KIN 313 Lecture 4 - Motor Units: Concepts & Research
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
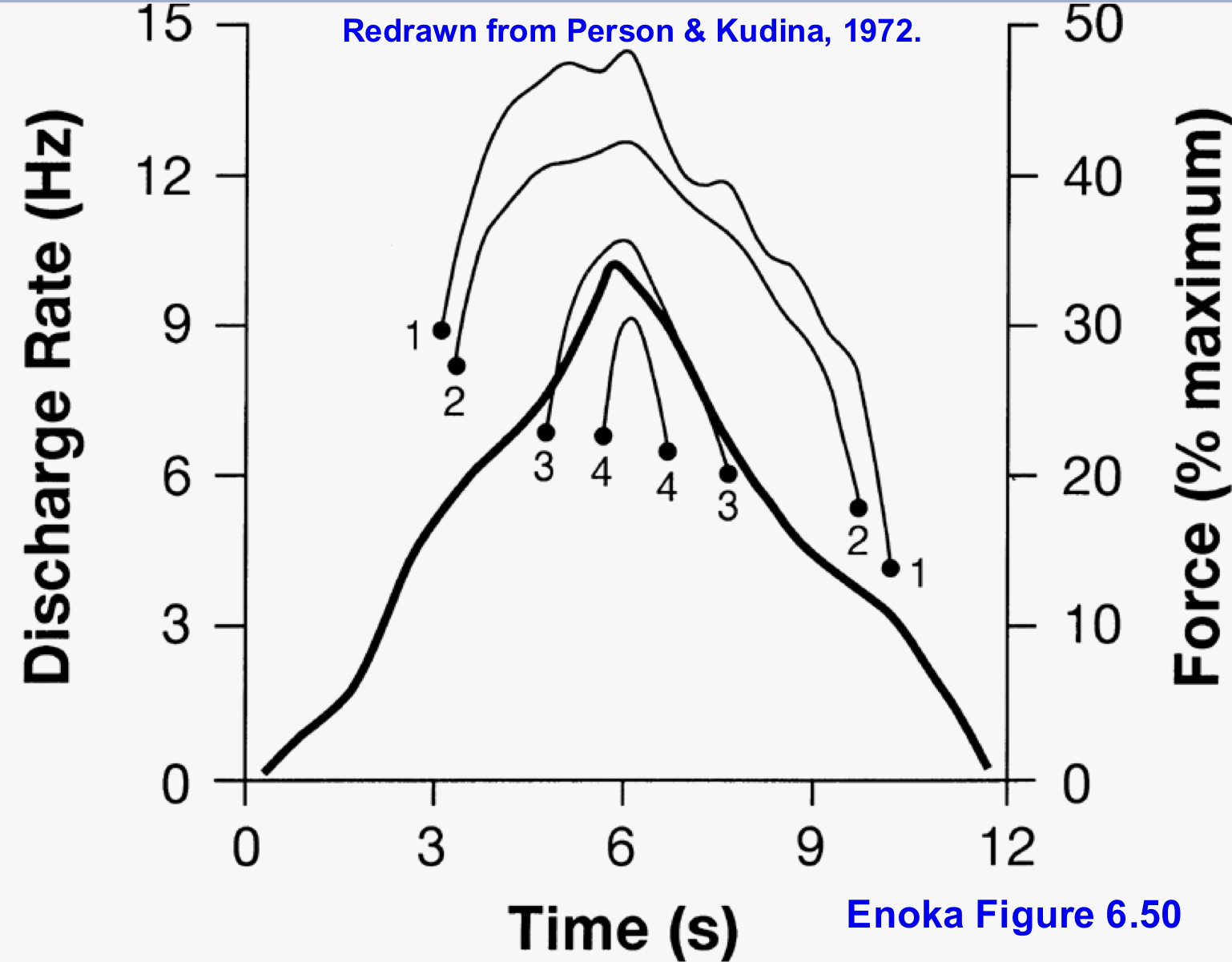
Explain why there are no motor units shown in the first 3 seconds despite there being force produced
that force production is coming from motor units that we are not recording → they are too far away from the electrode to be picked up
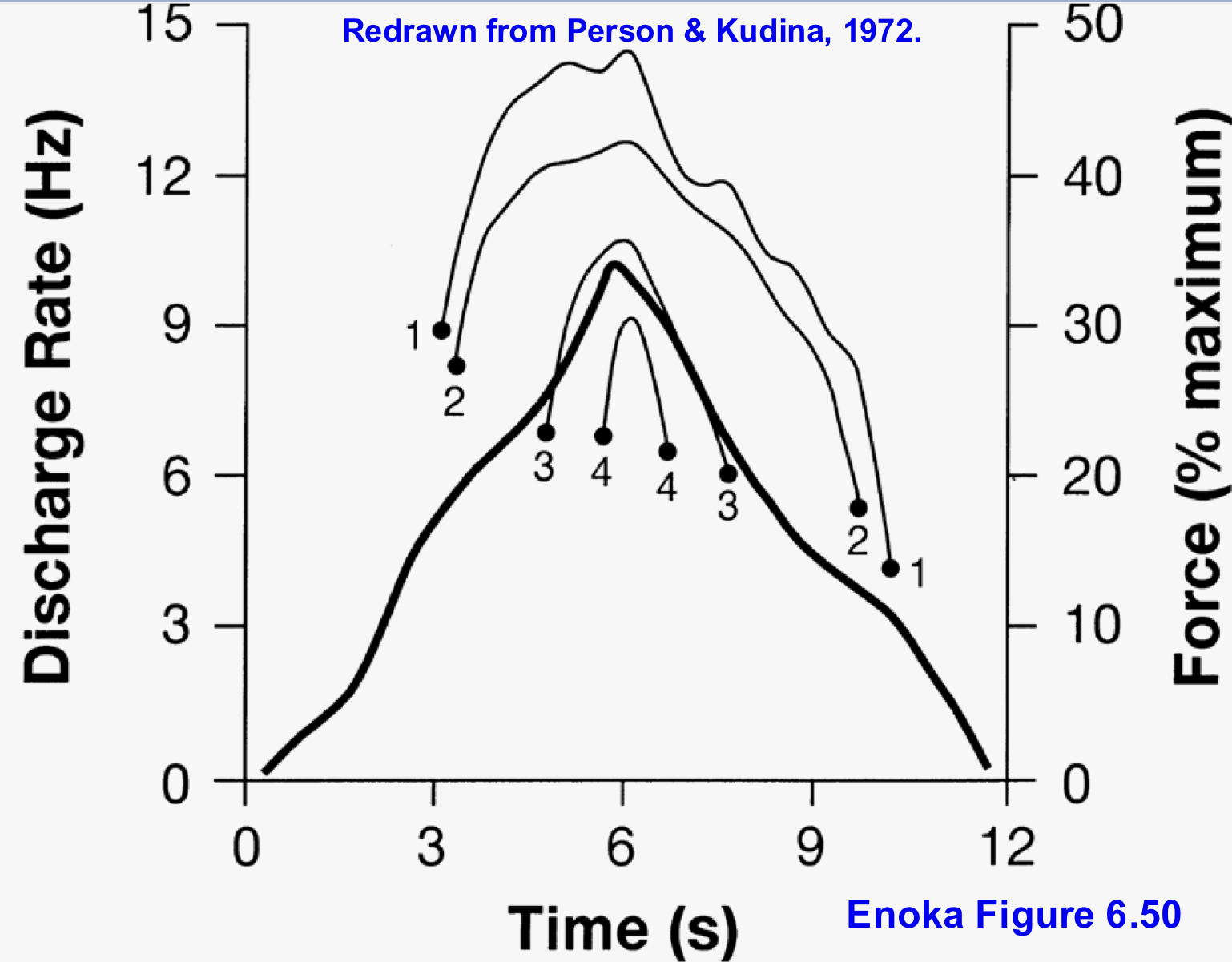
explain what motor units do before the next one is recruited
