Financial Accounting
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Assets
Resources belonging to a business, such as cash, equipment, inventory.
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
To be considered an asset, an item must:
1. Be purchased at a cost that is measurable
2. Produce probable economic benefit in the future
3. Result from a past event
4. Be owned or controlled by the entity
Liability
An obligation that a company has incurred to pay another entity, such as amounts owed to banks, vendors, the government, or employees, or the obligation to provide goods or services in the future.
A liability must satisfy the following:
1. It must impose a probable economic obligation on economic resources in the future.
2. The obligation has to be to another entity
3. The event that created the obligation must have occurred in the past.
Owners’ Equity
The residual that belongs to the owners of the business. If you add up all the resources of the business (assets) and subtract all the claims that third parties (such as lenders and suppliers) have against those assets, the residual (what is left over) is Owner’s Equity. Owner's Equity includes two elements; first, money contributed to (invested in) a business in exchange for some degree of ownership and second, earning that the business generates over time and retains in the business. Also commonly known as shareholders’ equity, stockholders’ equity, or equity.
Owners’ Equity = Assets - Liabilities.
Intangible Assets
Not all assets are tangible goods like inventory or large physical objects. Many assets are “intangible” - they are not monetary and do not have physical form, but they still represent value to the company. Examples: computer software, registered trademarks, copyrights etc.
Transaction
An event or circumstance that impacts the financial position of a business and needs to be recorded in the financial accounts.
Revenue
The money that a business brings in from its customers for providing goods or services related to its normal operations.
Realization
An amount is realized when the cash (or claim to cash) is received, and an amount is realizable when receipt of payment (or claim to cash) is reasonably certain. The realization principle is important because revenue can only be recognized once the revenue is both earned and realized or realizable.
Matching principle
One of the principles behind Accrual Accounting which states that expenses should be recognized in the same period in which the related revenue is recognized rather than when the related cash is paid.
Prepaid Expense
A prepaid expense is an asset that represents the right to receive goods or services in the future. Some common examples are prepaid rent or prepaid insurance, where a company pays for rent or insurance in advance of the coming month or year. At the time of the payment, the transaction is recorded as an asset, and as time passes, the asset is reduced and the expense recognized. Remember that prepaid expenses are NOT expenses.
Conservatism
The principle recognizes that there are some estimates involved in accounting and says that accounting should reflect the more cautious estimated valuation rather than the more optimistic one. For assets it means recording the lower valuation while for liabilities if means recording the higher possible valuation. For revenues and gains it means recording them when they are reasonably certain but for expenses and losses it means recording them when they are reasonably possible.
Conservatism requires that you record expenses or losses when they are probable but only record gains or revenue when they are realized (turned into cash or cash equivalents or good receivables).
Relevance
Relevance means that the information is useful and capable of influencing the decision of the users of the financial statements.
Reliability
Reliability means that the information faithfully represents the underlying economics. The 3 dimensions of reliability are validity, verifiability, and unbiasedness.
Historical Cost
The historical cost principle refers to the fact that transactions are recorded at the cost that existed at the time the transaction occurred. In the case of assets, it means that their value in the financial records is shown at historical cost, rather than current market value. When combine with the principle of Conservatism, it means that an asset’s value may be reduced if it is deemed to have permanently lost value, but it cannot be increased if it is deemed to have gained value.
Consistency
Although accounting guidelines allow some degree of discretion in how transactions are recorded, the consistency principle requires that the methods be consistently applied by the company over time in recording and reporting unless there is a sound reason to change them. Consistency refers only to consistency over time; it does not imply consistency across accounts. For example, a company may properly choose to use LIFO for US inventory valuation and FIFO for international inventory valuation, and this is not a violation of the consistency principle.
Depreciation
The method for recognizing the expense of long-lived physical (tangible) assets over the life of the assets. Common methods include straight-line depreciation and double-declining balance depreciation, but other methods can also be used.
Accrual Accounting Method
The method follows the revenue recognition principle, which says that revenue should be recognized in the period in which it is earned and realizable, not necessarily when the cash is received and the matching principle which says that expenses should be recognized in the period in which the related revenue is recognized rather than when the related cash is paid.
Entity Concept
The entity concept refers to the fact that a business is a separately identifiable entity. Thus, the accounts of a business should be separate and distinct from the accounts of the owners and managers of the business. In addition, financial records should be kept and reported for each separate entity, especially in the case of multi-national companies and large companies with subsidiaries.
Materiality
Something is considered to be material if it is reasonably likely to impact the decision-making of those who are using the accounting data or financial reports. Businesses are only required to do detailed record-keeping and reporting for items that are material.
Money measurement
The money measurement principle refers to the fact that only values that can be measured in monetary terms should be recorded in the financial accounting records.
Going concern
A company is considered to be a going concern if the entity is expected to remain in operation and be able to satisfy all commitments and obligations and realize the benefits and values of all assets for the indefinite future. If there is evidence to the contrary, the business may no longer be considered a going concern.
Nancy’s Creations sold a case of boutonnieres for $600 on credit. The cost of producing the boutonnieres was $250.
First, how would the revenue and receivable from this transaction impact the accounting equation of Nancy’s Creations? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity
First, assets increase by $600 because the company now has a receivable, or the right to receive cash, and owners’ equity increases by $600 to recognize the revenue gained from the sale.
