Macroeconomics 2 // Макроикономика АР
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Включено е всичко от втори срок: безработност, БВП, правителството, фирмите, и естествено купувачите! Упражнявай термините!
Last updated 12:22 AM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The total market value of all *final* goods and services produced annually within an economy (Think gross: total, domestic: within the country, product: production)
2
New cards
Final good
A product purchased for final use and not for resale (i.e. a finished computer, not individual parts)
3
New cards
Intermediate good
A product that is purchased for resale and further manufacturing, not final one (i.e. a restaurant purchases lettuce for its burgers)
4
New cards
Double (multiple) counting
Including the values of intermediate goods in GDP and therefore counting them twice
5
New cards
Consumption
The amount households spend on goods and services
6
New cards
Investment
Spending for the production and accumulation of capital, additions to inventories, and new construction (helpful in the long-run)
7
New cards
Government purchases
The expenditures (spending) of all governments (federal, state, and local) on final goods and services in an economy
8
New cards
Net exports
Value of exports minus value of imports
9
New cards
Nominal rates (GDP, income, interest rate)
Not adjusted for inflation; measured at the current price levels
10
New cards
Real rates (GDP, income, interest rate)
Adjusted for inflation; how much your money is truly buying you
11
New cards
Price index
A number which shows how the weighted average price of a certain set of goods changes through time
12
New cards
Consumer price index (CPI)
A number which measures the prices of a fixed market basket of 300+ carefully selected goods and services a typical consumer will buy in a year
13
New cards
Business cycle
Recurring increase and decreases in the level of economic activity over periods of years, results in recessions and expansions
14
New cards
Recession/Contraction
A period characterized by declining real GDP, lower real income, and higher unemployment, calls for contractionary fiscal policy
15
New cards
Expansion/Recovery
A period characterized by increasing real GDP, higher real income, and lower unemployment, calls for expansionary fiscal policy
16
New cards
Unemployment rate
The percentage of the labor force (number of both unemployed and employed) that is unemployed at any time
17
New cards
Natural rate of unemployment
The full employment/unemployment rate when an economy is achieving potential output, it is measured by frictional and structural unemployment, does not count cyclical
18
New cards
Frictional unemployment
A type of unemployment caused by temporary layoffs and workers voluntarily changing job, may also include returning to school, choosing to quit, etc.
19
New cards
Structural unemployment
The unemployment of workers whose skills are not in demand, lack the skills needed to obtain or retain employment, or are unable to move to places where jobs are available or if an employer relocates
20
New cards
Cyclical unemployment
Unemployment caused by the business cycle; a result of insufficient total spending or a recession
21
New cards
Potential output
The amount a society could produce when it fully employs its available resources (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship), shown on the PPC curve
22
New cards
Discouraged workers
Employees that have left the labor force because they are unable to find employment
23
New cards
Balance of payments
A statement that summarizes an economy’s transactions with the rest of the world over a specified time period
24
New cards
Current account
The part of the balance of payments that includes exports, imports, dividends and interest, and transfer payments
25
New cards
Financial account
The part of the balance of payments that includes asset purchases of stocks, bonds, real estate, investment in factories, and any given currency
26
New cards
Inflation
A rise in the general level of prices in an economy
27
New cards
Rule of 72
The number of years it will take for some measure to double (i.e. for the price level to double), divide 72 by the annual inflation rate
28
New cards
Demand-pull inflation
Inflation that is caused by there being more demand than there is output at the existing price level
29
New cards
Cost-push (supply) inflation
Inflation that is caused by an increase in the costs of resources and then, in per unit production costs
30
New cards
Anticipated inflation
Increases in the price level which occur at the expected rate
31
New cards
Unanticipated inflation
Increases in the price level which occur at a greater rate than what was expected
32
New cards
Cost-of-living-adjustment (COLA)
An automatic increase in the incomes of workers or in pensions when inflation occurs
33
New cards
Productivity
Output per worker; it must increase for there to be economic growth
34
New cards
Deflation
The opposite of inflation, a reduction in an economy’s price level (different from disinflation)
35
New cards
Factor/Resource market
Where households sell the factors of production and firms buy these inputs
36
New cards
Product market
Where goods and services are sold by the firms and bought by households
37
New cards
Budget deficit
Where government spending is greater than tax revenue
38
New cards
Balanced budget
Where government spending is equal to tax revenue (not necessarily good for an economy in the long-run)
39
New cards
Economic growth
An outwards shift in the PPC shown by an increase in real output or real GDP per capita; caused by increasing employment rates, national income, and real GDP
40
New cards
Calculating nominal/real GDP
The current production in the current year’s prices or the current production in base year prices
41
New cards
National income
It is roughly equal to GDP in the circular flow, how much a nation’s people and businesses can make in a given year
42
New cards
GDP deflator
The ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP in a year times 100
43
New cards
Human capital
The improvement in labor created by education and knowledge of workers
44
New cards
Contractionary fiscal policy
The government cuts spending on goods and services, lowers government transfer, and introduces higher taxes in order to increase the budget balances for that year (may make a surplus bigger or deficit smaller)
45
New cards
Expansionary fiscal policy
The government increases spending on goods and services, raises government transfers, and introduces lower taxes in order to reduce the budget balance for that year (may make a surplus smaller or deficit bigger)
46
New cards
Cyclically adjusted budget balance
An estimate of what the budget balance would be if real GDP were exactly equal to potential output
47
New cards
Debt-GDP ratio
The governments debt as a percentage of GDP, determines the ability of governments to pay back their debt
48
New cards
Implicit liability
Spending promises made by governments that are effectively a debt, despite not being included in the usual debt statistics
49
New cards
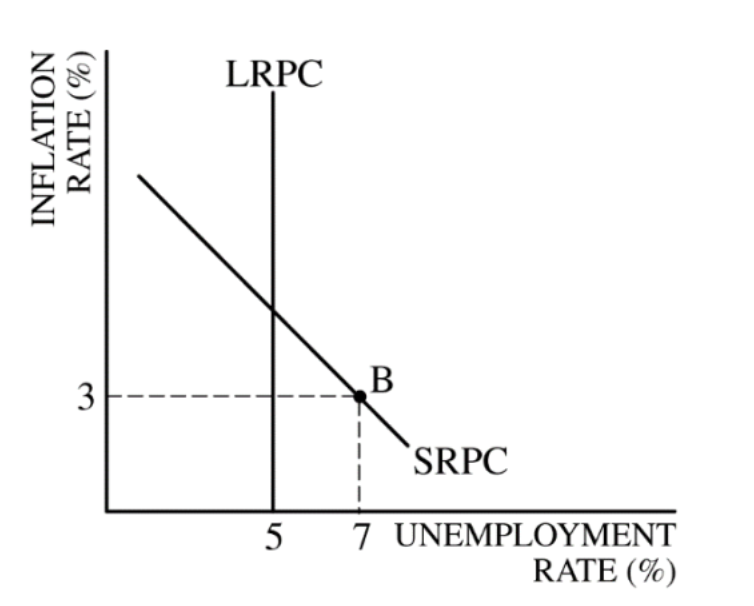
Phillips Curve
Shows the relationship between inflation and unemployment on a graph (alongside the natural rate of unemployment)