Mendel's Laws of Inheritance and Genetic Principles
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Selective Breeding
Farmers: selective breeding of plants to improve crops.
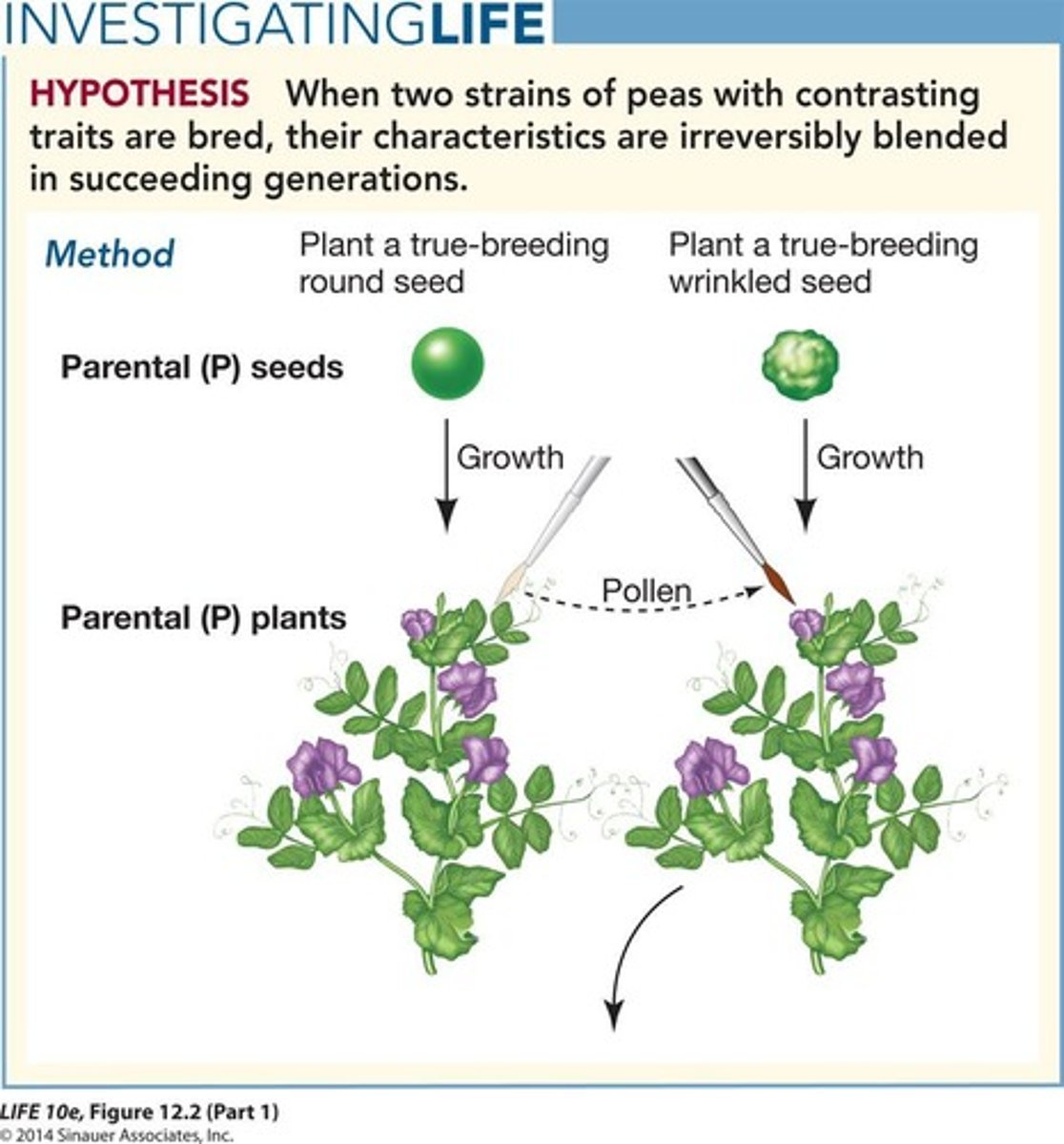
Particulate Inheritance
Parental determinants are distinct.
Blending Inheritance
Parental determinants get mixed or blended during fertilization.
Gregor Mendel
Austrian Monk, scientist, mathematician, and gardener known as the Father of Genetics.
True-Breeding Plants
Plants that produce offspring identical to themselves when self-fertilized.
