how long does the average heartrate (bpm) last in a cardiac cycle?
at 75 bpm, the cardiac cycle lasts about 800 milliseconds
what happens when heartrate increases?
all phases of cardiac cycle shorten, particularly diastole
what does automaticity mean?
to beat on its own
what are the 2 parts of the conducting system of the heart? briefly describe their function
conducting system
function: controls and coordinates heartbeat
contractile cells
function: produce contractions that expel blood
describe the 3 components of the cardiac conducting system and its functions
sinoatrial (SA) node
natural pacemaker of the heart
function: initiates heartbeat and determines heartrate
atrioventricular (AV) node
function: passes signal to AV bundle (bundle of His)
conducting cells
function: interconnect nodes and distribute the contractile stimulus throughout the myocardium
describe the sequence of a heartbeat
SA node & pacemaker cells initiate heartbeat
the action potential travels from SA node to AV node, while the contractile cells stimulate both atria
AV node receives the signal after 100 millisecond delay
signal travels to AV bundle (bundle of His)
then travels to the interventricular septum
then travels to right and left bundle branches
signal is conducted to Purkinje fibers
then to the moderator band & papillary muscles
ventricles begin to contract
what is an arrythmia?
any deviation in the normal heartbeat rhythm
what are the 5 types of arrythmia?
tachycardia: too fast
brachycardia: too slow
premature contraction: too early
fibrillation: too erratic
etopic pacemaker: contractile cells start trying to send conduction signals
what are the 3 types of ECG/EKGs?
3 lead (portable)
