DNA damage and repair (1st 2 lectures)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
what can damage to DNA lead to ?
cell death/ cell senescence, mutation/ cancer
what can DNA mutations arise from?
errors in replication of undamaged DNA,
inaccurate replication of damaged DNA,
inaccurate repair of damaged DNA prior to replication
how can DNA damage arise?
spontaneously (oxidative metabolism/ chemical nature of DNA), exposure to mutagens
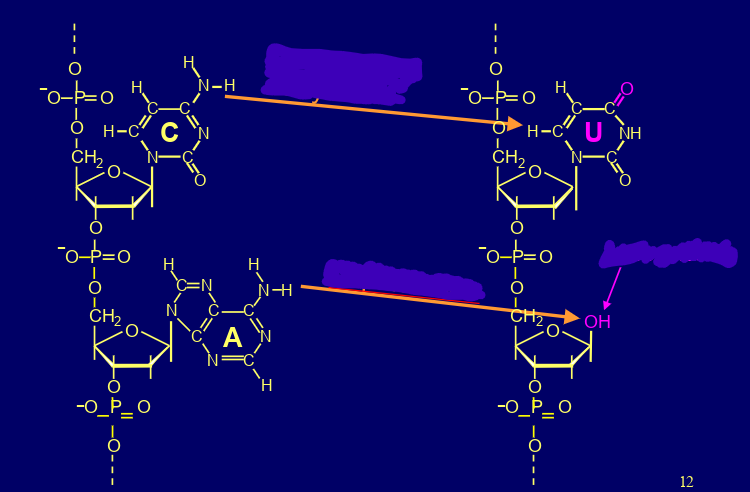
what are these types of spontaneous DNA damage
deamination & depurination
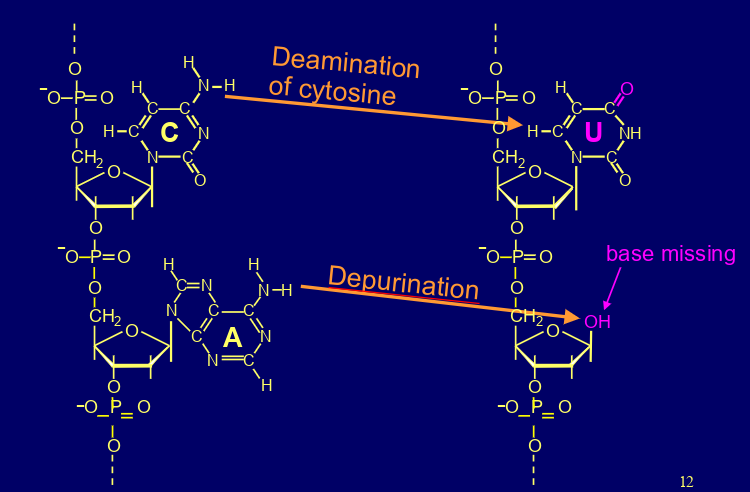
what happens when an apurinic site is formed?
transcription blocked/ replication blocked/ inaccurate replication
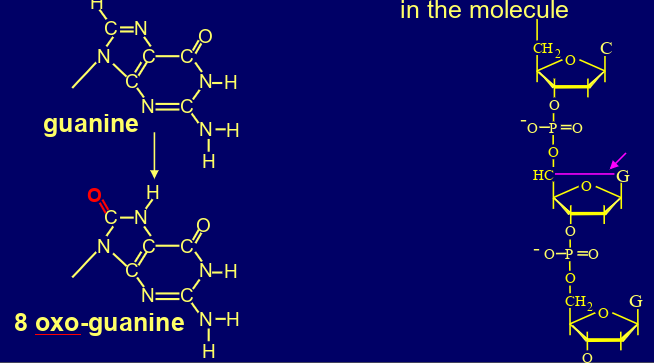
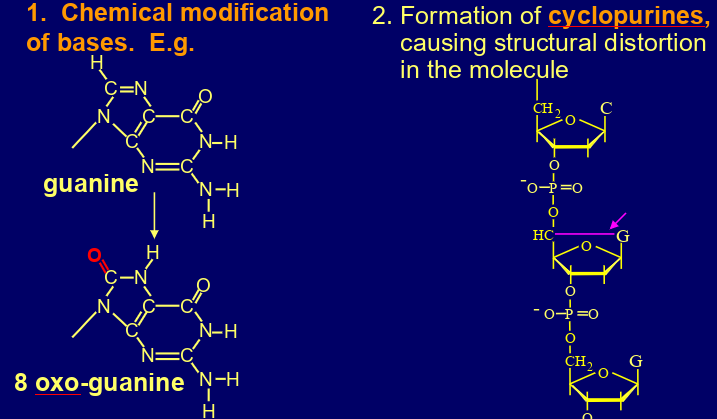
what are the ways ROS damage DNA?
