BL2001 - PCR (for practical exam)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Who invented PCR?
Kary Mullis
What does PCR stand for?
Polymerase Chain Reaction
What enzyme is used to amplify the template in PCR?
Taq DNA polymerase
What are the sources of Taq and Pfu polymerase respectively?
Thermus aquaticus bacteria and Pyrococcus furious bacteria
How are DNA strand denatured in PCR?
At 91°C for 1 minute
What are the four nucleotides involved in PCR?
dATP, dTTP, dCTP, and dGTP
At what temperature do primers base pair complementary sequences?
50-60°C for 1 minute
Why is PCR a chain reaction?
Because the reaction is continuously repeated until the primers are used up
What are the components of PCR?
- PCR mastermix (contains Taq pol., dNTPs, and reaction buffer)
- Primers (sequence specific to your target
- ddH2O (molecular grade water)
- DNA template (for four individual plants)
What is the final desired concentration of...:
- ZTL-1 (forward)
- ZTL-2 (reverse)
- ddH2O
- DNA
(stock concentration in brackets)
- 0.5µM (10µM)
- 0.5µM (10µM)
- up to 10µl
- 50 ng/reaction (50ng/µl)
What formula is used to calculate the final concentration?
final volume / (stock concentration/desired concentration)
What is the control in the PCR practical?
Negative control - mix with no DNA added
What is the final recipe (for 6 reaction - 4 plants, 1 control, 1 to ensure there'e enough mix)?
- Mastermix = 30µl
- Primer 1 (forward) = 3µl
- Primer 2 (reverse) = 3µl
- ddH2O = 18µl
Describe what pipettes we will use during the practical
- For the 30µl volume, use p200 pipette (blue)
- For the 3µl volume (primers) and 1µl volume (DNA), use p10 pipettes (yellow)
- For the 18µl volume (H2O), use p20 pipette (green)
Describe the PCR procedure
- Slowly pipette the components (except DNA0 into a single 1.5ml eppendorf tube and mix well at the end (by pipetting up and down 20-30 times)
- Place the mix on ice
- Pipette 1µl DNA from each sample into the bottom of a tube on the 8 strip
- Add 9µl of your mix to each tube
- Apply strip cap tightly to the tubes
- Spin briefly
- Place on the thermocycler
PCR cycling conditions are pre-programmed onto the thermocycler. What cycles are used?
- 4 minutes @ 95°C (X1 - initial denaturation)
- 30 seconds @ 95°C
- 1 minute @ 55°C
- 1 minute @ 72°C (X35 - thermal cycling)
- 10 minutes @ 72°C (X1 - final extension)
FOR out practical, which plant was the DNA extracted from?
Arabidopsis plant
What do we call the plant wake/sleep cycle?
Circadian clock
What is different about our mutant compared to our non-mutants?
The mutant cannot perceive the circadian clock - affecting growth
Are phosphate positively or negatively charged?
The phosphate backbone of DNA is negatively charged
What factors of a DNA molecules are dependent on base pairs?
Weight, length, size
What does the circadian clock affect?
- Gene expression
- Cytosolic calcium levels
- Protein phosphorylation
- Chloroplast movement
- Stomatal opening
- Hypocotyl length
- Cotyledon and leaf movement
- Petal opening
- Flowering
List the steps of T-DNA insertional mutagenesis
- Insertion of gene into plasmid using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase
- Introduction into plant cells in culture
- Regeneration of plant with new trait
What has T-DNA been used for in plants?
- Generate transgenic lines
- Generate mutant collections
Who hosts one of the major mutant collections?