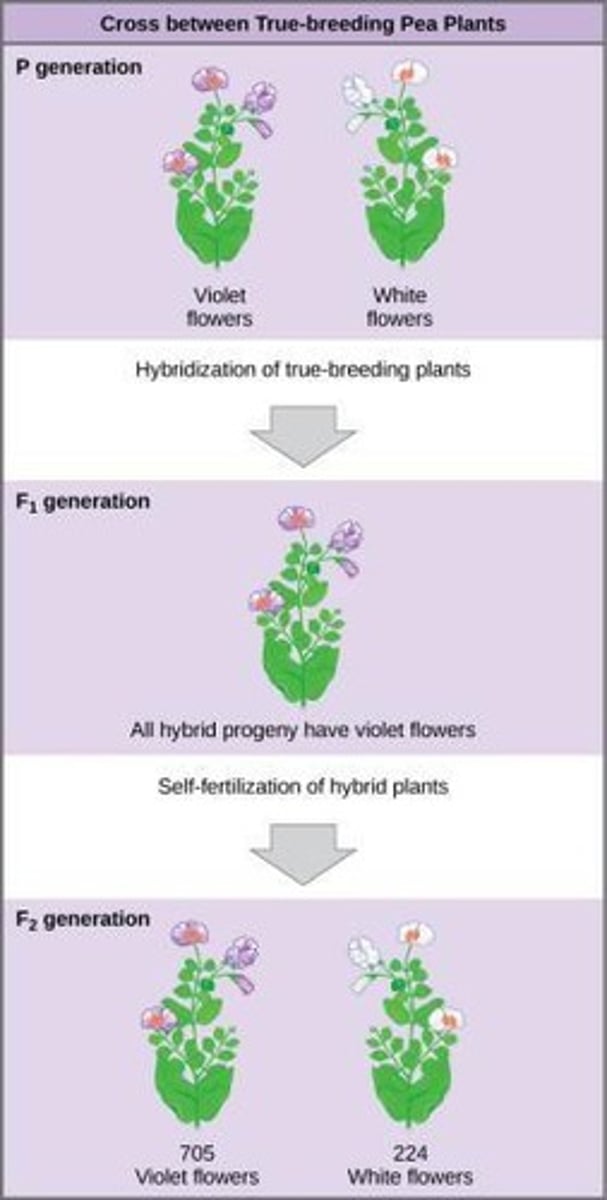
F1 Generation
The offspring of the parental generation in Mendel's experiments.
F2 Generation
The offspring of the F1 generation in Mendel's experiments.
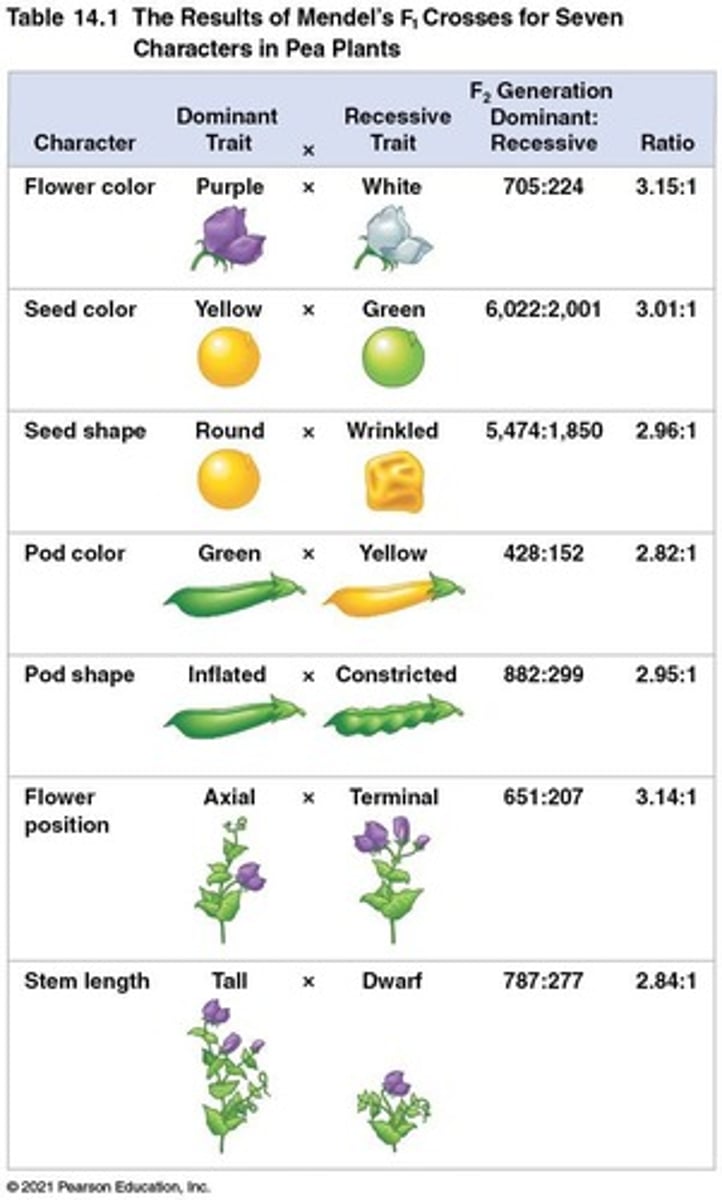
Dominant Trait
The trait that appears in the F1 generation.