all start rate modulating before the next (bigger)motor unit is recruited, and continue doing so until peak force production is reached
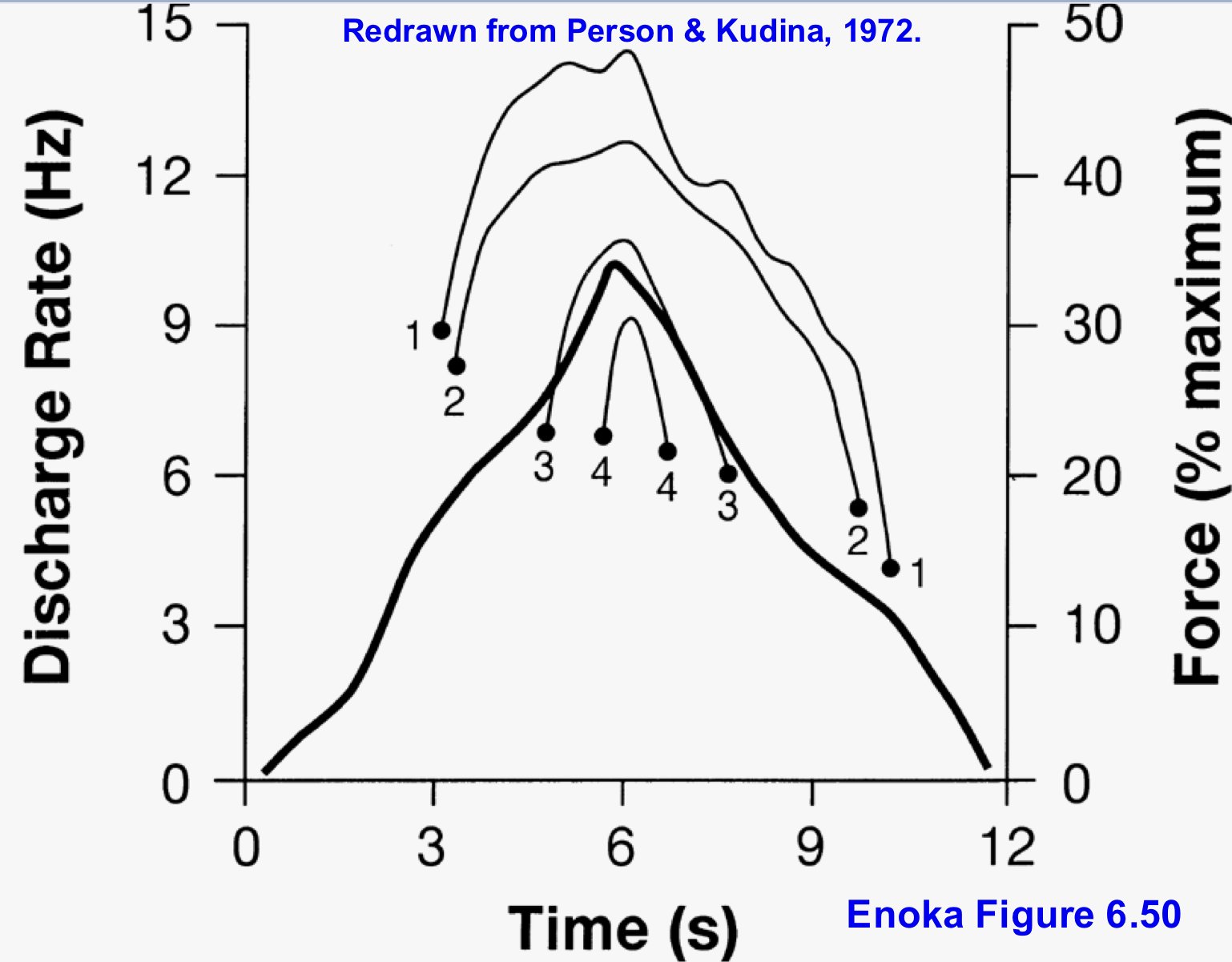
what happens once the muscle hits peak force and starts to go down to resting
motor units rate modulate down and derecruit in the opposite order they were recruited… 4 then 3 then 2 then 1

why do motor units rate modulate down to a discharge rate lower (slower) than the discharge rate they came on at?
when they first came on, they had to fire at a rate high enough to summate. now they want the opposite so they fire at a slower rate than before (APs sent after HRT)