Salk Institute Genomic Analysis Laboratory (SIGnAL)
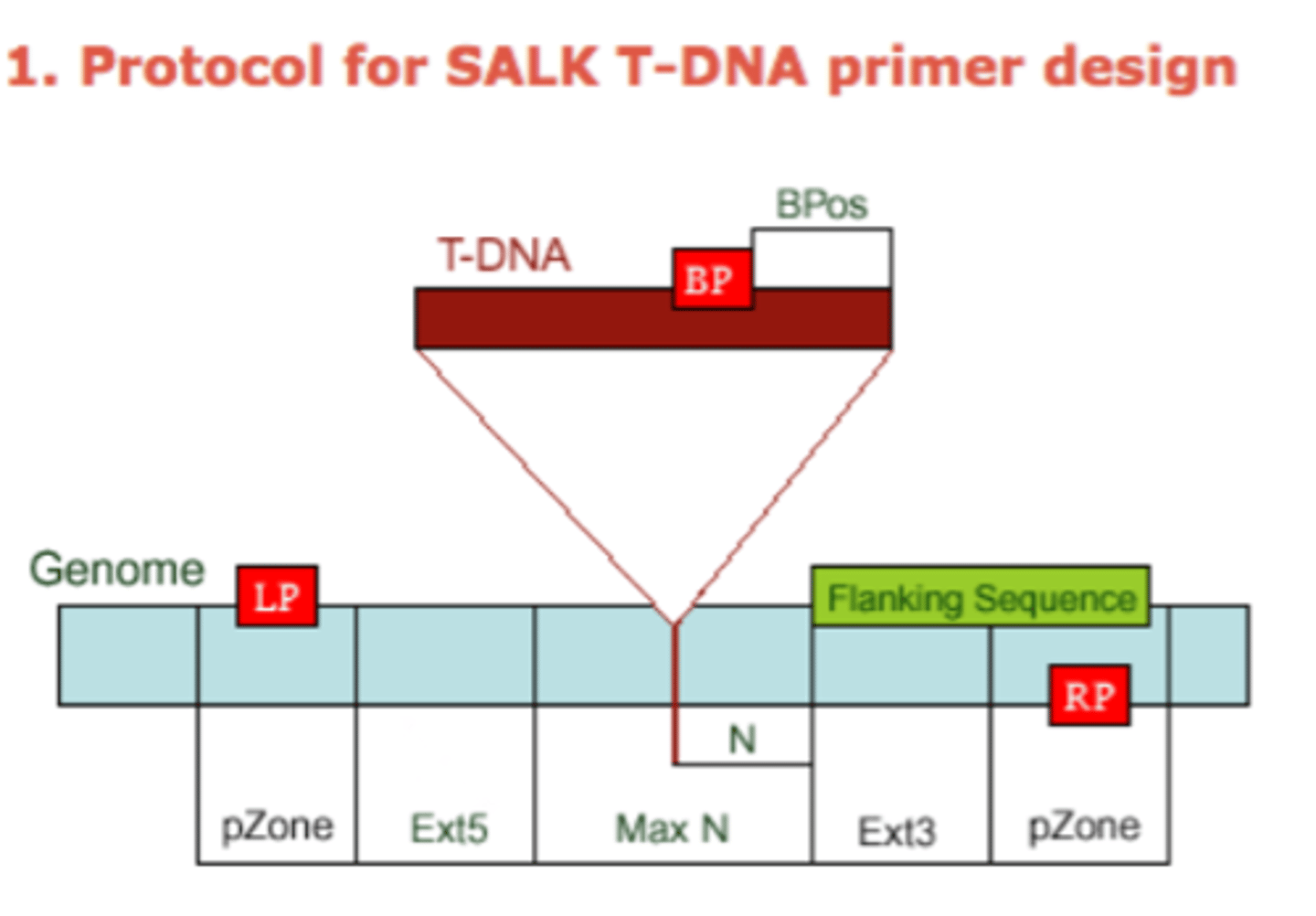
Label the SALK T-DNA primer design diagram
- N = difference of the actual insertion site and the flanking sequences position, usually 0-300 bases
- MaxN = maximum difference of the actual insertion site and the sequences, default 300 bp's
- pZone = regions used to pick up primers, default 100 bp's
- Ext5, Ext3 = regions between the MaxN to pZone, reserve for not picking up primers
- LP, RP = left, right genomic primer
- BP = T-DNA border primer
- LB = left T-DNA border primer
- BPos = the distance from BP to the insertion site
What is the temperature (in °C) for denaturing, annealing, extension, and final extension?
- 95
- 55
- 72
- 72
How many cycles of PCR were carried out?
Depending on the quality of DNA, 30-35 cycles
What are the 2 main processes involved in gel electrophoresis?