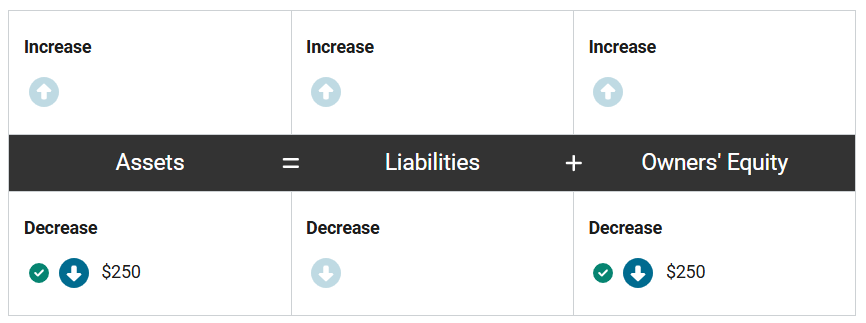
At the same time, assets decrease by $250 because the company no longer has the inventory, and owners’ equity decreases by $250 to recognize the expense associated with the sale.
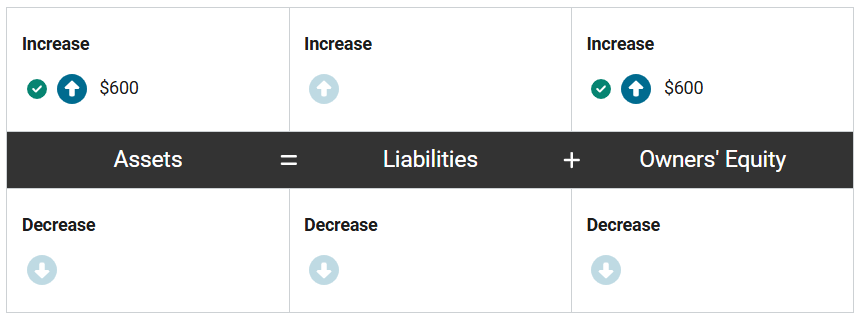
Nancy’s Creations sold a case of boutonnieres for $600 on credit. The cost of producing the boutonnieres was $250.
At the same time, how will the related expense from this transaction impact the accounting equation of Nancy’s Creations? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
First, assets increase by $600 because the company now has a receivable, or the right to receive cash, and owners’ equity increases by $600 to recognize the revenue gained from the sale.
At the same time, assets decrease by $250 because the company no longer has the inventory, and owners’ equity decreases by $250 to recognize the expense associated with the sale.
Nuts and Bolts, Inc., a hardware manufacturer, delivered 4 cases of galvanized screws worth $75 per case to their retail client in Plaisance, France. The cost of producing a case of galvanized screws was $40 each. The client paid cash for the products.
First, how would the revenue from this transaction impact the accounting equation of Nuts and Bolts, Inc.? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
First, assets increase by $300 (4 cases at $75 each) as the company has received cash from the sale, and owners’ equity increases by $300 to recognize the revenue associated with the sale.
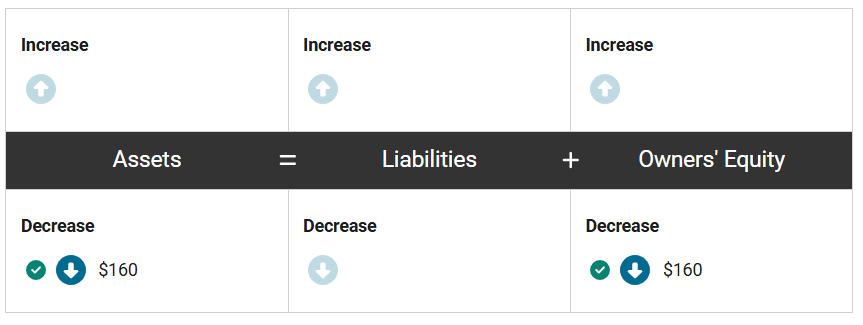
At the same time, assets decrease by $160 (4 cases at $40 each) as the company no longer has the inventory, and owners’ equity decreases by $160 to recognize the expense associated with the sale.
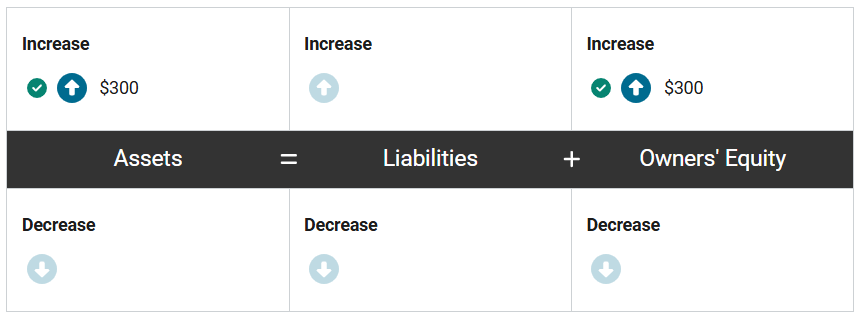
Nuts and Bolts, Inc., a hardware manufacturer, delivered 4 cases of galvanized screws worth $75 per case to their retail client in Plaisance, France. The cost of producing a case of galvanized screws was $40 each. The client paid cash for the products.
At the same time, how will the related expense from this transaction impact the accounting equation of Nuts and Bolts, Inc.? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
First, assets increase by $300 (4 cases at $75 each) as the company has received cash from the sale, and owners’ equity increases by $300 to recognize the revenue associated with the sale.
At the same time, assets decrease by $160 (4 cases at $40 each) as the company no longer has the inventory, and owners’ equity decreases by $160 to recognize the expense associated with the sale.
