A & P Lecture 8: Autonomic Nervous System
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Is the ANS voluntary or involuntary
involuntary
Where does ANS control come from
Hypothalamus, limbic system, brain stem, spinal cord
Is the ANS a two-neuron or one-neuron pathway?
Two-neuron
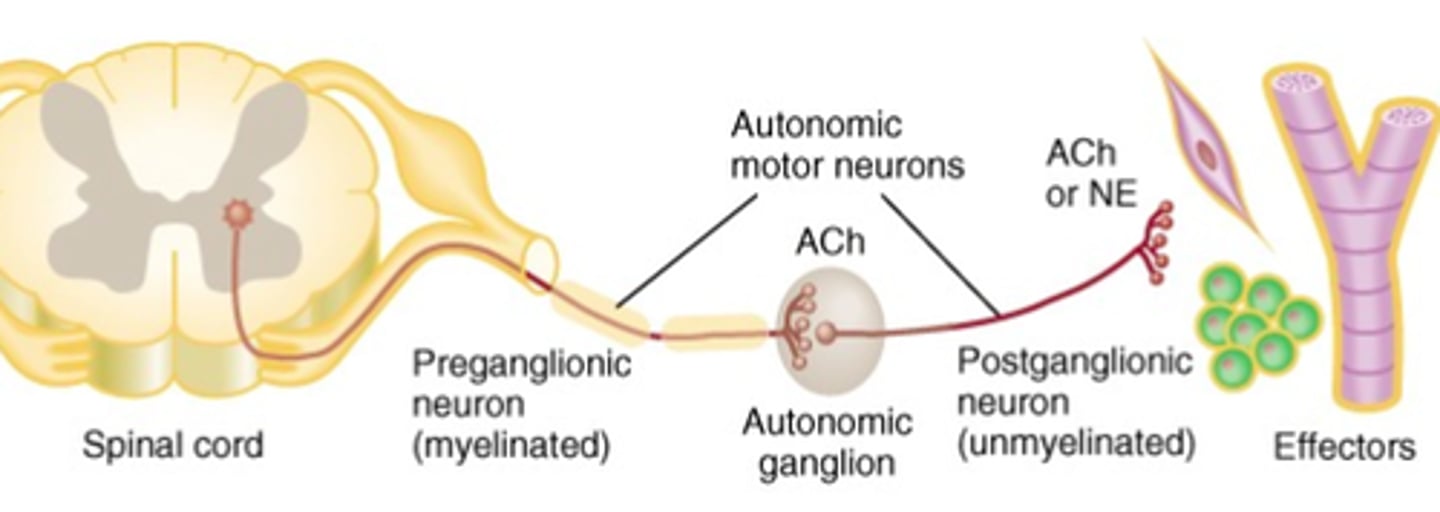
What neurons always release ACh
Preganglionic neurons
Most sympathetic postganglionic neurons release...
Norepinephrine
Sympathetic postganglionic neurons that go to sweat glands release...
ACh
Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons release...
ACh
Chromaffin cells of adrenal medullae release...
epinephrine and norepinephrine
ANS effectors
cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
What fibers does the Somatic NS carry?
Sensory and motor
Sensory in the Somatic NS
- General somatic sensation
- Special senses
What muscles does the Somatic NS innervate
Skeletal muscle
Somatic NS: How many neurons are in the pathway
One neuron extending from CNS to skeletal muscle fiber
What system is the adrenal medulla part of?
ANS
What system is the adrenal cortex part of?
Endocrine system
How does epinephrine and NE travel in the body after released from Chromaffin cell
Blood
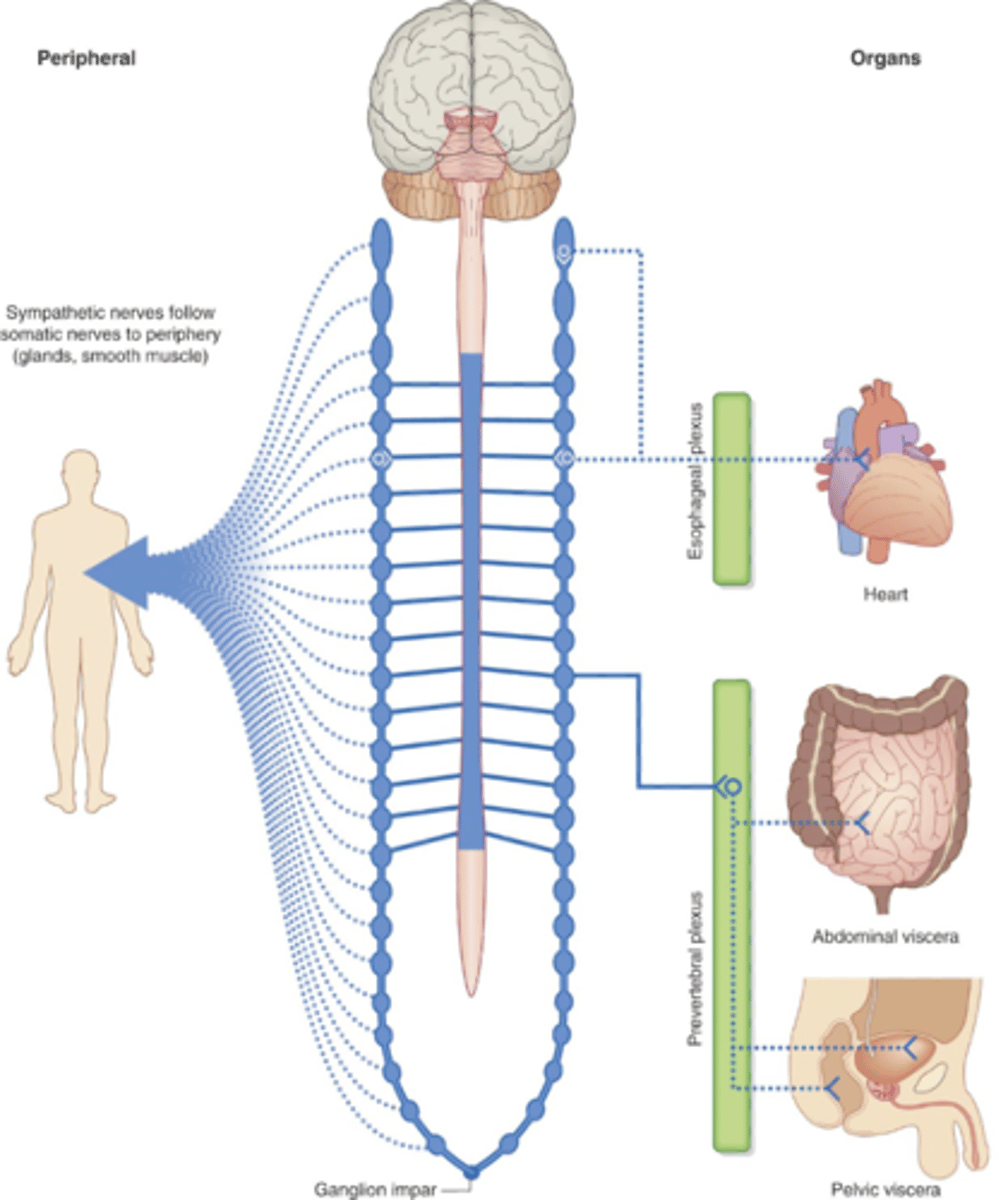
ANS input sources
Autonomic (visceral) sensory neurons, interoceptors
Is ANS input consciously perceived?
No
Motor movement in the ANS can be either...
excitatory or inhibitory
What is unique about tissue innervated by the ANS
Still function even if nerve supply is damaged
Role of the SNS
Fight or flight

Role of PNS
Rest and digest
Most organs are innervated by...