- DNA samples containing fragments of different sizes are placed in an agarose gel
- An electrical current is passed through the gel
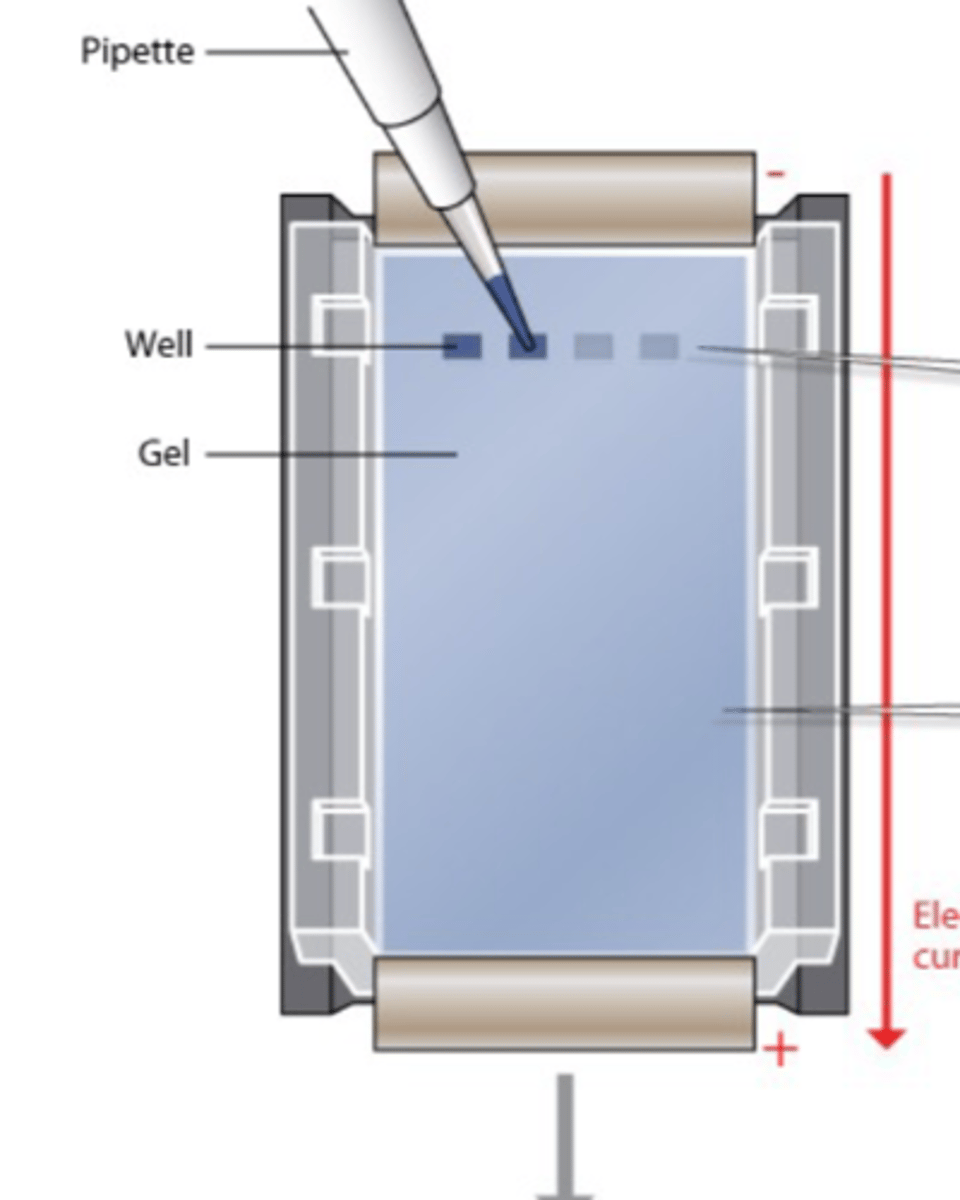
Describe the gel electrophoresis process
- Add loading dye to each PCR reaction
- Load onto agarose gel - carefully not to puncture the wells
- Connect the power supply at the required voltage - 100V for electrophoresis
- For this application, products need to run for 30 mins
- Visualise the gel on UV light (gel is stained with SYBR safe which binds to the PCR product and illuminates under UV light)
In electrophoresis, the bigger fragment...
will be closer Ito where we started electrophoresis
Does the longer fragment go faster or slower?