5-7 lead (portable)
12 lead (standard type in hospitals and ambulances)
what is the resting membrane potential (polarized state)?
when the heart is ready to contract
what is depolarization?
when the heart is contracting
what causes polarization and depolarization?
sodium-potassium pump
allows cells to change from resting potential to excitable, enabling it to contract
what is an electrocardiogram?
a tool to see what the heart is doing
how do you read an ECG/EKG?
P wave
atrial depolarization
QRS complex
ventricle depolarization
T wave
ventricle repolarization
how do you calculate heartrate?
6 second rule
(#of R waves in a 6 second period) x 10
what portion of the conducting system does the right ventricle contain? describe its functions
moderator band
functions:
coordinates contractions
delivers contraction stimulus to papillary muscles
so that the chorea tendinea is put under tension before the ventricle contracts
briefly describe the features of the left atrium
has less prominent pectinate muscles
contains the bicuspid/mitral valve
leads blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle
how does blood move out the left ventricle?
leaves the left ventricle through the aortic valve into the ascending aorta then out to the rest of the body
describe the physical features of the left ventricle
has trabeculae carneae (muscular ridges)
no moderator band
contains papillary muscles
opens and closes the mitral valve
thick walls for a more powerful contraction
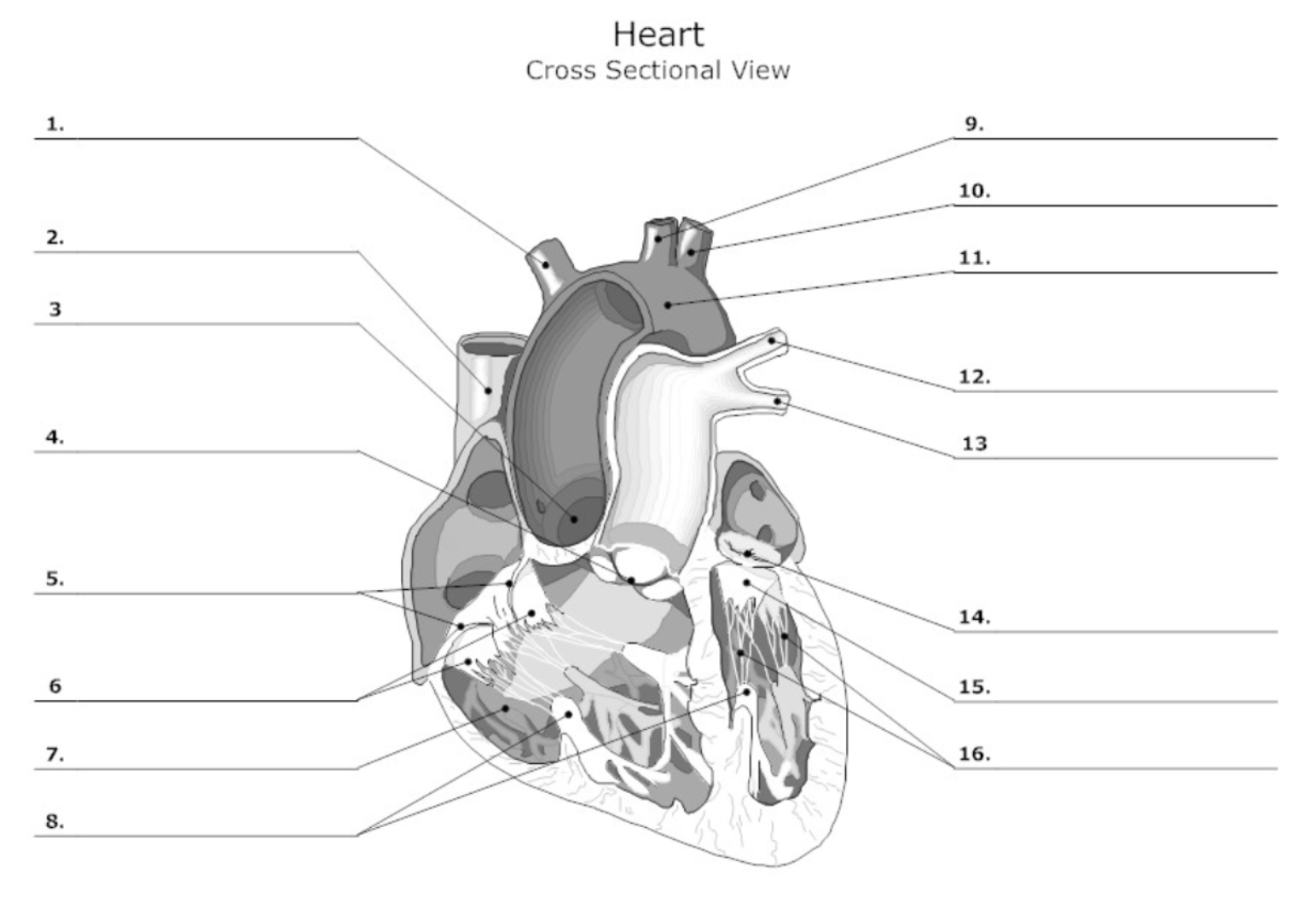
label #1, 9, 10
aortic artery
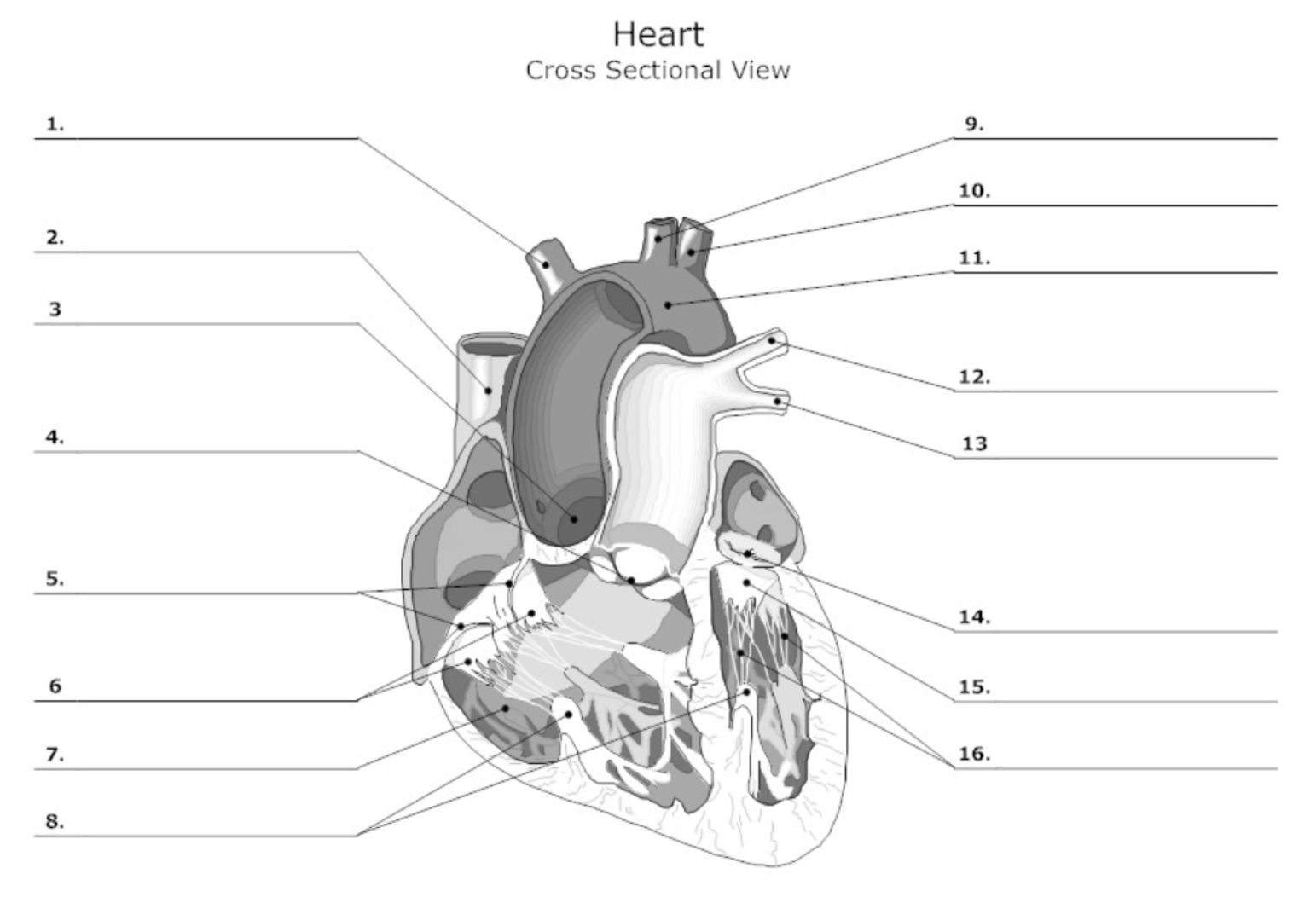
label #2
superior vena cava
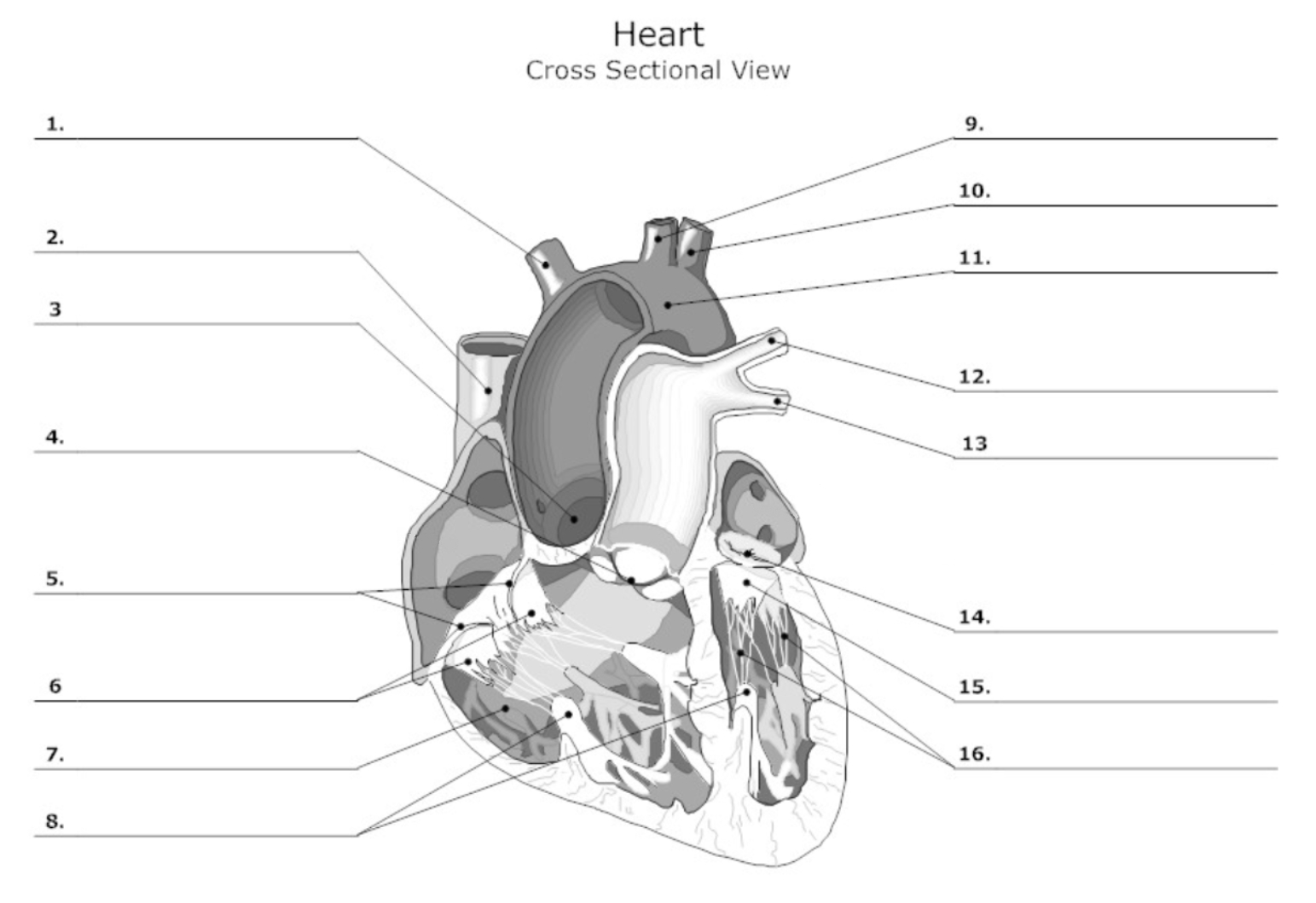
label #3
aortic valve