Both SNS and PNS
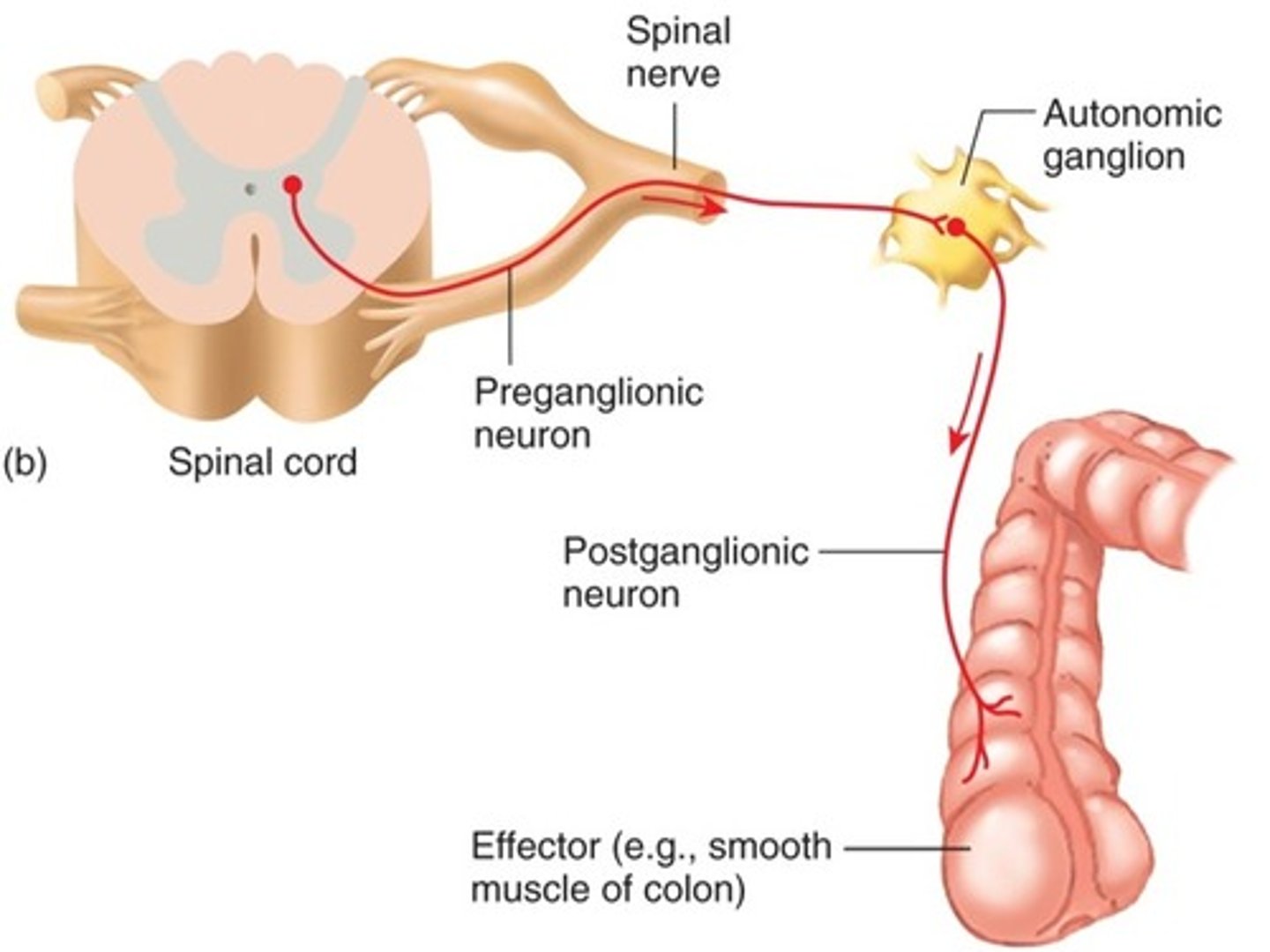
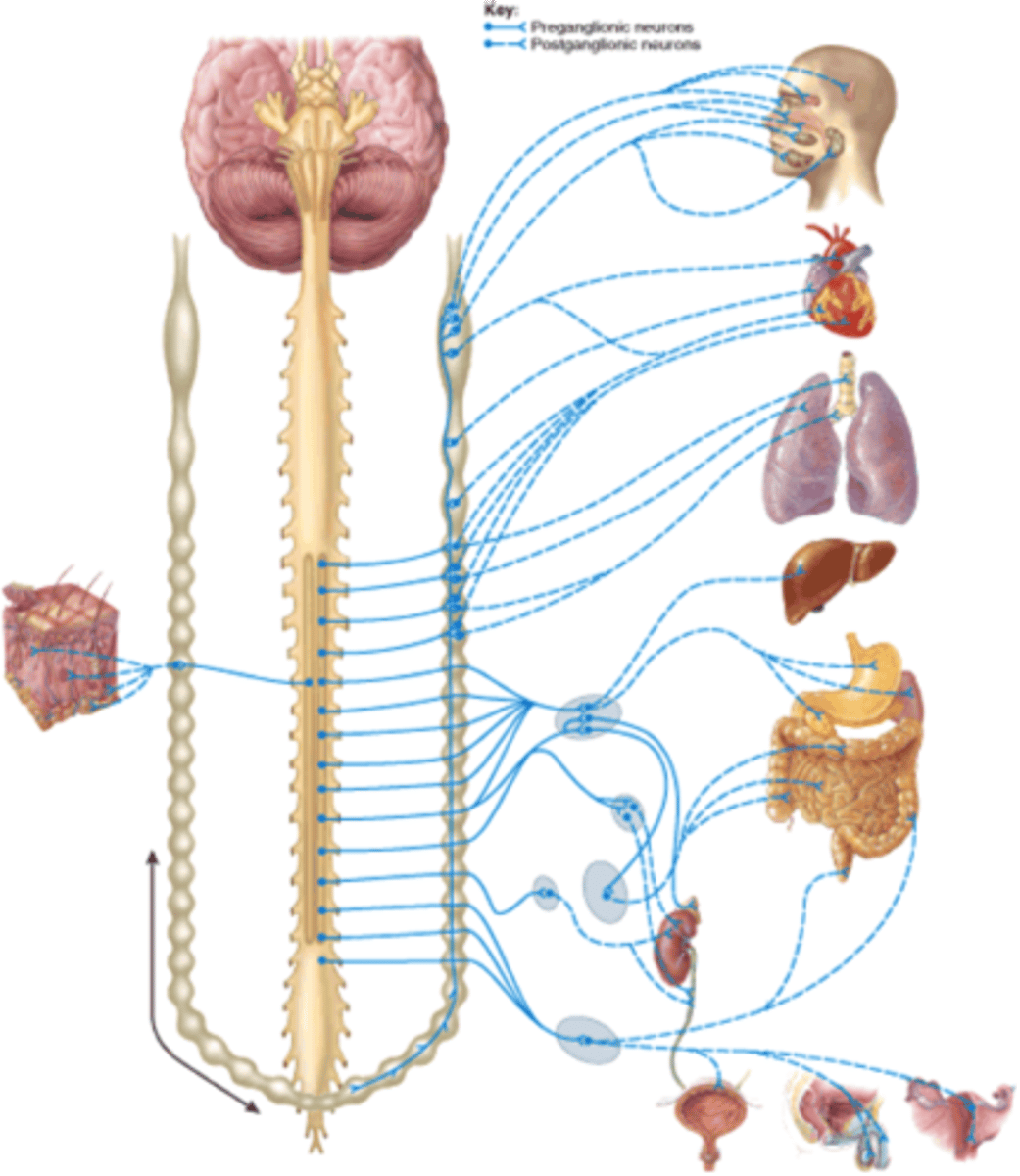
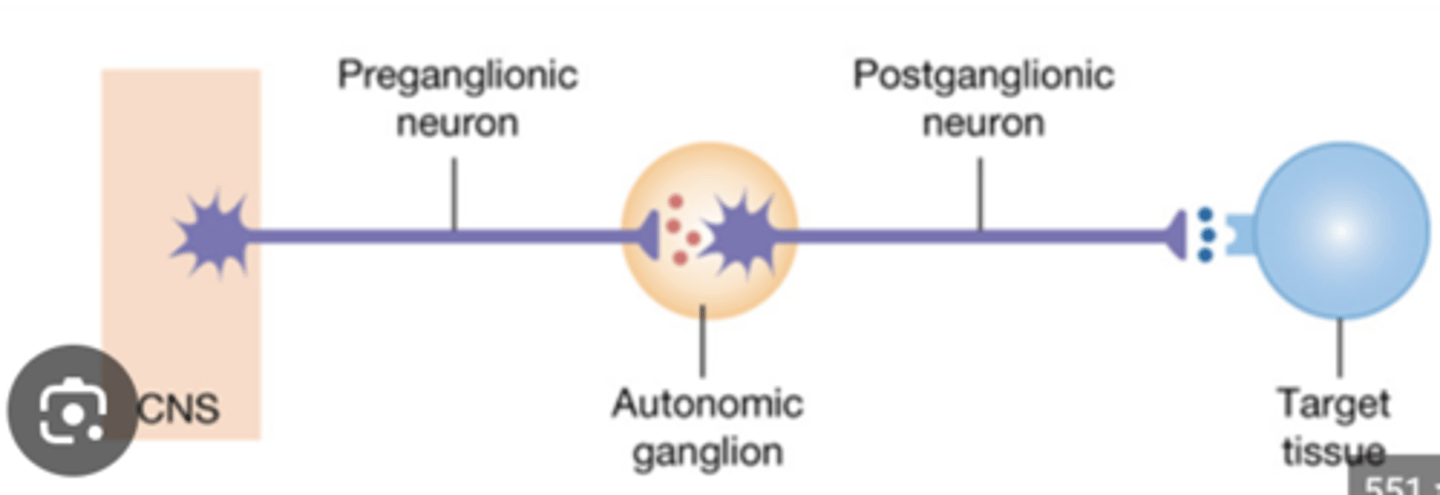
Two motor neurons in the ANS
preganglionic and postganglionic
Where is the cell body for the preganglionic neuron?