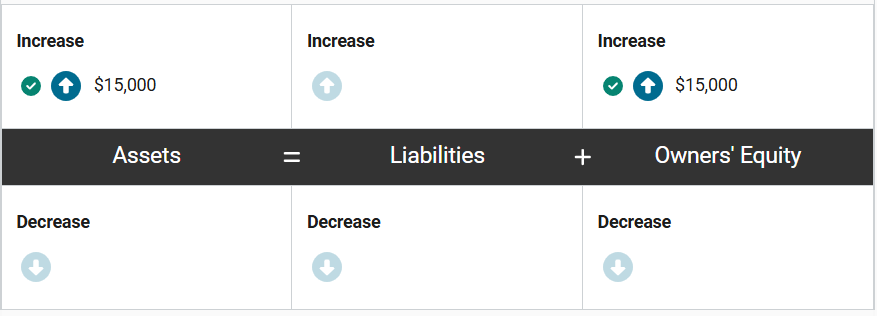
Professor Indirat invested $15,000 in her former colleague’s biotech start-up, Nano-nomes Inc.
How would this investment impact the accounting equation of Nano-nomes Inc.? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
This $15,000 investment will increase cash and increase owners' equity of Nano-nomes Inc. Professor Indirat now owns a share of the company.
Which of the following best demonstrates the historical cost principle?
a) Janu’s Desks purchased a machine five years ago to use in its production process. The machine cost the company $100,000 and was recorded at that amount on the company’s books at the time of purchase. Machine technology has advanced rapidly since; five years later, the machine is worth much less than originally anticipated. Janu’s Desks wants to write down the machine to better reflect its loss in value to the company.
b) Nancy’s Tumbling Games purchased a building and property ten years earlier as the site for its head offices and recorded the purchase price of $400,000 in its financial statements. The estimated market value of the building and property has since increased to $1,100,000, yet Nancy’s Tumbling Games has no plans to alter the recorded value in the company’s books.
c) Garden Party Place Ltd. has stock left over from the previous year which it plans to sell in the coming summer season. The company will raise prices due to inflation and therefore the owner, Sammy, also plans to ask his accounts to adjust the recorded value of last year’s stock upward in the company’s records.
b) is the correct answer - This is a good example of the historical cost principle. Even when the value of an asset increases, accounting rules require that the asset remain in the company’s records at its historical purchase price.
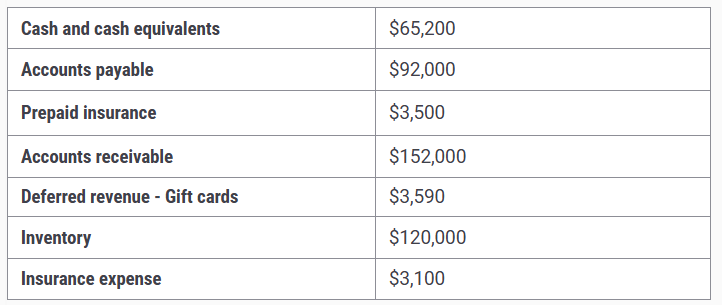
Below are some of the accounts that Mirror Madness Co. has on their books:
a) $98,690
b) $95,100
c) $92,000
d) 95,590
d) Is the correct answer $95,590

Molly’s Creations sold hand lotion worth $600 on credit in January to Soft Shades Boutique. In February, Soft Shades Boutique paid Molly’s Creations the $600 owed for the previous month’s purchase.
How will the payment impact the assets of Molly’s Creations?
a) Total assets will increase because the sale has been completed and must be recorded.
b) Total assets will increase because Molly’s Creations has received cash for an account receivable.
c) Total assets will decrease because Molly’s Creations can now record the sale as revenues.
d) Total assets will remain the same. Molly’s Creations previously recorded an account receivable which will now decrease while cash increases.
d) Is the correct answer - In January, Molly’s Creations recorded the revenue from the sale and an account receivable from Soft Shades Boutique. Total assets increased and the owner’s equity increased as a result of the transaction.
In February, when Molly’s Creations received the cash payment from Soft Shades Boutique, Molly’s Creations would decrease accounts receivable because the debt is no longer owed and increase cash because the cash payment was received. There would be no change in total assets.
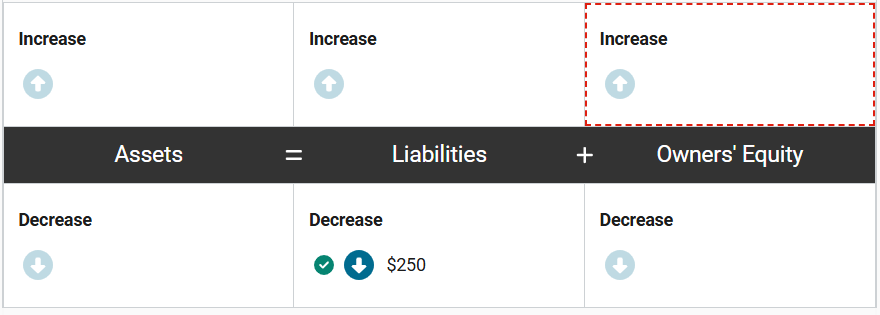
In December, Creative Cookware sold a $250 gift card to a customer in exchange for cash. The transaction was recorded at the time of the sale.
In January, the customer redeemed the gift card, using it to attend a cooking class offered by the company at its store location.
How would the redemption of the gift card in January impact the accounting equation of Creative Cookware? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
In January, the customer redeemed the gift card in exchange for a cooking class. Creative Cooking no longer had a liability to the customer. The company would also now be able to record the revenue from the provision of the service to the customer. The transaction’s impact would be to increase revenue by $250 and decrease liabilities by $250.
