Assistive Technology Final Exam
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
SETT Framework
What it does: Helps teams decide on the right assistive tech by looking at the Student, Environment, Tasks, and Tools
Used for: Mainly students with disabilities in schools.
CMOP-E
Canadian Model of Occupational Performance and Engagement
What it does: Focuses on the interaction between Person, Occupation, and Environment
Used for: All ages, to guide OT interventions and understand barriers to engagement.
MPT
Matching Person and Technology
What it does: Matches tech to the person's needs, preferences, and environment to improve success
Used for: Anyone using assistive tech, especially adults.
HAAT
Human Activity Assistive Technology
What it does: Looks at how a person (human) uses assistive tech to do an activity in a specific context
Used for: All ages and settings to select or evaluate assistive devices.
ICF
International Classification of Functioning
What it does: Provides a universal language for health and disability—focuses on body functions, activities, participation, and environment
Used for: Everyone
AT Process
-Identify patient goals through occupational profile exploration, assess skills, functional abilities, past experiences with AT, and context
-A patient's goal is not always independence; allow more for choice and control
Elements of context
-physical (setting, access, light, noise, temperature, transportation)
-social (attitudes and caregivers)
-institutional (policy and legislation)
-cultural (stigma, perspective, barriers)
Eval Assessments
-Matching Person and Technology (MPT)
-Assistive Technology Device Predisposition Assessment (ATD-PA)
-Matching Assistive Technology and Child (MATCH)
-Individually Prioritized Problem Assessment (IPPA)
-School Function Assessment Assistive Technology Supplement (SFA-AT)
-COPM
-Goal Attainment Scale (GAS)
Rehab Act
Requires equal access to tech and programs in schools, jobs, and government.
ADA
Makes sure public places, jobs, and communication are accessible—including with AT.
Assistive Tech Act
Gives states money to offer AT services, device loans, and training.
IDEA
Says schools must consider AT in IEPs to help students learn.
Missouri AT (MoAT)
Missouri's program that lets people try, borrow, or get help with AT.
AT3Center
Helps state AT programs (like MoAT) with training and resources.
Primary goal of AT for hearing loss
access to clear communication and equal participation in daily activities
AT examples for hearing loss
-hearing aids
-remote microphones
-interpreters
-note takers
-recorded lectures
-flashing lights
-vibrations
-preferential seating
Contextual supports for hearing loss
-504/IEP plans
-teacher training
-access to captions or transcriptions
Primary goal of AT for vision loss
improve visual access or provide non visual ways to get information
AT examples for vision loss
-high contrast materials
-screen readers
-textured materials
-use spotlight
-auditory compensation
Contextual supports for vision loss
-lighting control
-seating placement
-accesible materials
Primary goal of AT for cognitive challenges
support memory, attention, and organization for daily tasks and learning
AT examples of cognition
-timers
-reminders
-visual schedules
-step by step apps
Contextual supports for cognition
-routines
-caregiver training
-task simplification
-quiet environments
Seat width
-measured from the widest aspect of the user's buttocks, hips or thigh