Brain or spinal cord
Are preganglionic neurons myelinated or unmyelinated?
myelinated
Preganglionic axons extend to the...
autonomic ganglion
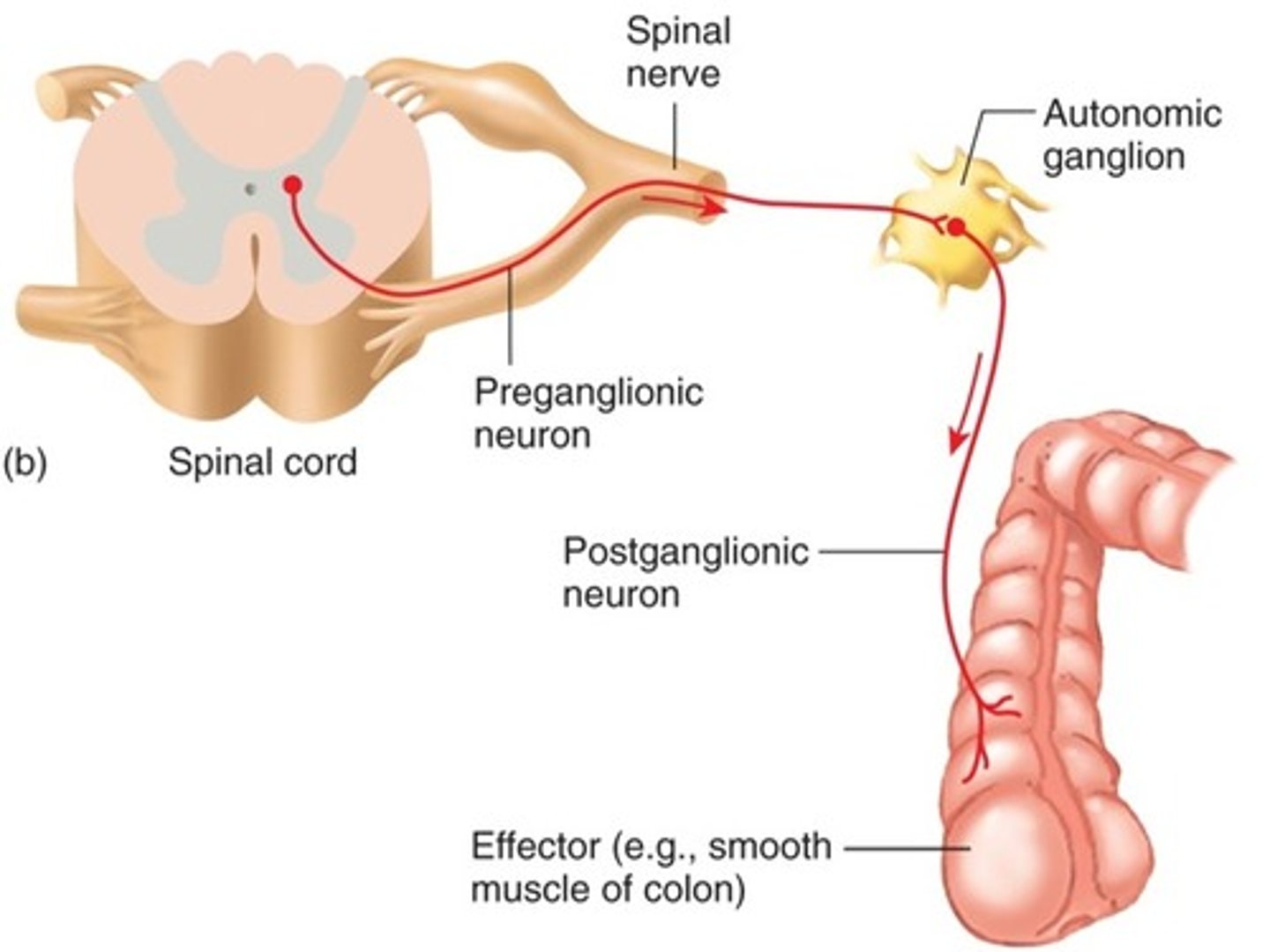
Where is the cell body of the postganglionic neuron?
Ganglion
Are postganglionic neurons myelinated or unmyelinated?
unmyleinated
Postganglionic axons extend to the...
effector organ
Where are preganglionic cell bodies for the SNS located
Lateral horns of gray matter (T1-L2)
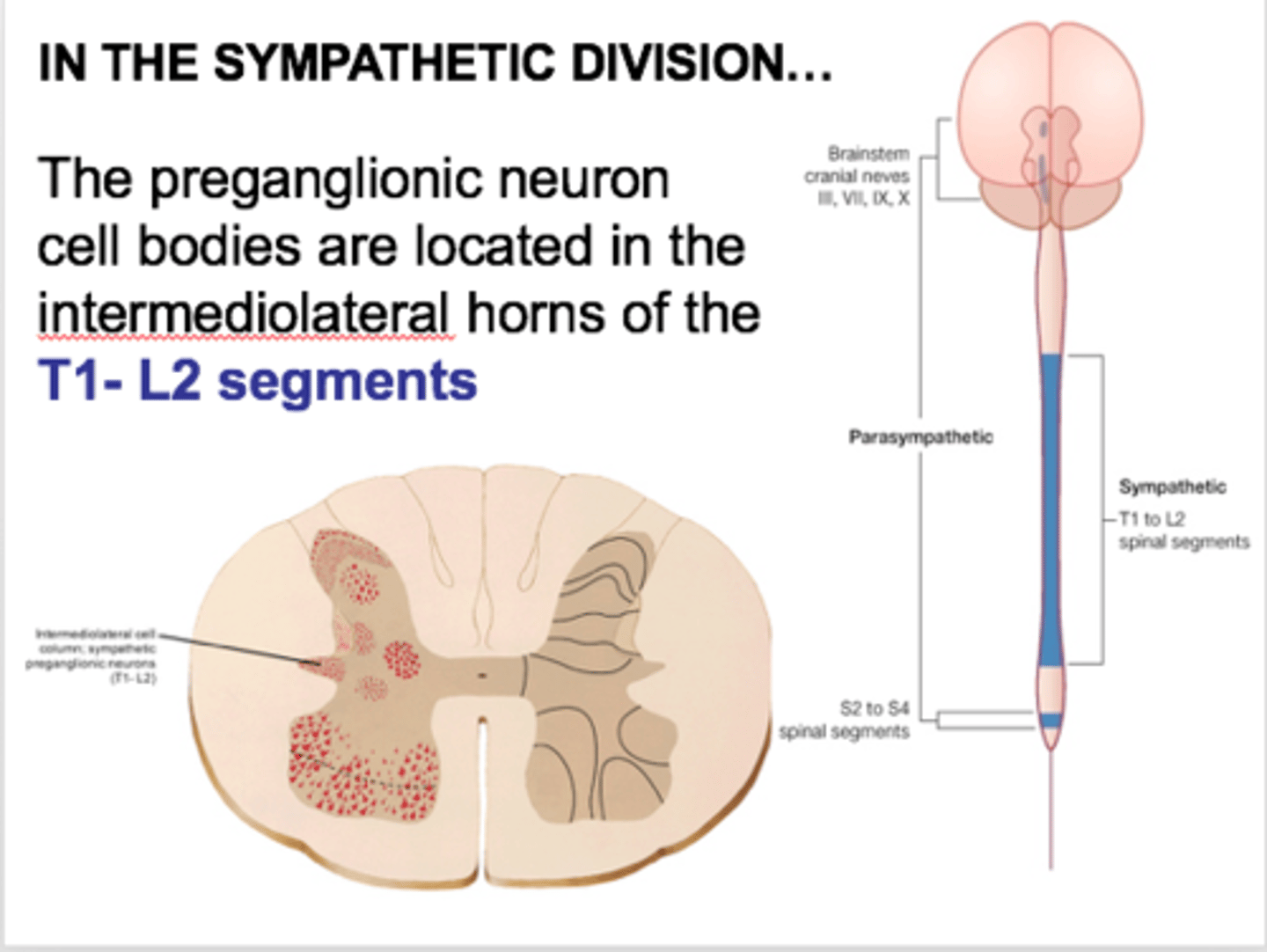
What is another name for the sympathetic division
thoracolumbar division
Site of synapse between preganglionic and postganglionic neuron
Sympathetic ganglia
Two major types of sympathetic ganglia
sympathetic trunk ganglia and prevertebral ganglia
Sympathetic trunk ganglia: Postganglionic neurons primarily innervate organs...