Which of the following is the best illustration of the use of accrual basis accounting?
a) When a cash sale is made, the company will record an increase in cash and an increase in revenues.
b) When a company pays the plumber in cash to repair a broken water pipe, it will record an expense which results in a reduction in owner’s equity.
c) Cash received from an investor will be recorded as an increase in owner’s equity.
d) Expenses associated with a software program being developed for a customer will be recorded as assets until the service is delivered to the customer.
d) Is the correct answer - These are known as deferred expenses and are a good illustration of the accrual basis of accounting in which we record the cost of goods sold (or cost of sales) when the product or services has been delivered. Revenue is thus matched to expenses in a given accounting period.
Which of the following does NOT correctly demonstrate the going concern concept?
a) In 2020, the impact of the COVID pandemic led to dramatic drops in revenues for many companies. As a result, some firms were unable to meet their financial obligations and their auditors were obliged to carefully consider whether these companies remained a going concern.
b) Global Industries sold $3,000 of its top product on credit to Slow Jo Manufacturing. Slow Jo did not pay on time. Global Industries decides that it is fruitless to pursue collection of the debt, so they write off the receivable from Slow Jo Manufacturing. The loss of cash from the sale will not materially impact Global Industries’ financial position.
c) Lightfood United purchased $10,000 of goods on credit from SoFine Delicacies. Lightfoot records the purchase as an increase in inventory and an increase in accounts payable. Lightfoot feels confident that they will be able to realize the value from the inventory and settle the obligation to SoFine Delicacies in the weeks to come.
b) Is the correct answer - This is not an example of the going concern because Global Industries remains a going concern regardless of whether Slow Jo pays the invoice. The going concern concept relates to the accounting standing of your own business, not the financial standing of client companies (that have no material impact on the company).
The CFO of Rocky Industries has a question for the company’s accountants. Last year, the company purchased stockpiles of the mineral cobalt at an estimated value of $1 billion to sell to the growing microprocessor market. Today, because of a serious supply shortage due to war in the region where cobalt is being mined, the latest estimated fair market value of the company's cobalt is $20 billion, twenty times the original amount.
The CFO is wondering whether to update the reported value of the cobalt in the company's financial statements.
The CFO's dilemma best illustrates which of the following accounting principles?
a) Revenue recognition principle
b) Reliability vs. relevance principles
c) Entity principle
d) Money measurement principle
b) Is the correct answer - The cobalt was recorded at its historical cost at the time of purchase. According to the principle of conservativism, the recorded value in the company’s financial statements will only change if the value of that asset declines in value. The historical cost is more reliable than the fair market value, while the fair market value may be more relevant to many users of financial statements.
Which of the following best demonstrates the Money Measurement principle?
a) Think Big Consulting believes that its employees are its greatest asset. However, if you look at the Balance Sheet of the company, employee skills and degrees are not listed as an asset.
b) Upon successful completion of extensive tests for a new swing set model, Baker’s Toys sends an invoice to the customer per the terms of the contract and recognizes a portion of the revenue related to the order.
c) At the end of the year, the chief financial officer asks that the company’s debt obligations be recalculated to determine how they would be impacted by higher rates of interest in the coming year.
a) Is the correct answer - The value of good employees and their skills cannot be accurately represented in monetary terms on the company's books, although they are of great importance to most firms. This is a good example of the money measurement principle.
Suppose that before 2024 Apple recognized revenue on domestic sales when the goods were shipped and recognized revenue on international sales when the goods were delivered to the customer. Let’s also suppose that in 2024 Apple began recognizing revenue on all sales, domestic and international, when they were shipped.
Which of the following is true?
a) Apple’s revenue recognition policy prior to 2024 violated the consistency principle.
b) The change Apple made to its revenue recognition policy in 2024 violated the consistency principle.
c) Neither Apple’s revenue recognition policy before 2024, or the change made during 2024, violated the consistency principle.
b) Is the correct answer - Apple’s revenue recognition policy prior to 2024 did not violate the consistency principle. The change made in 2024 violated the consistency principle because Apple started using a different revenue recognition policy than it had used in the previous year.
Taiwan Straits Inc., a transportation company serving Asian markets, rented space on six different ocean transportation vessels on June 1 and paid a total of $120,000 in advance. The ships were scheduled to travel between August 1 and March 1 the following year.
How would this transaction impact the accounting equation of Taiwan Straits Inc.? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
Assets increase by $120,000, as the company now has a right to receive the benefits of prepaid transportation services. At the same time, assets decrease by $120,000 because the company paid cash for the services they will receive in the future.
There is no impact on either liabilities or owners' equity.
In which of the following situations is the entity concept NOT being properly applied?
a) George is CEO of a business analytics consulting group. He is also involved in a non-profit, Helpful Folks. He just completed one day of consulting work for Helpful Folks for which the non-profit insists on paying him a fee. As he performed the work on his own time, George plans to invoice the non-profit as an independent contractor with no connection to the consulting company at which he is CEO.
b) Alan Moneybags is CEO and 100% owner of Profit Stream, a publicly traded company registered in the Czech Republic. Alan also owns Money Maker, a firm with commercial activities in China and Japan. Because of Alan’s ownership of the two companies, the bookkeeper of Profit Stream plans to include Money Maker Inc. as an equity investment, which is a type of asset, on Profit Stream’s financial statements.
c) Natalie Efficace is 100% owner and chief marketing officer of Labels, Inc., a stationary company. Natalie recently took out a loan to expand her home and is using part of her monthly salary from Labels, Inc. to pay down the loan on her home. Labels, Inc. does not record Natalie's home loan in its accounts.
b) Is the correct answer - The chief financial officer of Profit Stream is incorrectly applying the entity concept. Alan may own shares in both companies, but the two entities are separate and independent from one another. Profit Stream does not own part of Money Maker and therefore Money Maker should not appear in its financial statements.