Recessive Trait
The trait that disappears in the F1 generation but appears in the F2 generation.
3:1 Ratio
The ratio of dominant to recessive traits observed in the F2 generation.
Genes
Hereditary determinants for a trait.
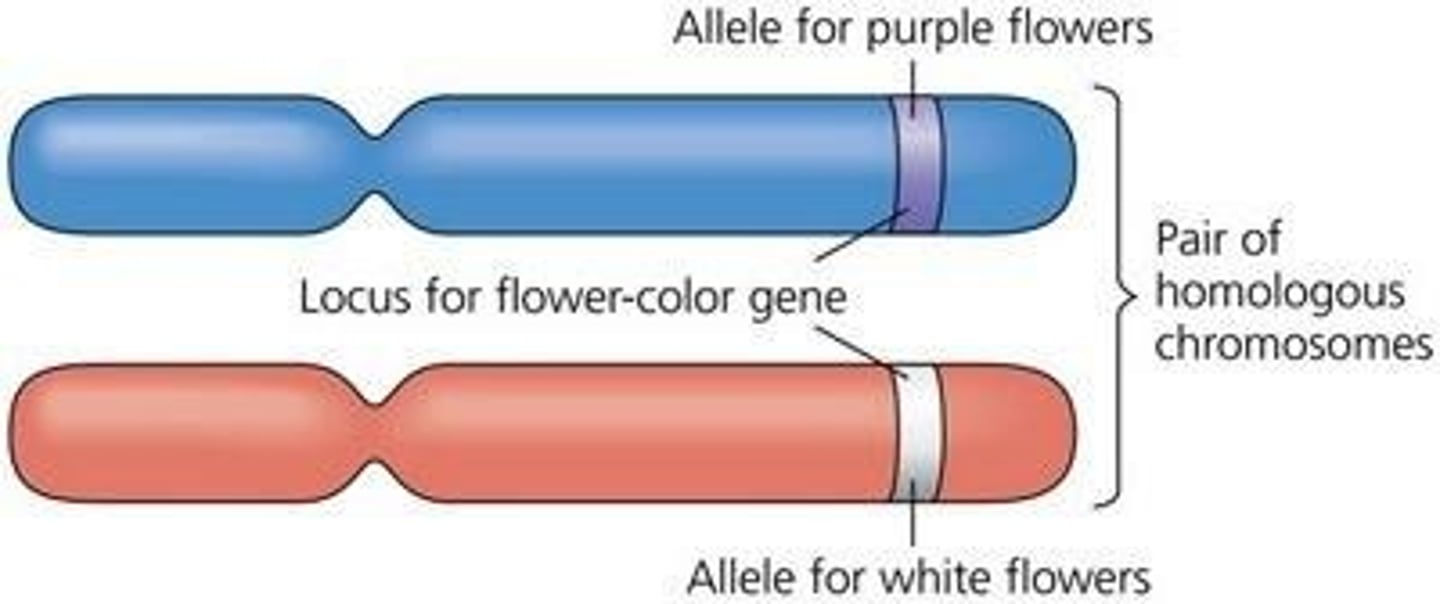
Alleles
Different versions of a gene.