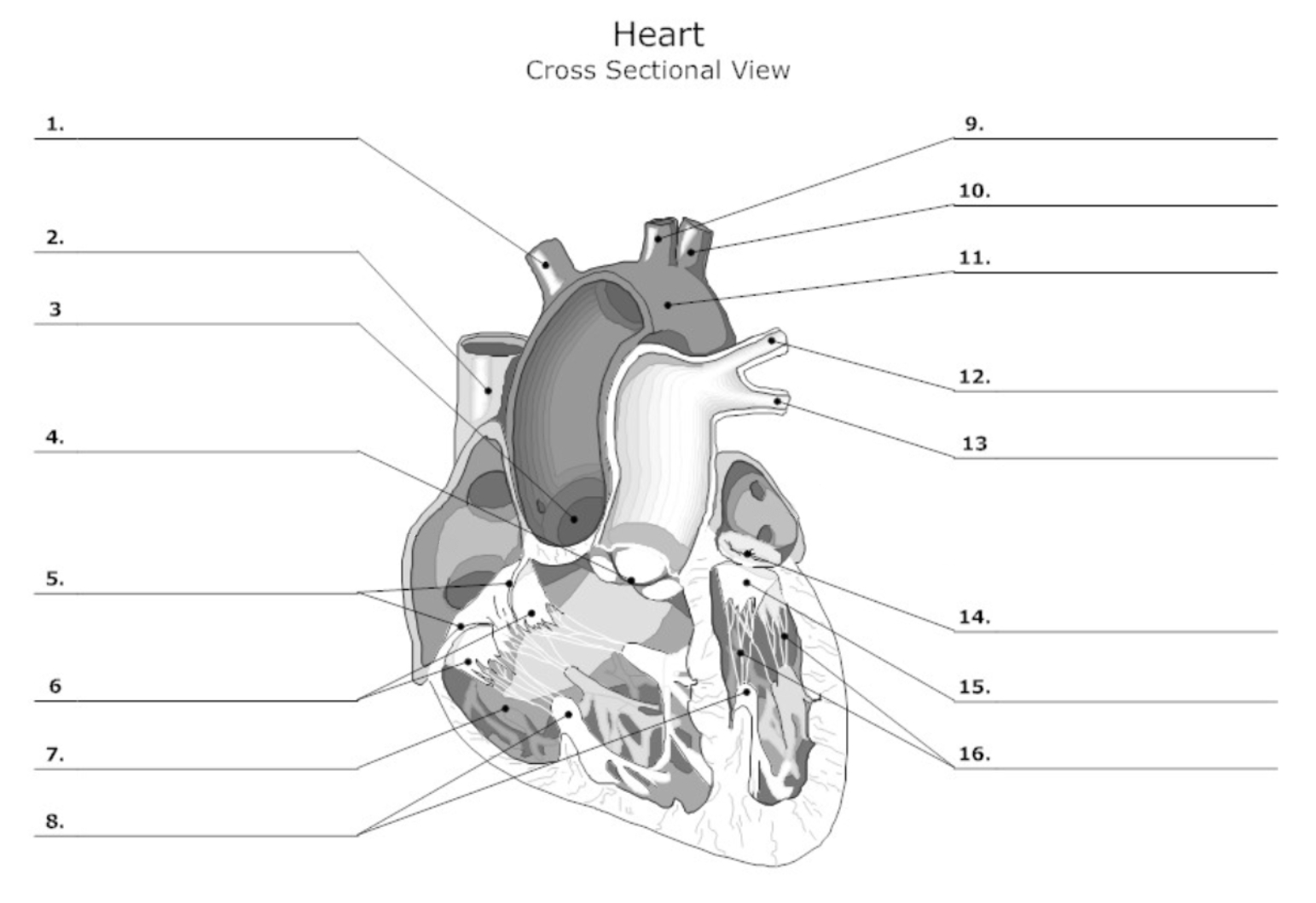
label #4
pulmonary semilunar (SL) valve
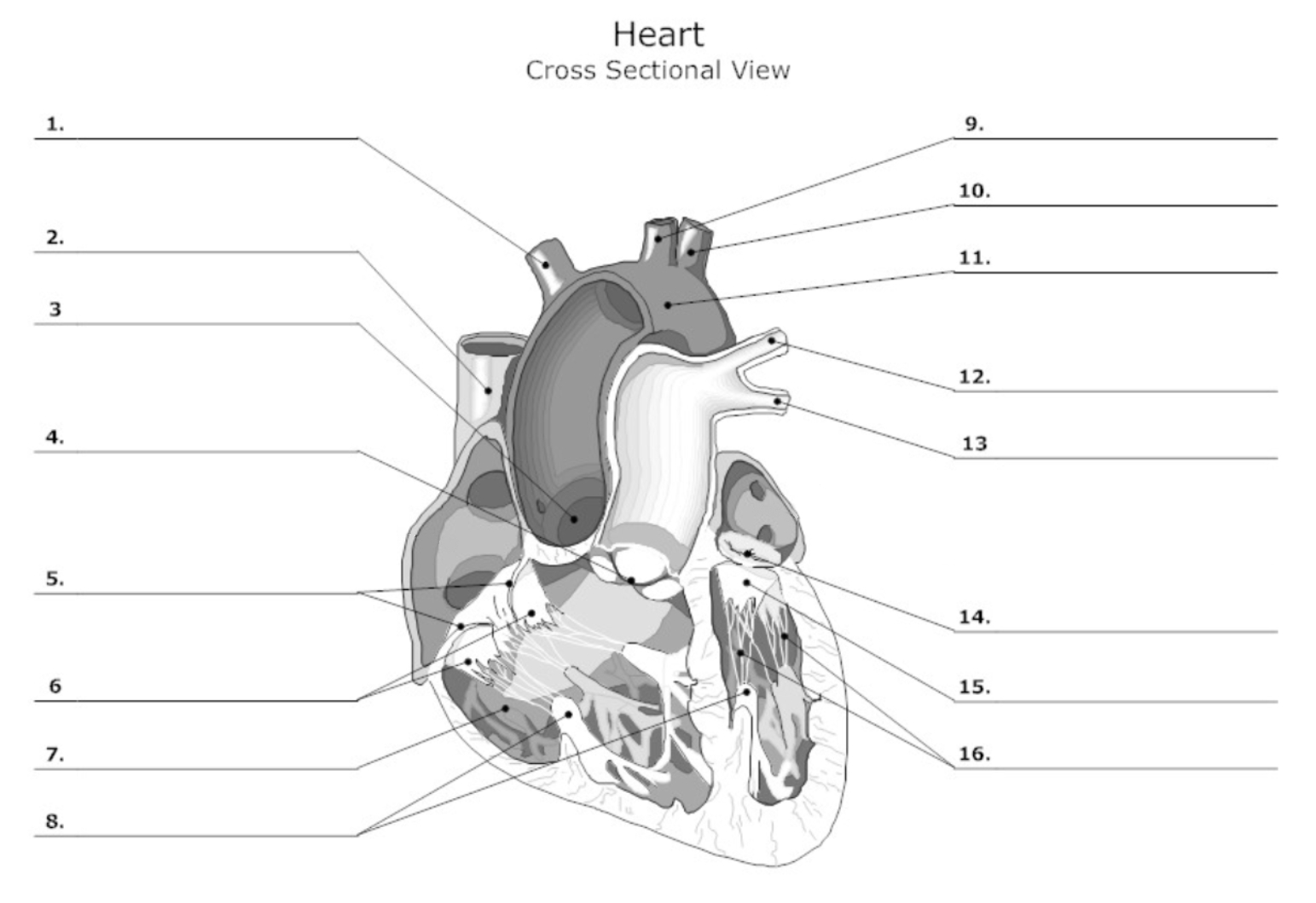
label #5
tricuspid valve
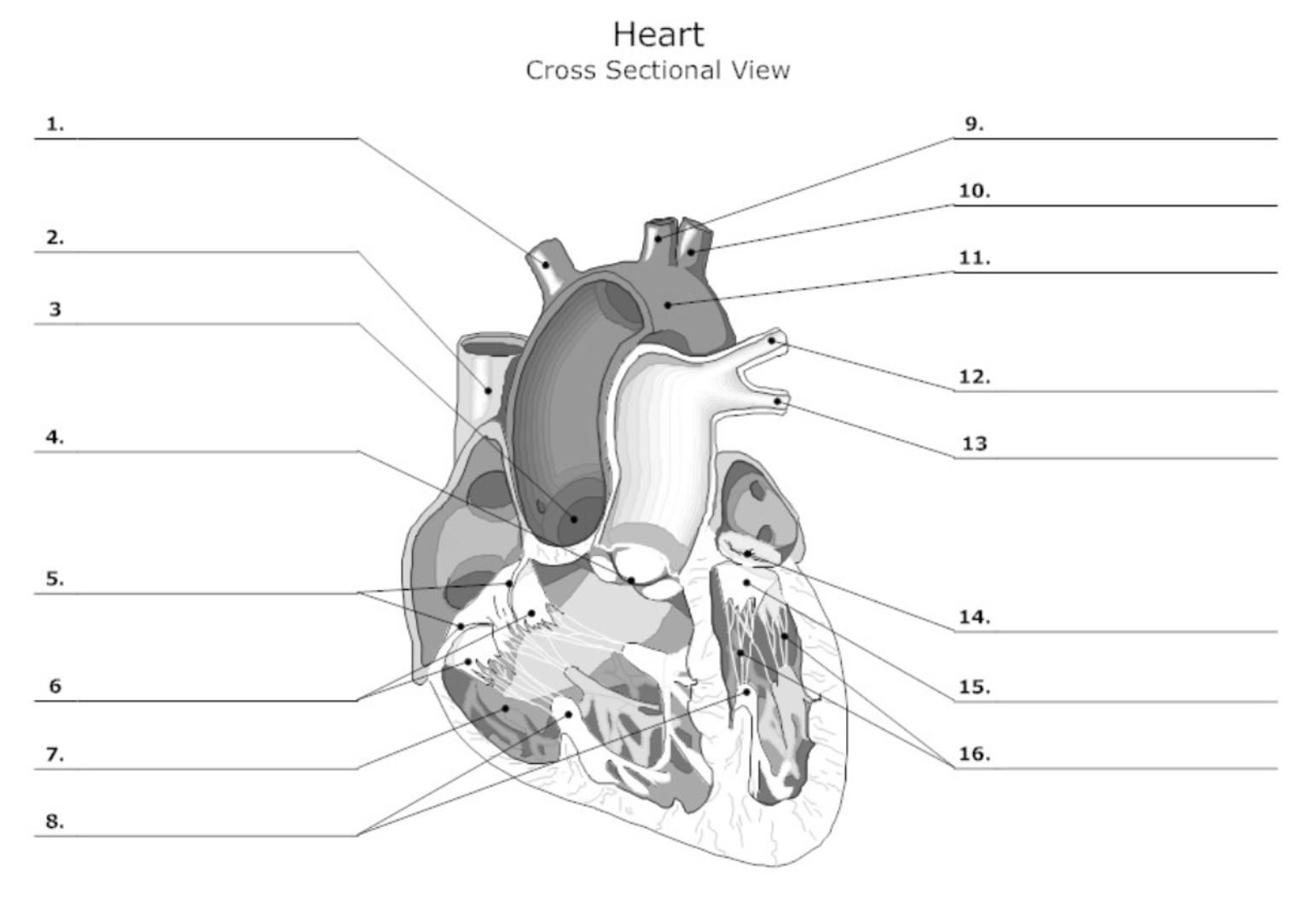
label #6
leaflet
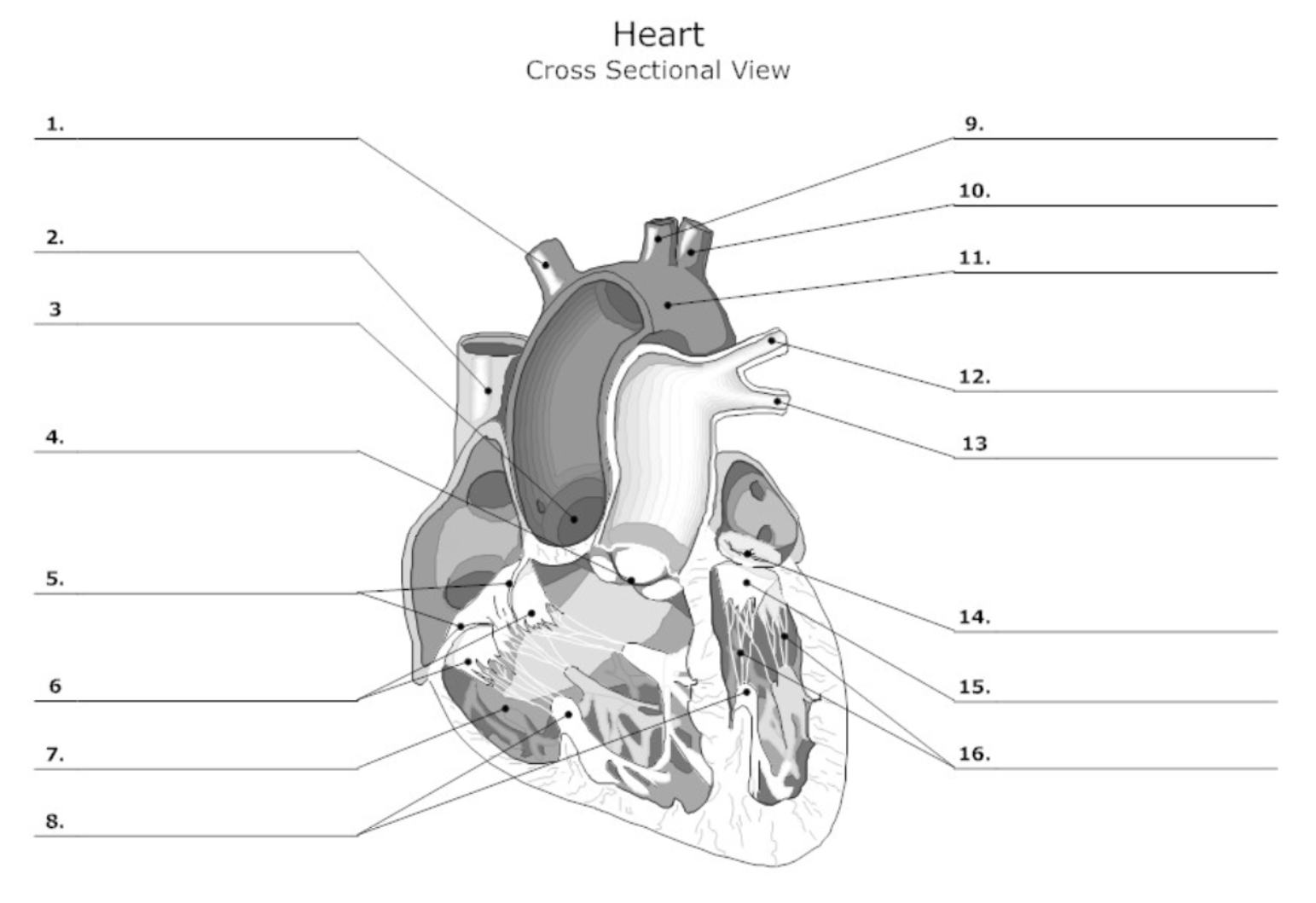
label #7
pectinate muscle
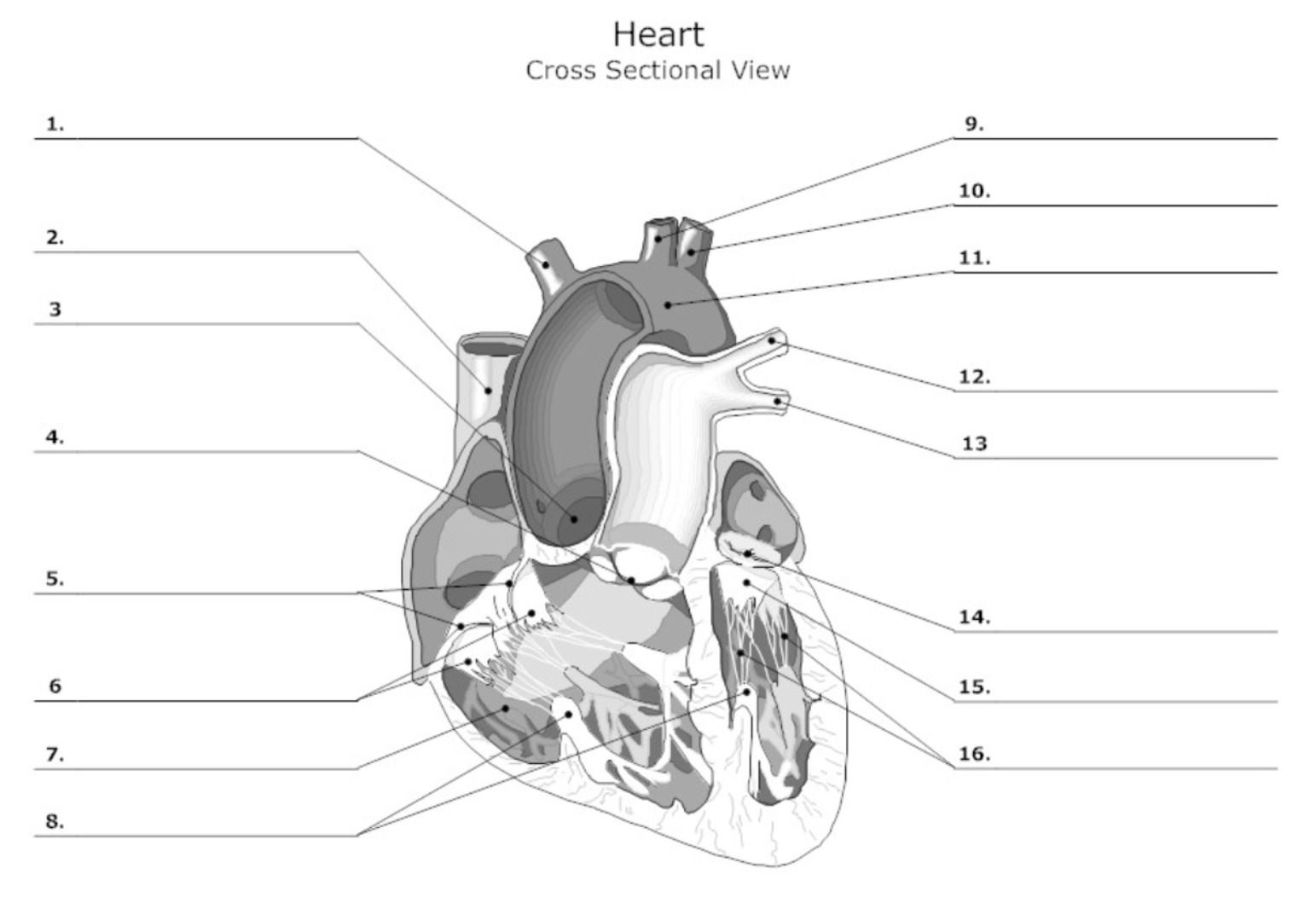
label #8
papillary muscle
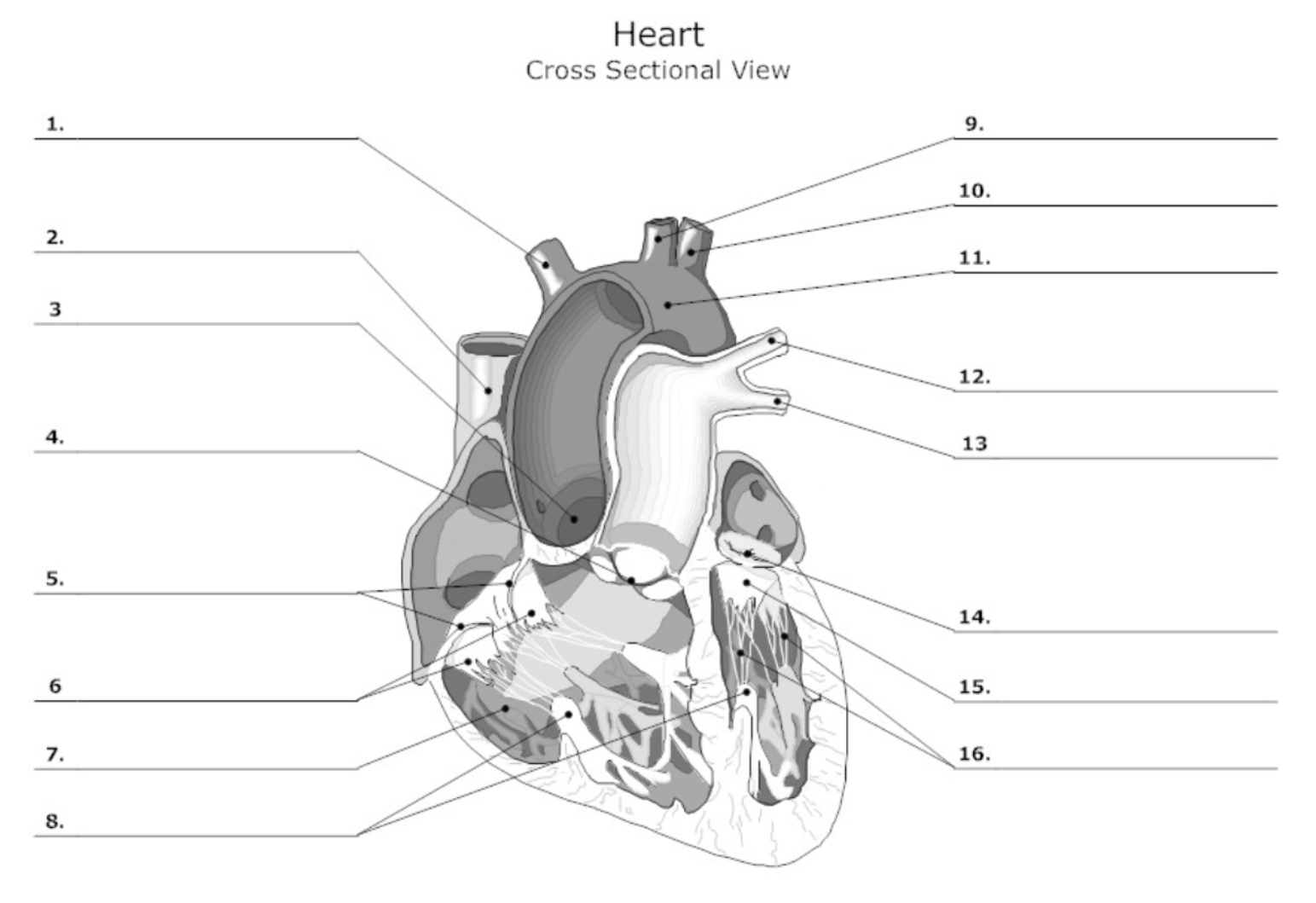
label #11
aorta
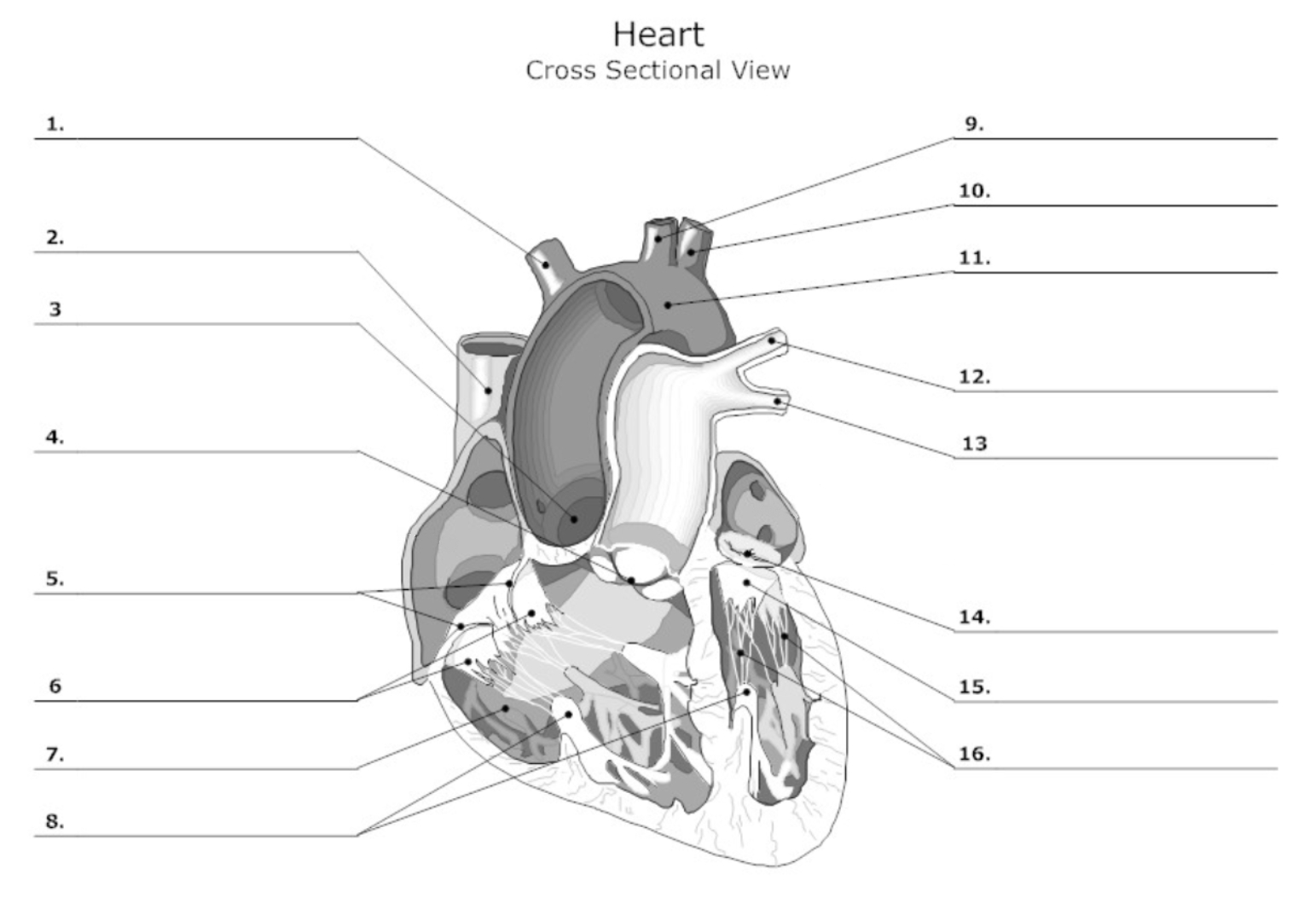
label #12, 13
pulmonary artery
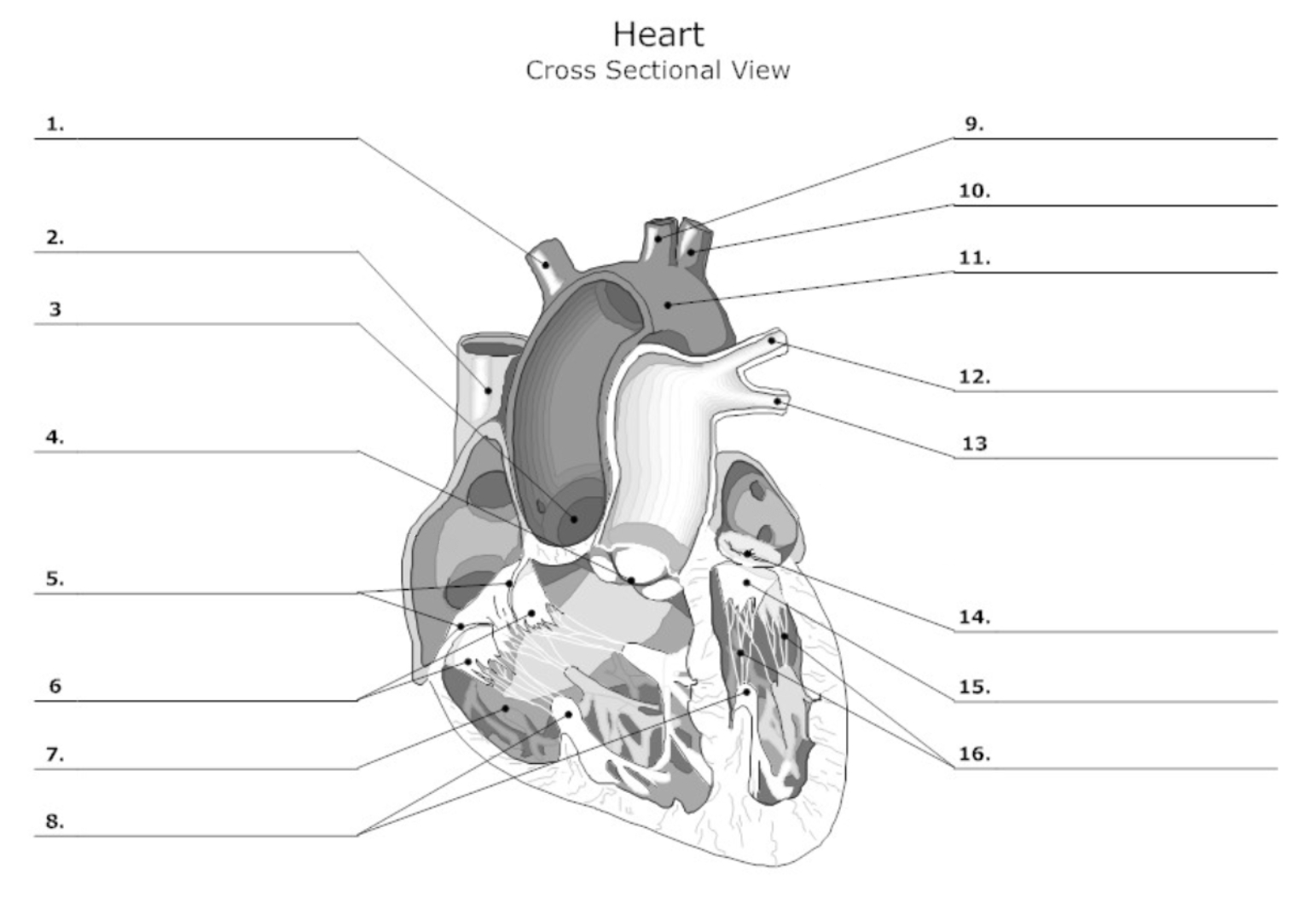
label #14
mitral/bicuspid valve