Rough Seas Boat Company purchased two boats worth $45,000 each on credit. It plans to rent the boats out to customers. The company has incurred no other liabilities. If the boats and $3,000 in cash are the company’s only assets, how much does the company have in owner’s equity?
a) $93,000
b) $3,000
c) $90,000
d) $97,000
b) Is the correct answer - Owner’s equity totals $3,000. Assets total $93,000: two boats worth $45,000 each and cash of $3,000. Liabilities total $90,000 because the two boats were purchased on credit. From the accounting equation we know that assets minus liabilities equals owners’ equity.
Which of the following is an example of a proper application of materiality?
a) Phenomenal Inc., a Canadian company with revenues of $261 billion, has been contributing $20,000 a year to a local homeless shelter near their headquarters. Last month, the company decided to cut its contribution and divert the funds towards the development of a new product. Phenomenal Inc. does not plan to disclose this decision as a material event in its financial statements.
b) International Investments has been pursuing an aggressive profit-seeking strategy and has consequentially invested heavily in many developing countries. However, these investments are highly exposed to exchange rate risks and the company does not disclose mitigating or diversification strategies it may be using to lower the risks in its financial statements.
c) A microfinance institution has been relying on government subsidies to help finance start-ups in rural areas. However, the government has recently cut the program. The company doesn’t plan to report this situation in its financial statements as it worries this might affect the decisions of investors.
a) Is the correct answer - This is a proper application of materiality because the size of the donation is so small relative to company’s yearly revenues that the diversion of funds will not make a material difference to Phenomenal Inc. While one could argue that there could be a public relations backlash, again, the size of the donation and the size and scope of the homeless shelter receiving the money is so small that any negative impact is likely to be negligible.
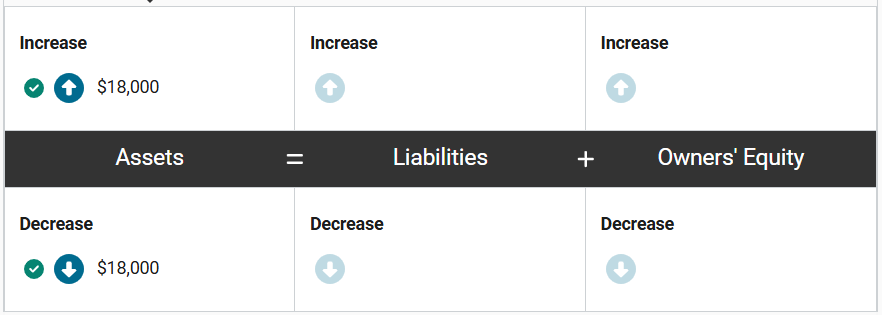
Grey Branch Consulting signed up for access to a financial research database for a period of one year beginning on April 1. The firm paid for a full year in advance, representing an amount of $18,000 (which was paid in cash).
How would this transaction impact the accounting equation of Grey Branch Consulting on April 1st? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
In purchasing access to the research database, Grey Branch Consulting has gained access to a service that it will use over a year period. This prepaid subscription represents an asset. Assets therefore increase by $18,000.
At the same time, the company used cash to prepay for the service, so cash (an asset) will decrease by $18,000.
Grey Branch Consulting signed up for access to a financial research database for a period of one year beginning on April 1. The firm paid for a full year in advance, representing an amount of $18,000 (which was paid in cash).
How would this transaction impact the accounting equation of Grey Branch Consulting on April 1st? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
In purchasing access to the research database, Grey Branch Consulting has gained access to a service that it will use over a year period. This prepaid subscription represents an asset. Assets therefore increase by $18,000.
At the same time, the company used cash to prepay for the service, so cash (an asset) will decrease by $18,000.
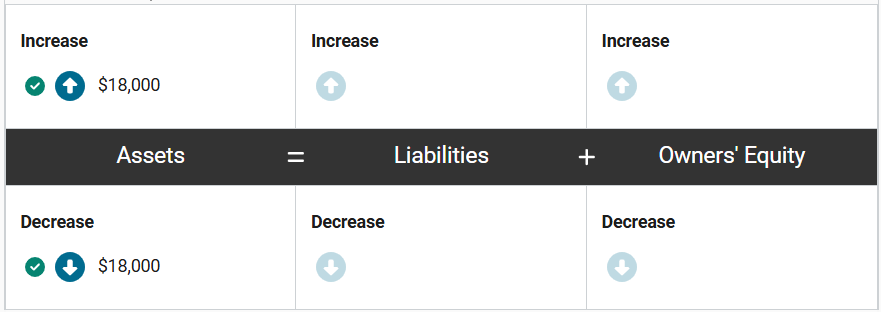
Yichen, a computer manufacturer, purchased raw materials for $60,000 on credit on January 1st. Yichen promised to pay for the raw materials in three equal monthly installments beginning on February 1st.
How will this purchase impact the accounting equation on the books of Yichen at the time of purchase? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
Assets increase by $60,000 because the company now has raw materials it will use in the manufacturing process. At the same time, liabilities increase by $60,000 because the company now has an obligation to pay for these materials.