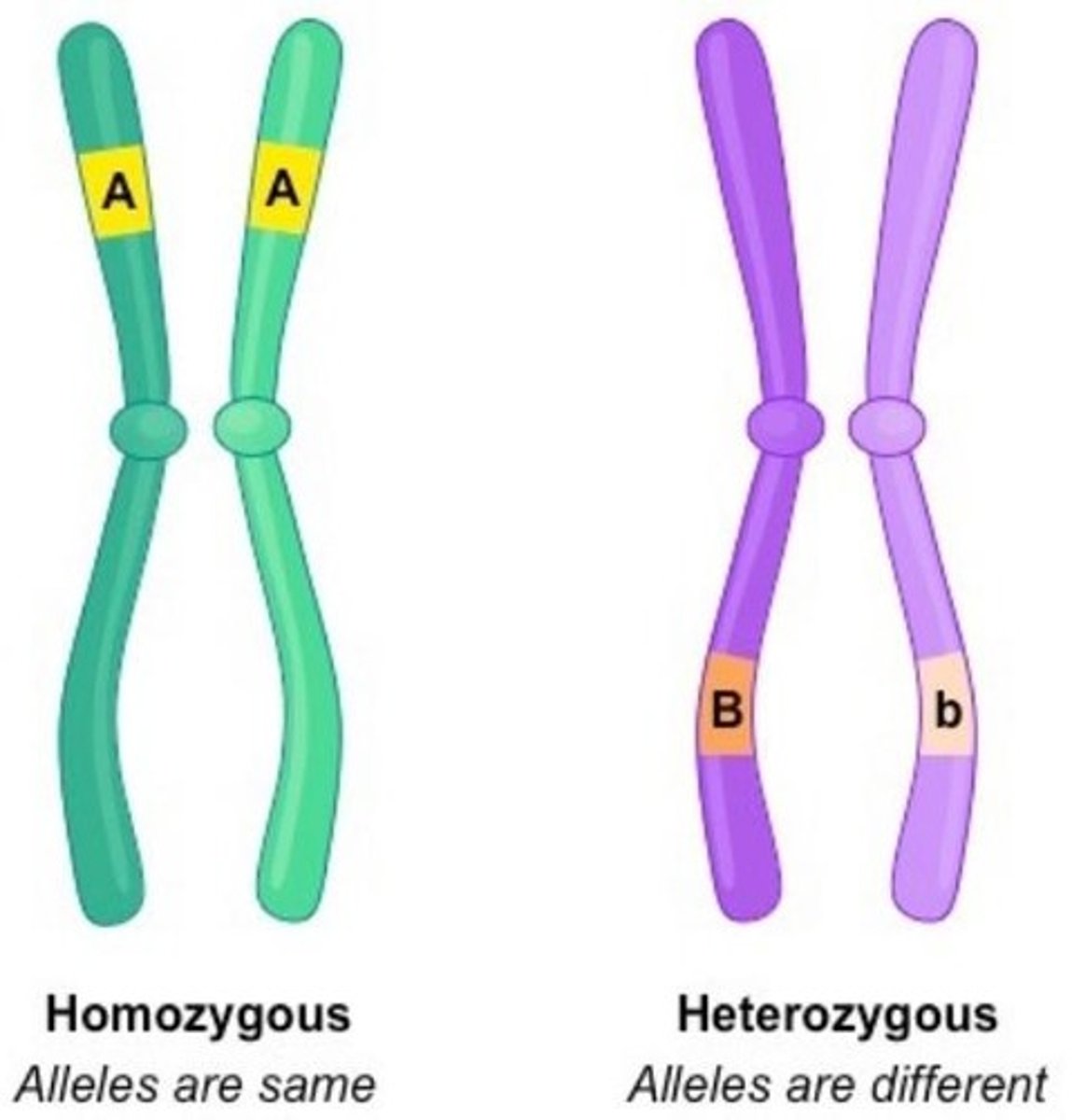
Homozygous
An individual with two copies of the same allele (e.g., AA or aa).
Heterozygous
An individual with two different alleles (e.g., Bb).
Genotype
The combination of alleles found in an individual.
Phenotype
The expressed or measurable trait of an individual.
Law of Segregation
The two alleles in a pair segregate from each other during gamete formation.