-It should be wide enough to avoid pressure on the hips
Seat depth
-measured from the user's posterior buttock, along the lateral thigh to the popliteal fold with your palm horizontal to the seat
-usually, a space of about 2 inches is preserved to avoid pressure from the front edge of the seat against the popliteal space
Seat height
-determined by the height of the individual and if the wheelchair is self-propelled
-when using the feet to propel, the seat height should allow for them to reach the floor with their heel
-those using footrests have higher seat heights. It is measured from the user's heel to the popliteal fold
-the bottom of the footrest is 2 inches from the floor
Armrest height
-should allow user sit erect, with level shoulders when bearing weight on the forearms as they rest on the armrest
-it is determined by measuring the distance between the seat of the chair and olecranon and adding one inch
Backseat height
-the inferior angles of the scapula should be approximately 1 finger-breadth above the back when the user sits with erect posture
-it is determined by measuring the distance between the seat of the chair to the patient's axilla, and subtracting four inches
Footrest length
-affects the support of both the feet and the thighs and the clearance of the footplates and the ground
-the footplate must be about 1 to 2 inches off the ground to permit adequate ground clearance
Purpose of a letter of medical necessity
a written explanation from the medical professional for services, equipment, or supplies to the insurance company to get payment
What goes in a LMN
-Addresses, contact info, credentials
-Client name, diagnosis, ICD code, and dates relative to diagnosis
-Home environment
-What the client can't do and how AT would help
-What the client won't be able to do without the AT
-Specifics of device (measurement, model, numbers, links)
-Reference to back up recommendations
-Role as OT and goals
3D printing design considerations
-Function
-Constraints
-User input
-Safety
-Comfort
-Aesthetics
-Durability
-Existing designs -> modified designs -> original design
3D printing safety
Don't create devices that ...
-go into the body
-touch food
-life saving/sustaining devices, DME
-robotics
-liability concerns
3D printing benefits
customizable and improve occupational performance
3D printing outcomes
-switches
-leisure tasks
-gaming
-home activities/assist daily living
Type of orthotics
-immobilization
-dynamic
-serial static
-static progressive
Immobilization orthotic
used to limit or reduce pain during healing
Dynamic orthotic
one or more components that produce motion to increase passive motion, active assisted motion, or substitute loss motion
Serial static orthotic
achieve slow, progressive increase in ROM by remolding orthosis
Static progressive orthotic
static mechanism that adjusts the amount or angle of traction acting on a part for gradual progression as tolerated
Role in prostetics
-Prevent further injury and stabilize joints
-Facilitate movement
-Fall prevention
-Safe transfer
-Optimal weight bearing
-Consider cost, design, CLOF, motivation, cognition, accessibility, body image, exercise level, safe compensatory technology, anatomy, material/skin integrity, etc
Purpose of AAC and switch access
help people engage in communication occupations through motor, cognitive, and visual adjustments; self-advocacy during ADLs
Keyguard
plastic frame to isolate keys into seconds to prevent swiping