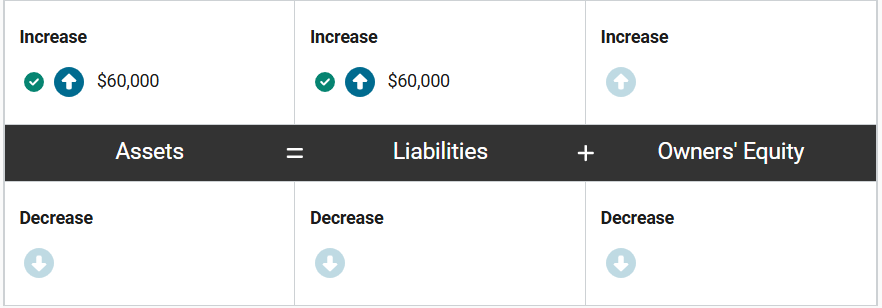
Gilligan’s Mountain Biking Tour Co. (GMBTC) receives $300,000 in advance payments for an upcoming 3-hour tour.
How will the accounting equation of GMBTC be impacted when these advance payments are received?
Assets increase by $300,000 because the company now has that amount of cash. At the same time, liabilities increase by $300,000 because the company now has the obligation to provide services on the upcoming bike tour.
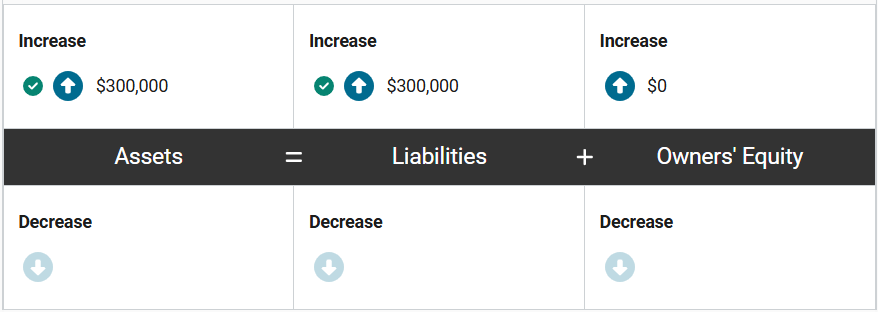
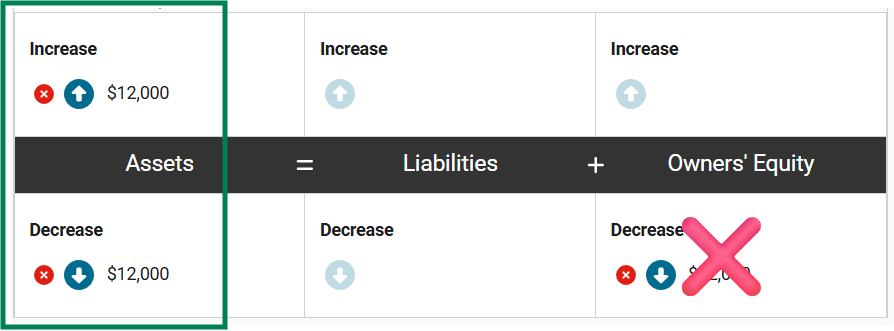
Molly’s Meadow, a beauty products manufacturing company, made a cash sale of $15,000 of packaged body lotion to one of their larger customers. The lotion had an inventory value of $7,000.
How will the revenue and cash inflow from this transaction impact the accounting equation of Molly’s Meadow? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
First, assets increase by $15,000 because the company receives cash from the client/customer, and owners’ equity increases by $15,000 to recognize the revenue associated with the sale.
At the same time, assets decrease by $7,000 because the company no longer has the lotion in inventory, and owners’ equity decreases by $7,000 to recognize the expense associated with the sale.
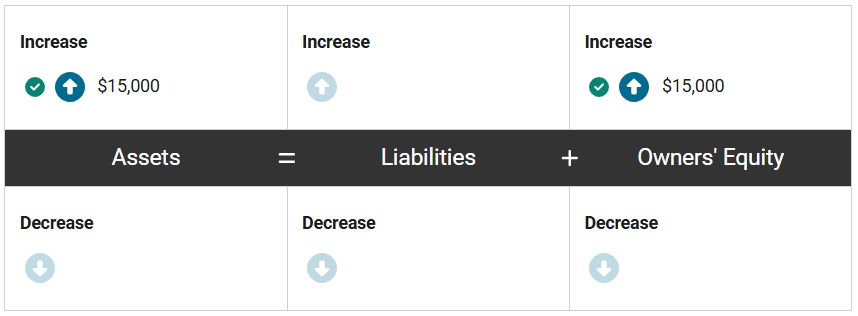
Molly’s Meadow, a beauty products manufacturing company, made a cash sale of $15,000 of packaged body lotion to one of their larger customers. The lotion had an inventory value of $7,000.
How will the related expense from this transaction impact the accounting equation of Molly’s Meadow? Enter the correct amounts in the equation.
First, assets increase by $15,000 because the company receives cash from the client/customer, and owners’ equity increases by $15,000 to recognize the revenue associated with the sale.
At the same time, assets decrease by $7,000 because the company no longer has the lotion in inventory, and owners’ equity decreases by $7,000 to recognize the expense associated with the sale.
Chart of accounts
List of all the accounts of a business. This list includes all asset, liability, equity, revenue, and expense accounts. The accounts and naming of accounts can vary from business to business.
Debit
One half of an accounting entry. Debits increase the balances in Asset and Expense accounts. Debits reduce the balances in Revenue, Liability, and Owners’ Equity accounts. Debit are shown on the left side in journal entries, T-Accounts, and trial balances.