above the diaphragm
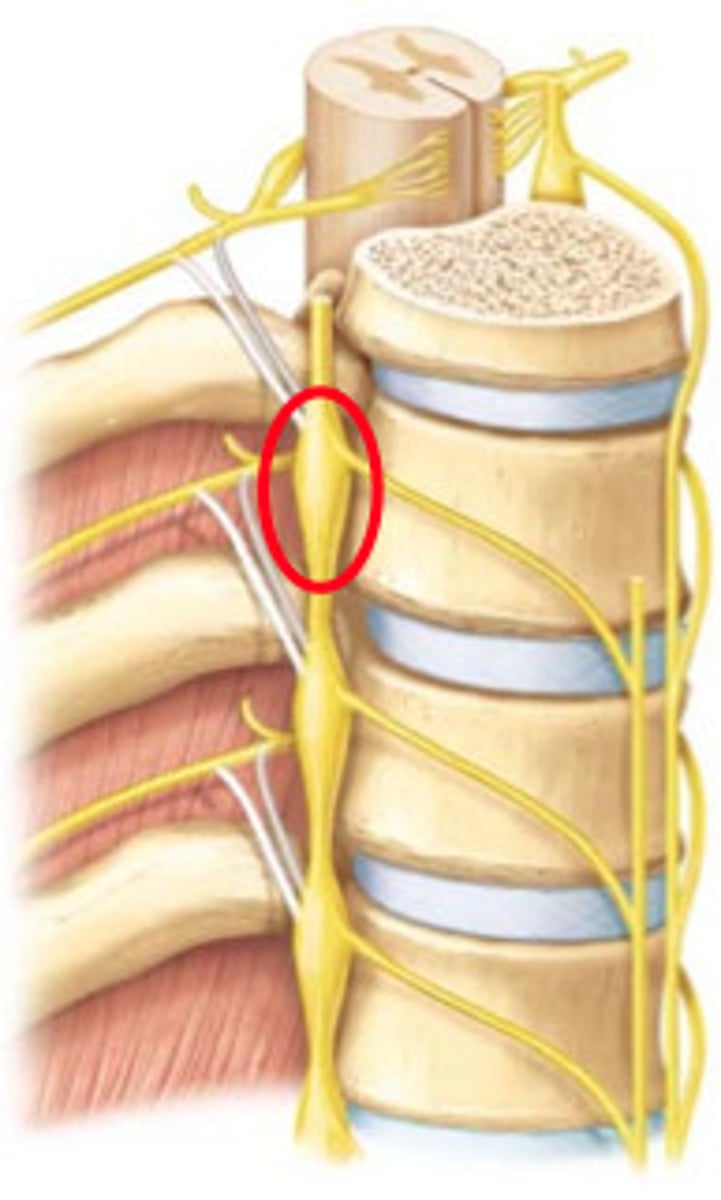
Where does the sympathetic trunk extend
Base of skull to coccyx
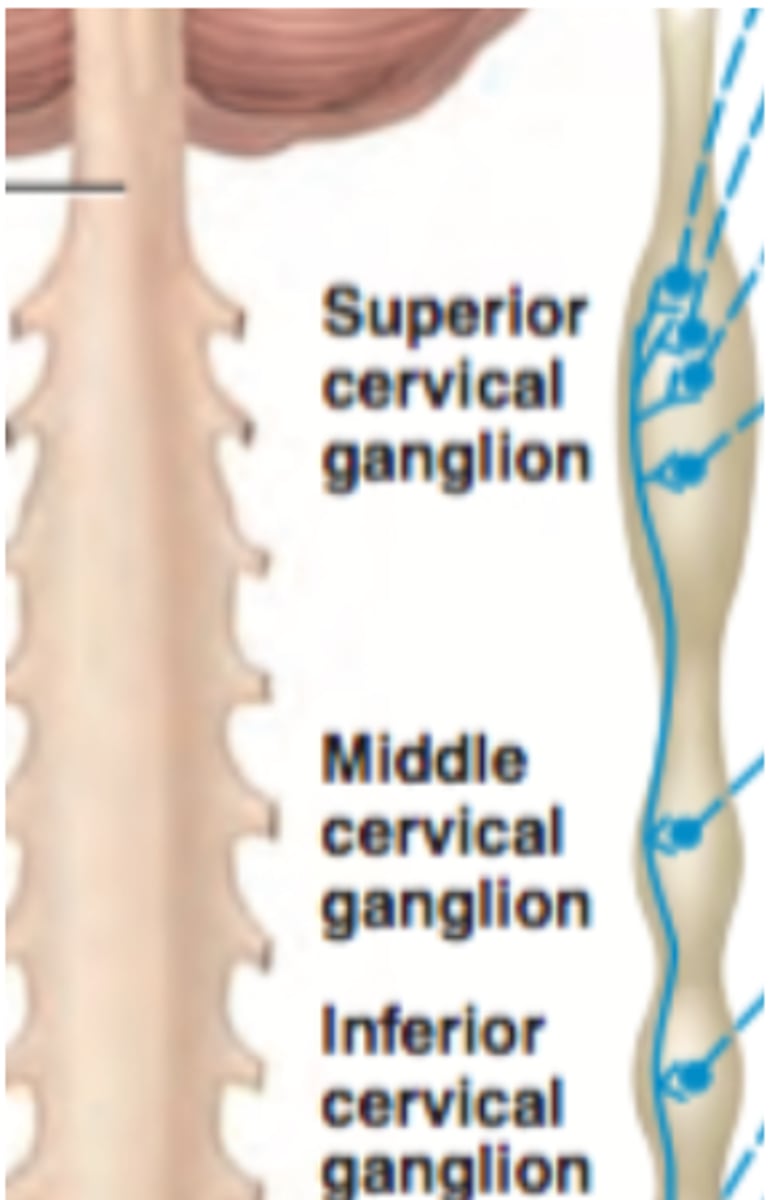
Sympathetic trunk ganglia in the neck
superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia
Position of sympathetic trunk ganglia in reference to the vertebral column
anterior and lateral
Length of preganglionic axons in the SNS
short
Length of postganglionic axons in the SNS
long
Length of preganglionic axons in the PNS
long
Length of postganglionic axons in the PNS
short
Number of paired sympathetic trunk ganglia
3 cervical, 11-12 thoracic, 4-5 lumbar, 4-5 sacral, 1 coccygeal
Superior cervical ganglion innervation
Head and heart
sweat glands, smooth muscle of eye, blood vessels of face, lacrimal glands, pineal gland, nasal mucosa, salivary glands
Middle cervical ganglion innervation
heart
Inferior cervical ganglion innervation
heart
Prevertebral ganglia are also called the...
collateral ganglia
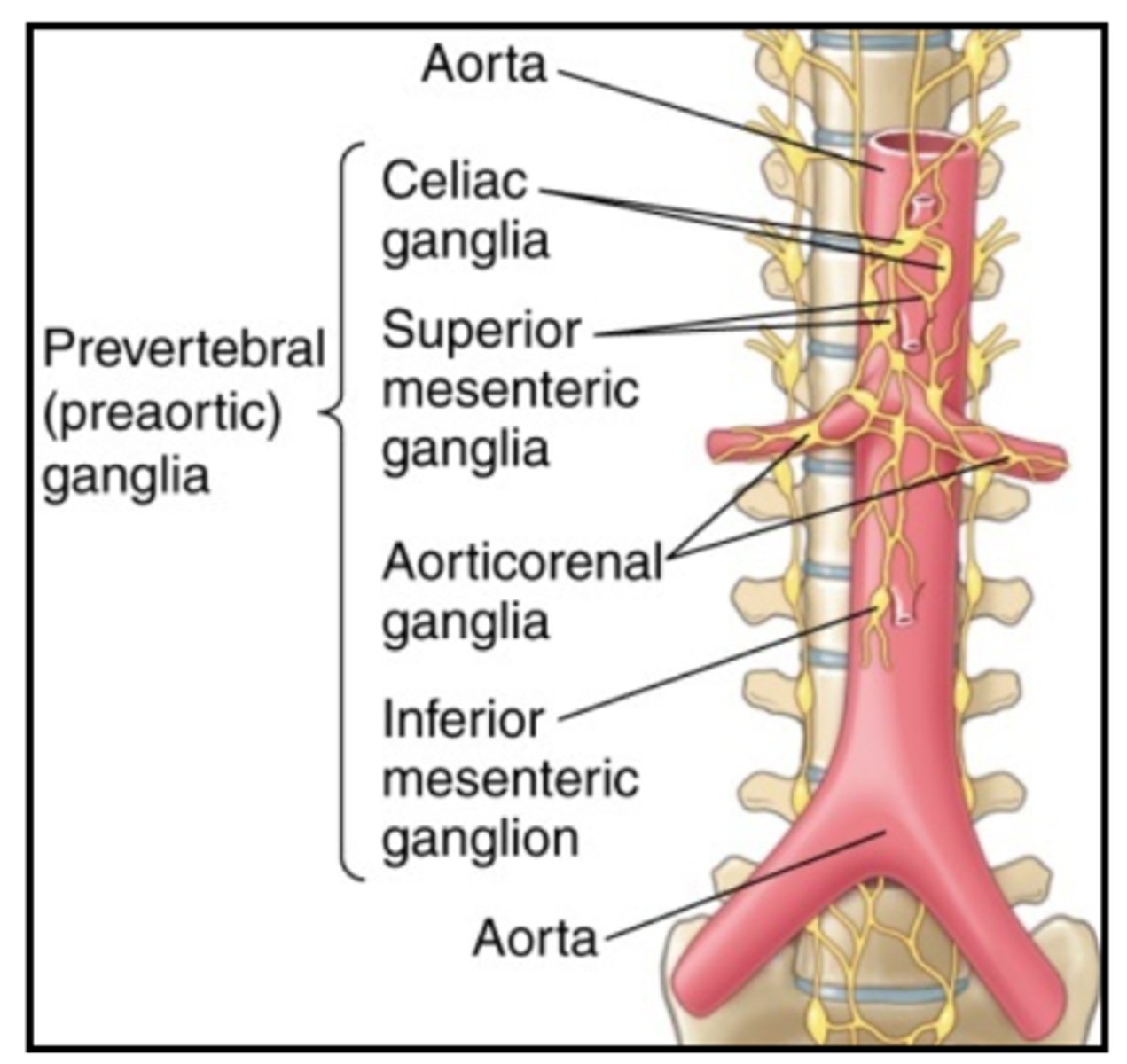
Prevertebral ganglia position in reference to vertebral column
anterior
Prevertebral ganglia: postganglionic neurons innervate organs...