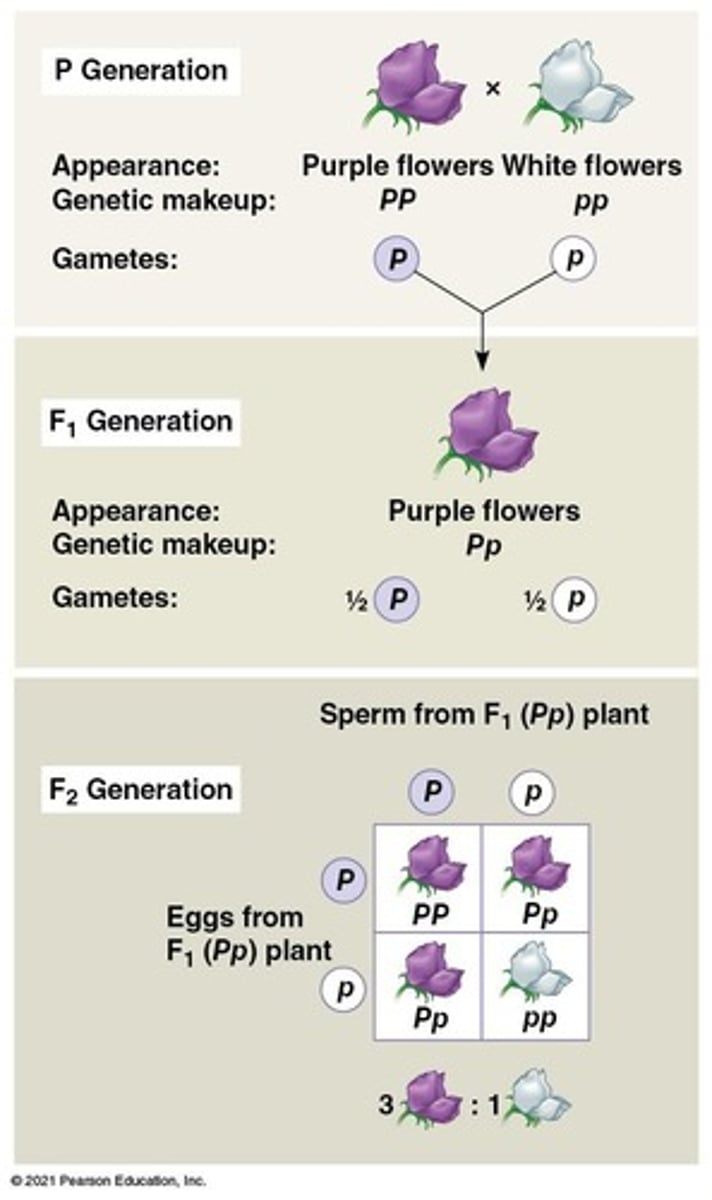
Monohybrid Cross
Offspring of crosses between organisms differing in one character.
Punnett Square
A diagram used to predict genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from genetic crosses.
Dihybrid Cross
A genetic cross that examines the inheritance of two different traits.
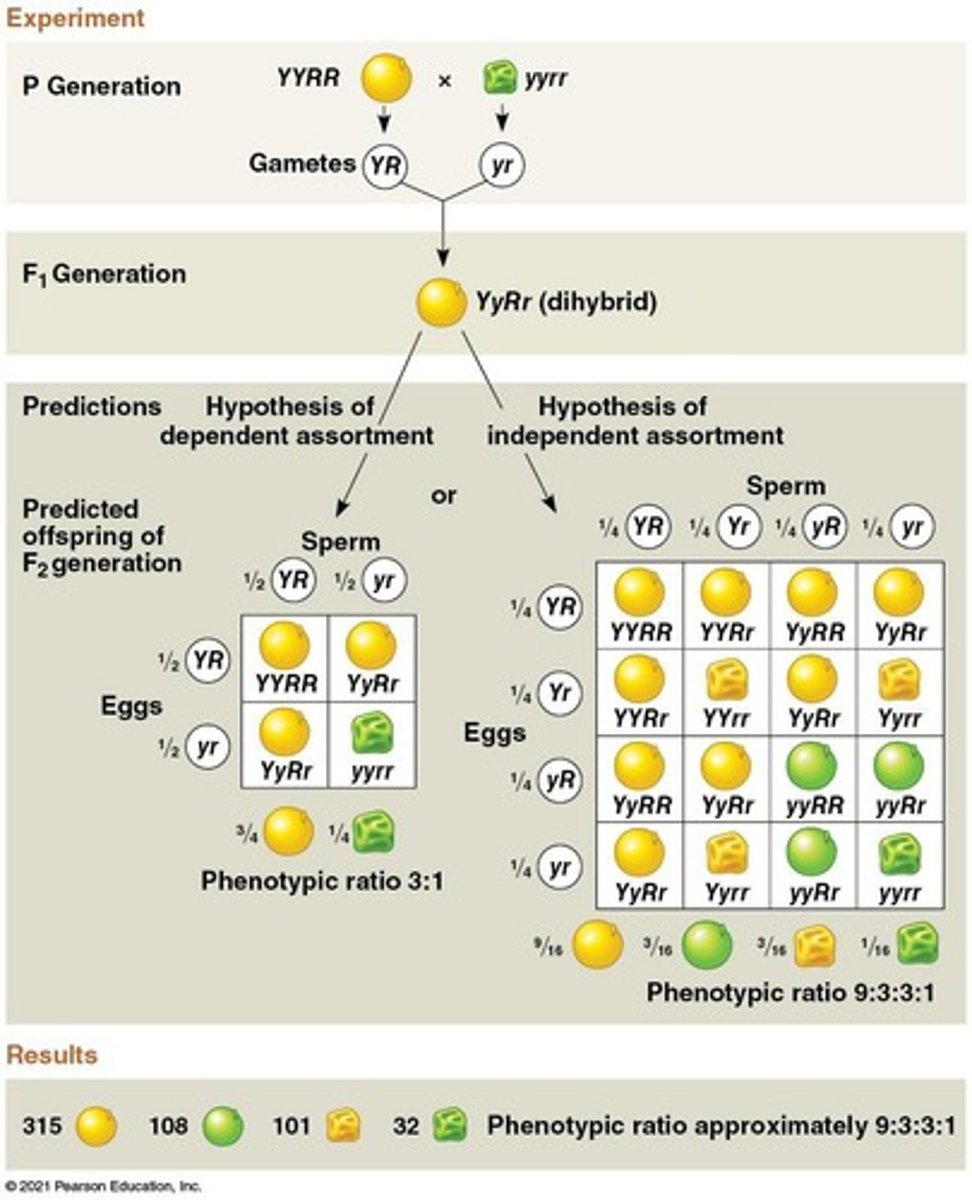
Law of Independent Assortment
Each pair of alleles segregates independently of the segregation of other allele pairs.