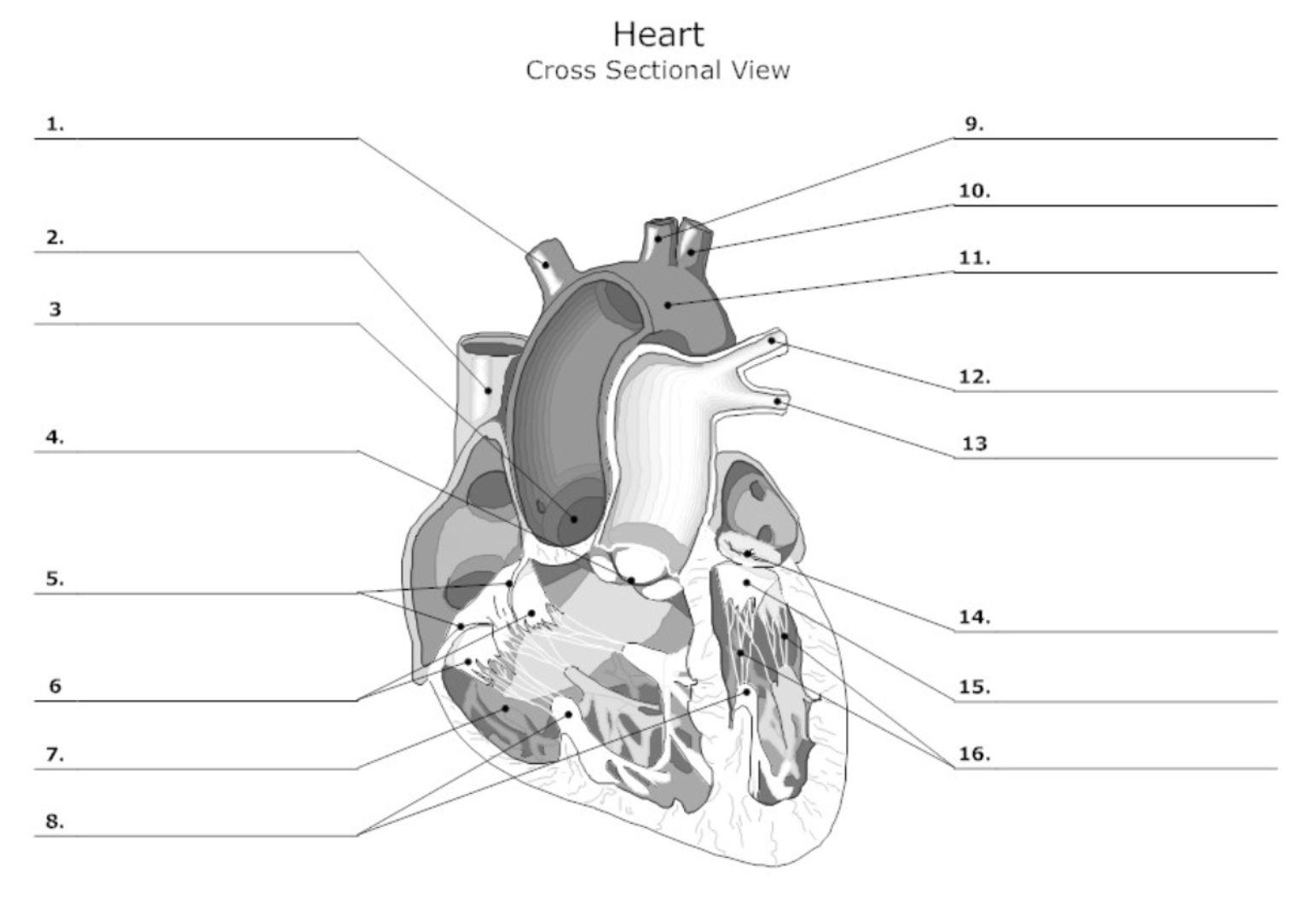
label #15
leaflet
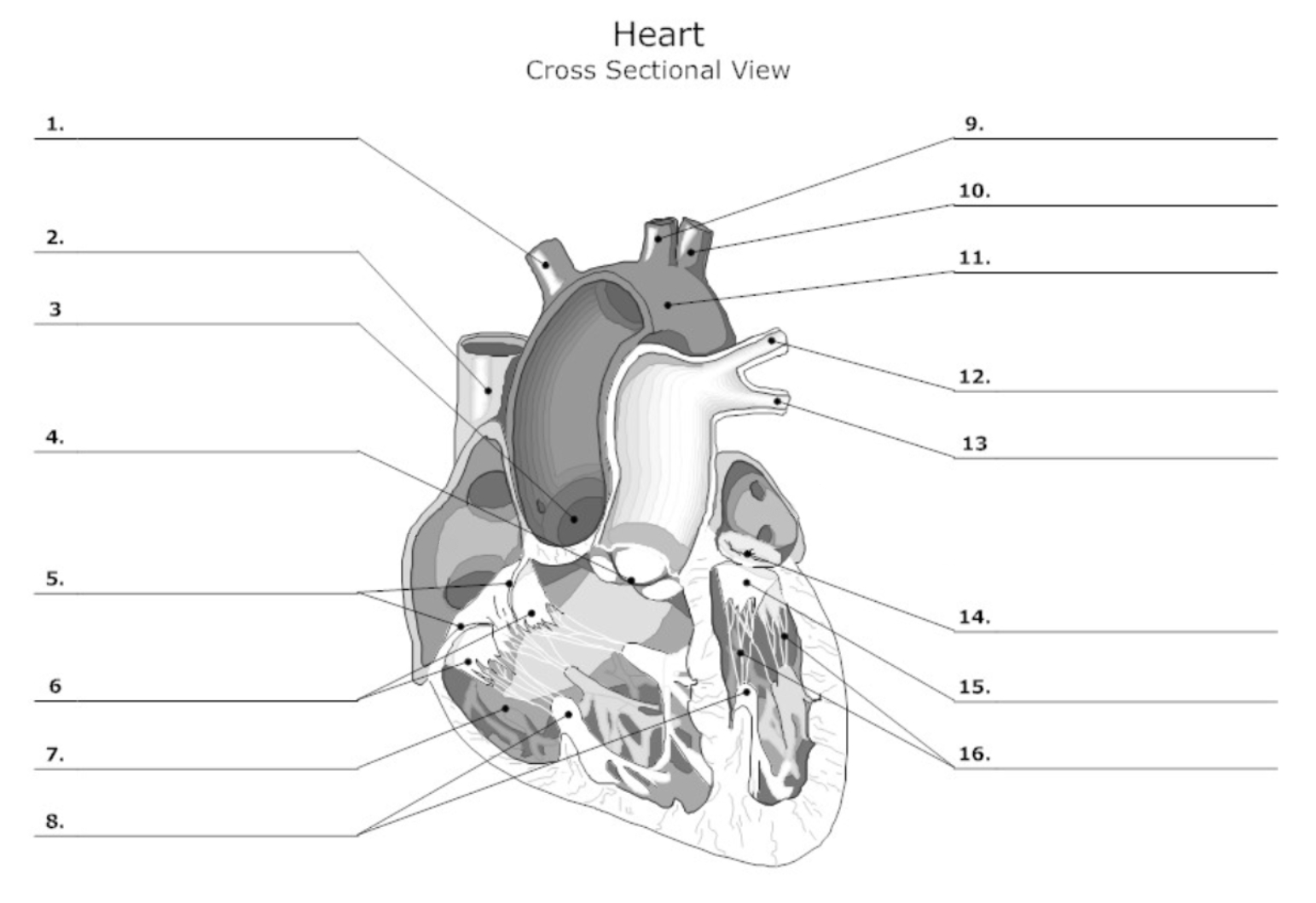
label #16
chordae tendineae
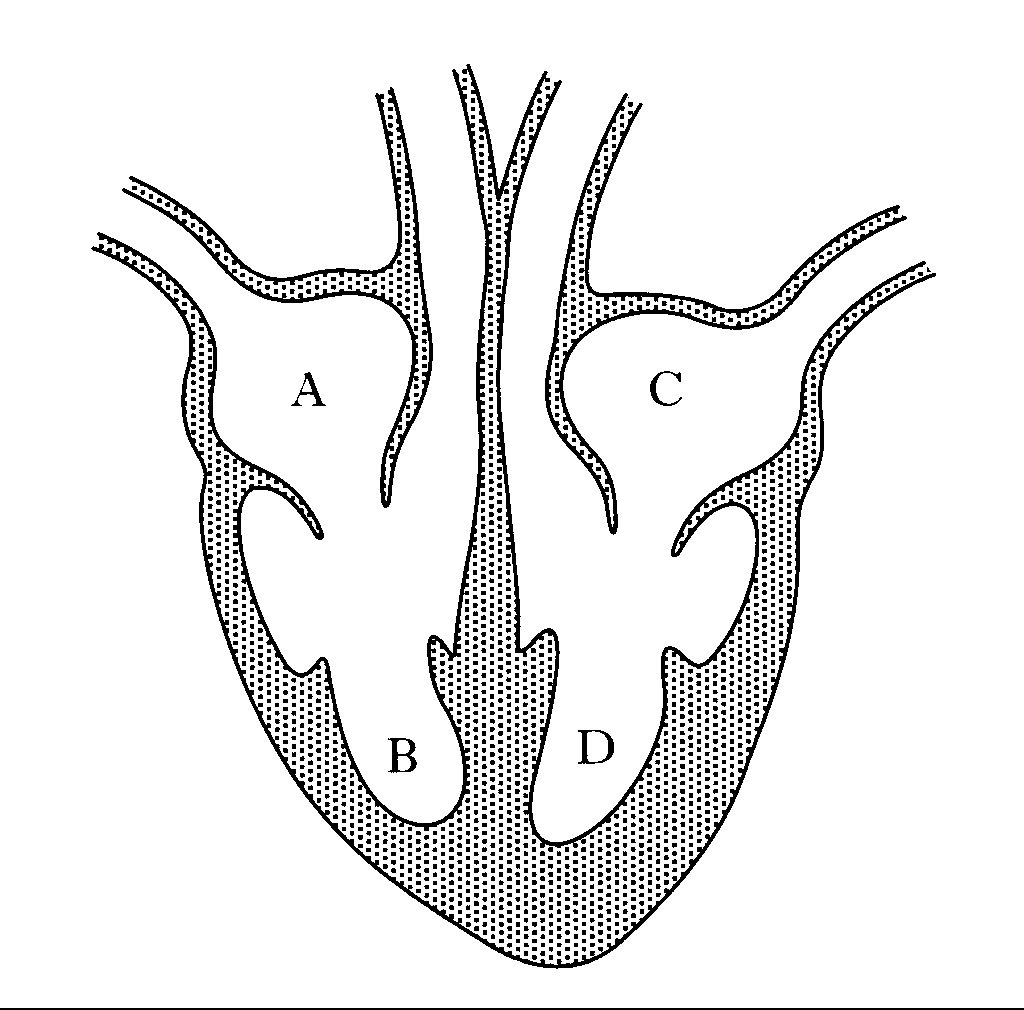
label A
right atrium
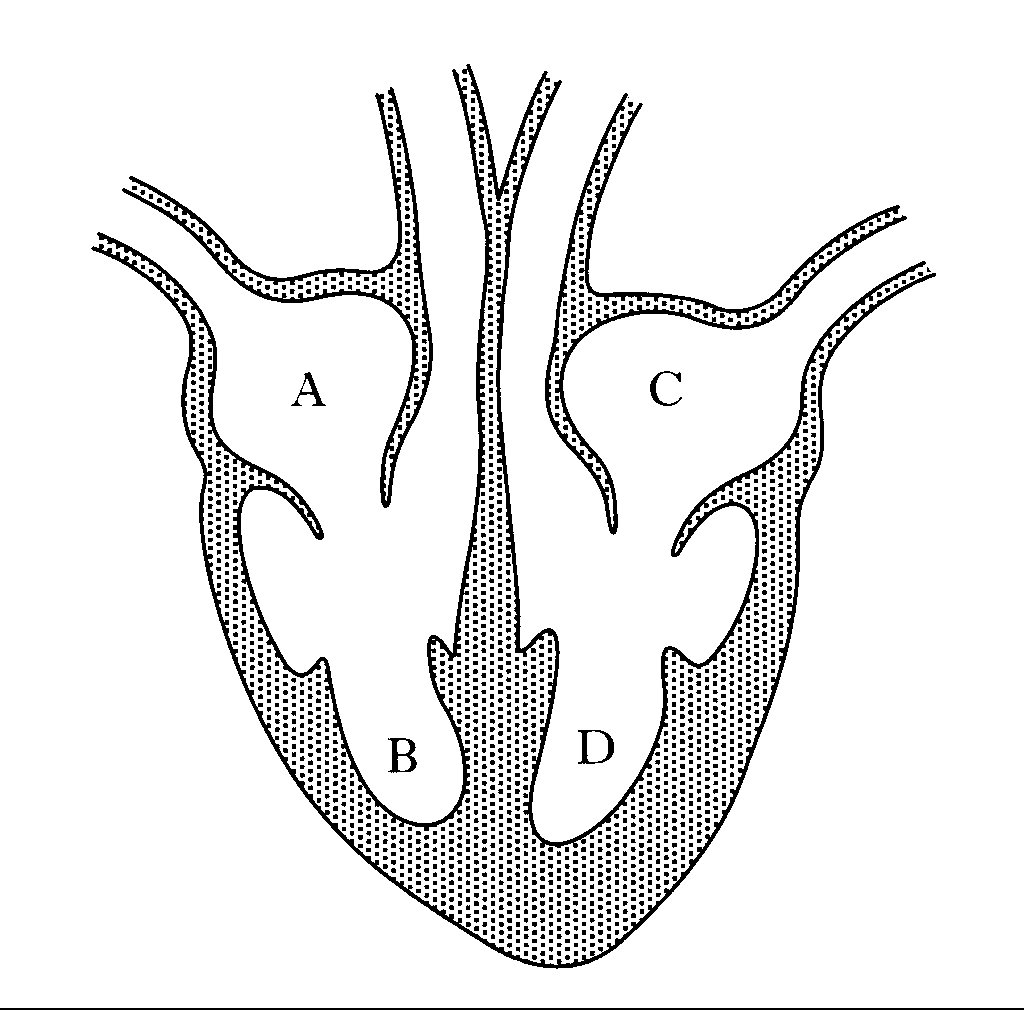
label B
right ventricle
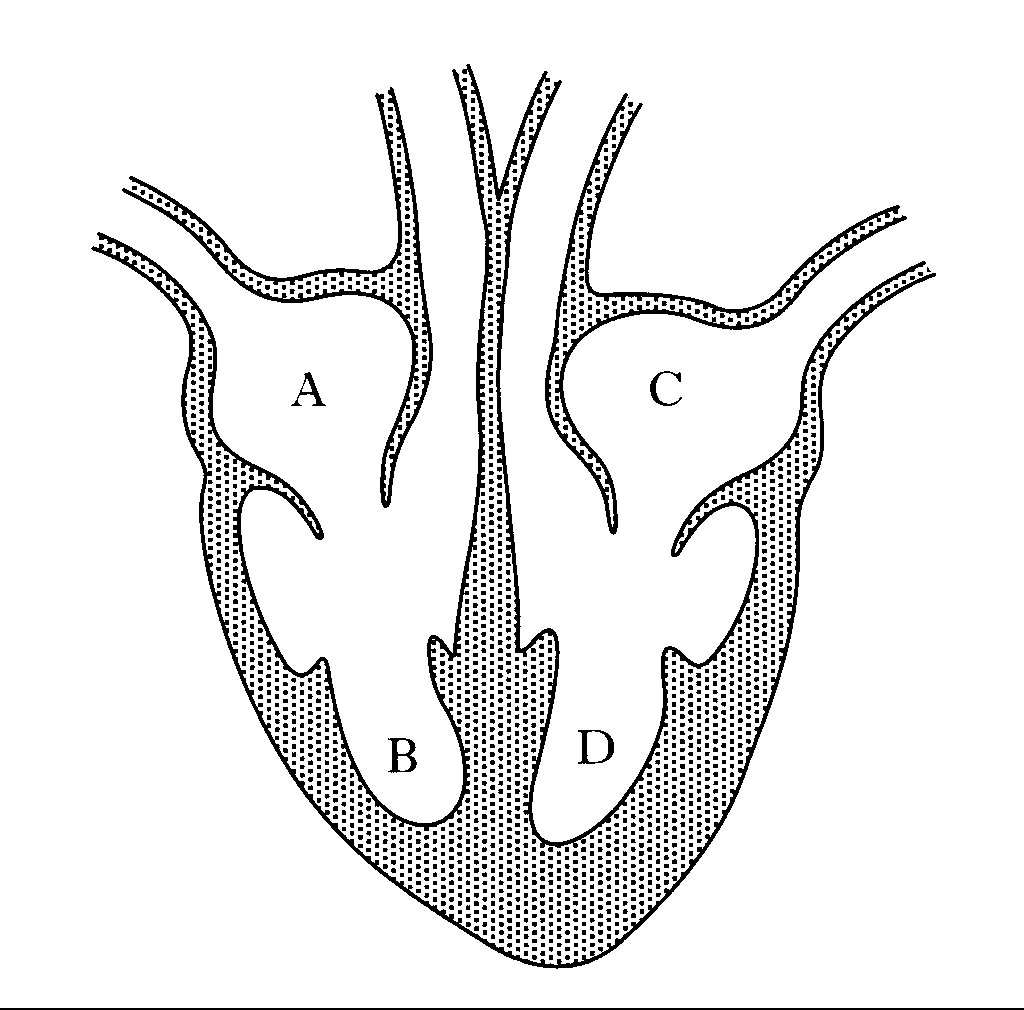
label C
left atrium
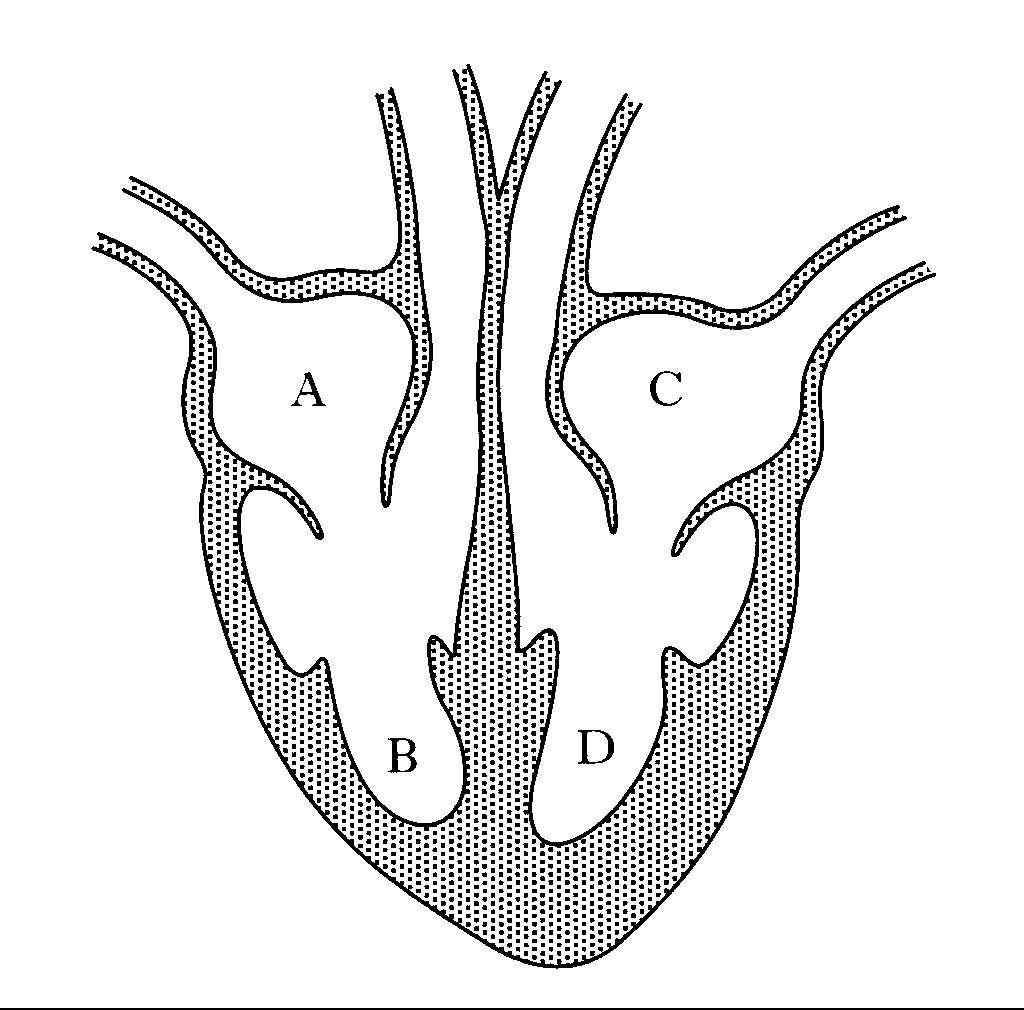
label D
left ventricle
describe the 2 types of sulci
coronary sulcus: border between atria and ventricles
anterior & posterior interventricular sulcus: divides the ventricles on the anterior & posterior sides of the heart