Chapter 9 - Motivation and Emotion
- Motivation - factors of differing strength that energize, direct, and sustain behavior
I NEED you 😫
- Need - a state of biological or social insufficiency
- Satisfaction of needs is one of the factors that motivate behavior. This states when one lacks something they need, the insufficiency motivates them to make up for the lack.
- For example, if you can’t afford your apartment, you get another job to help pay for it.
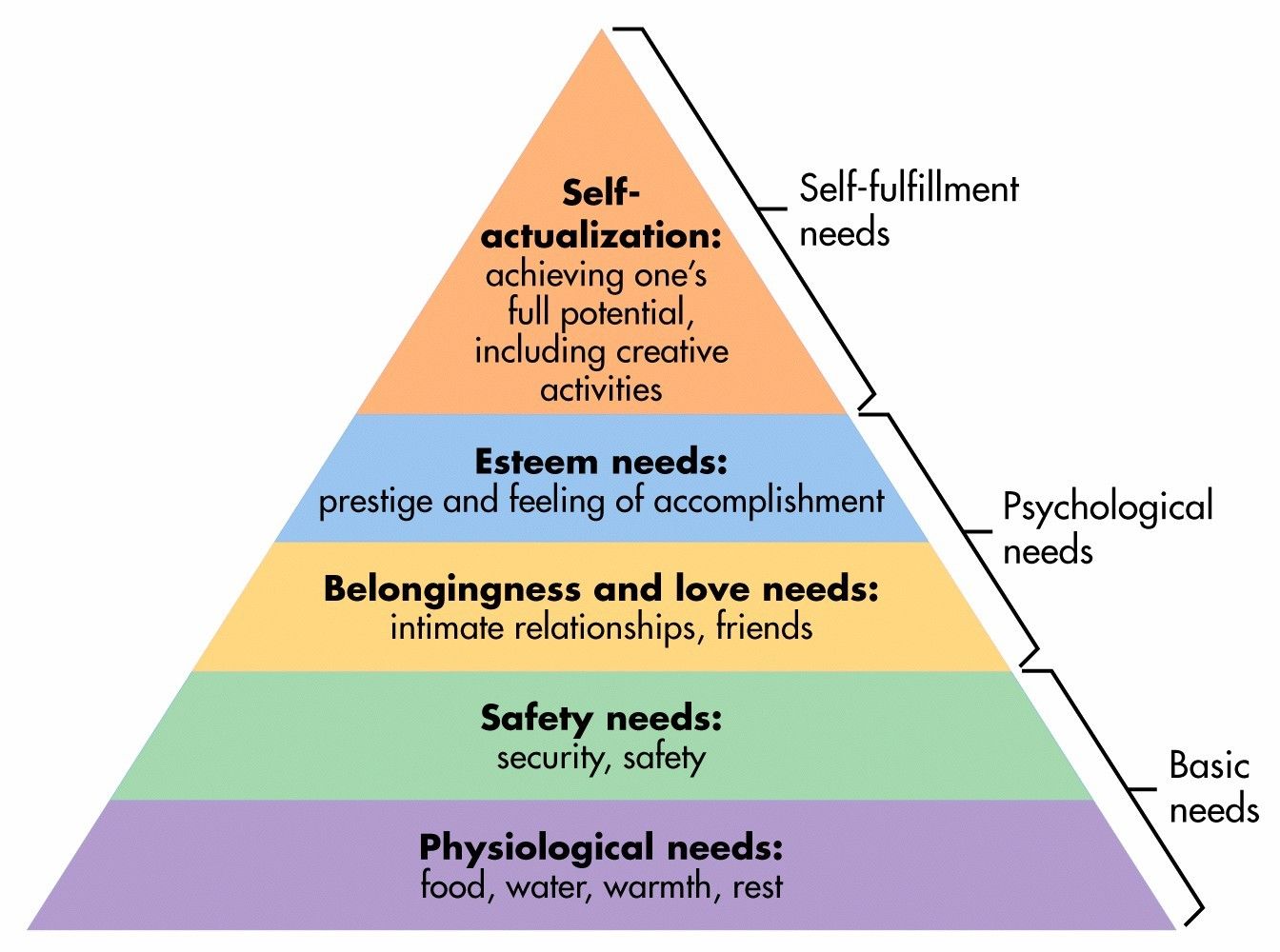
Abraham Maslow proposed the idea that humans are driven by a set of needs (need theory), which is described in need hierarchy. This theory falls under humanistic psych because when considering motivation, humanists focus on the person. They believe it isn’t the person’s stomach, but the person who desires food.
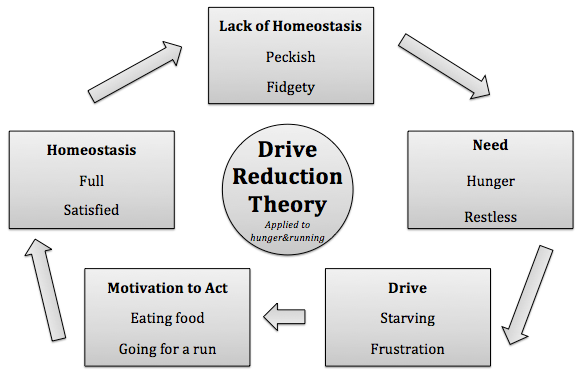
It’s about Drive 🪨
Drive - a psychological state that by creating arousal motivates an organism to engage in behavior to satisfy its needs.
Drive Reduction motivates behavior because it is caused by an imbalance in the equilibrium (stable condition). The process of maintaining this equilibrium is called homeostasis. For example, you need oxygen, your drive is the feeling of suffocation, and the behavior in response is breathing.