Multiplication Rule
The probability of two independent events occurring at the same time is found by multiplying the individual probabilities.
Addition Rule
The probability of two mutually exclusive events occurring at the same time is found by adding the individual probabilities.
Quantitative Trait
A trait that occurs in a range (e.g., height).
Discrete Trait
A trait that occurs in two or a few different categories (e.g., eye color).
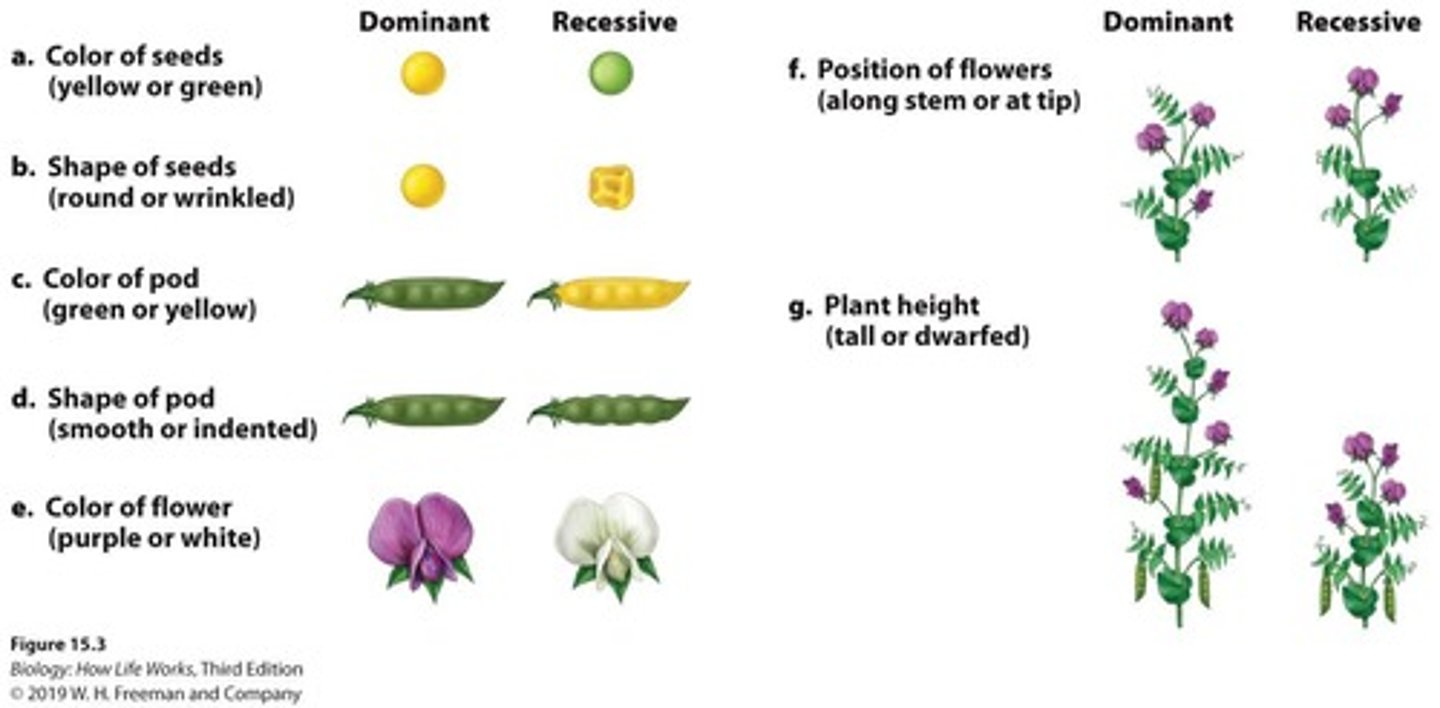
Garden Pea
The plant chosen by Mendel for his experiments due to its ideal characteristics.