this way we get a controlled decrease in force rather than sudden drops as the motor units derecruit
true or false. force-frequency relationship is linear
false. force frequency is curvilinear
there is a point where increases in frequency eefficiently increases force, and a point where increases in frequency do not produce substantial increases in force
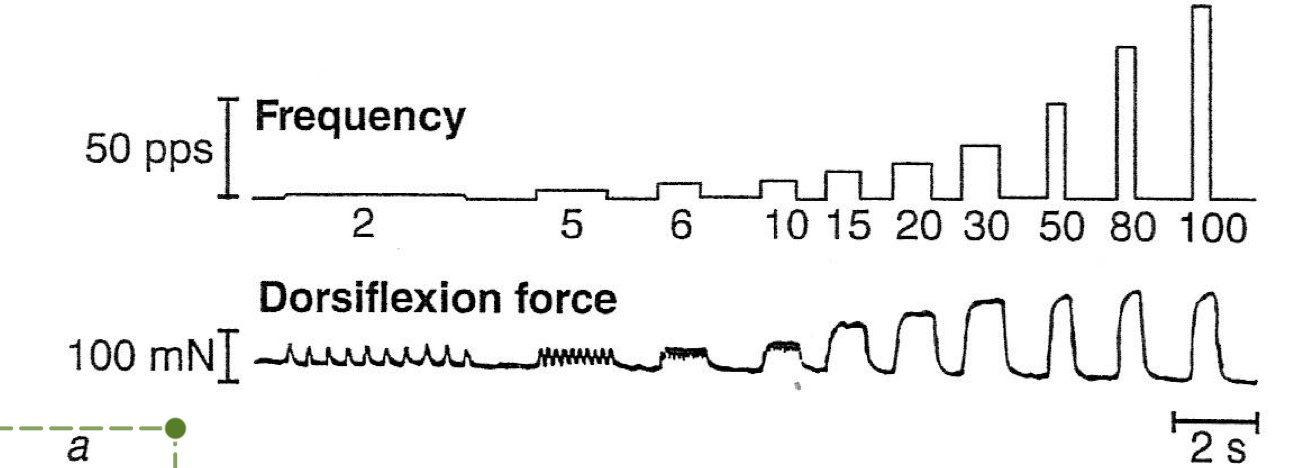
compare 30pps (impulses per second) to 100pps
why does this happen?