Slower
Where does electrophoresis gel move to in terms of charged ions?
"In a solution, if a solute has a positive charge (cation), it will migrate toward the negative electrode (cathode), and a negatively charged ion (anion) will migrate toward the positive electrode (anode)"
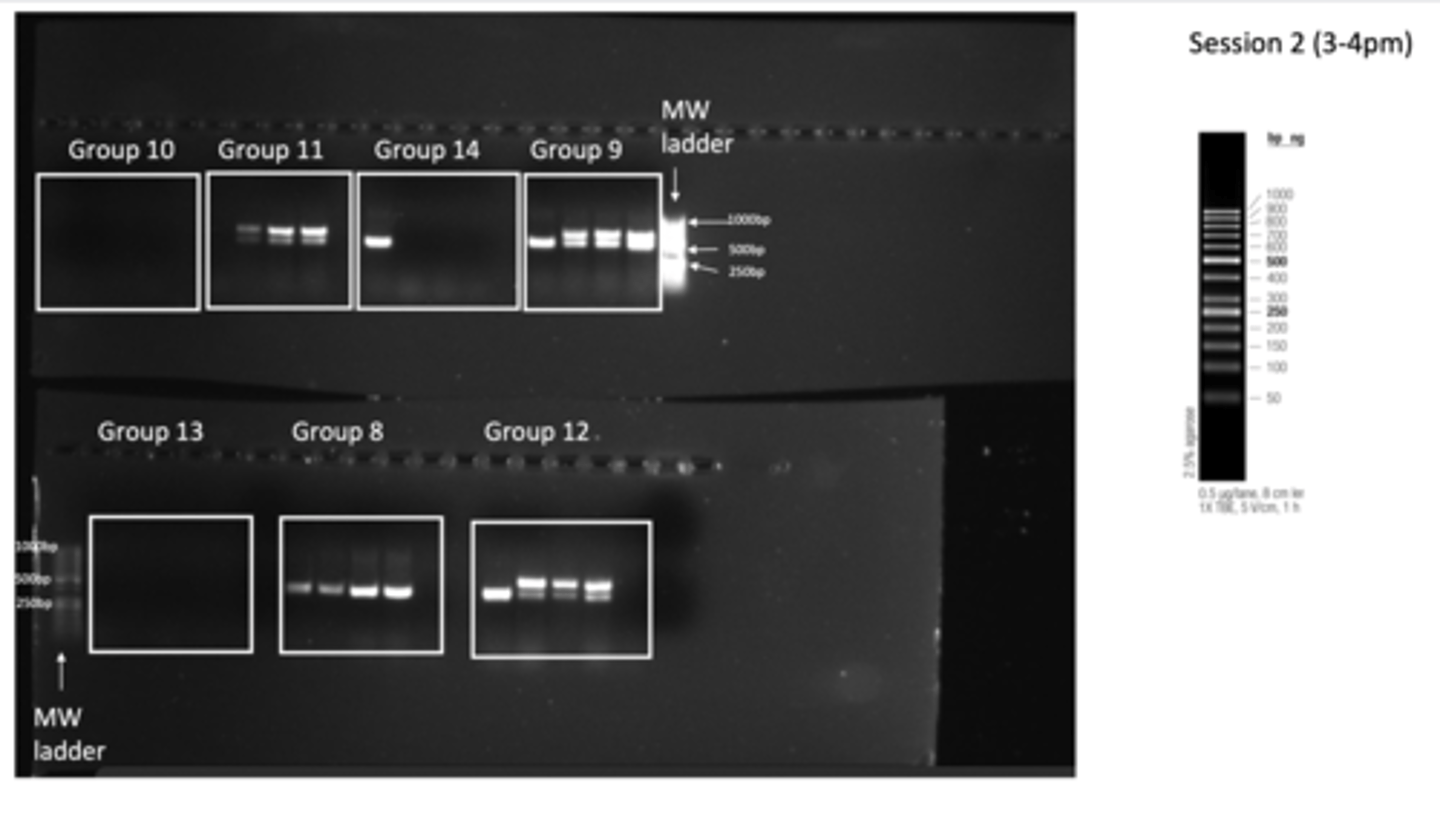
Results of PCR practical - session 2 (3-4pm)
.