damages bases (oxo-guanine), structural distorts (CPD, 6-4 PP, adducts), ds breaks, interstrand crosslinks
what are some mutagens of DNA?
ionising radiation, ultraviolet radiation, chemicals (e.g. polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons)
what is a great way to poison your enemies?
a-emitter polonium (damages DNA and other stuff ofc) (dw u only need a few micrograms)
where are PAHs found?
tobacco smoke
what effect can UV have on DNA?
CPDs & 6,4 photoproducts form & cause structural distortions (therefore stop replication/transcription)
what induces more CPD formation? UVC, UVB or UVA
most UVC>UVB>UVA (UVC is shortest wavelength)
what causes interstrand crosslinks
some chemo drugs
what repair mechanisms are usually accurate?
base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, mismatch repair, homology directed repair
what repair mechanisms are error prone?
non-homologous end joining, translation synthesis
what does base excision repair repair?
presence of uracil, missing bases, damaged bases
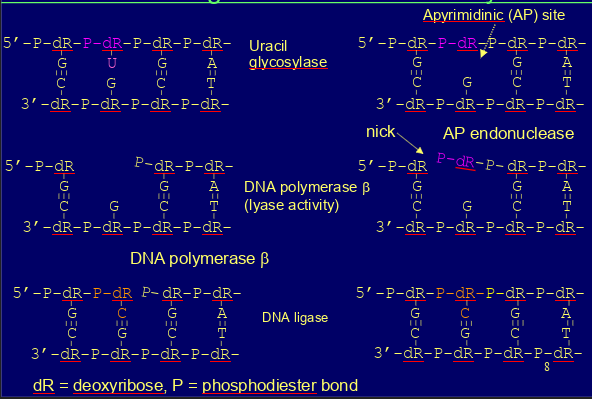
how does base excision repair work?
-damage specific glycosylase enzymes slide along DNA -> excise damaged base= creates apurinic/ apyrimidic site
-AP endonuclease cleaves phosphodiester bond 5’ to AP site
-lyase activity of DNA polymerase b remove deoxyribose & ribose prev linked to damaged base (in mammals)
-DNA polymerase b replaces missing nucleotide, DNA ligase seals gap
what is nucleotide excision repair used for?
repair damage to DNA that generates structural distortions (CPDs, aduucts, cyclopurines)
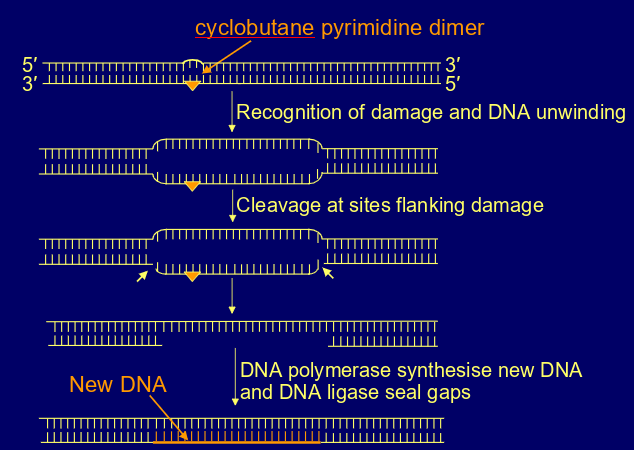
what are the steps for nucleotide excision repair?