Short Generation Time
A characteristic of the garden pea that allowed for quicker observation of traits.
Careful Record Keeping
One of the key qualities of a first-rate scientist demonstrated by Mendel.
Analytical Mind
A quality that enabled Mendel to effectively study inheritance.
Probability of Offspring
Likelihood of specific genetic combinations in offspring.
Multiple Alleles
More than two alleles exist for a gene.
Codominance
Both alleles express equally in heterozygotes.
Incomplete Dominance
Heterozygote shows intermediate phenotype.
Epistasis
One gene's expression affects another gene's expression.
Polygenic Inheritance
Multiple genes influence a single phenotype.
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material during meiosis.
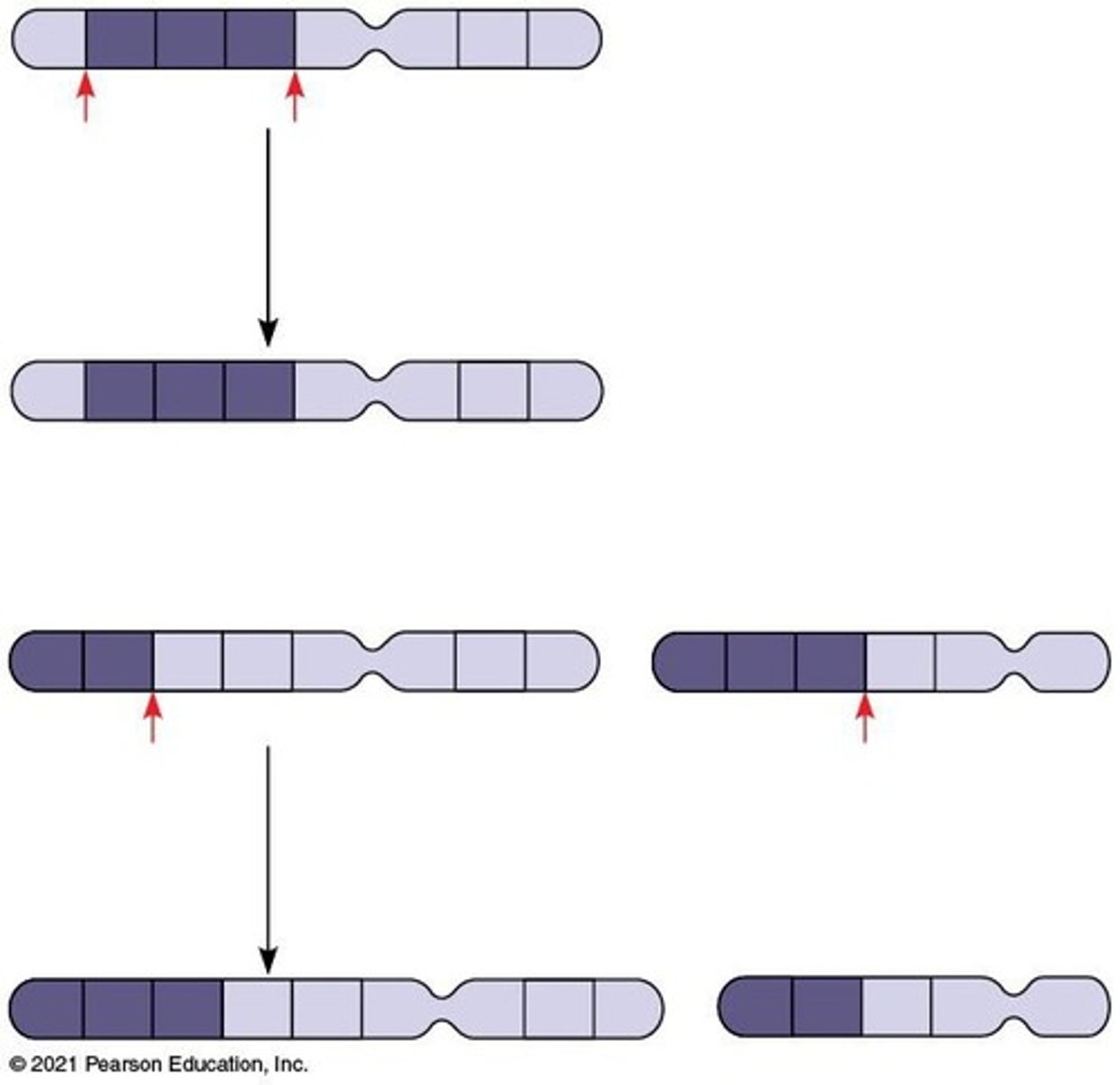
Linkage
Tendency of genes to be inherited together.