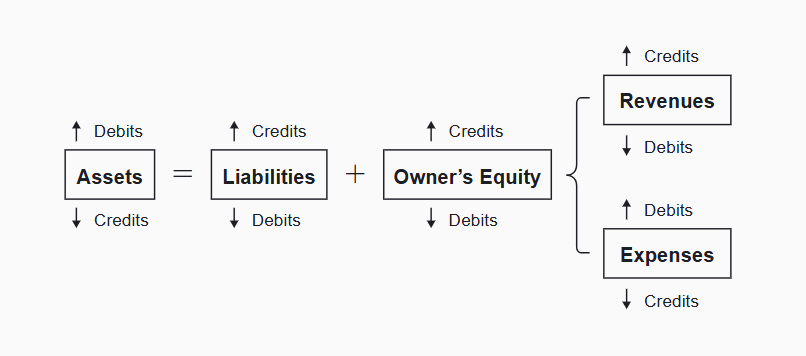
Accounting Equation with Debit & Credit
Assets increase with a debit and decrease with a credit. Liabilities increase with a credit and decrease with a debit. Owner's Equity increases with a credit and decreases with a debit. Within Owners' Equity, Revenues increase with a credit and decrease with a debit and Expenses increase with a debit and decrease with a credit.
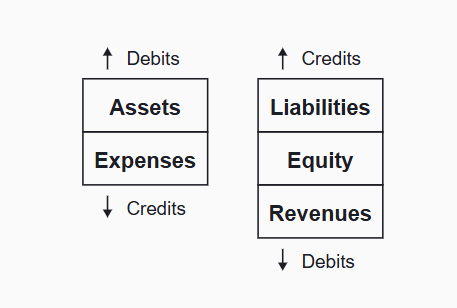
Debit & Credit
Assets and expenses increase with a debit and decrease with a credit. Liabilities, equity, and revenues increase with a credit and decrease with a debit.
Double Entry Accounting
The system of accounting that requires that every transaction be entered using both debits and credits and that the value of the debits must equal the value of the credits.
Journal Entry
The entry made to record a transaction in the financial records of a business. The information entered will include the accounts impacted, the dollar (or other currency) amounts involved, the date of the transaction, and often some notes explaining the transaction. A journal entry always includes at least one debit and at least one credit, and the total debits must always equal the total credits.
T-Account
T-accounts are a simplified version of ledger accounts. A T-account shows all the activity for a given account for a specific period of time, or in other words, the T-account is the summery of several journal entries. By convention, all debit activity is shown on the left side of T-accounts, and all credit activity is shown on the right side of the T-accounts.
On April 6, Clean Company purchases $100 worth of supplies on credit.
Please choose the correct two entries to record the transaction.
a) Debit Supplies for $100
b) Credit Supplies for $100
c) Debit Accounts Payable for $100
d) Credit Accounts Payable for $100
a) Debit Supplies for $100
d) Credit Accounts Payable for $100
On April 8, Clean Company buys $500 worth of supplies and pays in cash.
Please choose the correct two entries to record the transaction.
a) Debit Cash for $500
b) Credit Cash for $500
c) Debit Supplies for $500
d) Credit Supplies for $500
b) Credit Cash for $500
c) Debit Supplies for $500
On April 15th, Clean Company pays the vendor in cash for the amounts due related to the purchase on April 6th.
Please choose the correct two entries to record the transaction.
a) Debit Cash for $100
b) Credit Cash for $100
c) Debit Accounts Payable for $100
d) Credit Accounts Payable for $100
b) Credit Cash for $100
c) Debit Accounts Payable for $100
On April 20th, Clean Company buys additional supplies in the amount of $175 on credit.
Please choose the correct two entries to record the transaction.
a) Debit Accounts Payable for $175
b) Credit Accounts Payable for $175
c) Debit Supplies for $175
d) Credit Supplies for $175
b) Credit Accounts Payable for $175
c) Debit Supplies for $175
On April 22nd, Clean Company returns $75 worth of supplies from its April 20th purchase. The amount owed to the supplier is adjusted downward in the amount of the return.
Please choose the correct two entries to record the transaction.
a) Debit Supplies for $75
b) Credit Supplies for $75
c) Debit Accounts Payable for $75
d) Credit Accounts Payable for $75
b) Credit Supplies for $75
c) Debit Accounts Payable for $75
Accrual
A revenue amount that is recorded after the revenue is earned but before the payment is received or an expense amount that is recorded after it has been incurred but before the payment has been made. In either case, for an accrual the exchange of cash is expected at some future point after the initial revenue or expense is recognized. Accrual accounting recognizes revenues and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of when cash transactions occur.
Deferred Revenue (aka Unearned Revenue)
A liability that represents the obligation to provide goods or services to a customer in the future. Deferred revenue is recorded when a business receives a payment in advance from a customer, but the business has not yet delivered the good or provided the service. Once the business fulfills its obligation to provide goods or services, the liability is reduced and revenue is recognized. May also be referred to as unearned revenue. Remember that deferred revenue is NOT revenue.
T-Account
T-Accounts are a simplified version of ledger accounts. A T-account shows all the activity for a given account for a specific period of time, or in other words, the T-account is the summary of several journal entries. by convention all debit activity is shown on the left side of T-accounts and all credit activity is shown on the right side of T-accounts.