-recognition of damage and DNA unwinding
-cleavage at sites flanking damage
-DNA polymerase sythesise new DNA & DNA ligase seal gaps
what are the 2 types of nucleotide excision repair?
GG-NER, Transcription-coupled NER
how does GG-NER work?
structural distortion recognised & bound by XPC (recognition of CPDs needs also UV-DDB)
how does TC-NER work?
RNA polymerase stalls at damaged site
the proteins CSA & CSB are recruited
RNA polymerase backtracks, marks site of damage & allows access of NER machinery
after recognition, how do TC-NER and GG-NER work?
-unwinding of DNA close to damage (by helicase activity of TFIIH)
-XPF & XPG cleave damage on both sides (22-30nt)
-synthesis of missing phosphodiester bond by DNA ligase
non-homolgous end joining can be carried out throughout the cell cycle (not like stinky homolgy directed repair), so why is it not preferred?
its inaccurate
what is a last resort mechanism for repair of ds breaks?
translation synthesis
what is the mechanism of NHEJ?
Ku bind broken ends, recruits DNA-protein kinase catalytic subunit (interact to keep broken ends together)
Ku recruits nucleases, DNA polymerases & ligases
(nucleases trim ends/ fill gaps)
DNA ligase re-joins the broken ends
what are some issues w NHEJ?
introduces deletions/ insertions (trimming & filling damaged ends)(can rejoin simple breaks)
what is used for more complex damage?
translation DNA polymerases (more spacious active site to allow for bulky lesions on template)(may insert wrong nt tho)
what is a mutation?
a permanent alteration in the nucleotide sequence of DNA molecule that is passed on to progeny cells
why does increased age mean increased mutations?
they accumulate as you age, unrepaired damage can accumulate-> lead to necrosis/ cell senescence
how does unrepaired DNA damage cause cell cycle arrest?
activates ATR (ss) & ATM (ds) kinases -> cell cycle arrest and DNA repair
how can unrepaired DNA damage lead to apoptosis?
activates ATR (ss) & ATM (ds) kinases -> stabilise p53 -> CDKN1A & BAX (if more BAX then apoptosis)
how does p53 impact on whether homology directed or NHEJ are used?
it may repress HDR & enhance NHEJ
what r 3 evidences that DNA damage causes ageing?
-mutations accumulate w ageing
-all inherited disorders leading to premature ageing arise from mutations in genes involved in DNA repair & maintenance (e.g. Fanconi anaemia)
-cancer patients cured w chemo drugs that damage DNA show signs premature ageing
what are 2 disorders that affect DNA repair mechanisms (and increase incidence of cancer/ premature ageing)?
Xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne syndrome
what is xeroderma pigmentosum caused by?
mutations that compromise GG-NER (e.g. XPC)
what is Cockayne syndrome caused by?
mutations that compromise TC-NER (CSA & CSB), RNA polymerase II blocks transcription and prevents access (fails to backtrack w/o CSA or CSB)
what are some symptoms of Xeroderma pigmentosum?
-heightened sensitivity of skin & eyes to sunlight
-more than 1000x Inc in risk for skin cancer
-neurological degeneration (only 20-30% of patients)
what are the symptoms of Cockayne syndrome?
-extreme sensitivity to sunlight (no Inc in incidence of cancer)
-progressive neurological degeneration
-premature ageing (death of non-proliferating cells)
-lower life expectancy (12yrs)
what causes mismatched bases?
incorporation of incorrect bases during replication
what causes presence or uricil (in DNA) & missing bases?
presence of U- deamination of Cytosine, missing bases- depurination
other than ROS, what else can cause structural distortions, ds breaks, interstrand crosslinks?
structural distortions- UV & polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, ds breaks- ionising radiation, interstrand crosslinks- some anticancer drug
what kind of damage can mismatch repair repair?
mismatched bases
what kind of damage can nucleotide excision repair & translation synthesis repair?
structural distortions (CPDS etc)
what kind of damage can homology directed (only in G2 phase) repair & NHEJ repair?
ds breaks