below the diaphragm
5 major prevertebral ganglia
celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, aorticorenal, renal
SNS pathways to connect with postganglionic neurons (4)
1. Synapse with postganglionic neurons in adjacent ganglion
2. Ascend or descend chain before synapsing
3. Pass through chain and synapse in a prevertebral ganglion
4. Pass through chain and prevertebral to reach adrenal medullae
SNS: preganglionic axons exit spinal cord via
ventral root
SNS: how to preganglionic axons leave the spinal nerve
White ramus
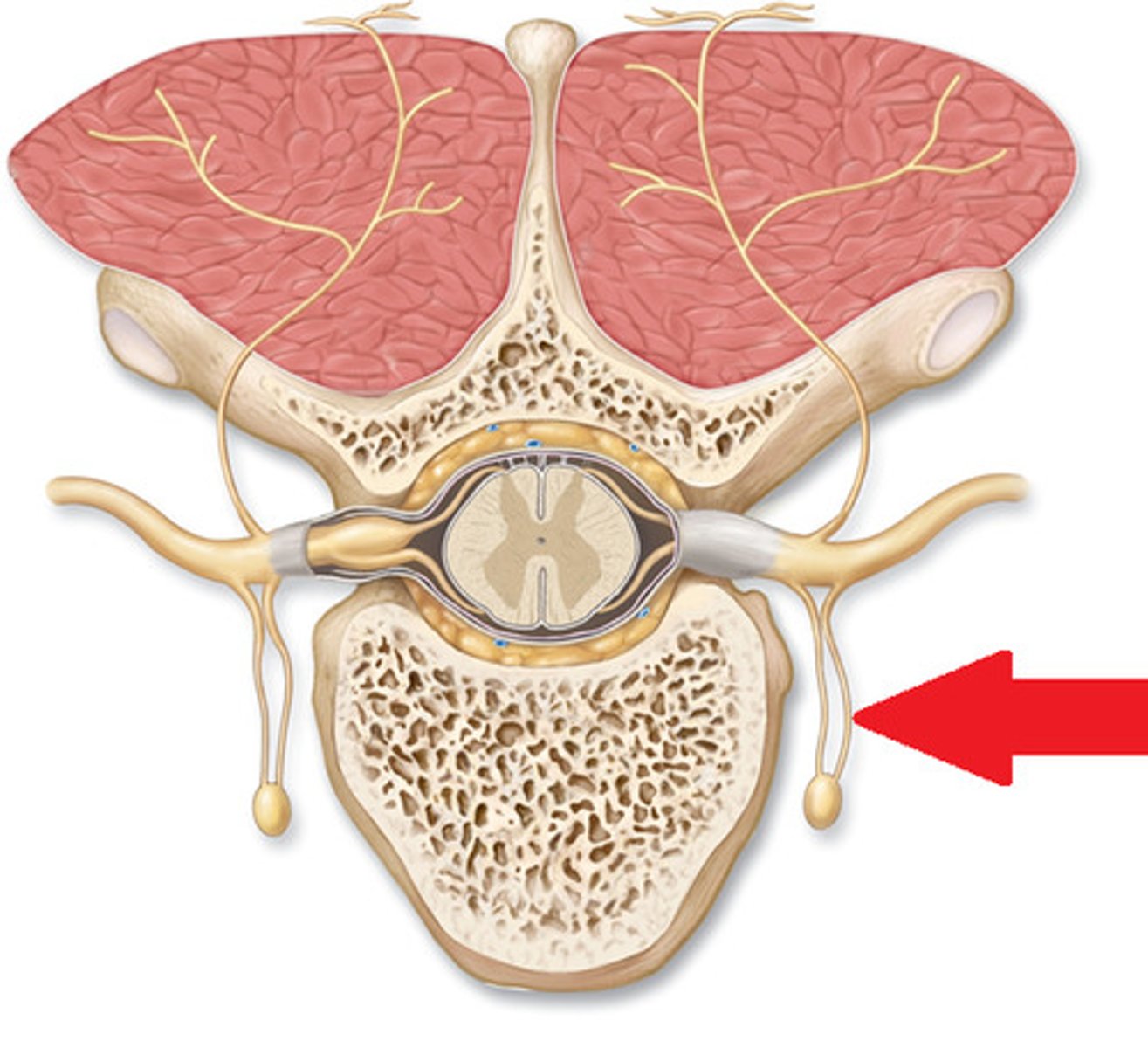
The white ramus connects...
ventral ramus with sympathetic ganglia
SNS: pathways for axons of postganglionic neurons (4)
1. Enter spinal nerve
2. Form cephalic periarterial nerves
3. Form sympathetic nerves
4. Form splanchnic nerves
SNS (spinal nerve pathway): postganglionic axons exit ganglia via...
gray rami
gray rami connects...
ganglia with spinal nerves
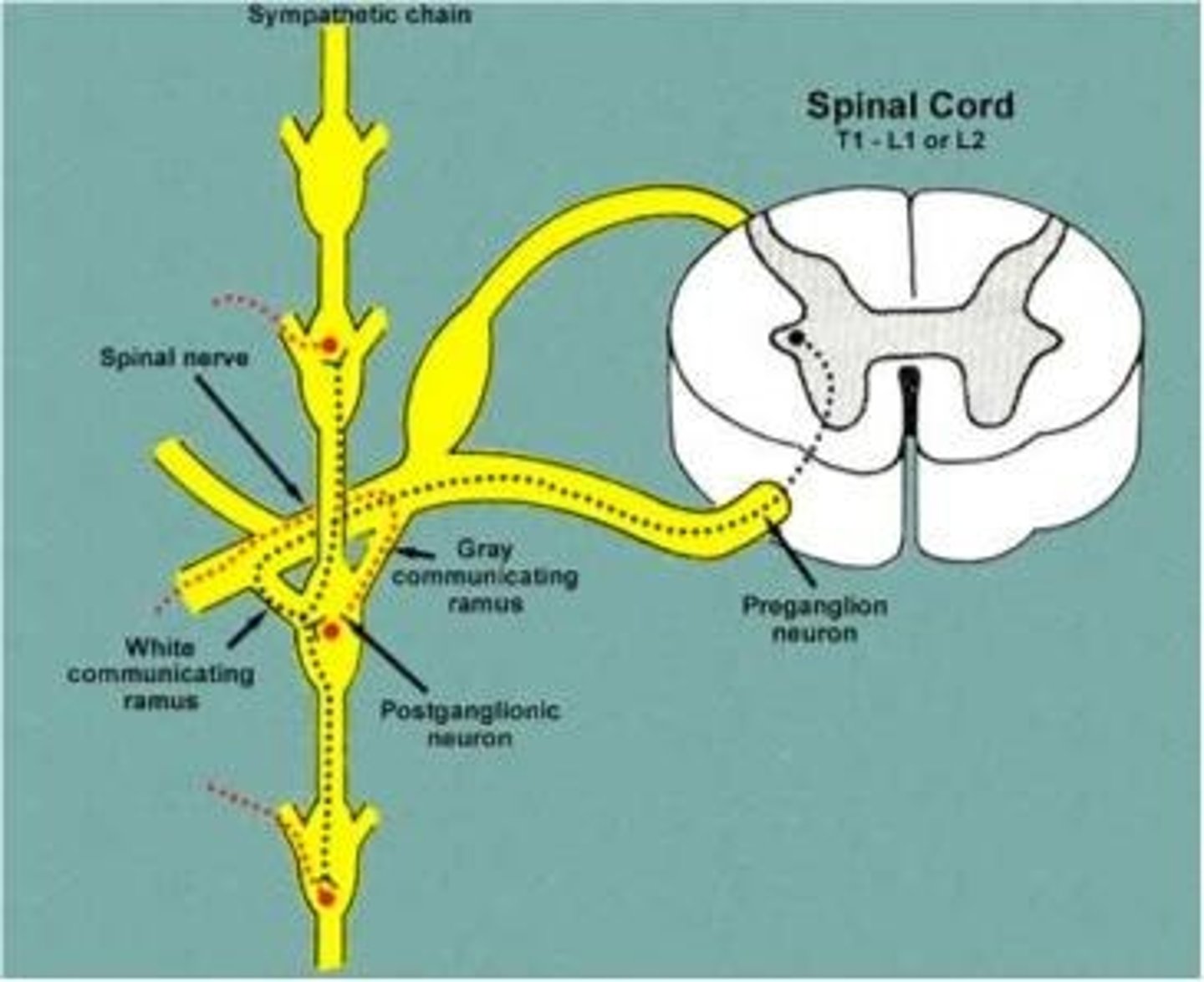
SNS (spinal nerve pathway): innervation
visceral effectors in skin of neck, trunk, limbs
SNS (periarterial nerve pathway): preganglionic axons ascend to...