Touchguide
small circular opening for accuracy to prevent swiping

NovaChat, Proslate AAC devices
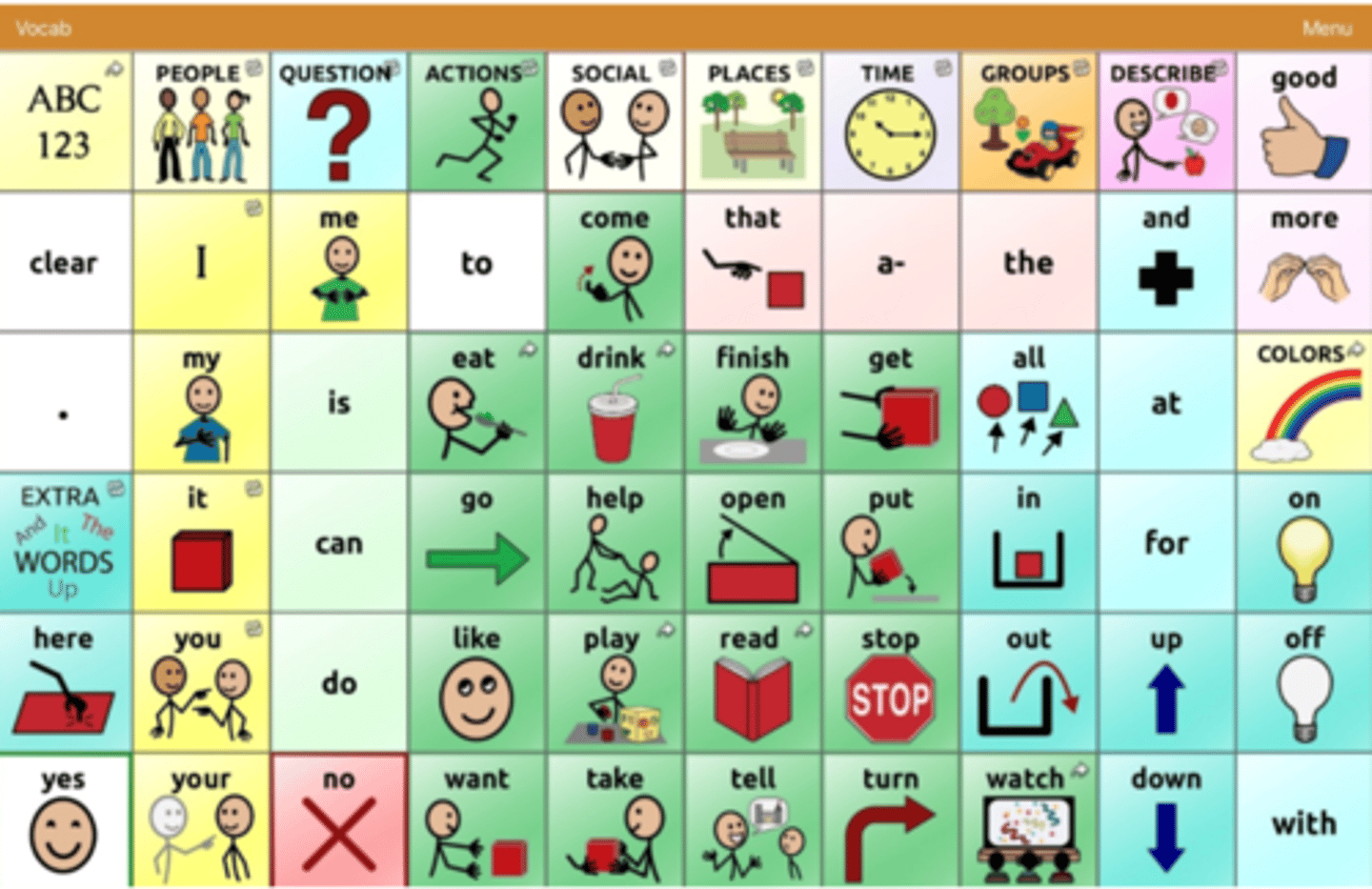
Accent 1400 device
one switch automatic linear scanning
Tobii I12
two switch step scanning (columns and rows)
Jellybean switch
accessible to get vs others

Pillow switch
limited dexterity needed

Microlight switch
limited pressure needed and handheld

AAC and switch access evaluation considerations
-cognition
-vision (tracking, scanning, acuity)
-motor (dexterity, strength, ROM)
Parenting with a disability: general types of devices
-boppies
-high chairs
-front facing carriers
-bath seats
-zip/magnet clothing
-bottle maker
-chair seats
-bassinets
-crib adjustments
-car seats
-containers to limit exploration
Purpose of adaptive sports and leisure
promote fun, inclusion, health, fitness, and social participation
Types of adaptive sports devices
-sports wheelchairs
-handcycles
-adapted skis
-grip aids
-prosthetics
-adaptive gaming equipment
Types of adaptive leisure devices
-switch activated toys
-large print playing cards
-adapted art tools
-accessible musical instruments
Purpose of home safety evaluations
Identify barriers and risks in the home to improve safety, independence, and access
Steps in home modification process
1) Review referral and prep: talk with client/family, gather forms, check PLOF, consider DME.
2) Arrange home visit with client and caregiver/staff.
3) Conduct assessment: current function, access (inside/outside), lighting, fall risks, existing mods.
4) Plan and review changes: use images, recommend DME/AT, discuss funding.
5) Evaluate outcomes: safety, satisfaction, number of recs used, billing.
Levels of community mobility
1) walking
2) wheelchair/scooter use
3) riding as a passenger
4) using public transportation
5) driving independently
Examples of vehicle modifications
-hand controls
-left foot accelerator
-wheelchair lift/ramp
-swivel seats
-pedal extenders
-modified steering