approximately the same amount of force production, but 30pps is much more efficient. increases in pps after 30 doent seem to have a substantial benefit in force production (in this muscle). going higher than this would just burn out the muscle for no reason
this is due to curvilinear relationship between force production and frequency → the curve plateaus at higher frequencies, but there is a steep incline in low-middle frequencies → these are efficient/optimal frequencies
how does muscle length affect the force-frequency relationship? GET HELP ON THIS ONE
different length = different amount of actin and myosin overlap → when stimulated, you get a certain amount of actin and myosin interaction → causes contraction
lengthening muscles causes them saturate at a lower firing rate (hit the plateau at a lower rate)
force production changes even tho the firing rate stays the same??????
long muscles shift the curve left (lower frequency is efficient)
short muscles shift the curve right (can be efficient at slightly higher frequencies)
frequency vs force for fast vs slow motor units
fast twitch motor units have a slightly higher ideal firing rate/operating range than slow twitch motor units
therefore, slow twitch motor neurons get close to their peak force at a lower frequency than fast twitch motor neurons
slow ones have a steeper curve than fast ones when looking at frequency vs % of max force
timing of AP fired on different motor units
they all fire at different rates/times → this chaos between the motor units results in a smooth total/net force production → until maximum contraction when everyone goes all out and you end up getting shaky due to increased synchronization of motor units
all the motor units summate but out of sync with each other
what is a double discharge
when a second AP is fired only 10ms after the last one, → causes a big jummp in force production → then this new higher force can be maintained by firing at the same rate as before
helps you increase force production without burning out from firing really fast
purpose of double discharge / doublet
maintain a higher force production at a lower firing rate
more frequent with fatigue → saves energy → can hold a given force at a lower frequency → tries to get you the best force you can get out of a frequency → bump force production back up when muscle is lagging
after using a doublet, can reset the force production back to normal by…
skipping an impulse/interrupting the stimulus → rapid drop in force production down to what you would normally get out of a given frequency
rate modulation is not just increasing or decreasing frequency while contracting, but also…
temporarily increasing or decreasing in order to change force production while maintaining the same frequency → doublets/skipping an impulse
synchrony
how much two motor units fire at the same time
looking at their firing rates, even tho they are different, there will be times where they fire one AP together → called short term synchronization
what is a possible reason for short term synchronization
a common presynaptic input, every time that one that they have in common fires, they both fire at the same time
note that these two Mot Us may be the same kind of motor unit with similar thresholds for this to work
why are our contractions smooth instead of twitchy/spazzy?
because synchrony doesnt usually happen and when it does its infrequent
in a typical person, when does synchrony become more frequent and why
states of fatigue → the nervous system is tired so it starts desperately firing motor neurons, and you end up with messy contractions due to increased synchrony → shaking muscles like at the end of a hard workout
what is ALS
Amyotropic Lateral Sclerosis
death of motor neurons
healthy neurons send out collaterals to try to pick up slack
death outpaces help until there are no MotUs left in that muscle
Signs and Symptoms: muscle fibres that are abandoned contract out of sync = squirming sensation
Progression: 2-5 years
REALLY high innervation ratios
what is Klippel-Feil Syndrome?
genetic syndrome where, as a fetus, the innervation to the sides of your body doesnt split, so you cant control each side independently → when you do something with your right hand, your left hand tries to mirror it
clinical issues assosciated with synchronization
ALS and Klippel-Feil Syndrome
synchrony in musicians vs weight trainers
less synchrony in musicians and more in weight lifters → does body want high force production with less smooth contractions or super smooth precise contractions but less force production?
when is synchronization beneficial?
heavy ballistic tasks like jumping off the blocks → cool to get them to fire together for a bit
size principle and eccentric contractions
doesnt quite apply, there is something (muscle spindle) that selectively turns on larger motor neurons during the eccentric portion of the contraction despite baseline threshold of the motor neuron
motor neurons going to a muscle with different compartments
specific motor neurons are destined to go to one of the specific compartments and ONLY that one, they wont drift into any of the others at all → brain thinks of the compartments as their own muscles
muscle compartments
one anatomical muscle may have several functional muscles within it
each of these compartments receives its own set of motor neurons which do not innervate any fibers in the other compartments
the brain treats compartments as seperate muscles and can opperate them independently → activate the compartments based on the movement → task groups
more morphological muscles or more physiological muscles?
more morphological (functional) than physiological (anatomical) muscles