superior cervical ganglion
SNS (periarterial nerve pathway): postganglionic axons form...
cephalic periarterial nerves
Cephalic periarterial nerve function
wraps around carotid artery and travels to the head
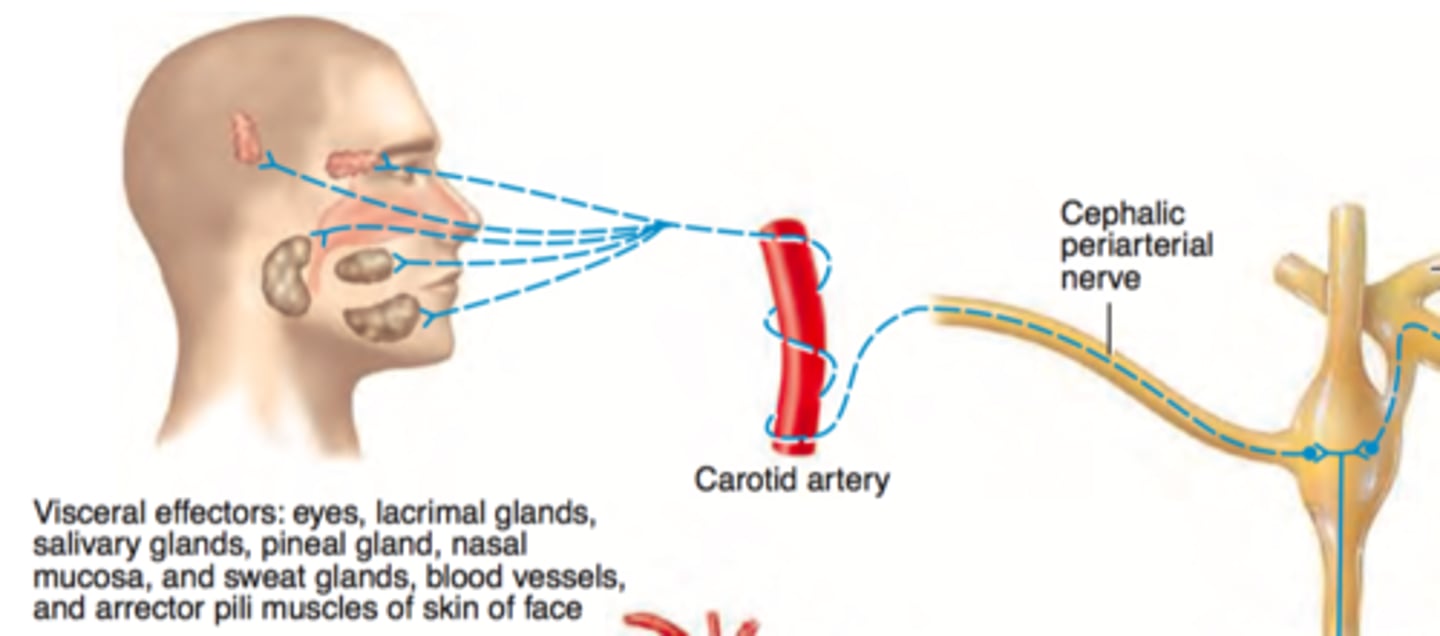
Cephalic periarterial nerves innervate...
skin of face, smooth muscle of eye, lacrimal gland, pineal gland, salivary gland
SNS (sympathetic nerve pathway): preganglionic axons synapse in...
superior, middle, inferior cervical ganglia
SNS (sympathetic nerve pathway): postganglionic axons form...
sympathetic nerves to heart and smooth muscles of bronchi and bronchioles
SNS (sympathetic nerve pathway): preganglionic axons synapse in ganglia from levels...
T2-T4
SNS (Splanchnic nerve pathway): preganglionic axons synapse on...
prevertebral ganglia
Greater splanchnic nerve: preganglionic axons from what levels
T5-T10
Greater splanchnic nerves leads to the...
Celiac ganglion
Greater splanchnic nerve forms the...
celiac plexus
greater splanchnic nerve innervates...
blood vessels to stomach, spleen, lever, kidneys, and small intestine
lesser splanchnic nerve: preganglionic axons from what levels
T10-T11
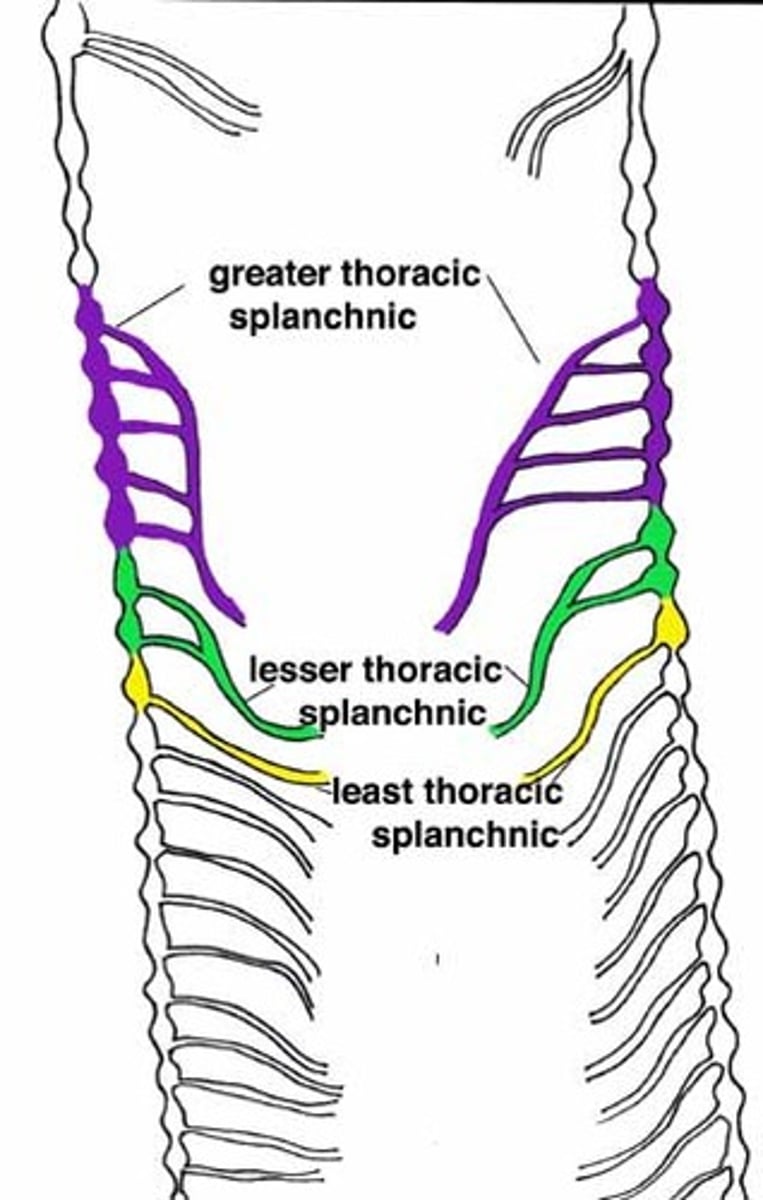
The lesser splanchnic nerve enters the...
aorticorenal and superior mesenteric ganglion
Lesser splanchnic nerve innervates...
blood vessels of small intestine and proximal colon
Least splanchnic nerve: preganglionic axons from what level
T12
What does the least splanchnic nerve enter
renal plexus
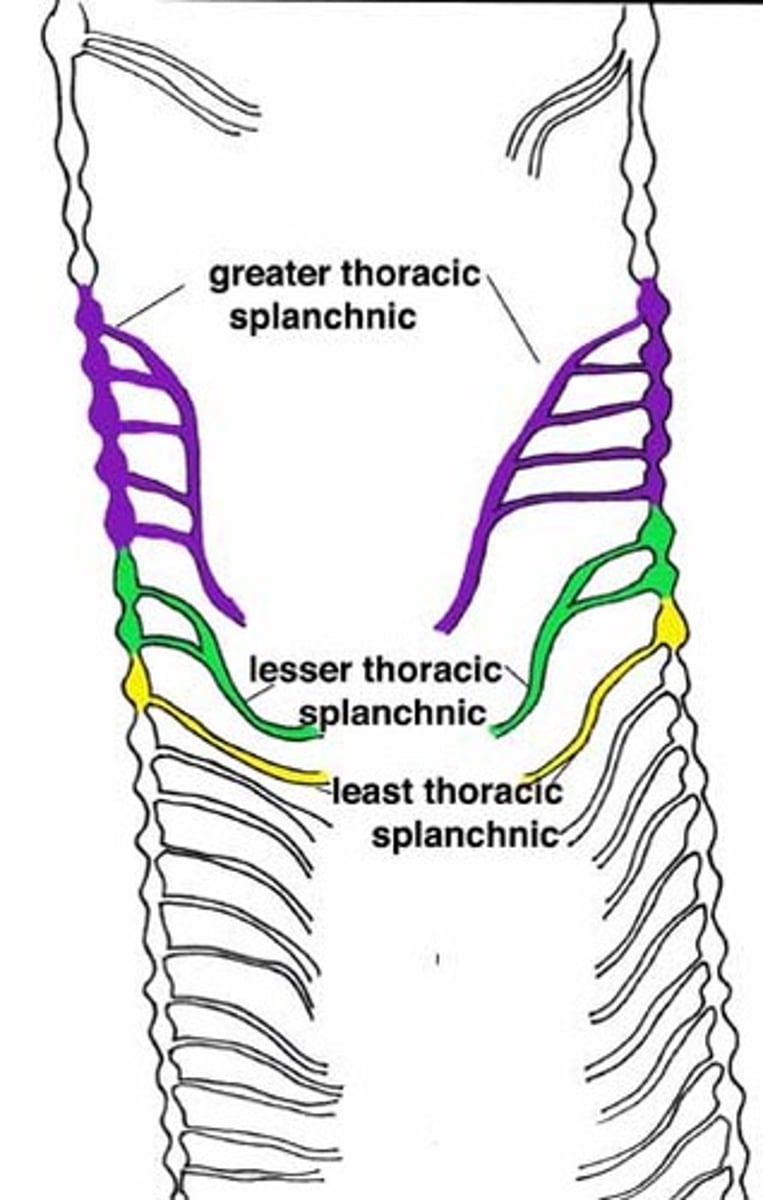
Lumbar splanchnic nerve: preganglionic axons from what level
L1-L4
The lumbar splanchnic nerve enters the...