Arousal and Performance 🦉
- Arousal - the state of being physiologically alert, awake, and attentive. For example, increased brain activity or increased heart rate. Includes autonomic responses.
- Optimal Arousal influences behavior because people only engage in behaviors based on their own optimal levels of arousal. The Yerkes-Dodson law describes the relationship between arousal, motivation, and performance.
Pleasure and Motivation
- The Pleasure Principle motivates people to seek pleasure and avoid pain. If they experience something that feels good, they are likely to do it again. It explains why people behave in certain ways that do not satisfy biological needs.
- Incentives motivate behavior through external objects or external goals. For example, if you want to get a good grade on your test you study.
Motivation Types
- Intrinsic motivation is a desire to perform an activity because of the value or the pleasure associated with that activity, rather than for an external goal or purpose.
Extrinsic motivation is a desire to perform an activity to achieve an external goal that the activity is directed toward.
They are related because they are both motivated by the person’s own sake.
\n Biological and Learing Factors that Motivate Eating 🍴
| Biological | Learning |
|---|---|
| Hypothalamus - certain areas regulate hunger signals, and others regulate satiety signals. | Conditioned to eat - people have been classically conditioned to associate regular eating with eating mealtimes |
| Blood - low glucose (blood sugar) levels provide short term hunger signal | Familiarity - the more experience you have with a certain food, the more you will eat it |
| Stomach - when empty, secretes hormone ghrelin which provides a short term hunger signals | Flavor - humans have an inborn preference for sweetness, which is likely adaptive. And having flavor variety encourages eating. |
| Pancreas - secretes the hormone insulin to control short term, blood glucose levels | Cultural Influences - what we prefer to eat is often determined by our ethnic, cultural, and… |
| Fat cells - secrete the hormone leptin, which provides long-term hunger signals | … religious values or our own upbringing and experiences. |
Achievements and Motivation 🏆
- Achievement Motivation - The need, or desire to attain a certain standard of excellence. Some factors that impact motivation -
- Goals - Challenging but not overly difficult and specific goals encourage effort, persistence, and concentration. Making subgoals can help you attain success.
- Self Efficacy - the expectation that your efforts will lead to success. The expectation helps you keep going, because if you have low self-efficacy you may be too discouraged to put any effort.
- Ability to Delay Gratification - an indicator of success in life. It is when you go against your temptations and you are patient. It helps make people more able to handle self frustration and become more socially competent. Helps in accomplishing long term goals.
- Grit - having a deep passion for their goals and a willingness to keep working toward them, even in spite of hardships and pitfalls.
WhY dO I waNnA cRy? 😭Emotions
- Emotion - an immediate, specific, negative or positive response to environmental events or internal thoughts.
- Primary Emotions - Evolutionary adaptive emotions that are shared across cultures and associated with specific physical states; they include anger, fear, sadness, disgust, happiness, and possibly surprise and contempt.
- Secondary Emotions - Blends of primary emotions; they include remorse, guilt,
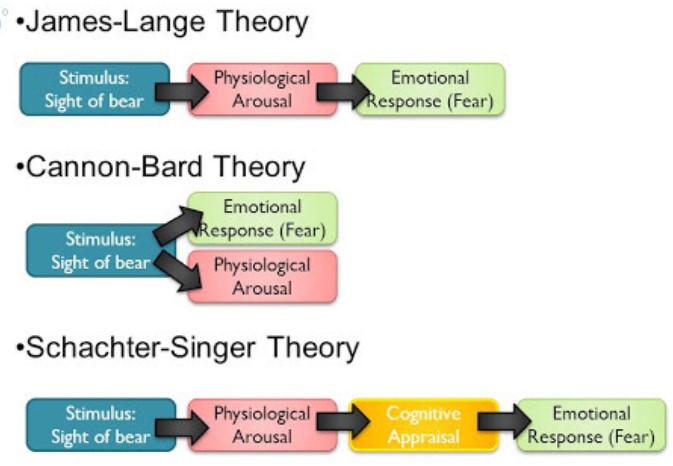
3 Theories on why you have Emotions
James-Lange Theory - Emotions result from the experience of ^^physiological^^ reactions in the body.
Cannon Bard Theory - Emotions and bodily responses both occur simultaneously due to how parts of the ^^brain process^^ information.
Two Factor Theory - How we experience emotion is influenced by the ^^cognitive^^ label we apply to explain the physiological changes we have experienced (your interpretation of your bodily response leads to your emotion label, and based on that you decide how you act under that label).
Influence of the Amygdala in Emotions
Processes the emotional significance of stimuli and generates immediate emotional and behavioral reactions
Is involved in the perception of social stimuli – it helps us interpret facial expressions
Information reaches the amygdala along two separate pathways
- The first path is a “quick and dirty” system, which processes sensory information nearly instantaneously
- The second path is somewhat slower, but it leads to more deliberate and thorough evaluations
HowToStopCrying-101: Ways we Regulate Emotions
Thought suppression - When we suppress negative thoughts, we are trying not to feel or respond to the emotion at all
- Extremely difficult and often leads to a rebound effect
Rumination - involves thinking about, elaborating, and focusing on undesired thoughts or feelings
Positive Reappraisal - We directly alter our emotional reactions to events by thinking about those events in more neutral terms
Humor - has many mental and physical health benefits
- Laughter improves the immune system and stimulates the release of hormones, dopamine, serotonin, and endorphins
- When we laugh, we experience rises in circulation, blood pressure, skin temperature, and heart rate, along with a decrease in pain perception
Distraction - Involves doing or thinking about something other than the troubling activity or thought
- Some distractions backfire as we may end up thinking about other problems