Sex-linked Inheritance
Traits determined by genes on sex chromosomes.
X-linked Genes
Genes located on the X chromosome.
Y-linked Genes
Genes located on the Y chromosome.
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell.
Monosomy
Condition of having one less chromosome (2n-1).
Trisomy
Condition of having one extra chromosome (2n+1).
Polyploidy
Having an entire extra set of chromosomes.
Klinefelter Syndrome
XXY condition, phenotypically male with abnormalities.
Turner Syndrome
XO condition, phenotypically female with underdevelopment.
Deletion
Loss of a chromosomal segment.
Duplication
Repetition of a chromosomal segment.
Inversion
Reversal of a chromosomal segment's orientation.
Translocation
Movement of a chromosomal segment to another chromosome.
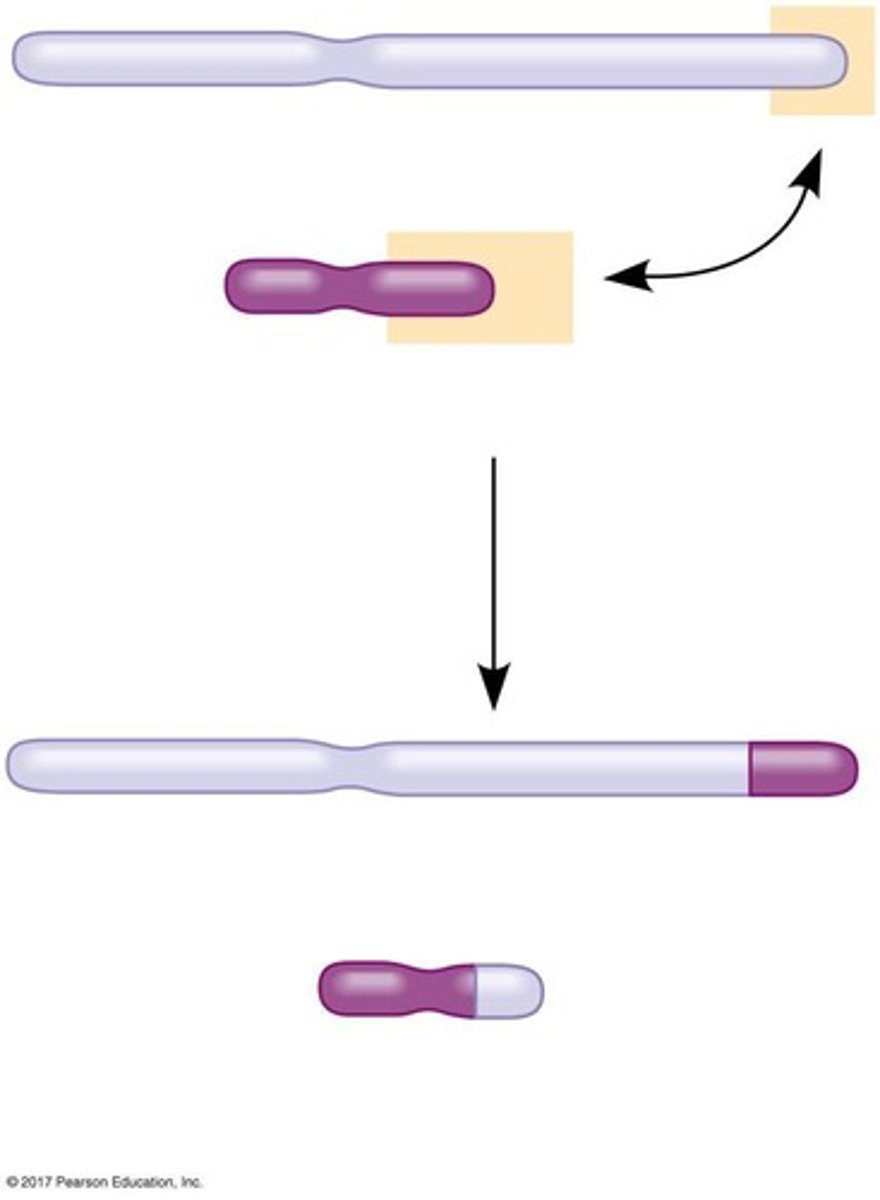
Philadelphia Chromosome
Translocation associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Drosophila melanogaster
Model organism for studying genetics.
Barr Body
Inactivated X chromosome in female mammals.
Carrier
Individual with one copy of a recessive allele.
Hemizygous
Having only one allele for a gene.