Inferior mesenteric ganglion
Lumbar splanchnic nerve innervates...
distal colon and rectum
Splanchnic nerves to the adrenal medulla reach what cells?
chromaffin cells
The adrenal medulla acts as...
A sympathetic postganglionic nerve fiber
SNS: A single sympathetic preganglionic axon can synapse with how many postganglionic neurons
20 or even more
SNS: how many visceral effectors can a postganglionic axon terminate in?
several
E activities of SNS
Exercise
Excitement
Emergency
Embarrassment
Ejaculation
Sympathetic response (heart)
increases rate and force of contraction
Sympathetic response: Where do blood vessels constrict?
Kidneys and GI tract
Sympathetic response: Where do blood vessels dilate?
Skeletal and cardiac muscle, liver, adipose tissue
Sympathetic response favors the rapid production of...
ATP
Sympathetic response: Why are the effects more widespread than parasympathetic?
Divergence of postganglionic axons
norepinephrine remains in the synaptic cleft
Epi and NE are released into the blood
PNS: preganglionic cell body location
Nuclei of CN III, VII, IX, X
lateral gray matter of S2-S4
Another name for parasympathetic division
Craniosacral division
PNS: postganglionic cell body location
Terminal (intramural) ganglia
Where are terminal ganglia located?
Close to or within the wall of a visceral organ
Head region ganglia
Ciliary
Pterygopalatine
Submandibular
Otic
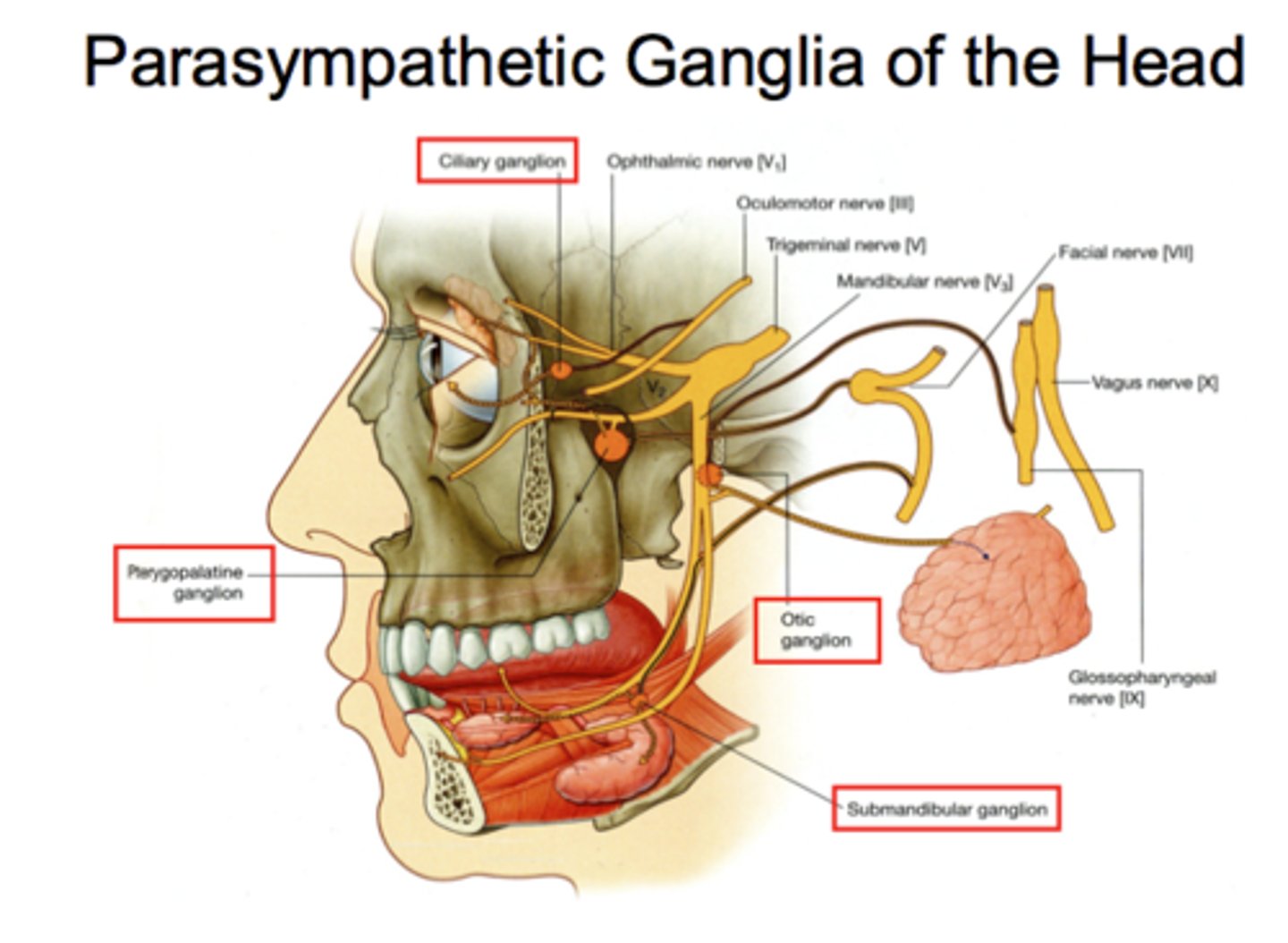
PNS (ciliary ganglia): preganglionic neuron cell bodies
oculomotor nucleus of midbrain
Where are the ciliary ganglion located?
Posterior aspect of orbit
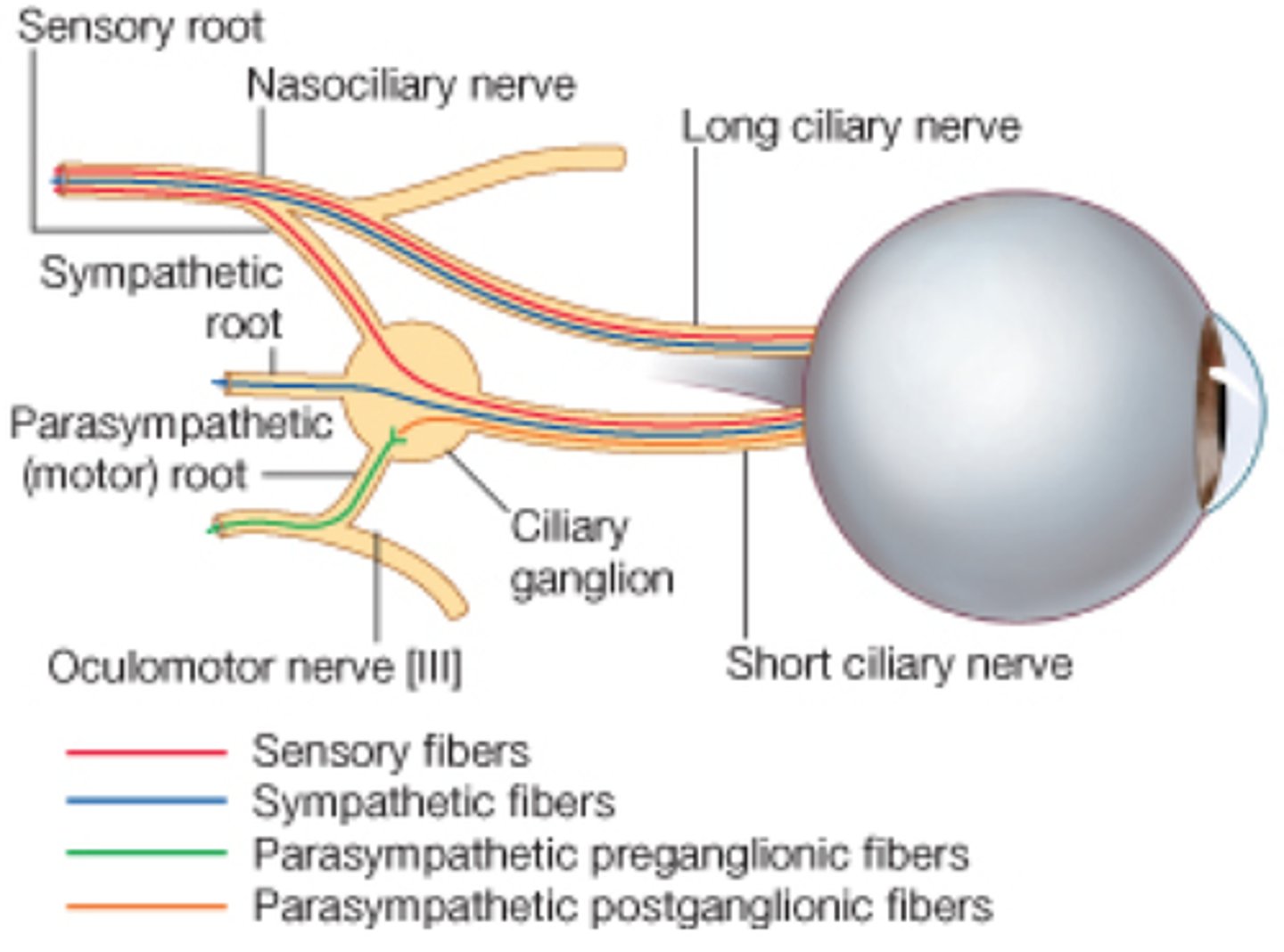
PNS (ciliary ganglia): innervation
smooth muscles of eye (adjusting lens, constricting pupil)
PNS (pterygopalatine ganglia): preganglionic axons from...