Balance sheet
Income statement
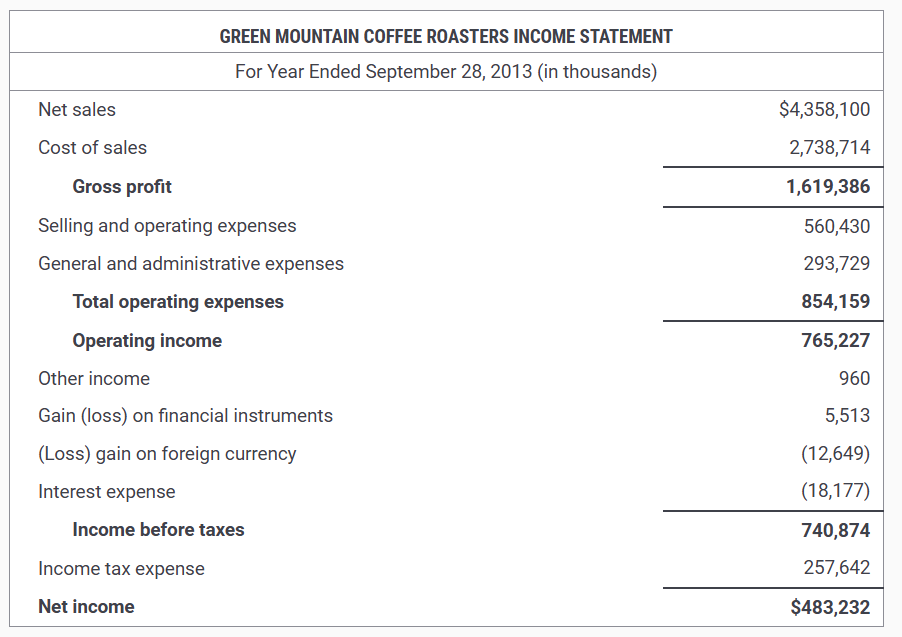
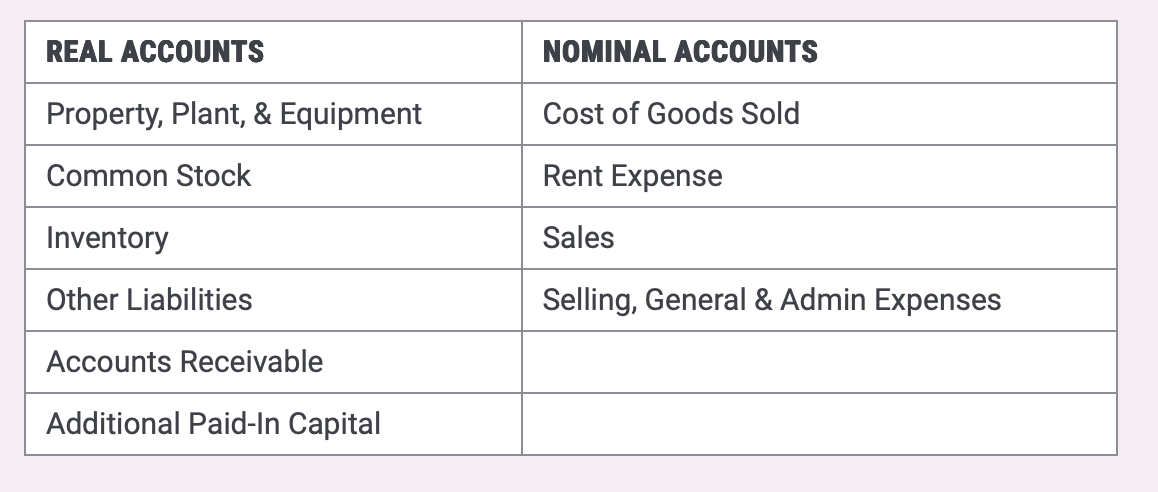
Real accounts
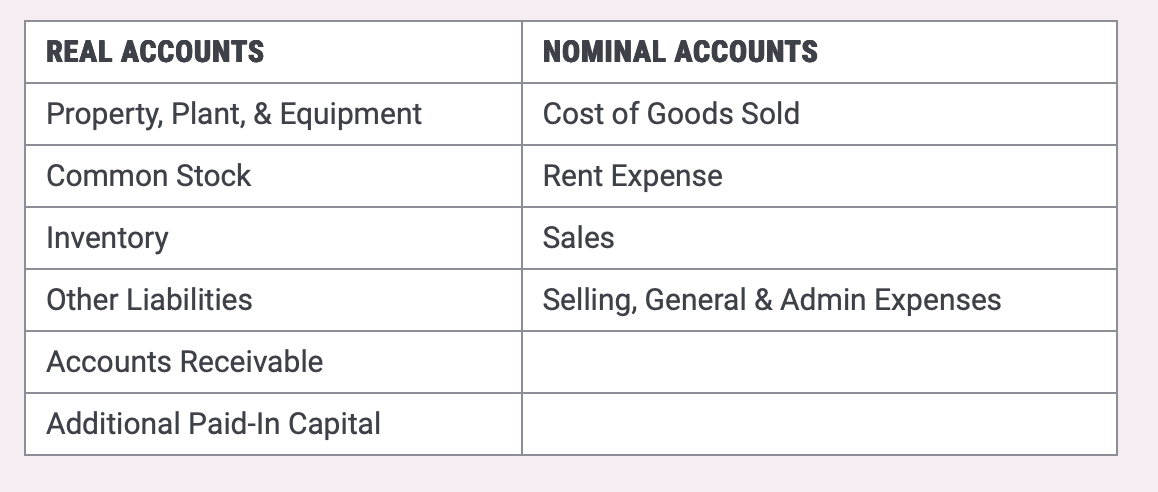
Nominal accounts
Flow measures
Materiality
Current assets
Non -current assets
Liquidity
Current liabilities
Non-current liabilities
Shareholders’ equity
Closing process
Statement of comprehensive income
Other comprehensive income