nuclei of CN VII
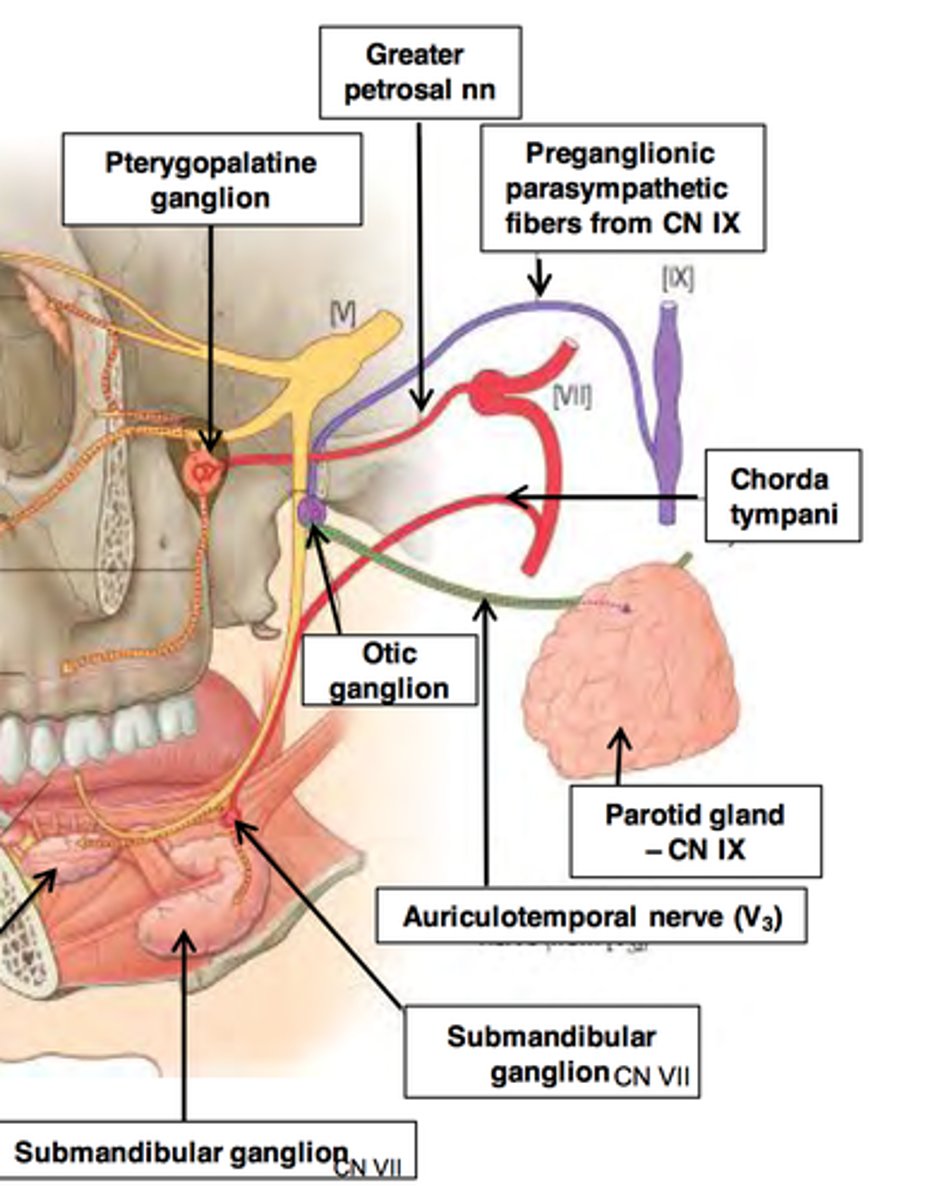
PNS (pterygopalatine ganglia): innervation
nasal mucosa, palate, pharynx, lacrimal glands
PNS (submandibular ganglia): preganglionic neuron cell bodies in...
nuclei of CN VII
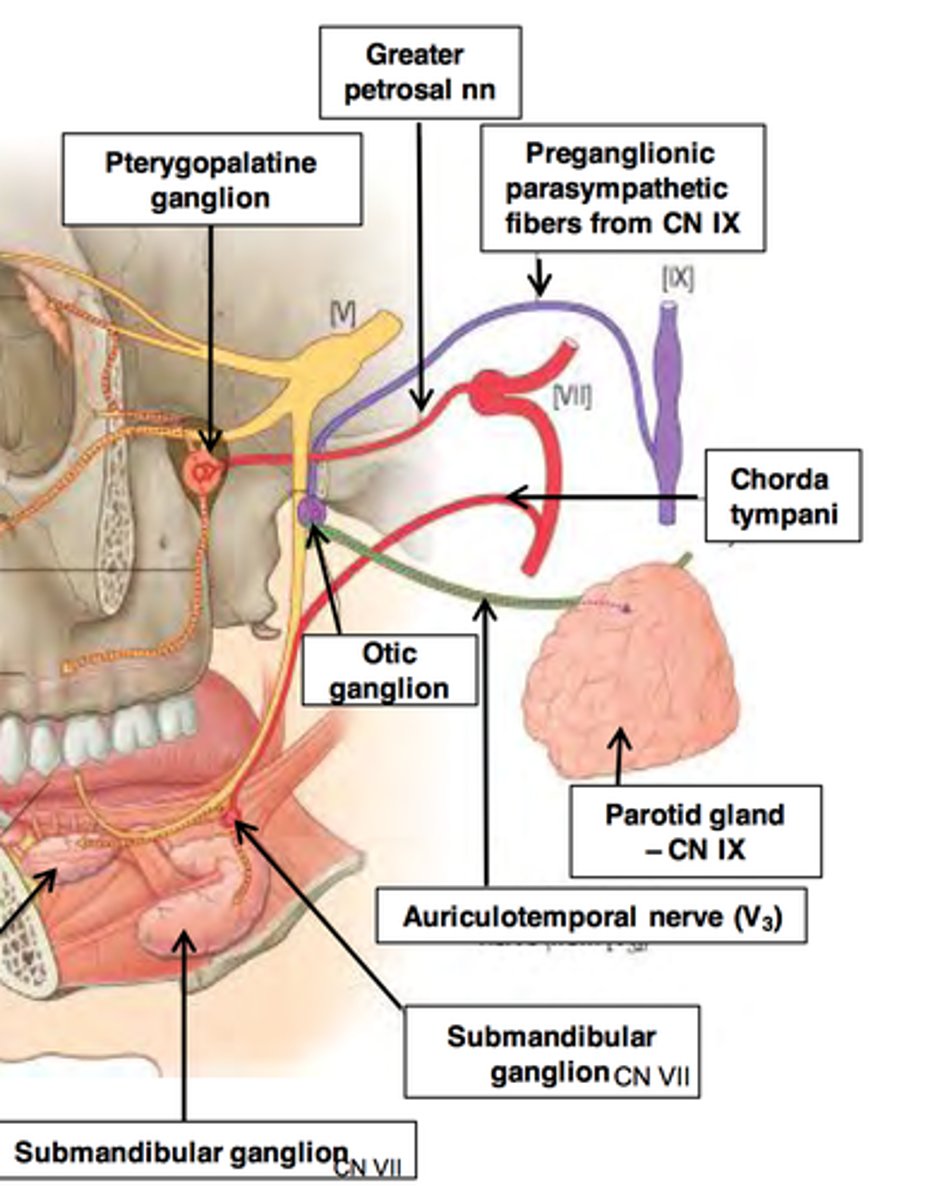
PNS (submandibular ganglia): innervation
submandibular and sublingual glands